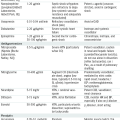
Acute infection occurs 2 to 6 wk from the time of viral transmission.
Acute infection occurs 2 to 6 wk from the time of viral transmission.• It most often is a self-limited mononucleosis-like illness: pharyngitis, rash, splenomegaly, and lymphadenopathy, occasionally w/hepatitis and aseptic meningitis.
• The p24 antigen and the HIV PCR are detected; HIV serology first becomes (+) 1 mo later.
 HIV viral Ab screening tests include:
HIV viral Ab screening tests include:• Enzyme immuno assay (EIA): A (-) EIA excludes infection except during the acute phase following primary infection (window period) before seroconversion occurs. A (+) EIA is confirmed by western blot. Combination of (+) EIA and (+) western blot has 99.5% sensitivity and 99.9% specificity.
• Rapid serologic screening HIV antigen–coated gelatin or latex particle agglutination assays: They are less sensitive and specific than standard ELISA tests.
• Western blot confirmatory test: performed when EIA is (+). It identifies specific viral antigens.
• Tests are (+) when both core and envelope antigens are present.
• Indeterminate when either antigen is present: A false(+) result occurs if unchanged during 6 mo.
• An FDA-approved at-home HIV screening test is also available. It uses swabs of oral fluids from upper and lower gums. A positive test requires confirmatory testing in the office. Negative home tests should be repeated within 3 months.
 Early stage (CD4 cells >400/mm3): Diffuse lymphadenopathy may be present. Levels of viral replication, 109 copies/day, occur at this stage even though the pt remains asymptomatic.
Early stage (CD4 cells >400/mm3): Diffuse lymphadenopathy may be present. Levels of viral replication, 109 copies/day, occur at this stage even though the pt remains asymptomatic. Middle stage (CD4 cells, 200-400/mm3)
Middle stage (CD4 cells, 200-400/mm3)• Mycobacterium tuberculosis infections, recurrent herpes zoster, persistent mucocutaneous herpes simplex infections, and recurrent bacteremias caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae and Salmonella spp occur.
• Kaposi’s sarcoma, oral candidiasis, and hairy leukoplakia appear.
 AIDS: advanced HIV infection (CD4 cell count <200/mm3). The classic opportunistic infections PCP, cerebral toxoplasmosis, cryptococcosis occur when CD4 cell count is <200/mm3; infections with CMV and MAC occur when CD4 cell count is <50/mm3.
AIDS: advanced HIV infection (CD4 cell count <200/mm3). The classic opportunistic infections PCP, cerebral toxoplasmosis, cryptococcosis occur when CD4 cell count is <200/mm3; infections with CMV and MAC occur when CD4 cell count is <50/mm3.Management Strategies
 Initial testing: CD4 cell count and HIV viral load (VL) are measured q3-6mo to guide decisions about antiretroviral use and prophylaxis against PCP and MAC infection.
Initial testing: CD4 cell count and HIV viral load (VL) are measured q3-6mo to guide decisions about antiretroviral use and prophylaxis against PCP and MAC infection. Other testing: This identifies latent infections that may become reactivated because of loss of T-cell function but can be prevented by the use of specific agents.
Other testing: This identifies latent infections that may become reactivated because of loss of T-cell function but can be prevented by the use of specific agents.• Serology to Toxoplasma gondii (IgG): Clinical infection may be prevented by TMP-SMZ used as prophylaxis for PCP.
• VDRL test: LP should be performed in pts w/a confirmatory specific test (FTA). Rx w/IM benzathine PCN if the CSF formula is nl, and IV PCN × 10 days if the CSF VDRL test is reactive or CSF pleocytosis, protein, or hypoglycorrhachia is present.
• PPD skin test showing induration of ≥5 mm, or pts w/exposure to someone w/active TB: Treat w/INH 300 mg/day for 9 mo or, in case of INH-induced hepatitis, rifampin 600 mg PO qd (only for those not receiving PIs or NRTIs) × 4 mo.
 Immunizations: Pts should receive the annual influenza vaccine each fall. Pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine is recommended for all pts w/HIV infection and is most effective in those w/CD4 counts >200. Invasive pneumococcal infections occur w/↑ frequency in HIV-infected pts; these pts should be revaccinated every 5 yr. Hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for pts who have no evidence of prior infection. They should also receive hepatitis A vaccine.
