Trauma (e.g., crush syndrome, burns, electrical shock)
Trauma (e.g., crush syndrome, burns, electrical shock) Muscle ischemia (e.g., thrombosis, embolism, vasculitis, sickle cell disease, pressure necrosis, tourniquet shock)
Muscle ischemia (e.g., thrombosis, embolism, vasculitis, sickle cell disease, pressure necrosis, tourniquet shock) Drugs: Drug-induced rhabdo can occur through several mechanisms.
Drugs: Drug-induced rhabdo can occur through several mechanisms. Infections
Infections Excessive muscle stress (e.g., marathon runners, status epilepticus, delirium tremens)
Excessive muscle stress (e.g., marathon runners, status epilepticus, delirium tremens) Genetic defects (carnitine deficiency, phosphorylase deficiency, glucosidase deficiency, cytochrome disturbances)
Genetic defects (carnitine deficiency, phosphorylase deficiency, glucosidase deficiency, cytochrome disturbances) Miscellaneous: brown recluse spider bite, snake bite, hornet sting, polymyositis, dermatomyositis, heat stroke, DKA, hyponatremia, hypophosphatemia, myxedema, thyroid storm, RMSF, hypothermia, CO, cyclic antidepressants, phenylpropanolamine, codeine, phencyclidine (PCP), amphetamines, LSD, Reye’s syndrome
Miscellaneous: brown recluse spider bite, snake bite, hornet sting, polymyositis, dermatomyositis, heat stroke, DKA, hyponatremia, hypophosphatemia, myxedema, thyroid storm, RMSF, hypothermia, CO, cyclic antidepressants, phenylpropanolamine, codeine, phencyclidine (PCP), amphetamines, LSD, Reye’s syndromeDiagnosis
H&P
 Variable muscle tenderness. Rhabdo apart from statin use is manifested w/muscle sx only 50% of the time.
Variable muscle tenderness. Rhabdo apart from statin use is manifested w/muscle sx only 50% of the time. Weakness
Weakness Muscle rigidity
Muscle rigidity Fever
Fever Altered consciousness
Altered consciousness Muscle swelling
Muscle swelling Malaise, fatigue. In statin-induced rhabdo, fatigue (74%) is nearly as common as muscle pain (88%).
Malaise, fatigue. In statin-induced rhabdo, fatigue (74%) is nearly as common as muscle pain (88%). Dark urine (secondary to myoglobin in urine, will make dipstick false (+) for RBC’s)
Dark urine (secondary to myoglobin in urine, will make dipstick false (+) for RBC’s)Labs
 ↑↑ CK: Elevations may exceed 100,000 U/L in fulminant rhabdo; the development of renal failure is not directly related to the threshold level of CK; isoenzyme fractionation is useful: if CK-MB >5% of the total CK, involvement of the myocardium is likely.
↑↑ CK: Elevations may exceed 100,000 U/L in fulminant rhabdo; the development of renal failure is not directly related to the threshold level of CK; isoenzyme fractionation is useful: if CK-MB >5% of the total CK, involvement of the myocardium is likely. ↑Serum Cr: The etiology of the renal failure is uncertain and probably multifactorial (renal tubular obstruction by precipitated myoglobin, direct myoglobin toxicity, hypotension, dehydration, ↓ GFR, intravascular coagulation).
↑Serum Cr: The etiology of the renal failure is uncertain and probably multifactorial (renal tubular obstruction by precipitated myoglobin, direct myoglobin toxicity, hypotension, dehydration, ↓ GFR, intravascular coagulation). Serum K+: Preexisting hypokalemia is a contributing factor to rhabdo; fulminant rhabdo can result in life-threatening hyperkalemia secondary to ↑ K+ release from damaged muscle and impaired renal excretion.
Serum K+: Preexisting hypokalemia is a contributing factor to rhabdo; fulminant rhabdo can result in life-threatening hyperkalemia secondary to ↑ K+ release from damaged muscle and impaired renal excretion. Ca2+ and PO4-3: Initially, pts have hyperphosphatemia from muscle necrosis, secondary hypocalcemia from Ca2+ deposition in the injured muscle, and ↓ 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol; later (in the diuretic phase of renal failure), hypercalcemia is present as a result of remobilization of the deposited Ca2+ and secondary hyperparathyroidism.
Ca2+ and PO4-3: Initially, pts have hyperphosphatemia from muscle necrosis, secondary hypocalcemia from Ca2+ deposition in the injured muscle, and ↓ 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol; later (in the diuretic phase of renal failure), hypercalcemia is present as a result of remobilization of the deposited Ca2+ and secondary hyperparathyroidism. Myoglobin: This is present in the serum and urine; the urine is brownish, has granular casts, and is O-toluidine(+); a quick visual method to separate myoglobinuria from hemoglobinuria is to examine the urine and serum simultaneously: reddish brown urine and pink serum indicate hemoglobinuria, whereas brown urine and clear serum suggest myoglobinuria; ↑ in serum myoglobin precedes the ↑ in CK level and is useful to estimate the risk of renal failure (serum myoglobin levels >2000 μg/L may be associated w/renal insufficiency).
Myoglobin: This is present in the serum and urine; the urine is brownish, has granular casts, and is O-toluidine(+); a quick visual method to separate myoglobinuria from hemoglobinuria is to examine the urine and serum simultaneously: reddish brown urine and pink serum indicate hemoglobinuria, whereas brown urine and clear serum suggest myoglobinuria; ↑ in serum myoglobin precedes the ↑ in CK level and is useful to estimate the risk of renal failure (serum myoglobin levels >2000 μg/L may be associated w/renal insufficiency).Treatment
 Vigorous fluid replacement is given to maintain a good urinary output, at least until myoglobin disappears from the urine. Initially NS should be given at a rate of 1.5 L/hr w/close monitoring of cardiac, pulmonary, and electrolyte status. Maintain ↑ rate of IV fluids at least until CPK <1000 U/L. Pts may require >15 L of fluid in the initial 24 hr to achieve urine flow rates of 200 to 300 mL/hr.
Vigorous fluid replacement is given to maintain a good urinary output, at least until myoglobin disappears from the urine. Initially NS should be given at a rate of 1.5 L/hr w/close monitoring of cardiac, pulmonary, and electrolyte status. Maintain ↑ rate of IV fluids at least until CPK <1000 U/L. Pts may require >15 L of fluid in the initial 24 hr to achieve urine flow rates of 200 to 300 mL/hr. Administration of a single dose of mannitol (100 mL of a 25% solution IV during 15 min) remains controversial. Mannitol acts as an osmotic diuretic, renal vasodilator, and intravascular volume expander and may convert oliguric renal failure to nonoliguric.
Administration of a single dose of mannitol (100 mL of a 25% solution IV during 15 min) remains controversial. Mannitol acts as an osmotic diuretic, renal vasodilator, and intravascular volume expander and may convert oliguric renal failure to nonoliguric. Alkalinization of the urine w/addition of 44 mEq/L of NaHCO3 is advocated by some experts. The goal is to maintain urine pH >6.5. NaHCO3 may ↑ solubility of uric acid and myoglobulin; however, it may promote Ca deposition.
Alkalinization of the urine w/addition of 44 mEq/L of NaHCO3 is advocated by some experts. The goal is to maintain urine pH >6.5. NaHCO3 may ↑ solubility of uric acid and myoglobulin; however, it may promote Ca deposition. Hyperkalemia caused by rhabdo is most severe 10 to 40 hr after injury; initial treatment w/sodium polystyrene sulfonate may be indicated; hyperkalemia caused by rhabdo responds poorly to treatment w/glucose and insulin; attempts to correct hyperkalemia and initial hypocalcemia w/Ca infusion may result in metastatic calcifications and severe hypercalcemia in the recovery period; hemodialysis may be necessary in pts w/severe hyperkalemia, volume overload, uremic pericarditis, or uremic encephalopathy.
