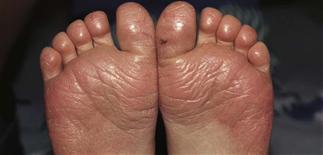
Red, shiny distal soles and toes associated with juvenile plantar dermatosis.
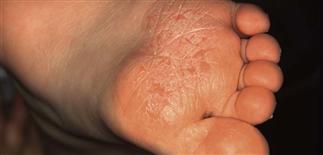
Red, scaly forefoot and toes in juvenile plantar dermatosis.
CLINICAL FEATURES
Erythema, fissuring, peeling and dryness of the weight-bearing surface of the foot are characteristic of juvenile plantar dermatosis.
The great toes are often the first involved, but involvement of the entire forefoot can occur. Involvement is quite symmetric.
Excessive hydration including sweating followed by rapid drying lead to cracking of the epidermis and chapping of the skin is frequently seen. Extensive involvement mimics tinea pedis (see DDx ref 68 Tinea (Dermatophyte Infections)) which may be excluded by examination of scale with potassium hydroxide and fungal culture. Allergic contact dermatitis usually present on the dorsum of the foot, not the weight-bearing surface.