Chapter 55 Hippotherapy
OVERVIEW.
Hippotherapy is an intervention that uses equine (horse) movement to improve a patient’s neurological function. The patient engages in controlled, enjoyable, and challenging activity while riding on a horse. The intent is not to improve horse riding skills.1 Horses provides sensory input through their movement. The movements are thought to mimic movements occurring during human gait.
SUMMARY: CONTRAINDICATIONS AND PRECAUTIONS.
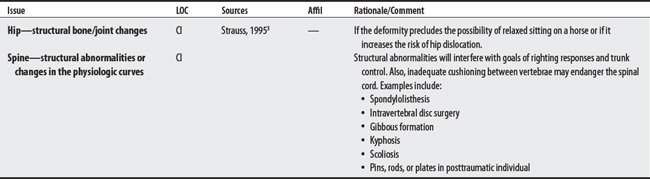
Two sources cited a total of 17 concerns for hippotherapy. Lelong et al2 cited one concern (for horse allergies), whereas Strauss3 listed 17. The largest proportion of concerns was for persons with neurological diseases (35%) and included issues such as the riding-related risks with epilepsy, spasticity-related sitting difficulties, or the concern of aggravating an existing condition (e.g., increased spasticity; fatigue-related deterioration). Horse allergy concerns were cited by both sources. Lelong et al2 advised that children be monitored for sensitivity.
CONTRAINDICATIONS AND PRECAUTIONS
D50-89 DISEASES OF BLOOD AND BLOOD-FORMING ORGANS AND CERTAIN DISORDERS
F00-F99 MENTAL AND BEHAVIORAL DISORDERS
G00-G99 DISEASES OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
I00-I99 DISEASES OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
M00-M99 DISEASES OF THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE
Q00-Q99 CONGENITAL MALFORMATIONS, DEFORMITIES, AND CHROMOSOMAL ABNORMALITIES
1 American Hippotherapy Association. www.americanhippotherapyassociation.org. accessed September 20, 2004
2 Lelong M, Castelain MC, Bras C, et al. An outbreak of allergy to horses in children: a review of 56 recent cases. Pediatrie. 1992;47:55-58. (from French abstract)
3 Strauss I. Hippotherapy: neurophysiological therapy on the horse. Thornhill, Ontario: Ontario Therapeutic Riding Association, 1995.
4 Harris SR, Lundgren BD. Joint mobilization for children with central nervous system disorders: indications and precautions. Phys Ther. 1991;71(12):890-896.