Hyperkalemia caused by rhabdo is most severe 10 to 40 hr after injury; initial treatment w/sodium polystyrene sulfonate may be indicated; hyperkalemia caused by rhabdo responds poorly to treatment w/glucose and insulin; attempts to correct hyperkalemia and initial hypocalcemia w/Ca infusion may result in metastatic calcifications and severe hypercalcemia in the recovery period; hemodialysis may be necessary in pts w/severe hyperkalemia, volume overload, uremic pericarditis, or uremic encephalopathy.Clinical Pearls
 The average length of time on statin Rx before rhabdo is 1 yr. The average time to onset of rhabdo after addition of fibrate to statin Rx is 32 days.
The average length of time on statin Rx before rhabdo is 1 yr. The average time to onset of rhabdo after addition of fibrate to statin Rx is 32 days. Statin-induced rhabdo is 12× more frequent when statins are combined w/fibrates compared w/statin monoRx.
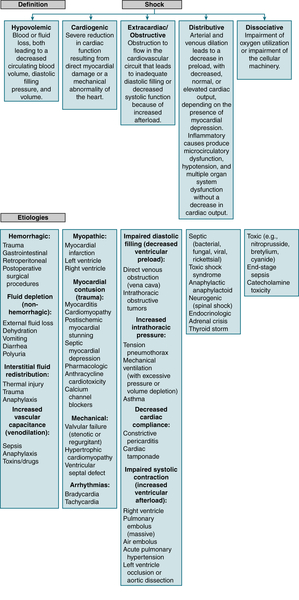
Statin-induced rhabdo is 12× more frequent when statins are combined w/fibrates compared w/statin monoRx.B. Shock
C. Hypothermia
Definition
Diagnosis
H&P
 The clinical presentation varies w/the severity of hypothermia; shivering may be absent if body temperature is <33.3° C (92° F) or in pts taking phenothiazines.
The clinical presentation varies w/the severity of hypothermia; shivering may be absent if body temperature is <33.3° C (92° F) or in pts taking phenothiazines. Hypothermia may masquerade as CVA, ataxia, or slurred speech, or the pt may appear comatose or clinically dead.
Hypothermia may masquerade as CVA, ataxia, or slurred speech, or the pt may appear comatose or clinically dead. Physiologic stages of hypothermia:
Physiologic stages of hypothermia:TABLE 13-1
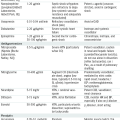
Types of Shock, Physiologic Response, and Basic Treatment
| Type of Shock | HR | Preload | Contractility | SVR | Treatment |
| Hypovolemic | ↑ | ↓↓ | ± | ↑ |
 High-flow oxygen High-flow oxygen Fluid resuscitation: evaluate perfusion after 60 mL/kg total volume bolused, then consider pressors Fluid resuscitation: evaluate perfusion after 60 mL/kg total volume bolused, then consider pressors |
| Septic (early, warm) | ↑ | ↓↓ | ± | ↓ |
 High-flow oxygen High-flow oxygen Fluid resuscitation Fluid resuscitation Antibiotics Antibiotics Pressors (dopamine, norepinephrine, phenylephrine) Pressors (dopamine, norepinephrine, phenylephrine) |
| Septic (late, cold) | ↑ | ↓↓ | ↓ | ↑ |
 High-flow oxygen High-flow oxygen Fluid resuscitation Fluid resuscitation Antibiotics Antibiotics Pressors (dopamine, norepinephrine, phenylephrine) Pressors (dopamine, norepinephrine, phenylephrine) |
| Anaphylactic | ↑ | ↓↓ | ↓ | ↓ |
 High-flow oxygen High-flow oxygen Epinephrine (IM) Epinephrine (IM) Fluid resuscitation Fluid resuscitation |
| Neurogenic | ↑ | ↓↓ | ± | ↓↓ |
 Fluid resuscitation Fluid resuscitation Pressors (norepinephrine) Pressors (norepinephrine) |
| Cardiogenic | ↑ | ↑ | ↓↓ | ↑ |
 High-flow oxygen High-flow oxygen Fluid resuscitation (5-10 mL/kg) Fluid resuscitation (5-10 mL/kg) CHF management (CPAP/BiPAP, diuretics, ACE inhibitors) CHF management (CPAP/BiPAP, diuretics, ACE inhibitors) Inotropes (milrinone, dobutamine) Inotropes (milrinone, dobutamine) |
| Obstructive | Cause dependent | Cause dependent | Cause dependent | Cause dependent |
 Therapy directed at primary etiology of shock Therapy directed at primary etiology of shock |

From Tschudy MM, Arcara KM: The Harriet Lane Handbook, 19th ed. Philadelphia, Mosby, 2012.
Labs
 Metabolic acidosis and respiratory acidosis are usually present. ↓ K+ initially, then ↑ K+ w/↓ temp; extreme hyperkalemia indicates a poor prognosis; ↓ Hct (caused by hemoconcentration), ↓ leukocytes, ↓ Plt (caused by splenic sequestration), ↑ clotting time
Metabolic acidosis and respiratory acidosis are usually present. ↓ K+ initially, then ↑ K+ w/↓ temp; extreme hyperkalemia indicates a poor prognosis; ↓ Hct (caused by hemoconcentration), ↓ leukocytes, ↓ Plt (caused by splenic sequestration), ↑ clotting timeImaging
 CXR: generally not helpful; may reveal evidence of aspiration (e.g., intoxicated pt w/aspiration pneumonia)
CXR: generally not helpful; may reveal evidence of aspiration (e.g., intoxicated pt w/aspiration pneumonia) ECG (Fig. 13-3): ↑ PR, QT, and QRS segments; ↑ ST segments, inverted T waves, AV block; hypothermic J waves (Osborn waves), characterized by notching of the junction of the QRS complex and ST segments, may appear at 25° C to 30° C.
ECG (Fig. 13-3): ↑ PR, QT, and QRS segments; ↑ ST segments, inverted T waves, AV block; hypothermic J waves (Osborn waves), characterized by notching of the junction of the QRS complex and ST segments, may appear at 25° C to 30° C.Treatment
 Secure an airway before warming all unconscious pts; precede ETT w/oxygenation (if possible) to ↓ the risk of arrhythmias during the procedure.
Secure an airway before warming all unconscious pts; precede ETT w/oxygenation (if possible) to ↓ the risk of arrhythmias during the procedure. Peripheral vasoconstriction may impede placement of a peripheral IV catheter; consider femoral venous access as an alternative to the jugular or subclavian sites to avoid ventricular stimulation.
Peripheral vasoconstriction may impede placement of a peripheral IV catheter; consider femoral venous access as an alternative to the jugular or subclavian sites to avoid ventricular stimulation. A Foley catheter should be inserted, and urinary output should be monitored and maintained >0.5 to 1 mL/kg/hr w/intravascular volume replacement.
A Foley catheter should be inserted, and urinary output should be monitored and maintained >0.5 to 1 mL/kg/hr w/intravascular volume replacement. Continuous ECG monitoring of pts is recommended; consider ventricular arrhythmia Rx w/bretylium; lidocaine is generally ineffective, and procainamide is associated w/incidence of VF in hypothermic pts.
