83 Jugular foramen syndrome
Salient features
History
Examination
• Sluggish movement of the palate when the patient says ‘aah’ on the affected side
• Absent gag reflex on the same side
• Flattening of the shoulder on the same side
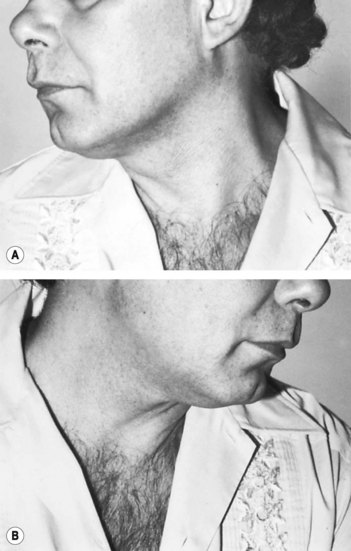
• Wasting of the sternomastoid (Fig. 83.1)
• Weakness when the patient moves her chin to the opposite side
• Difficulty in shrugging the shoulder on the same side (Fig. 83.2).
Advanced-level questions
Where is the jugular foramen located?
Between the lateral part of the occipital bone and the petrous portion of the temporal bones.
Do you know of any eponymous syndromes of the lower cranial nerves?
• Vernet syndrome: paresis of the ninth, tenth and eleventh cranial nerves caused by extension of tumour into the jugular foramen
• Collet–Sicard syndrome: fracture of the floor of the posterior cranial fossa, causing palsy of the last four cranial nerves
• Villaret syndrome: ipsilateral paralysis of the last four cranial nerves and cervical sympathetics
• Syndrome of Schmidt: vagus and accessory nerve involvement
• Syndrome of Hughlings Jackson: accessory and hypoglossal nerve involvement.
How would you test for eleventh cranial nerve palsy?
• Sternocleidomastoids are tested by having the patient turn the head forcibly against the examiner’s hand in a direction away from the muscle being tested while the muscle is observed and palpated.
• Upper portion of the trapezii is tested by having the patient forcibly elevate (shrug) the shoulder while the examiner attempts to depress the shoulder.