Chapter 16 How do drugs get into cells?
Absorption at the Cellular Level
Drugs or remedies cross cell membranes by the following methods:
Passive Diffusion (Absorption)
As the pH varies through the digestive tract, so do the characteristic of many compounds (see Chapter 8 ‘Acids and bases’, p. 55). This leads to certain compounds being more non-polar than others. This then affects how easily they can pass through the membrane. The condition of the digestive tract is therefore an important factor in chemical absorption.
Facilitated Passive Diffusion
• Passive Diffusion Through Protein Channels and how these Channels are ‘Gated’
Control of the opening and closing can be done in one of two ways:
Active Transport
Active transport requires a carrier mechanism, that uses energy to move a drug or remedy up a concentration gradient. The rate of movement does not depend on concentration but on the capacity of the carrier mechanism. The sodium–potassium pump is a form of active transport (see Figure 31.1, p. 236).
Distribution of the Drug
Three main factors that have to be considered in drug distribution:
The Importance of Blood Flow
The perfusion rate in different tissues varies as follows:
Other factors will also affect the drug or remedy distribution:
Plasma Protein Binding
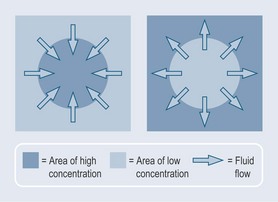
A drug or remedy can be bound to circulating plasma proteins (usually albumin) or it can move around freely in an unbound state. If the remedy is bound then it is not free to be used and is said to be inactive, therefore only the unbound remedy works. As these unbound molecules leave the circulation, molecules are released from the blood proteins because the concentration of free molecules is lower (see Figure 16.1, p. 124).