Continuous ECG monitoring of pts is recommended; consider ventricular arrhythmia Rx w/bretylium; lidocaine is generally ineffective, and procainamide is associated w/incidence of VF in hypothermic pts.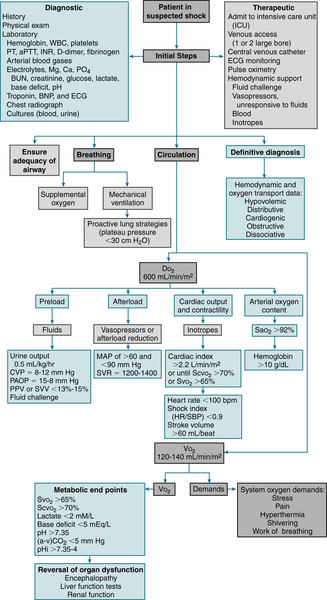
FIGURE 13-2 General hemodynamic management. DO2, (system) oxygen delivery; PAOP, pulmonary artery occlusion pressure; pHi, intestinal mucosal pH; PPV, pulse pressure variation; SVV, stroke volume variation; VO2, (systemic) oxygen consumption. (From Goldman L, Schafer AI [eds]: Goldman’s Cecil Medicine, 24th ed. Philadelphia, Saunders, 2012.)
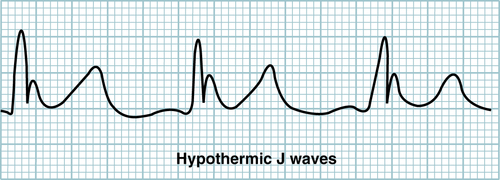
FIGURE 13-3 Hypothermic J waves. (From Ferri F, Practical Guide to the Care of the Medical Patient, 8th ed, St. Louis, Mosby 2011)
TABLE 13-2
Vasopressor Agents
| Agent | Dose Range | Peripheral Vasculature | Cardiac Effects | Typical Use | |||
| Vasoconstriction | Vasodilation | HR | Contractility | Dysrhythmias | |||
| Dopamine | 1-4 μg/kg/min | 0 | 1+ | 1+ | 1+ | 1+ | “Renal dose” does not improve renal function; may be used with bradycardia and hypotension |
| 5-10 μg/kg/min | 1-2+ | 1+ | 2+ | 2+ | 2+ | ||
| 11-20 μg/kg/min | 2-3+ | 1+ | 2+ | 2+ | 3+ | Vasopressor range | |
| Vasopressin | 0.04-0.1 U/min | 3-4+ | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1+ | Septic shock, post–cardiopulmonary bypass shock state; no outcome benefit in sepsis |
| Phenylephrine | 20-200 μg/min | 4+ | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1+ | Vasodilatory shock; best for supraventricular tachycardia |
| Norepinephrine | 1-20 μg/min | 4+ | 0 | 2+ | 2+ | 2+ | First-line vasopressor for septic shock, vasodilatory shock |
| Epinephrine | 1-20 μg/min | 4+ | 0 | 4+ | 4+ | 4+ | Refractory shock, shock with bradycardia, anaphylactic shock |
| Dobutamine | 1-20 μg/kg/min | 1+ | 2+ | 1-2+ | 3+ | 3+ | Cardiogenic shock, septic shock |
| Milrinone | 37.5-75 μg/kg bolus followed by 0.375-0.75 μg/min | 0 | 2+ | 1+ | 3+ | 2+ | Cardiogenic shock, right heart failure; dilates pulmonary artery; caution in renal failure |
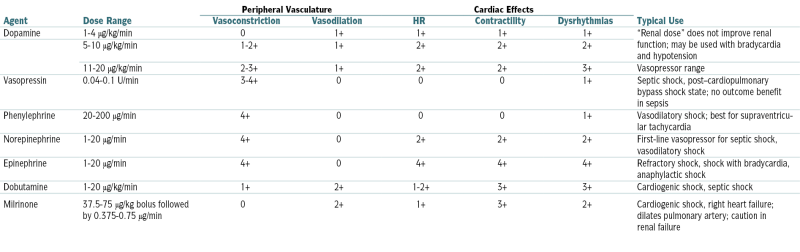
From Goldman L, Schafer AI (eds): Goldman’s Cecil Medicine, 24th ed. Philadelphia, Saunders, 2012.
 Correct severe acidosis and electrolyte abnlities.
Correct severe acidosis and electrolyte abnlities. Hypothyroidism, if present, should be promptly treated (refer to the section on myxedema coma in Chapter 5).
Hypothyroidism, if present, should be promptly treated (refer to the section on myxedema coma in Chapter 5). If clinical evidence suggests adrenal insufficiency, administer IV methylprednisolone.
If clinical evidence suggests adrenal insufficiency, administer IV methylprednisolone. In pts unresponsive to verbal or noxious stimuli or w/ΔMS, 100 mg of thiamine, 0.4 mg of naloxone, and 1 ampule of 50% dextrose may be given.
In pts unresponsive to verbal or noxious stimuli or w/ΔMS, 100 mg of thiamine, 0.4 mg of naloxone, and 1 ampule of 50% dextrose may be given. Warm (104° F-113° F [40° C-45° C]), humidified O2 should also be given if it is available.
Warm (104° F-113° F [40° C-45° C]), humidified O2 should also be given if it is available. Specific treatment:
Specific treatment:D. Heat Stroke
Definition
Diagnosis
H&P
 Neurologic manifestations (seizures, tremor, hemiplegia, coma, psychosis, and other bizarre behavior)
Neurologic manifestations (seizures, tremor, hemiplegia, coma, psychosis, and other bizarre behavior)Labs
 ↑ BUN, Cr, Hct
↑ BUN, Cr, Hct Hyponatremia or hypernatremia, hyperkalemia or hypokalemia
Hyponatremia or hypernatremia, hyperkalemia or hypokalemia ↑ LDH, AST, ALT, CPK, bili
↑ LDH, AST, ALT, CPK, bili Lactic acidosis, respiratory alkalosis (secondary to hyperventilation)
Lactic acidosis, respiratory alkalosis (secondary to hyperventilation) Myoglobinuria, hypofibrinogenemia, fibrinolysis, hypocalcemia
Myoglobinuria, hypofibrinogenemia, fibrinolysis, hypocalcemiaTreatment
 Remove the pt’s clothes, and place the pt in a cool and well-ventilated room.
Remove the pt’s clothes, and place the pt in a cool and well-ventilated room. If the pt is unconscious, position the pt on his/her side and clear the airway. Protect the airway and augment oxygenation (e.g., nasal O2 at 4 L/min to keep SaO2 >90%).
If the pt is unconscious, position the pt on his/her side and clear the airway. Protect the airway and augment oxygenation (e.g., nasal O2 at 4 L/min to keep SaO2 >90%). Monitor body temperature q5min. Measurement of the pt’s core temperature w/rectal probe is recommended. Goal is to ↓ the body temperature to 39° C (102.2° F) in 30 to 60 min.
Monitor body temperature q5min. Measurement of the pt’s core temperature w/rectal probe is recommended. Goal is to ↓ the body temperature to 39° C (102.2° F) in 30 to 60 min. Spray the pt w/cool mist, and use fans to enhance airflow over the body (rapid evaporation method).
Spray the pt w/cool mist, and use fans to enhance airflow over the body (rapid evaporation method). Immersion of the pt in ice water, stomach lavage w/iced saline solution, IV administration of cooled fluids, and inhalation of cold air are advisable only when the means for rapid evaporation are not available. Immersion in tepid water (15° C [59° F]) is preferred to ice water immersion to minimize risk of shivering.
