Chapter 30 Inflammation and the immune system
The Function of the Immune System
The construction of the immune system allows it to adapt so as to mount a more rapid and vigorous attack each time it encounters a particular pathogen.
Components of the Immune System
Leucocytes
• Neutrophils
Other Components
How Does the Immune System Work?
Pathogens that invade the body stimulate the immune system, which has three main stages of response:
The effector phase is one of the following:
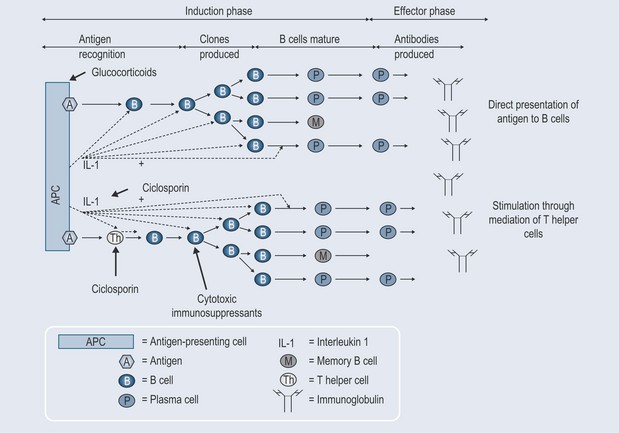
Humoral Response
A humoral-mediated response (Figure 30.1):
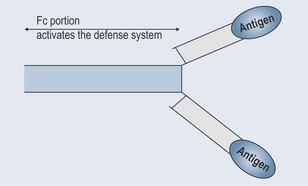
Antibodies or immunoglobulins (hence the shorthand Ig) have two main functions:
There are five classes of antibody: IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG and IgM.
• The Complement System
This is similar in mechanism to the coagulation cascade (see Figure 28.1, p. 212). It is activated by interaction in several ways:
The final part of complement activation produces a membrane attack complex, which creates holes in the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria (see Figure 29.1, p. 218).
The complement cascade has a feedback mechanism, which in theory should limit its action. However, several of the products of the complement cascade are powerful inflammatory stimulants, so it is possible for the inflammatory response to get out of hand.
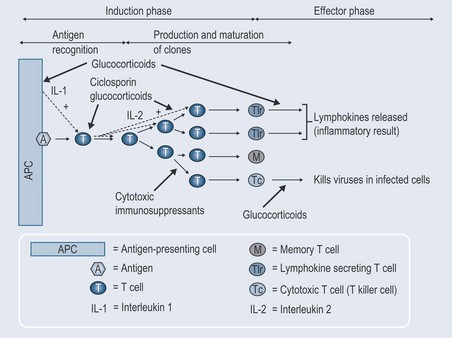
Cell-Mediated Response (Figure 30.3)
The Inflammatory System
The Inflammatory Response
The inflammatory response occurs in the following way:
Inappropriate T-cell activity underlies all types of hypersensitivity.
Components Involved in Inflammation
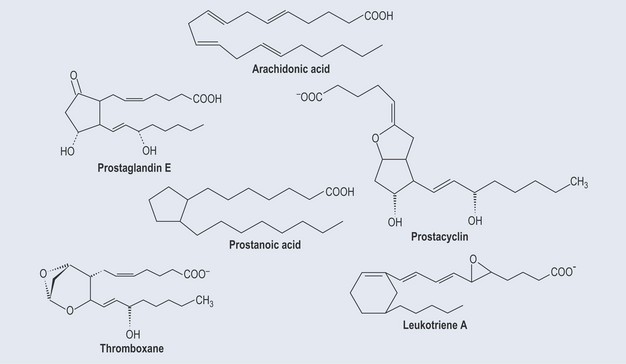
Prostaglandins
Thromboxanes
Proteins Involved in the Inflammatory and Immune Systems
Anti-Inflammatory Medication
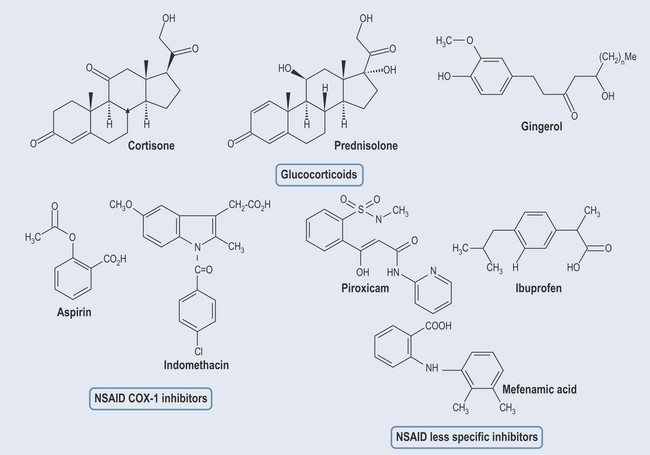
Glucocorticoids (Corticosteroids)
Prednisolone is a commonly used oral steroid.
• Adverse Effects
Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
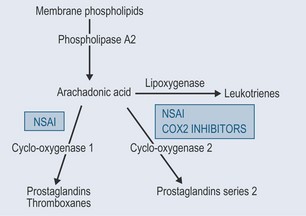
The anti-inflammatory effect of non-steroidal anti-inflammatories (NSAIDs) is due to inhibition of the COX enzyme (Figure 30.5). These drugs have three major effects:
• Anti-Inflammatory Effect
Different NSAIDs work on different COX enzymes (Figure 30.6):
Although the NSAIDs reduce inflammation, the mechanism is still not well understood.
• Analgesic Effect
PGE1 and PGE2 sensitize pain fibres to bradykinin or 5-hydroxytryptamine. Blocking their production will reduce this effect.
• Adverse Effects
• Aspirin
Adverse Effects
Immunosuppressants
There is an overlap between pure immunosuppressant drugs and chemotherapy (see Chapter 39 ‘Chemotherapy’, p. 309). Immunosuppressant drugs are used at much lower doses than for chemotherapy. They require lifelong use.