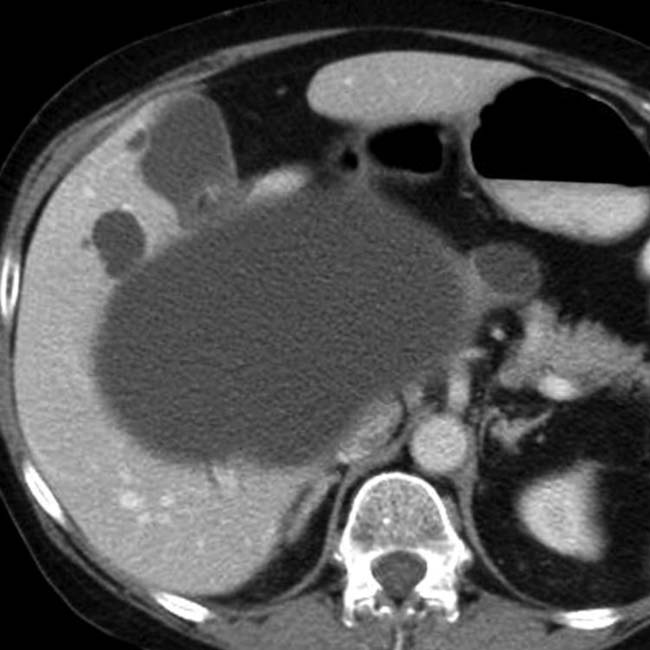
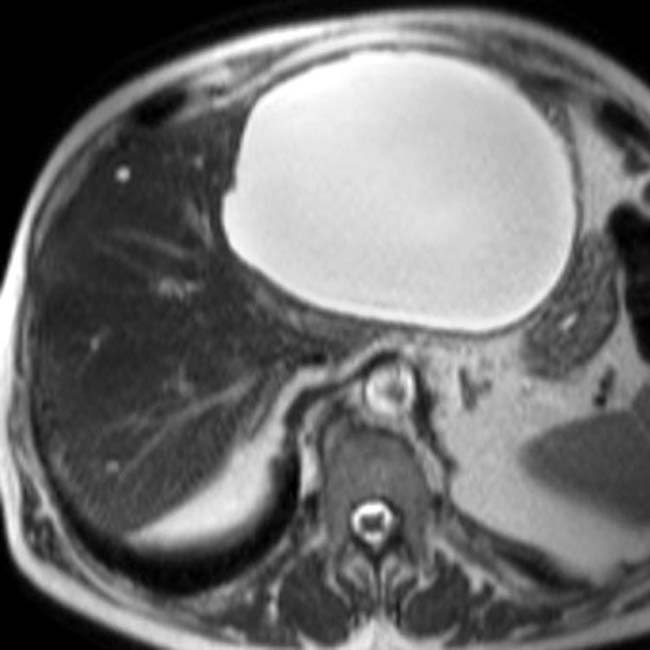
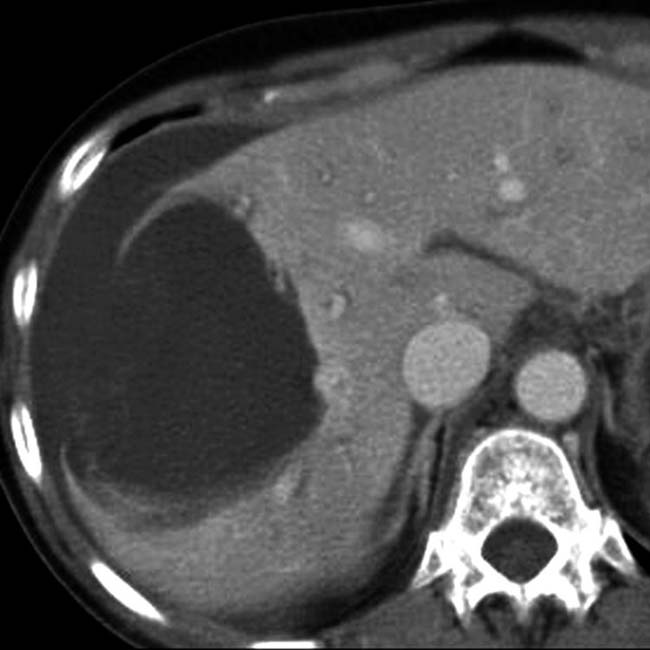
Simple hepatic or bile duct cyst
 with water density and homogeneous contents. No internal debris or wall irregularities are present. This is a classic simple cyst.
with water density and homogeneous contents. No internal debris or wall irregularities are present. This is a classic simple cyst.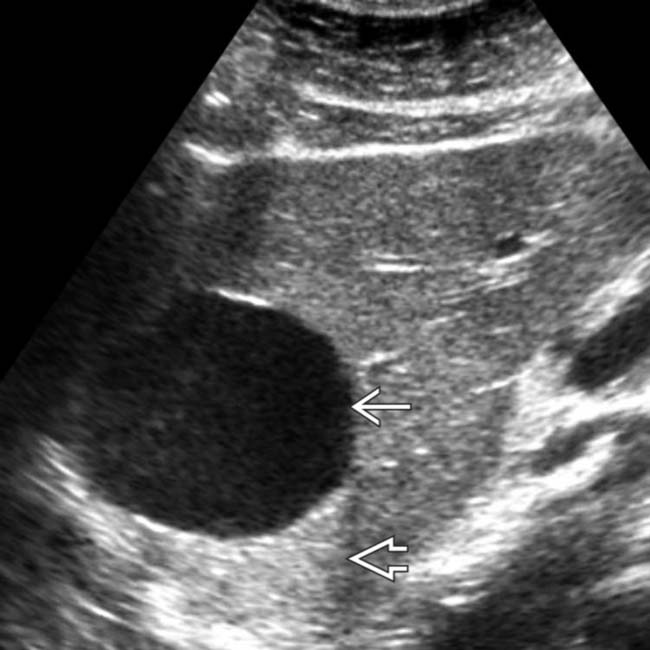
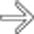
 with accentuated through-transmission
with accentuated through-transmission  . Either CT or US would have been sufficient to establish the diagnosis in this patient.