Immersion of the pt in ice water, stomach lavage w/iced saline solution, IV administration of cooled fluids, and inhalation of cold air are advisable only when the means for rapid evaporation are not available. Immersion in tepid water (15° C [59° F]) is preferred to ice water immersion to minimize risk of shivering. Use of ice packs on axillae, neck, and groin is controversial because the resulting peripheral vasoconstriction may induce shivering.
Use of ice packs on axillae, neck, and groin is controversial because the resulting peripheral vasoconstriction may induce shivering. Antipyretics are ineffective because the hypothalamic set point during heat stroke is nl despite the body temperature.
Antipyretics are ineffective because the hypothalamic set point during heat stroke is nl despite the body temperature. Intubate a comatose pt, insert a Foley catheter, and start nasal O2.
Intubate a comatose pt, insert a Foley catheter, and start nasal O2. Continuous ECG monitoring is recommended.
Continuous ECG monitoring is recommended. Insert at least two large-bore IV lines, and begin IV hydration w/NS or lactated Ringer’s solution.
Insert at least two large-bore IV lines, and begin IV hydration w/NS or lactated Ringer’s solution. Treat complications as follows:
Treat complications as follows:E. Malignant Hyperthermia
Definition
Etiology
Diagnosis
H&P
 Within minutes to hours after anesthetic is given, the pt develops muscle rigidity (especially masseter spasm), hyperthermia (≤45° C), tachycardia that may progress to other dysrhythmias, and hypotension. Skin initially reddens but then becomes cyanotic and mottled. There is also increased CO2 production.
Within minutes to hours after anesthetic is given, the pt develops muscle rigidity (especially masseter spasm), hyperthermia (≤45° C), tachycardia that may progress to other dysrhythmias, and hypotension. Skin initially reddens but then becomes cyanotic and mottled. There is also increased CO2 production. Rhabdomyolysis, acute renal failure, and DIC may soon follow.
Rhabdomyolysis, acute renal failure, and DIC may soon follow.Labs
 CBC, TSH, electrolytes (especially K+, Ca2+, and phosphorus), PT, PTT , BUN, creat, ALT, AST, and CK
CBC, TSH, electrolytes (especially K+, Ca2+, and phosphorus), PT, PTT , BUN, creat, ALT, AST, and CKTreatment
 The most important measures for treatment include stopping the anesthetic agents, starting dantrolene, ensuring physical cooling, and preventing sequelae. Antipyretics are not useful because the hypothalamic set point is not altered by cytokines.
The most important measures for treatment include stopping the anesthetic agents, starting dantrolene, ensuring physical cooling, and preventing sequelae. Antipyretics are not useful because the hypothalamic set point is not altered by cytokines. Cool the pt w/an ice bath, ice packs in the groin and axillae, cool spray with fans, or cooling blankets. In severe instances extracorporeal partial bypass or iced peritoneal lavage may be used. Stop cooling when core temperature reaches 38° C to prevent overcooling.
Cool the pt w/an ice bath, ice packs in the groin and axillae, cool spray with fans, or cooling blankets. In severe instances extracorporeal partial bypass or iced peritoneal lavage may be used. Stop cooling when core temperature reaches 38° C to prevent overcooling. Carefully monitor the pt’s cardiovascular and respiratory status with constant core temperature measurements.
Carefully monitor the pt’s cardiovascular and respiratory status with constant core temperature measurements. Dantrolene is the mainstay of treatment, starting with a bolus of 5 mg/kg IV, which should be repeated every 5 min until symptoms abate or a maximum of 10 to 20 mg/kg is reached. Then 24 hr of 10 mg/kg/day IV should be given.
Dantrolene is the mainstay of treatment, starting with a bolus of 5 mg/kg IV, which should be repeated every 5 min until symptoms abate or a maximum of 10 to 20 mg/kg is reached. Then 24 hr of 10 mg/kg/day IV should be given. β-Blockers or lidocaine may be useful for dysrhythmias, but verapamil should be avoided because its use with dantrolene has been shown to depress cardiac function.
β-Blockers or lidocaine may be useful for dysrhythmias, but verapamil should be avoided because its use with dantrolene has been shown to depress cardiac function. NaHCO3 may be necessary to reverse acidosis.
NaHCO3 may be necessary to reverse acidosis.F. Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS)
Etiology
 Neuroleptic drugs have different potencies for inducing NMS:
Neuroleptic drugs have different potencies for inducing NMS:Diagnosis
H&P
 Muscle rigidity (hypertonia, cogwheeling, or “lead pipe” rigidity)
Muscle rigidity (hypertonia, cogwheeling, or “lead pipe” rigidity) Hyperthermia (38.6° C-42.3° C, usually <40° C)
Hyperthermia (38.6° C-42.3° C, usually <40° C) Autonomic sx: diaphoresis, sialorrhea, skin pallor, urinary incontinence
Autonomic sx: diaphoresis, sialorrhea, skin pallor, urinary incontinence Tachycardia, tachypnea
Tachycardia, tachypnea Labile BP (HTN or postural hypotension)
Labile BP (HTN or postural hypotension) ΔMS (agitation, catatonia, fluctuating consciousness, obtundation)
ΔMS (agitation, catatonia, fluctuating consciousness, obtundation)Labs
 ↑ CPK (>71% of pts, w/mean value of 3700 U/L)
↑ CPK (>71% of pts, w/mean value of 3700 U/L) Urinary myoglobin
Urinary myoglobin Leukocytosis, usually 10,000 to 40,000/mm3
Leukocytosis, usually 10,000 to 40,000/mm3 Electrolytes and renal function
Electrolytes and renal function ABGs
ABGs Drug levels
Drug levelsTreatment
 Stop all neuroleptic agents, and reinstitute any recently discontinued dopaminergic agents.
Stop all neuroleptic agents, and reinstitute any recently discontinued dopaminergic agents. Initiate active cooling (cooling blanket and antipyretics).
Initiate active cooling (cooling blanket and antipyretics). IV benzos (e.g., diazepam 2-10 mg, w/total daily dose of 10-60 mg) are given to relax muscles and to control agitation.
IV benzos (e.g., diazepam 2-10 mg, w/total daily dose of 10-60 mg) are given to relax muscles and to control agitation. Bromocriptine 2.5 to 10 mg IV q8h and by 5 mg/day is given until clinical improvement is seen. The drug should be continued for ≥10 days after the syndrome has been controlled and then tapered slowly.
Bromocriptine 2.5 to 10 mg IV q8h and by 5 mg/day is given until clinical improvement is seen. The drug should be continued for ≥10 days after the syndrome has been controlled and then tapered slowly. Dantrolene 0.25 mg/kg IV q6-12h is followed by a maintenance dose up to 3 mg/kg/day. After 2 to 3 days, pts may be given the drug PO (25-600 mg/day in divided doses). Oral dantrolene Rx (50-600 mg/day) may be continued for several days afterward.
Dantrolene 0.25 mg/kg IV q6-12h is followed by a maintenance dose up to 3 mg/kg/day. After 2 to 3 days, pts may be given the drug PO (25-600 mg/day in divided doses). Oral dantrolene Rx (50-600 mg/day) may be continued for several days afterward. Electroconvulsive Rx w/neuromuscular blockage is indicated in pharmacologically refractory cases. Succinylcholine should not be used because it may cause hyperkalemia and cardiac arrhythmias in pts w/rhabdo or dysautonomia.