Immunizations: Pts should receive the annual influenza vaccine each fall. Pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine is recommended for all pts w/HIV infection and is most effective in those w/CD4 counts >200. Invasive pneumococcal infections occur w/↑ frequency in HIV-infected pts; these pts should be revaccinated every 5 yr. Hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for pts who have no evidence of prior infection. They should also receive hepatitis A vaccine.Prophylactic Agents
 PJP prophylaxis if CD4 cell level is <200/mm3
PJP prophylaxis if CD4 cell level is <200/mm3• TMP-SMZ (1 DS qd): most effective agent. It also provides protection against infections with T. gondii, Nocardia spp, and enteric pathogens.
• Adverse reactions to TMP-SMZ (GI distress, fever, rash, and leukopenia): occur in 40%. Discontinuation of drug may be necessary.
• Dapsone indicated w/TMP-SMZ rash; 30% w/TMP-SMZ toxicity develop reaction to dapsone.
• Aerosolized pentamidine, 300 mg/mo, and atovaquone, 750 mg bid, are third-line agents.
 Prophylaxis against MAC in pts w/CD4 cell counts <50/µL Azithromycin 1200 mg weekly is the most effective agent.
Prophylaxis against MAC in pts w/CD4 cell counts <50/µL Azithromycin 1200 mg weekly is the most effective agent. Prophylaxis for several opportunistic infections can be discontinued if there has been a sustained CD4 cell count ↑ >200 associated w/ART (PCP, toxoplasmosis, cryptococcosis) and 100 for MAC for more than 3 to 6 mo.
Prophylaxis for several opportunistic infections can be discontinued if there has been a sustained CD4 cell count ↑ >200 associated w/ART (PCP, toxoplasmosis, cryptococcosis) and 100 for MAC for more than 3 to 6 mo. Prophylaxis against toxoplasmosis if CD4 cell count <100/µL and positive serology: TMP-SMZ (IDS qd).
Prophylaxis against toxoplasmosis if CD4 cell count <100/µL and positive serology: TMP-SMZ (IDS qd). Prophylaxis against tuberculosis if TST>5 mm or +IGRA: INH, 300 mg/day × 9 months.
Prophylaxis against tuberculosis if TST>5 mm or +IGRA: INH, 300 mg/day × 9 months.Antiretroviral Therapy (ART)
 Rx goals are maximal and durable suppression of VLs (<50 copies/mL), restoration of immunologic function (CD4 cell count), prevention of HIV disease progression, and prevention of transmission to an uninfected partner.
Rx goals are maximal and durable suppression of VLs (<50 copies/mL), restoration of immunologic function (CD4 cell count), prevention of HIV disease progression, and prevention of transmission to an uninfected partner. Agents in six separate drug classes are now available: NRTIs, NNRTIs, PIs, fusion inhibitors, co-receptor inhibitors, and integrase inhibitors.
Agents in six separate drug classes are now available: NRTIs, NNRTIs, PIs, fusion inhibitors, co-receptor inhibitors, and integrase inhibitors. The standard regimen is two NRTIs (TNF/3TC) plus an NNRTI (efavirenz [Sustiva] or rilpivirine), ritonavir-boosted PI agent (darunavir, lopinavir, atazanavir, fosamprenavir), or an integrase inhibitor (raltegravir, elvitegravir).
The standard regimen is two NRTIs (TNF/3TC) plus an NNRTI (efavirenz [Sustiva] or rilpivirine), ritonavir-boosted PI agent (darunavir, lopinavir, atazanavir, fosamprenavir), or an integrase inhibitor (raltegravir, elvitegravir). ART should be offered to all pts with HIV infection regardless of CD4 count and HIV VL. The rationale for early Rx is that the disorders associated with long-term viral replication—coronary artery disease, bone demineralization, renal disease, and possibly neurocognitive changes—may be averted or delayed if HIV VL is reduced with ART. ART at this stage may prevent transmission to an uninfected partner.
ART should be offered to all pts with HIV infection regardless of CD4 count and HIV VL. The rationale for early Rx is that the disorders associated with long-term viral replication—coronary artery disease, bone demineralization, renal disease, and possibly neurocognitive changes—may be averted or delayed if HIV VL is reduced with ART. ART at this stage may prevent transmission to an uninfected partner. Indications for initiation of ART according to DHHS guidelines are: symptomatic HIV infection, CD4 cell count <500/µL, history of AIDS-defining opportunistic infection or malignancy, presence of HIV-associated nephropathy, active co-infection with hepatitis B or C virus, pregnancy (to prevent perinatal transmission).
