138 Hypothyroidism
Salient features
History
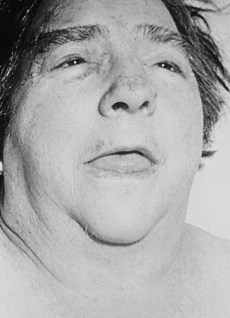
• Hair dryness or loss (Fig. 138.1)
• Change in the voice (hoarse, husky)
• Moderate weight gain in spite of loss of appetite
• Menstrual irregularity especially menorrhagia
• Radioiodine therapy for previous Graves’ disease (the patient may have associated eye signs of Graves’ disease)
• Medications and other compounds such as lithium carbonate and iodine-containing compounds (e.g. amiodarone, radiocontrast agents, expectorants containing potassium iodide and kelp)
• Family history of thyroid dysfunction, pernicious anaemia, diabetes mellitus, primary adrenal insufficiency
• Obtain history of hypercholesterolaemia, angina pectoris and hypertension (remember hypertension occurs in 10% of these patients and disappears with thyroxine replacement).
Questions
What is the cause for delayed relaxation in hypothyroidism?
The exact cause is not known. It is probably caused by decreased muscle metabolism.
What are the neurological manifestations of hypothyroidism?
• Delayed deep tendon reflexes (Woltman’s sign)
• Carpal tunnel syndrome, peripheral neuropathy
• Deafness to high tones (Trotter syndrome; Br Med Bull 1960;16:92)
• In Pendred syndrome, babies are born with a goitre, deafness and mental retardation
• Cerebellar syndrome (Lancet 1960;ii: 225)
• Hoffmann syndrome (i.e. muscle aches with myotonia in myxoedema). In infants, muscle involvement may result in Kocher–Debré–Sémélaigne syndrome or ‘infant Hercules’.
What do you understand by the term sick euthyroid syndrome?
• decrease in extrathyroidal conversion of T4 to T3, the active form of the thyroid hormone
• a decrease in TSH secretion, which causes decreased thyroidal secretion and, in time, decreases in serum T4 concentrations and further decreases in serum T3 concentrations—the latter as a result of both decreased secretion of T4 by the thyroid and diminished availability of T4 for peripheral conversion to T3
• decreased production or diminished affinity for thyroidal hormones of one or more major serum thyroid hormone-binding proteins: thyroxine-binding globulin, transthyretin and albumin. These decreases can result in decreased serum total T4 levels but not in free T4 or T3. Serum concentrations of reverse T3 (which is inactive) are increased because its deiodination is impaired.
What are the components of Grover’s disease?
Treatment for hypothyroidism with sheep thyroid extract was first reported by Murray in 1891.
Johann Hoffmann (1857–1919), a German neurologist.
In 1914 Thyroid hormone was crystallised by Kendall.
In 1952, triiodothyronine was discovered by Pitt-Rivers and Gross.
In 1970, the endogenous generation of T3 from T4 was described by Ingbar, Sterling and Braverman.