Electroconvulsive Rx w/neuromuscular blockage is indicated in pharmacologically refractory cases. Succinylcholine should not be used because it may cause hyperkalemia and cardiac arrhythmias in pts w/rhabdo or dysautonomia.G. Anaphylaxis
Etiology
 Caused by sudden systematic release of histamine and other inflammatory mediators from basophils and mast cells → swelling of the mucous membranes and urticarial rash on the skin. Virtually any substance may induce anaphylaxis.
Caused by sudden systematic release of histamine and other inflammatory mediators from basophils and mast cells → swelling of the mucous membranes and urticarial rash on the skin. Virtually any substance may induce anaphylaxis. Foods and food additives: peanuts, tree nuts, eggs, shellfish, fish, cow’s milk, fruits, soy
Foods and food additives: peanuts, tree nuts, eggs, shellfish, fish, cow’s milk, fruits, soy Medications: antibiotics, especially penicillins, insulin, allergen extracts, opiates, vaccines, NSAIDs, contrast media, streptokinase
Medications: antibiotics, especially penicillins, insulin, allergen extracts, opiates, vaccines, NSAIDs, contrast media, streptokinase Bee or wasp sting, snake venom, fire ant venom
Bee or wasp sting, snake venom, fire ant venom Blood products, plasma, immunoglobulin, cryoprecipitate, whole blood
Blood products, plasma, immunoglobulin, cryoprecipitate, whole blood Latex
LatexDiagnosis
H&P
 Urticaria, pruritus, skin flushing, angioedema
Urticaria, pruritus, skin flushing, angioedema Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, difficulty swallowing
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, difficulty swallowing Hypotension, tachycardia, weakness, dizziness, malaise, vascular collapse
Hypotension, tachycardia, weakness, dizziness, malaise, vascular collapseDifferential Diagnosis
 Endocrine disorders (carcinoid, pheochromocytoma)
Endocrine disorders (carcinoid, pheochromocytoma) Globus hystericus, anxiety disorder
Globus hystericus, anxiety disorder Systemic mastocytosis
Systemic mastocytosis PE, serum sickness, vasovagal reactions
PE, serum sickness, vasovagal reactions Severe asthma (the key clinical difference is the abrupt onset of symptoms in anaphylaxis versus a history of progressive worsening of symptoms)
Severe asthma (the key clinical difference is the abrupt onset of symptoms in anaphylaxis versus a history of progressive worsening of symptoms) Septic shock or other form of vasodilatory shock
Septic shock or other form of vasodilatory shock Airway foreign body
Airway foreign bodyLabs
 Generally tests are not helpful because anaphylaxis is typically diagnosed clinically.
Generally tests are not helpful because anaphylaxis is typically diagnosed clinically. ABG analysis may be useful to exclude PE, status asthmaticus, and foreign body aspiration.
ABG analysis may be useful to exclude PE, status asthmaticus, and foreign body aspiration. ↑ Serum and urine histamine levels and serum tryptase levels can be useful for dx of anaphylaxis, but these tests are not commonly available in the emergency setting.
↑ Serum and urine histamine levels and serum tryptase levels can be useful for dx of anaphylaxis, but these tests are not commonly available in the emergency setting.Imaging
 Imaging is generally not helpful.
Imaging is generally not helpful. CXRs for evaluation of foreign body aspiration or pulmonary disease are indicated in pts with acute respiratory compromise.
CXRs for evaluation of foreign body aspiration or pulmonary disease are indicated in pts with acute respiratory compromise. Consider ECG in all pts with sudden loss of consciousness, chest pain, dyspnea and in any elderly pt. ECG in anaphylaxis usually reveals sinus tachycardia.
Consider ECG in all pts with sudden loss of consciousness, chest pain, dyspnea and in any elderly pt. ECG in anaphylaxis usually reveals sinus tachycardia.Treatment
 Establish and protect the airway. Provide supplemental O2 if indicated.
Establish and protect the airway. Provide supplemental O2 if indicated. IV access should be rapidly established, and IV fluids (i.e., NS) should be administered. The pt should be placed supine or in Trendelenburg’s position if hemodynamically unstable.
IV access should be rapidly established, and IV fluids (i.e., NS) should be administered. The pt should be placed supine or in Trendelenburg’s position if hemodynamically unstable. Cardiac monitoring is recommended.
Cardiac monitoring is recommended. Epinephrine: IM injection at a dose of 0.3 mg of aqueous epinephrine for adults and children >30 kg. Epinephrine 0.15 mg should be given for children <30 kg (1:1000 concentration). IM is preferred because it provides more reliable and quicker rise to effective plasma levels. The dose may be repeated after ≈5 to 15 min if symptoms persist.
Epinephrine: IM injection at a dose of 0.3 mg of aqueous epinephrine for adults and children >30 kg. Epinephrine 0.15 mg should be given for children <30 kg (1:1000 concentration). IM is preferred because it provides more reliable and quicker rise to effective plasma levels. The dose may be repeated after ≈5 to 15 min if symptoms persist. Adjunct therapies: These include H1 and H2 receptor antagonists, diphenhydramine 25 to 50 mg IV or IM, or PO in mild cases, and famotidine 20 to 40 mg IV, or PO in mild cases.
Adjunct therapies: These include H1 and H2 receptor antagonists, diphenhydramine 25 to 50 mg IV or IM, or PO in mild cases, and famotidine 20 to 40 mg IV, or PO in mild cases. Corticosteroids are not useful in the acute episode because of their slow onset of action; however, they should be administered in most cases to prevent prolonged or recurrent anaphylaxis. Commonly used agents are prednisone, methylprednisolone 40 to 250 mg IV in adults (1-2 mg/kg in children), or longer-acting dexamethasone.
Corticosteroids are not useful in the acute episode because of their slow onset of action; however, they should be administered in most cases to prevent prolonged or recurrent anaphylaxis. Commonly used agents are prednisone, methylprednisolone 40 to 250 mg IV in adults (1-2 mg/kg in children), or longer-acting dexamethasone. Aerosolized β-agonists (e.g., albuterol, 2.5 mg, repeat PRN 20 min) are useful to control bronchospasm.
Aerosolized β-agonists (e.g., albuterol, 2.5 mg, repeat PRN 20 min) are useful to control bronchospasm. Vasopressor therapy with epinephrine (1:10,000), or dopamine is indicated in pts with refractory hypotension after crystalloid resuscitation.
Vasopressor therapy with epinephrine (1:10,000), or dopamine is indicated in pts with refractory hypotension after crystalloid resuscitation.H. Alcohol Withdrawal
Diagnosis
 Tremulous state (early alcohol withdrawal, “impending delirium tremens,” “shakes,” “jitters”)
Tremulous state (early alcohol withdrawal, “impending delirium tremens,” “shakes,” “jitters”) Alcoholic hallucinosis: Hallucinations are usually auditory but occasionally are visual, tactile, or olfactory; usually there is no clouding of sensorium as in delirium (clinical presentation may be mistaken for an acute schizophrenic episode). Disordered perceptions become most pronounced after 24 to 36 hr of abstinence.
Alcoholic hallucinosis: Hallucinations are usually auditory but occasionally are visual, tactile, or olfactory; usually there is no clouding of sensorium as in delirium (clinical presentation may be mistaken for an acute schizophrenic episode). Disordered perceptions become most pronounced after 24 to 36 hr of abstinence. Withdrawal seizures (“rum fits”)
Withdrawal seizures (“rum fits”) Delirium tremens (DTs)
Delirium tremens (DTs)Treatment
Inpatient
 Admit to medical ward (private room); monitor VS q4h; institute seizure precautions; maintain adequate sedation.