Indications for initiation of ART according to DHHS guidelines are: symptomatic HIV infection, CD4 cell count <500/µL, history of AIDS-defining opportunistic infection or malignancy, presence of HIV-associated nephropathy, active co-infection with hepatitis B or C virus, pregnancy (to prevent perinatal transmission). After initiation of ART, measure CD4 counts and VLs at 1 and 4 mo. The criteria used to assess initial ART efficacy are as follows:
After initiation of ART, measure CD4 counts and VLs at 1 and 4 mo. The criteria used to assess initial ART efficacy are as follows:• >1.0 log ↓ in HIV VL within 4 wk and undetectable VL (HIV RNA <50 copies/mL) within 4 mo
 Pts should be evaluated q3mo at first to assess VL responses. In adherent pts with undetectable HIV VL, pts may be evaluated q6mo. A new regimen should be initiated in pts whose initial regimen has failed (rebound viremia).
Pts should be evaluated q3mo at first to assess VL responses. In adherent pts with undetectable HIV VL, pts may be evaluated q6mo. A new regimen should be initiated in pts whose initial regimen has failed (rebound viremia). CD4 counts on an average boost to 250 cells above baseline value within 1 to 2 yr of Rx; failure to achieve this boost in adherent pts with undetectable VL does not indicate ART failure and does not warrant changing the regimen.
CD4 counts on an average boost to 250 cells above baseline value within 1 to 2 yr of Rx; failure to achieve this boost in adherent pts with undetectable VL does not indicate ART failure and does not warrant changing the regimen. Drug resistance testing should be performed when there is ART failure; a new regimen should be selected on the basis of antiviral hx and absence of mutations to ART-included agents on resistance testing. Once resistance develops to an agent in one class, cross-resistance to other drugs in the same class frequently occurs.
Drug resistance testing should be performed when there is ART failure; a new regimen should be selected on the basis of antiviral hx and absence of mutations to ART-included agents on resistance testing. Once resistance develops to an agent in one class, cross-resistance to other drugs in the same class frequently occurs. An ideal regimen should include preferably three agents from two separate drug classes to which the virus retains susceptibility. Agents frequently included in a new regimen include the following:
An ideal regimen should include preferably three agents from two separate drug classes to which the virus retains susceptibility. Agents frequently included in a new regimen include the following:• Raltegravir (400 mg bid) or elvitegravir: integrase inhibitors
• Maraviroc inhibits viral binding to co-receptor CCR5. A viral tropism assay must be first measured before initiation to ensure that the virus is an R5 strain.
• Etravirine (200 bid): an NNRTI to which certain NNRTI-resistant strains (K103N mutants) remain susceptible
• Darunavir/ritonavir (600/100 bid): a PI to which certain PI-resistant strains remain susceptible
 NRTI agents and their toxicities
NRTI agents and their toxicities• Zidovudine (Retrovir, AZT) 300 mg bid with lamivudine (Epivir, 3TC) 150 mg bid (Combivir). Transient myalgias, headache, and fatigue are common. Hematologic toxicity (leukopenia and anemia) is related to HIV disease status.
• Tenofovir (TNF, Viread) 300 mg/day in combination w/emtricitabine (FTC) 200 mg/day (Truvada). Nephrotoxicity is the major adverse reaction, w/declines in GFR of 8%.
• Abacavir (Ziagen) 300 mg bid; combined w/3TC (Epzicom, 1 tablet qd). Risk of abacavir hypersensitivity ↑ to 8% in pts w/HLA-B5701 genotype. Testing for the haplotype is indicated before starting abacavir.
• Zalcitabine (Hivid, ddC) 0.75 mg tid. It is rarely used because of relative lack of potency and tid schedule.
• Didanosine (Videx, ddI) 200 mg bid, or 400 mg enteric-coated tablet once qd. It is rarely used because of toxicities: pancreatitis (10%); peripheral neuropathy (15%).
 NNRTI agents and their toxicities
NNRTI agents and their toxicities• Efavirenz (Sustiva) 600 mg every night used in combination with Truvada (Atripla, once daily): Transient neurologic or psychiatric sx—insomnia, dizziness, or impaired concentration—occur in 50% of pts. The sx may progress and require discontinuation of the drug. Delusions and acute depression may also occur. Transient rash may also occur but rarely requires discontinuation of the drug.
