CHAPTER 24 Immunology and Vaccines
I. Introduction: The immune system consists of physical and chemical barriers and specific and nonspecific mechanisms to eliminate antigens.
II. Components of the Immune System
B. Polymorphonuclear leukocytes or neutrophils (PML or PMN)
2. Eosinophils
G. Cytokines
III. Immunization/Vaccinations
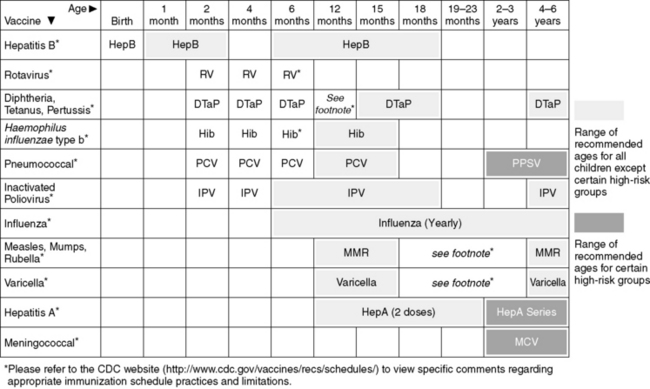
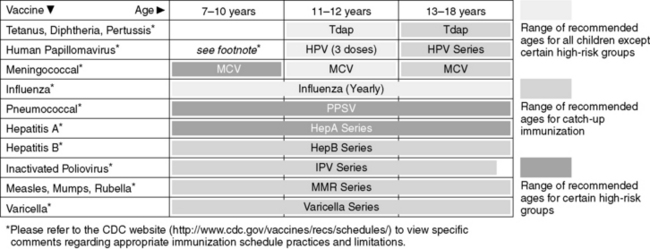
B. Common Vaccines (Figures 24-1 and 24-2)
1. Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (DTaP, DT, Rd, Tdap) vaccines
a. Daptacel (DTaP) diphtheria, tetanus toxioids, and acellular pertussis
b. Pediarix (DTaP-HBV-IPV) diphtheria, tetanus toxoids, and acellular pertussis, hepatitis B (recombinant), inactivated poliovirus vaccine
c. Infanrix (DTaP; diphtheria, tetanus toxoids, and acellular pertussis)
(2) Dose is IM injection of 0.5 mL each at 2, 4, and 6 months; one booster at 15–20 months and another booster at 4–6 years of age (total of 5 doses)
d. Adacel (Tdap) tetanus toxoid, reduced diphtheria toxoid, and acellular pertussis
2. Haemophilus influenzae vaccines
a. Combivax (Haemophilus b conjugate [meningococcal protein conjugate]) and hepatitis B [recombinant] vaccine)
(1) Indicated for infants 6 weeks to 15 months for Haemophilus influenzae type b and hepatitis B virus (HBsAg-negative mothers)
3. Pneumococcal vaccines
4. Poliovirus vaccines
5. Influenza vaccines
NOTE: Other TIV vaccine brands (Agriflu, Flulaval, Fluarix) are available.
a. Fluzone TIV (influenza virus trivalent inactivated vaccine, TIV)
(2) Dose is IM injection
b. Fluvirin TIV (influenza virus trivalent inactivated vaccine, TIV)
6. Measles, mumps, rubella (MMR) vaccine: live vaccine for measles, mumps, and rubella
7. Varicella virus vaccine (chickenpox vaccine)
8. Combined varicella and MMR vaccine
9. Meningococcal (meningitis) vaccines
a. Menomune MPSV4 (meningococcal polysaccharide serogroups A, C, Y, and W-135)
(2) Dose is SC injection of single dose of 0.5 mL; use within 30 minutes of reconstitution; protective antibody levels achieved within 7–10 days after vaccination
11. Human papillomavirus vaccine (HPV vaccine)
12. Rotavirus vaccines
a. RotaTeq (rotavirus vaccine, live, oral, pentavalent)
(1) Indicated for infants and children for prevention of rotavirus gastroenteritis caused by serotypes GI, G2, G3, and G4
b. Rotarix (rotavirus vaccine, live, oral, of serotypes G1 and non-G2 (G3, G4, and G9)
(1) Indicated for infants and children for prevention of rotavirus gastroenteritis caused by G1 and non-G2 (G3, G4, and G9)
13. Hepatitis A vaccines
a. Vaqta (inactivated virus vaccine)
b. Havrix (inactivated virus vaccine)
(2) Dose is IM injection
14. Combined hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccines
a. Twinrix (inactivated virus vaccine [recombinant], a combined hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccine)
(1) Indicated for adults, 18 years of age or older, against disease caused by hepatitis A virus; active immunization against disease caused by hepatitis A virus and hepatitis B virus (all known subtypes)
15. Hepatitis B vaccines
a. Engerix-B (recombinant)
(1) Indicated for all known subtypes of hepatitis B virus; it is expected that hepatitis D will be prevented by Engerix-B
(2) Dose is IM injection
(a) Adults (older than 19 years): three doses at 0, 1, and 6 months in a 20 mcg/mL suspension; first dose given on the elected date, second dose given 1 month later, third dose given 6 months after the first dose
PATIENT PROFILE
Patient Consultation: For recent exacerbations of COPD and community-acquired pneumonia, SV was hospitalized for 5 days and just completed her antibiotic therapies as an outpatient. SV wonders if there are any strategies to help her stay healthy and prevent another hospital admission.