Admit to medical ward (private room); monitor VS q4h; institute seizure precautions; maintain adequate sedation. Labs: serum electrolytes, BUN, Cr, Mg2+, PO4-3, Ca2+ levels, glucose, CPK
Labs: serum electrolytes, BUN, Cr, Mg2+, PO4-3, Ca2+ levels, glucose, CPK Administer oxazepam or lorazepam as follows:
Administer oxazepam or lorazepam as follows:Clinical Pearl
I. Acute Poisoning
1. Acetaminophen Poisoning
Diagnosis
H&P
 Clinical presentation varies by dose ingested and time from ingestion.
Clinical presentation varies by dose ingested and time from ingestion.Labs
 Initial labs should include a STAT plasma acetaminophen level with a second level drawn approximately 4 hr after the initial ingestion. Subsequent levels can be obtained every 2 to 4 hr until the levels stabilize or decline. These levels should be plotted on the Rumack-Matthew nomogram (Fig. 13-4) to calculate potential hepatic toxicity. The nomogram cannot be used with pts who present >24 hr after ingestion, extended-release preparations, long-term ingestions, or when the time of ingestion is unknown.
Initial labs should include a STAT plasma acetaminophen level with a second level drawn approximately 4 hr after the initial ingestion. Subsequent levels can be obtained every 2 to 4 hr until the levels stabilize or decline. These levels should be plotted on the Rumack-Matthew nomogram (Fig. 13-4) to calculate potential hepatic toxicity. The nomogram cannot be used with pts who present >24 hr after ingestion, extended-release preparations, long-term ingestions, or when the time of ingestion is unknown. Transaminases (AST, ALT), bilirubin level, INR, BUN, and creat should be initially obtained on all pts.
Transaminases (AST, ALT), bilirubin level, INR, BUN, and creat should be initially obtained on all pts. Serum and urine toxicology screen for other potential toxic substances is also recommended on admission. Screening for infectious hepatitis should also be considered. β-hCG should be obtained in all women of childbearing age.
Serum and urine toxicology screen for other potential toxic substances is also recommended on admission. Screening for infectious hepatitis should also be considered. β-hCG should be obtained in all women of childbearing age.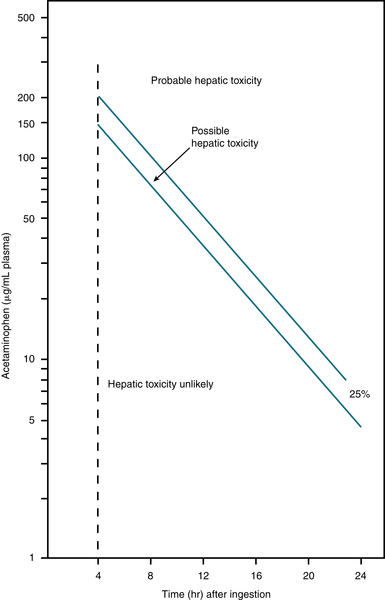
FIGURE 13-4 Rumack-Matthew nomogram for acetaminophen poisoning. (From Rumack BH, Matthew H: Pediatrics 55:871, 1975. In Rosen P [ed]: Emergency Medicine, 4th ed. St. Louis, Mosby, 1998.)
Treatment
 Consultation with a Poison Control Center is recommended for pts who have ingested a large amount of acetaminophen and/or other toxic substances. A single toxic dose of acetaminophen usually exceeds 7 g or 150 mg/kg in the adult.
Consultation with a Poison Control Center is recommended for pts who have ingested a large amount of acetaminophen and/or other toxic substances. A single toxic dose of acetaminophen usually exceeds 7 g or 150 mg/kg in the adult. Hepatotoxicity is defined as any ↑ ALT or AST >1000 IU/L, and hepatic failure is hepatotoxicity with hepatic encephalopathy. For those who cannot be risk stratified using the nomogram, the American College of Emergency Physicians recommends that N-acetylcysteine be administered without delay to those >12 yr and >8 hr after ingestion at presentation.
Hepatotoxicity is defined as any ↑ ALT or AST >1000 IU/L, and hepatic failure is hepatotoxicity with hepatic encephalopathy. For those who cannot be risk stratified using the nomogram, the American College of Emergency Physicians recommends that N-acetylcysteine be administered without delay to those >12 yr and >8 hr after ingestion at presentation. Administer activated charcoal 1 g/kg PO if the pt is seen within 1 hr of ingestion or the clinician suspects polydrug ingestion that delays gastric emptying.
Administer activated charcoal 1 g/kg PO if the pt is seen within 1 hr of ingestion or the clinician suspects polydrug ingestion that delays gastric emptying. Determine blood levels 4 hr after ingestion; if in the toxic range, start N-acetylcysteine (NAC) either IV (Acetadote) or PO (Mucomyst). Acetylcysteine IV loading dose is 150 mg/kg ×1 diluted in 200 mL D5W over 15 to 60 min. Maintenance dose is 50 mg/kg diluted in 500 mL D5W over 4 hr, followed by 100 mg/kg diluted in 1000 mL D5W over 16 hr. The dose does not require adjustment for renal or hepatic impairment or for dialysis. Total administration time is 21 hours.
Determine blood levels 4 hr after ingestion; if in the toxic range, start N-acetylcysteine (NAC) either IV (Acetadote) or PO (Mucomyst). Acetylcysteine IV loading dose is 150 mg/kg ×1 diluted in 200 mL D5W over 15 to 60 min. Maintenance dose is 50 mg/kg diluted in 500 mL D5W over 4 hr, followed by 100 mg/kg diluted in 1000 mL D5W over 16 hr. The dose does not require adjustment for renal or hepatic impairment or for dialysis. Total administration time is 21 hours. Oral administration is 140 mg/kg PO as a loading dose, followed after 4 hr by 70 mg/kg PO q4h for a total of 17 doses. N-acetylcysteine Rx should be started within 24 hr of acetaminophen overdose. Total administration time is 72 hours.
Oral administration is 140 mg/kg PO as a loading dose, followed after 4 hr by 70 mg/kg PO q4h for a total of 17 doses. N-acetylcysteine Rx should be started within 24 hr of acetaminophen overdose. Total administration time is 72 hours. Advantages of IV administration include more reliable absorption, fewer doses, and shorter duration of treatment.
Advantages of IV administration include more reliable absorption, fewer doses, and shorter duration of treatment. Monitor acetaminophen level; use a graph to plot possible hepatic toxicity. Repeat AST/ALT and APAP levels after 12 to 14 hr of IV acetylcysteine infusion and continue infusion for >16 hr if transaminases are elevated, if acetaminophen concentration is measurable, or if coagulopathy exists (INR >1.5-2.0).
Monitor acetaminophen level; use a graph to plot possible hepatic toxicity. Repeat AST/ALT and APAP levels after 12 to 14 hr of IV acetylcysteine infusion and continue infusion for >16 hr if transaminases are elevated, if acetaminophen concentration is measurable, or if coagulopathy exists (INR >1.5-2.0). Provide adequate IV hydration (D5½NS at 150 mL/hr).
Provide adequate IV hydration (D5½NS at 150 mL/hr). In pts on IV N-acetylcysteine who have liver failure, frequent monitoring of VS, O2sat by pulse ox, AST, Cr, hypoglycemia, and infection is essential.
In pts on IV N-acetylcysteine who have liver failure, frequent monitoring of VS, O2sat by pulse ox, AST, Cr, hypoglycemia, and infection is essential. If acetaminophen level is nontoxic, N-acetyl-cysteine Rx may be d/c.