• Rilpivirine (25 mg once daily) used in combination with Truvada (Complera, once daily). It may cause rash and is particularly effective in people whose baseline VL <100,000 copies.
• Etravirine 200 mg bid. It is used primarily as a second-line drug in pts who have resistance to Sustiva. Rash occurs as with nevirapine.
• Nevirapine (Viramune) 200 mg bid. Rash occurs in 10% of pts. Nevirapine should not be used in women w/CD4 cell counts >250 and men w/CD4 cell counts >400 because of risks of severe hepatotoxicity in this setting.
 PIs (in combination w/low-dose ritonavir) and their toxicities
PIs (in combination w/low-dose ritonavir) and their toxicities• The PIs have multiple drug interactions that result from their elimination by P-450 CYP3A.
• Metabolic complications associated w/all PI agents
• Older agents in this class (ritonavir in high dose, Kaletra) led to insulin resistance, fat accumulation, lipoatrophy, lipid disturbances; these have a reduced incidence with newer agents (darunavir).
• Serum cholesterol and lipid abnlities may occur. In addition to dietary changes (↑ fiber content of the diet along w/↓ the amount of saturated and hydrogenated fat), Rx w/statins may be necessary.
 Ritonavir (Norvir) (100 mg bid), a potent inhibitor of CYP3A4, is used to boost the concentration of a PI agent with which it is used. The particular PI agent would include:
Ritonavir (Norvir) (100 mg bid), a potent inhibitor of CYP3A4, is used to boost the concentration of a PI agent with which it is used. The particular PI agent would include:• Darunavir/R (Prezista) 600/100 bid. This agent is effective as a first-line agent or a second-line agent. It has a favorable lipid altering profile.
• Atazanavir (Reyataz)/ritonavir 300 mg PO qd/100 mg qd: A first-line PI agent because it does not lead to significant changes in cholesterol or TGs.
• Fosamprenavir/ritonavir 1400/200 qd. It has efficacy comparable to that of other PIs.
• Lopinavir/ritonavir (Kaletra) 400 mg bid/100 mg bid or 800/200 mg qd. This is now a second-line agent because it causes lipid abnlities.
• Saquinavir/ritonavir (1000 mg bid/100 mg bid) and indinavir/ritonavir 800 mg bid/100 mg bid and nelfinavir (Viracept) 1250 mg bid are no longer used because they are not as potent as the preceding agents.
 Integrase inhibitors
Integrase inhibitors• Raltegravir (Isentress) 400 bid. This is a potent regimen in combination with Truvada with minimal side effects.
• Elvitegravir used in combination with cobicistat (to boost level) and Truvada (Stribild, once daily). It is a potent once daily regimen with minimal side effects.
Postexposure Prophylaxis (PEP)
 PEP for occupational exposures: The transmission rate of HIV after an exposure w/o antiviral use is low—0.3%. Truvada/raltegravir is indicated for pts w/high-risk exposures (visible blood on device causing injury from a known HIV-infected person w/high VL), preferably within 24 hr of exposure for a 1-mo duration.
PEP for occupational exposures: The transmission rate of HIV after an exposure w/o antiviral use is low—0.3%. Truvada/raltegravir is indicated for pts w/high-risk exposures (visible blood on device causing injury from a known HIV-infected person w/high VL), preferably within 24 hr of exposure for a 1-mo duration.Preexposure Prophylaxis (PrEP)
 Truvada should be considered in selected situations for uninfected persons who have high-risk encounters with known HIV-infected persons. PrEP is effective only when taken regularly.
Truvada should be considered in selected situations for uninfected persons who have high-risk encounters with known HIV-infected persons. PrEP is effective only when taken regularly.HIV in Pregnancy
 The goals of ART in pregnant women are to provide Rx for the mother and to ↓ vertical transmission (in utero or perinatally). Rx should be initiated during the second trimester.
The goals of ART in pregnant women are to provide Rx for the mother and to ↓ vertical transmission (in utero or perinatally). Rx should be initiated during the second trimester. Efavirenz is not recommended for women in their first trimester of pregnancy.
Efavirenz is not recommended for women in their first trimester of pregnancy. Possible strategies to improve adherence
Possible strategies to improve adherence• Several strategies can be used to improve adherence, which is critical to maintain >95% to prevent resistance and to maintain durability of the regimen.
