Chapter 56 Hypnosis
OVERVIEW.
Hypnosis (i.e., under hypnosis) is a state resembling sleep but induced by suggestion whereby the individual is responsive to imaginative experiences. During a session, the individual is guided to respond to suggestions for changes in thoughts, behaviors, sensations, perceptions, or subjective experiences.1
Abreaction is a specific technique that involves the reliving (dramatic) of traumatic events under hypnosis for the treatment of trauma victims (e.g., child abuse cases; posttraumatic stress disorder). Patients may present with massive psychogenic amnesia, or loss of a single functional system such as limb paralysis or psychogenic blindness. The technique serves to release repressed material that must then be followed up with psychotherapy to process the material.2
SUMMARY: CONTRAINDICATIONS AND PRECAUTIONS.
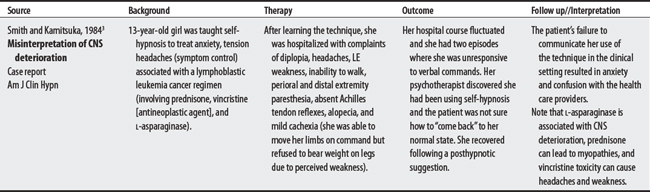
Note: Health care providers should probably be informed if their patients are undergoing hypnosis so that a patient’s induced behaviors don’t become confused with a real deterioration in medical status. In 1984, Smith and Kamitsuka3 reported a 13-year-old girl who used self-hypnosis to treat anxiety/tension headaches and confused health care workers into thinking that subsequent hypnotic-induced myopathies had an organic basis.
CONTRAINDICATIONS AND PRECAUTIONS
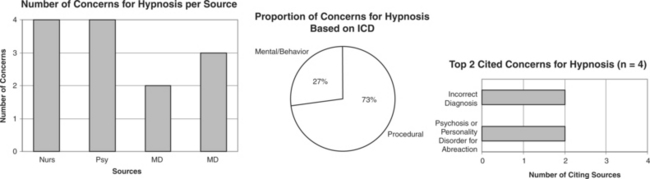
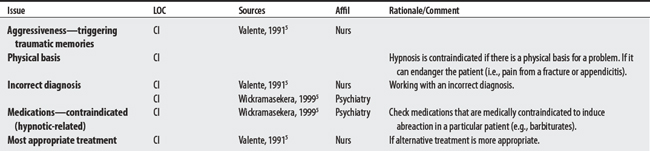
F00-F99 MENTAL AND BEHAVIORAL DISORDERS: FOR ABREACTION (SPECIFIC)
1 American Psychology Association Executive Committee, Division of Psychological Hypnosis. Web page Available at: http://www.apa.org. Accessed: November 30, 2005
2 Putnam FW. Using hypnosis for therapeutic abreaction. Psychiatr Med. 1992;10(1):51-65.
3 Smith MS, Kamitsuka M. Self-hypnosis misinterpreted as CNS deterioration in an adolescent with leukemia and vincristine toxicity. Am J Clin Hypn. 1984;26(4):280-282.
4 Wickramasekera I. Hypnotherapy. In: Jonas WB, Levin JS, editors. Essentials of complementary and alternative medicine. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 1999.
5 Valente SM. Using hypnosis with children for pain management. Oncol Nurs Forum. 1991;18(4):699-704.
6 Podoll E. The use and misuse of hypnosis in children. J Am Soc Psychosom Dent Med. 1981;28(2):57-62.