If acetaminophen level is nontoxic, N-acetyl-cysteine Rx may be d/c.2. Amphetamine Overdose
Diagnosis
H&P
 Tachycardia, HTN, mydriasis, agitation, seizures, diaphoresis, psychosis, hyperthermia
Tachycardia, HTN, mydriasis, agitation, seizures, diaphoresis, psychosis, hyperthermiaLabs
 Lytes, BUN, Cr, CPK
Lytes, BUN, Cr, CPKTreatment
 Activated charcoal
Activated charcoal Gastric lavage for acute large ingestion
Gastric lavage for acute large ingestion Sedation w/benzos (diazepam)
Sedation w/benzos (diazepam) Haloperidol for hallucinations and psychosis
Haloperidol for hallucinations and psychosis Propranolol or lidocaine for arrhythmias
Propranolol or lidocaine for arrhythmiasClinical Pearl
3. Barbiturate Overdose
Diagnosis
H&P
 Lethargy, respiratory depression, coma
Lethargy, respiratory depression, coma ↓ DTRs, extensor plantar response
↓ DTRs, extensor plantar responseLabs
 BMP, LFTs, Ca, Mg, PO4
BMP, LFTs, Ca, Mg, PO4 Serum and urine toxicology screen; ethanol, ASA, and acetaminophen level
Serum and urine toxicology screen; ethanol, ASA, and acetaminophen levelImaging
 CXR, ECG
CXR, ECGTreatment
 IV bolus NaHCO3, 2 mEq/kg IV push, then maintenance infusion begun (132 mEq NaHCO3 in 1 L D5W at 250 mL/hr)
IV bolus NaHCO3, 2 mEq/kg IV push, then maintenance infusion begun (132 mEq NaHCO3 in 1 L D5W at 250 mL/hr) Administration of activated charcoal (0.5-1 g/kg; max: ≤50 g PO) in water or sorbitol by NG tube
Administration of activated charcoal (0.5-1 g/kg; max: ≤50 g PO) in water or sorbitol by NG tube Gastric lavage w/early presentation
Gastric lavage w/early presentationClinical Pearl
4. Cocaine Overdose
Diagnosis
H&P
 Phase I
Phase I Phase II
Phase II Phase III
Phase III Psychological dependence manifested w/habituation, paranoia, hallucinations (cocaine “bugs”)
Psychological dependence manifested w/habituation, paranoia, hallucinations (cocaine “bugs”) CNS: cerebral ischemia and infarction, cerebral arterial spasm, cerebral vasculitis, cerebral vascular thrombosis, subarachnoid hemorrhage, intraparenchymal hemorrhage, seizures, cerebral atrophy, movement disorders
CNS: cerebral ischemia and infarction, cerebral arterial spasm, cerebral vasculitis, cerebral vascular thrombosis, subarachnoid hemorrhage, intraparenchymal hemorrhage, seizures, cerebral atrophy, movement disorders Cardiac: acute myocardial ischemia and infarction, arrhythmias and sudden death, dilated cardiomyopathy and myocarditis, infective endocarditis, aortic rupture
Cardiac: acute myocardial ischemia and infarction, arrhythmias and sudden death, dilated cardiomyopathy and myocarditis, infective endocarditis, aortic rupture Pulmonary (secondary to smoking crack cocaine)
Pulmonary (secondary to smoking crack cocaine) GI: gastroduodenal ulceration and perforation; intestinal infarction or perforation, colitis
GI: gastroduodenal ulceration and perforation; intestinal infarction or perforation, colitis Renal: AKI secondary to rhabdo and myoglobinuria; renal infarction; focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
Renal: AKI secondary to rhabdo and myoglobinuria; renal infarction; focal segmental glomerulosclerosis Obstetric: placental abruption, low infant weight, prematurity, microcephaly
Obstetric: placental abruption, low infant weight, prematurity, microcephaly Psychiatric: anxiety, depression, paranoia, delirium, psychosis, suicide
Psychiatric: anxiety, depression, paranoia, delirium, psychosis, suicideLabs
 Toxicology screen (urine): Cocaine is metabolized within 2 hr by the liver to major metabolites, benzoylecgonine and ecgonine methyl ester, that are excreted in the urine. Metabolites can be identified in urine within 5 min of IV use and ≤48 hr after PO ingestion.
Toxicology screen (urine): Cocaine is metabolized within 2 hr by the liver to major metabolites, benzoylecgonine and ecgonine methyl ester, that are excreted in the urine. Metabolites can be identified in urine within 5 min of IV use and ≤48 hr after PO ingestion. Blood: CBC, lytes, glucose, BUN, Cr, Ca
Blood: CBC, lytes, glucose, BUN, Cr, Ca ABGs
ABGs Serum CK and troponins
Serum CK and troponinsTreatment
 Inhalation: Wash nasal passages.
Inhalation: Wash nasal passages. Agitation:
Agitation: Hyperthermia:
Hyperthermia: Rhabdo:
Rhabdo: Seizure management (status epilepticus):
Seizure management (status epilepticus): HTN:
HTN: Chest pain:
Chest pain: Ventricular arrhythmias:
Ventricular arrhythmias:5. Ethanol Poisoning
Diagnosis
H&P
 Alcohol inhibits the conversion of lactate to glucose in the liver. Alcoholic ketoacidosis usually follows binge drinking.
Alcohol inhibits the conversion of lactate to glucose in the liver. Alcoholic ketoacidosis usually follows binge drinking. Abd pain, vomiting, starvation, volume depletion
Abd pain, vomiting, starvation, volume depletionLabs
 AG metabolic acidosis
AG metabolic acidosis ↑ Osmolal gap (difference between the measured and calculated serum osmolality)
↑ Osmolal gap (difference between the measured and calculated serum osmolality) N/↓ blood glucose
N/↓ blood glucose ↑ BUN, Cr, hypophosphatemia, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia
↑ BUN, Cr, hypophosphatemia, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemiaTreatment
 Volume repletion, thiamine and glucose administration
Volume repletion, thiamine and glucose administration Correction of hypophosphatemia, hypokalemia, and hypomagnesemia if present
Correction of hypophosphatemia, hypokalemia, and hypomagnesemia if presentClinical Pearl
6. Ethylene Glycol, Isopropyl Alcohol, and Methanol Poisoning
Diagnosis
H&P
 Ethylene glycol is a component of antifreeze and industrial solvents. It has a sweet taste and may be ingested accidentally or in suicide attempts. Methanol is a component of wood alcohol (moonshine liquor), copy machines, embalming fluid, paint removers, and windshield wiper fluid. Isopropyl alcohol is found in rubbing alcohol.
Ethylene glycol is a component of antifreeze and industrial solvents. It has a sweet taste and may be ingested accidentally or in suicide attempts. Methanol is a component of wood alcohol (moonshine liquor), copy machines, embalming fluid, paint removers, and windshield wiper fluid. Isopropyl alcohol is found in rubbing alcohol. CNS sx (lethargy, seizures, coma), renal failure, pulmonary, cardiac failure
CNS sx (lethargy, seizures, coma), renal failure, pulmonary, cardiac failure Dehydration
Dehydration Optic papillitis leading to blindness from metabolism of methanol to formaldehyde and formic acid
Optic papillitis leading to blindness from metabolism of methanol to formaldehyde and formic acidLabs
 AG acidosis in ethylene glycol and methanol poisoning. Isopropyl alcohol does not cause ↑ AG or ketoacidosis because the metabolite is acetone, but test results are (+) for ketones.