• Depression or substance abuse should be treated before Rx is initiated (except when antiretroviral Rx is urgently needed), and tools such as pill boxes, alarms, and charts should be provided.
Treatment of Symptomatic Pts w/AIDS-Defining Illness
 The use of ART in pts w/active opportunistic infections may be complicated by the immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS). IRIS usually involves constitutional sx along w/local reactions 1 to 2 mo after ART. Nonetheless, when both infections are diagnosed simultaneously, particular antimicrobial Rx for the opportunistic infection diagnosed should be started immediately and HAART should not be delayed, especially in pts w/low CD4 cell counts. IRIS may be managed w/anti-inflammatory agents while maintaining both the particular antimicrobial agent and ART Rx.
The use of ART in pts w/active opportunistic infections may be complicated by the immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS). IRIS usually involves constitutional sx along w/local reactions 1 to 2 mo after ART. Nonetheless, when both infections are diagnosed simultaneously, particular antimicrobial Rx for the opportunistic infection diagnosed should be started immediately and HAART should not be delayed, especially in pts w/low CD4 cell counts. IRIS may be managed w/anti-inflammatory agents while maintaining both the particular antimicrobial agent and ART Rx.Fungal Disorders
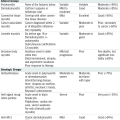
 Candida infection (thrush) may involve mucous membranes of the mouth.
Candida infection (thrush) may involve mucous membranes of the mouth.• Dx: by clinical appearance—whitish patches w/erythematous base; KOH preparation may demonstrate budding yeast and pseudohyphae.
• DDx: herpes simplex and aphthous ulcers (painful), oral hairy leukoplakia (as a result of EBV)
• Rx: clotrimazole troches 5×/day × 10 days; refractory cases fluconazole 100 mg PO × 10 days
 Esophagitis/oropharyngeal candidiasis is usually present when there is odynophagia or dysphagia.
Esophagitis/oropharyngeal candidiasis is usually present when there is odynophagia or dysphagia.• DDx: EBV, CMV, giant esophageal ulcers, and cancer, which should be considered in those pts not responding to antifungal Rx
• Rx: fluconazole 100 mg PO bid × 3 wk
 Cryptococcus (neoformans) infection
Cryptococcus (neoformans) infection• Pts may have headache, fever, ΔMS, meningismus (only 30%) w/cranial nerve palsies; Cryptococcus may disseminate to lungs, skin, blood, liver, and prostate. Nuchal rigidity may be absent. Dx is made by spinal fluid analysis; head CT scan should be performed first. Spinal WBC, glucose, and protein levels may all be nl. Cryptococcal antigen is the most sensitive (>1:16 in 95% cases). Serum cryptococcal antigen is reactive in >90% of pts w/CNS involvement.
• Initial Rx is w/amphotericin B (0.7 mg/kg/day) for 2 wk w/adjunctive flucytosine (100 mg/kg/day), unless preexisting cytopenias prohibit its use. Serum flucytosine levels must be monitored. Maintenance PO fluconazole Rx (200-400 mg/day) prevents relapse and may be withdrawn when ART-restored CD4 is >200.
 Coccidioidomycosis
Coccidioidomycosis• After initial Rx for coccidioidomycosis, lifelong suppressive Rx is recommended w/fluconazole 400 mg PO qd or itraconazole 200 mg PO bid.
• Recommendations for discontinuation of secondary prophylaxis (long-term maintenance Rx) in a pt w/a CD4 count >100 receiving ART are not available.
• Fluconazole and itraconazole have potential teratogenicity in pregnant women. Consider amphotericin B (preferred), especially during the first trimester. All HIV(+) women receiving azole Rx for coccidioidomycosis should maintain birth control precautions.
 Histoplasmosis
Histoplasmosis• Initial Rx for disseminated histoplasmosis is amphotericin B for 1 to 2 wk followed by long-term maintenance Rx w/itraconazole 200 mg PO bid.
• Discontinuation of long-term maintenance may be considered if the ART-restored CD4 count is >200.
• Itraconazole has teratogenicity and embryotoxicity and should not be offered during pregnancy. Rx w/amphotericin B is preferred during the first trimester. HIV-infected women receiving azole Rx should maintain effective birth control measures.
 Pneumocystis infection
Pneumocystis infection• Pts have SOB and nonproductive cough w/few findings on exam; CXR usually reveals an interstitial infiltrate but may be nl in initial stages.
• Dx is usually made by sputum induction or by BAL, w/visualization by monoclonal Ab, methenamine silver stain, or PCR.
• PO regimens: Rx in mild cases (Po2, >70; A-a gradient, <35 mm Hg) for a 3-wk course.
• TMP-SMZ (Bactrim DS, Septra DS) 15 mg/kg/day in three divided doses
• TMP-dapsone: trimethoprim 15 mg/kg/day and dapsone 100 mg/day (need to r/o G6PD deficiency w/dapsone)
• Primaquine and clindamycin: primaquine (also need to exclude G6PD deficiency) 30 mg/day and clindamycin 450 mg PO qid
• Atovaquone (may be less effective than TMP-SMZ) 750 mg PO tid
• IV regimens if moderate to severe (Po2 <70 mm Hg or A-a gradient >35 mm Hg)
• TMP-SMZ 15 mg TMP/kg/day in three individual doses
• Pentamidine 3 mg/kg/day; may need to observe for hypotension, pancreatitis, hypoglycemia, and azotemia
• Trimetrexate 45 mg/m2 once qd for pts intolerant of or refractory to TMP-SMZ or pentamidine; must be given w/leucovorin
• Adjunctive corticosteroid Rx: indicated when PO2 is <70 mm Hg or A-a gradient is >35 mm Hg to prevent early deterioration of oxygenation by ↓ inflammation. There is a risk of reactivation of latent infection (CMV, histoplasmosis, TB) w/steroid use.
Mycobacterial Infections
 M. tuberculosis may cause pulmonary involvement, extrapulmonary involvement, or both. Extrapulmonary TB may involve meningitis, lymphadenitis, or peritonitis. W/more advanced disease (CD4 <200), there may be atypical CXR findings (e.g., nonapical involvement).
M. tuberculosis may cause pulmonary involvement, extrapulmonary involvement, or both. Extrapulmonary TB may involve meningitis, lymphadenitis, or peritonitis. W/more advanced disease (CD4 <200), there may be atypical CXR findings (e.g., nonapical involvement).• Caution is required for the use of TB meds and ART. Rifampin should be substituted w/rifabutin w/the use of PIs and NNRTIs. Saquinavir hard-gel should not be given w/rifabutin; PIs (indinavir, nelfinavir, amprenavir) require dosage modifications.
• HIV-infected pregnant women w/(+) PPD test reaction or exposure to active TB should be considered for chemoprophylaxis. Isoniazid w/pyridoxine is the recommended Rx.
 Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex (MAC)
Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex (MAC)• Sx are fever, night sweats, and wasting. Dissemination may involve lymph nodes, liver, and bone marrow, causing marrow suppression, diarrhea w/abd pain, gastroenteritis, and, rarely, pulmonary involvement. Dx is made by blood culture (special lysis-centrifugation technique), which takes an average of 3 wk; cultures of tissue or bone marrow are rarely necessary to make the dx.
• Combination Rx w/at least two agents:
• Clarithromycin 500 mg PO bid (azithromycin, 500 mg/day PO, is alternative)
• Ethambutol 15 mg/kg/day PO. Addition of a third agent (rifabutin) may be considered.
• Medications to be considered in pts who have had relapsing disease are rifabutin, ciprofloxacin, and amikacin. Rifabutin 300 mg/day or ciprofloxacin 500 to 750 mg bid can be used as third agents.
• Primary prophylaxis (CD4 count <50/µL, d/c when CD4 count >100): azithromycin 1200 mg PO weekly or clarithromycin 500 mg PO bid
Bacterial Infections
 Pts w/HIV may develop infections from S. pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, or Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Fever w/productive cough and lobar infiltrates may occur. Functional humoral response to S. pneumoniae may be impaired, leading to recurrent infections caused by these pathogens. Other pathogens include the following:
Pts w/HIV may develop infections from S. pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, or Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Fever w/productive cough and lobar infiltrates may occur. Functional humoral response to S. pneumoniae may be impaired, leading to recurrent infections caused by these pathogens. Other pathogens include the following:• Salmonella spp: recurrent bacteremia; treat w/ampicillin, TMP-SMZ, ciprofloxacin, or third-generation cephalosporin, based on sensitivities and clinical presentation; GI sx may not be present. Avoid raw or undercooked eggs, poultry, meat, and seafood.
• Listeriosis: in HIV-infected individuals who are severely immunosuppressed. Soft cheeses and ready-to-eat foods (hot dogs, cold cuts) should be avoided or heated until steaming hot.