AG acidosis in ethylene glycol and methanol poisoning. Isopropyl alcohol does not cause ↑ AG or ketoacidosis because the metabolite is acetone, but test results are (+) for ketones. ↑ Osmolal gap (difference between the measured and calculated serum osmolality)
↑ Osmolal gap (difference between the measured and calculated serum osmolality) Ca oxalate crystals in the urine in ethylene glycol poisoning
Ca oxalate crystals in the urine in ethylene glycol poisoning Toxicology screen and quantification
Toxicology screen and quantificationTreatment∗
 Competitive inhibition of alcohol dehydrogenase w/fomepizole (preferred) or ethanol (when fomepizole is not available) and hemodialysis (in all cases when ethanol is used as Rx and in fomepizole Rx and profound acidemia and signs of optic or renal injury)
Competitive inhibition of alcohol dehydrogenase w/fomepizole (preferred) or ethanol (when fomepizole is not available) and hemodialysis (in all cases when ethanol is used as Rx and in fomepizole Rx and profound acidemia and signs of optic or renal injury) Criteria for initiation of Rx: ethylene glycol plasma concentration ≥20 mg/dL (3.2 mmol/L) or methanol plasma concentration >20 mg/dL (6.2 mmol/L); suspected ethylene glycol or methanol ingestion and two or more of the following criteria: arterial pH <7.3, Osmo gap >10 mOsm/L, serum CO2 level <20 mmol/L
Criteria for initiation of Rx: ethylene glycol plasma concentration ≥20 mg/dL (3.2 mmol/L) or methanol plasma concentration >20 mg/dL (6.2 mmol/L); suspected ethylene glycol or methanol ingestion and two or more of the following criteria: arterial pH <7.3, Osmo gap >10 mOsm/L, serum CO2 level <20 mmol/L Dosing of fomepizole:
Dosing of fomepizole: IV rehydration is indicated in all pts, with NaHCO3 administration in pts w/pH <7.3.
IV rehydration is indicated in all pts, with NaHCO3 administration in pts w/pH <7.3. In methanol poisoning, administer folinic acid (leucovorin) 1 mg/kg BW IV (≤50 mg) or stereospecific levoleucovorin at one-half dose of leucovorin. The administration of folate is beneficial because formic acid is catabolized to CO2 and water by tetrahydrofolate synthetase (enzyme dependent on stored folate).
In methanol poisoning, administer folinic acid (leucovorin) 1 mg/kg BW IV (≤50 mg) or stereospecific levoleucovorin at one-half dose of leucovorin. The administration of folate is beneficial because formic acid is catabolized to CO2 and water by tetrahydrofolate synthetase (enzyme dependent on stored folate). Pyridoxine may be beneficial in ethylene glycol poisoning (pyridoxine is a cofactor in metabolism of glycolic acid to glycine).
Pyridoxine may be beneficial in ethylene glycol poisoning (pyridoxine is a cofactor in metabolism of glycolic acid to glycine).Clinical Pearls
 The CNS dysfunction is primarily the result of the keto aldehyde metabolites.
The CNS dysfunction is primarily the result of the keto aldehyde metabolites. Intratubular obstruction and ARF may be caused by oxalate crystals in ethylene glycol poisoning.
Intratubular obstruction and ARF may be caused by oxalate crystals in ethylene glycol poisoning.7. Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
Etiology
 Exposure to smoke from fires; motor vehicle exhaust; or the burning of wood, charcoal, or natural gas for cooking or heating in poorly ventilated areas. CO is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, nonirritating gas. When inhaled, it produces toxicity by causing cellular hypoxia.
Exposure to smoke from fires; motor vehicle exhaust; or the burning of wood, charcoal, or natural gas for cooking or heating in poorly ventilated areas. CO is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, nonirritating gas. When inhaled, it produces toxicity by causing cellular hypoxia.Diagnosis
H&P
 Mild to moderately severe poisoning may manifest w/headache, fatigue, dizziness, nausea, dyspnea, confusion, or blurry vision.
Mild to moderately severe poisoning may manifest w/headache, fatigue, dizziness, nausea, dyspnea, confusion, or blurry vision. Severe poisoning may manifest w/arrhythmias, myocardial ischemia, pulmonary edema, lethargy, ataxia, syncope, seizure, coma, or cherry-red skin.
Severe poisoning may manifest w/arrhythmias, myocardial ischemia, pulmonary edema, lethargy, ataxia, syncope, seizure, coma, or cherry-red skin.Labs
 ↑ Carboxyhemoglobin (COHgb) level. Note: COHgb level >5% in nonsmokers confirms exposure. Heavy smokers may have levels of 10%.
↑ Carboxyhemoglobin (COHgb) level. Note: COHgb level >5% in nonsmokers confirms exposure. Heavy smokers may have levels of 10%. Direct measurement of SaO2. Note: Pulse oximetry and ABG may be falsely nl because neither measures SaO2 directly. Pulse oximetry is inaccurate because of the similar absorption characteristics of oxyhemoglobin and COHgb. ABG is inaccurate because it measures O2 dissolved in plasma (which is not affected by CO) and then calculates SaO2.
Direct measurement of SaO2. Note: Pulse oximetry and ABG may be falsely nl because neither measures SaO2 directly. Pulse oximetry is inaccurate because of the similar absorption characteristics of oxyhemoglobin and COHgb. ABG is inaccurate because it measures O2 dissolved in plasma (which is not affected by CO) and then calculates SaO2. Lytes, glucose, BUN, Cr, CPK, ABG (because lactic acidosis and rhabdo may develop)
Lytes, glucose, BUN, Cr, CPK, ABG (because lactic acidosis and rhabdo may develop) Pregnancy test in women of childbearing age (fetus at high risk)
Pregnancy test in women of childbearing age (fetus at high risk)Treatment
 Removal from site of CO exposure
Removal from site of CO exposure Ensuring of adequate airway
Ensuring of adequate airway Continuous ECG monitoring
Continuous ECG monitoring Fetal monitoring if pregnant
Fetal monitoring if pregnant 100% O2 by tight-fitting nonrebreather mask or ETT for 6 to 12 hr (↓ half-life of COHgb from 4-6 hr to 60-90 min)
100% O2 by tight-fitting nonrebreather mask or ETT for 6 to 12 hr (↓ half-life of COHgb from 4-6 hr to 60-90 min) Hyperbaric O2 (2.5-3 atm)
Hyperbaric O2 (2.5-3 atm) Half-life of COHgb to 20 to 30 min, amount of O2 dissolved in plasma
Half-life of COHgb to 20 to 30 min, amount of O2 dissolved in plasma Questionable whether there is any beneficial effect over normobaric O2
Questionable whether there is any beneficial effect over normobaric O2 May prevent the delayed neurologic sequelae of CO poisoning by ↓ cellular hypoxia and toxicity
May prevent the delayed neurologic sequelae of CO poisoning by ↓ cellular hypoxia and toxicity Consider for individuals with:
Consider for individuals with:Clinical Pearls
 Survivors of severe poisoning are at 14% to 40% risk for neurologic sequelae ranging from parkinsonism to neuropsychiatric sx (personality and memory disorders). Neurologic deficits are usually apparent within 3 wk of poisoning (but may manifest months later). Brain MRI may show changes in the white matter and basal ganglia.
Survivors of severe poisoning are at 14% to 40% risk for neurologic sequelae ranging from parkinsonism to neuropsychiatric sx (personality and memory disorders). Neurologic deficits are usually apparent within 3 wk of poisoning (but may manifest months later). Brain MRI may show changes in the white matter and basal ganglia. Sx of toxicity and prognosis do not correlate well w/COHgb levels.
Sx of toxicity and prognosis do not correlate well w/COHgb levels.∗ Data from Brent J: N Engl J Med 360:21, 2009.