• Sinusitis: It may be a routine bacterial infection or involve P. aeruginosa or fungi.
• Bacillary angiomatosis: an infection involving skin, w/red lesions that can be mistaken for Kaposi’s sarcoma; can involve viscera (liver, spleen, bone); caused by Rochalimaea henselae or Rochalimaea quintana; treat w/erythromycin or doxycycline. Other potential bacterial pathogens in HIV are Rhodococcus equi, which may cause cavitating pneumonia, and Nocardia.
Viral Infections
 Herpes simplex
Herpes simplex• May involve mucous membranes, cause genital herpes, or cause rectal or perirectal infection, resulting in proctitis
• Initial Rx: acyclovir 200 mg PO 5×/day × 10 days; recurrent episodes may need Rx w/400 mg PO 3 to 5×/day × 7 days or until clinically resolved. IV foscarnet or cidofovir can be used for acyclovir-resistant isolates of HSV.
 Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C• Pts w/HIV infection should be tested for HCV by enzyme immunoassay. If test result is (+), confirm w/RIBA or PCR for HCV RNA.
• Pts w/HCV and HIV should receive vaccination for hepatitis A if they are (−) for hepatitis A Abs.
• Pts w/HIV-HCV co-infection are at risk for chronic liver disease and should be evaluated for Rx by providers w/experience in treating both HIV and HCV.
 CMV: Infection from this virus may cause illness involving the retina, GI tract (including esophagus, colon), and CNS.
CMV: Infection from this virus may cause illness involving the retina, GI tract (including esophagus, colon), and CNS.• Chorioretinitis may develop in 25% of AIDS pts and also may be unilateral, w/viremia involving other organs; the pt usually reports ↓ vision or “floaters”; ophthalmologic evaluation may be necessary to confirm dx.
• Esophagitis: Deep ulcerations are seen, confirmed by the presence of inclusion bodies by bx.
• Colitis: usually associated w/diarrhea, weight loss, and fever. It occurs in approximately 10% of AIDS pts.
• CNS encephalitis or polyradiculopathy (areflexic paraplegia)
• Rx: Three agents are available. Rx may be discontinued if ART-restored CD4 cell counts are >200.
• Retinitis: Ganciclovir implant is effective in delaying progression of disease; PO valganciclovir is used to prevent systemic manifestations of disease.
• Ganciclovir: induction dose, 5 mg/kg bid × 14 days, followed by 5 mg/kg/day indefinitely for retinitis. It may cause granulocytopenia or neutropenia related to dose, which is compounded by the use of AZT and possibly by other antiretroviral medications.
• Foscarnet: induction dose, 60 mg/kg q8h IV for 2 to 3 wk; dosing depends on CrCl and requires adjustment. Maintenance Rx is 90 to 120 mg/kg q24h.
• Cidofovir: 5 mg/kg weekly for 2 wk, then every other week as maintenance
 Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: demyelinating disease most often involving posterior cortex of brain, resulting in slowly progressive cognitive impairments. Clinical and radiologic improvement or, in some cases, complete resolution may occur w/ART-associated restoration of CD4 cell counts.
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: demyelinating disease most often involving posterior cortex of brain, resulting in slowly progressive cognitive impairments. Clinical and radiologic improvement or, in some cases, complete resolution may occur w/ART-associated restoration of CD4 cell counts.Parasitic Infections
 Toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis• Sx of Toxoplasma encephalitis: headache, fever, encephalopathy, focal neurologic deficits. Pneumonia, myocarditis, and retinal involvement occur less often.
• Dx is usually presumptive, based on multifocal ring-enhancing and hypodense mass lesions on CT, (+) toxoplasmic IgG serology, and a clinical and radiologic response to antitoxoplasmic Rx. Other causes of CNS mass lesions in AIDS pts include CNS lymphoma, fungal infection (Aspergillus, Cryptococcus), tuberculoma, bacterial abscess.
• Rx
• Pyrimethamine + sulfadiazine: pyrimethamine 100 to 200 mg loading dose, followed by 50 mg/day PO; sulfadiazine 1 to 1.5 g PO q6h as initial Rx, followed by a maintenance dose of pyrimethamine 25 mg/day, sulfadiazine 500 mg q6h
• Clindamycin: 600 to 1200 mg IV or 600 mg PO q6h (2.4 g/day) and pyrimethamine 50 mg/day PO
• Atovaquone, TMP-SMZ, and macrolides may have anti-Toxoplasma properties and can be considered alternative Rxs.
 Cryptosporidiosis: protozoal infection causing watery diarrhea, abd pain, and dehydration, particularly worse in pts w/CD4 counts <50. Dx is made by a modified AFB stain of stool. There is no effective Rx for HIV-infected pts, although nitazoxanide has been used in immunocompetent pts. Azithromycin, when taken for MAC prophylaxis, may ↓ the risk for cryptosporidiosis.
Cryptosporidiosis: protozoal infection causing watery diarrhea, abd pain, and dehydration, particularly worse in pts w/CD4 counts <50. Dx is made by a modified AFB stain of stool. There is no effective Rx for HIV-infected pts, although nitazoxanide has been used in immunocompetent pts. Azithromycin, when taken for MAC prophylaxis, may ↓ the risk for cryptosporidiosis. Isosporiasis: another protozoal infection w/a presentation similar to that of Cryptosporidium infection, w/oocysts found in routine stain of stool. Rx w/Bactrim 1 DS tablet qid × 10 days is followed by maintenance.
Isosporiasis: another protozoal infection w/a presentation similar to that of Cryptosporidium infection, w/oocysts found in routine stain of stool. Rx w/Bactrim 1 DS tablet qid × 10 days is followed by maintenance. Microsporidiosis: also similar to Cryptosporidium infection, w/oocysts found in special modified trichrome stain of stool. Rx w/albendazole (400 mg bid) is effective only against certain species; atovaquone is effective against others.
Microsporidiosis: also similar to Cryptosporidium infection, w/oocysts found in special modified trichrome stain of stool. Rx w/albendazole (400 mg bid) is effective only against certain species; atovaquone is effective against others.Malignant Neoplasms
 Malignant neoplasms may be occurring more frequently, as prognosis has been improved w/ART and prevention of opportunistic infections w/prophylactic Rx. The following have been listed as AIDS-defining malignant neoplasms:
Malignant neoplasms may be occurring more frequently, as prognosis has been improved w/ART and prevention of opportunistic infections w/prophylactic Rx. The following have been listed as AIDS-defining malignant neoplasms:• Kaposi’s sarcoma: found most often in HIV-infected homosexual men and less frequently (<5%) in pts in other HIV risk groups. The lesions from Kaposi’s sarcoma may be multifocal, involving skin (79%), lymph nodes (70%), GI tract (45%), and lungs (10%). Rx is based on extent of involvement; Rx w/intralesional vinblastine and w/radiation Rx is recommended for localized or small numbers of lesions, and chemoRx w/vincristine and vinblastine, etoposide, or bleomycin for aggressive and disseminated disease. Use of many interleukins (e.g., interleukin-4), tumor necrosis factor, and pentoxifylline is investigational.
• Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: a B-cell tumor associated w/EBV; most often extranodal; 30% may occur in pts w/CD4 cell counts >200; GI tract, CNS, bone marrow, or liver (or other viscera in smaller percentages) is also affected. Combination chemotherapy regimen (CHOP, M-BACOD, MACOP-B, CHOP-R, ACVBP) have approximately 50% response. Dose-limiting multiagent Rx is myelosuppression.
• Primary CNS lymphoma: Most cases occur in pts w/CD4 counts <200, but one third occur w/CD4 counts >200. Most are unifocal ring-enhancing mass lesions that cause focal neurologic deficits or seizures. Brain bx establishes dx.
• AIDS-related cervical cancer: associated w/HPV. It often occurs in pts w/multiple sexual partners and is possibly related to primary association of HIV to cancer development.
 Other cancers associated w/HIV infection
Other cancers associated w/HIV infection• Hodgkin’s lymphoma: may occur in a pt who is an IV drug user or who has STD. EBV may be linked to both Hodgkin’s disease and NHL; pts usually present w/disseminated stage III or stage IV disease involving bone marrow (50%) or liver and lungs.
• Anal carcinoma: associated w/HPV and impaired immunity. Homosexual men are at risk.
AIDS-Related Cachexia
 Megestrol acetate can ↑ appetite and food intake in pts w/AIDS-related weight loss. It can result in a statistically significant weight gain and in pt-reported improvement in overall sense of well-being.
Megestrol acetate can ↑ appetite and food intake in pts w/AIDS-related weight loss. It can result in a statistically significant weight gain and in pt-reported improvement in overall sense of well-being.