. Either CT or US would have been sufficient to establish the diagnosis in this patient.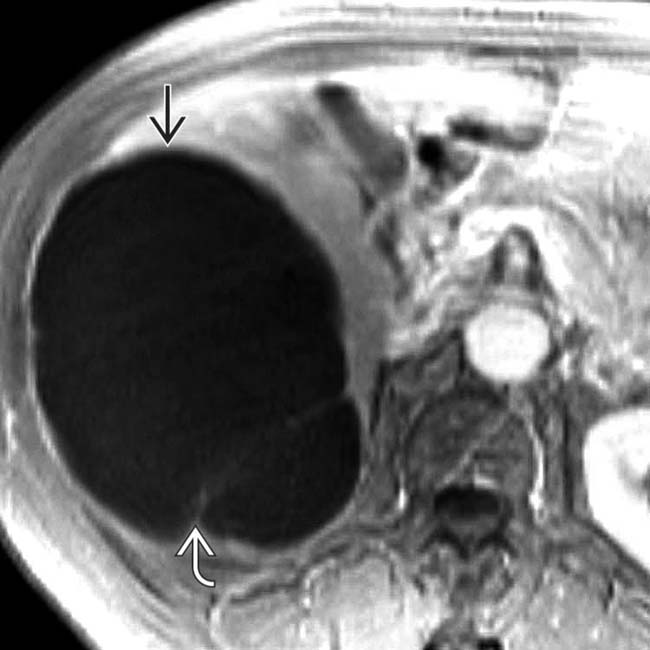
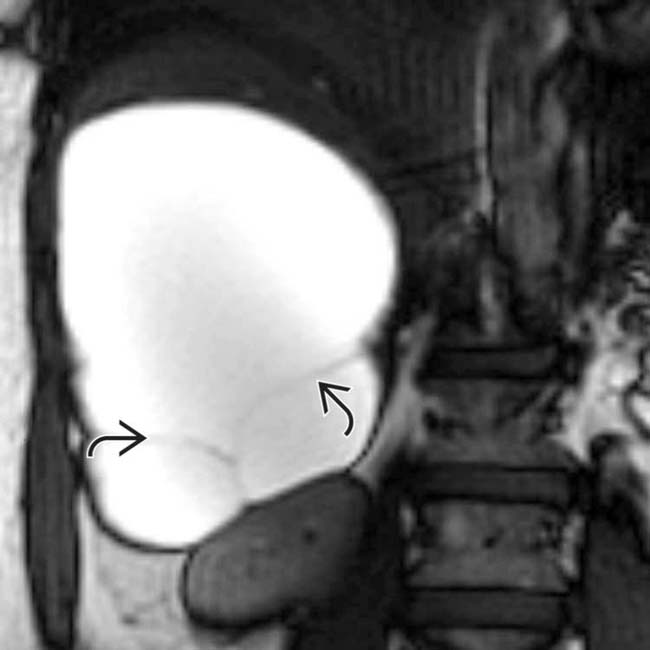
 that has homogeneous low intensity and several thin septa
that has homogeneous low intensity and several thin septa  .
.
 . The cyst has remained stable for years, and no other evaluation or intervention was performed.
. The cyst has remained stable for years, and no other evaluation or intervention was performed.IMAGING
General Features
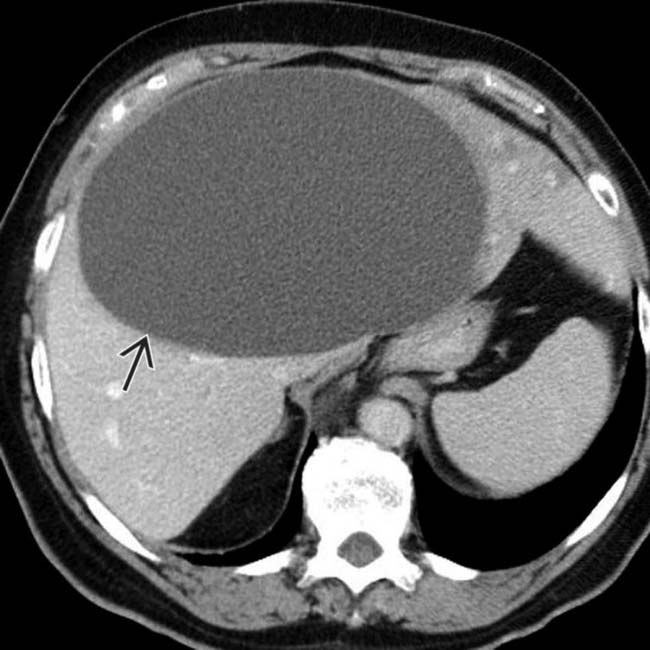
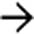 ; the cyst has water attenuation contents and a thin, smooth wall.
; the cyst has water attenuation contents and a thin, smooth wall.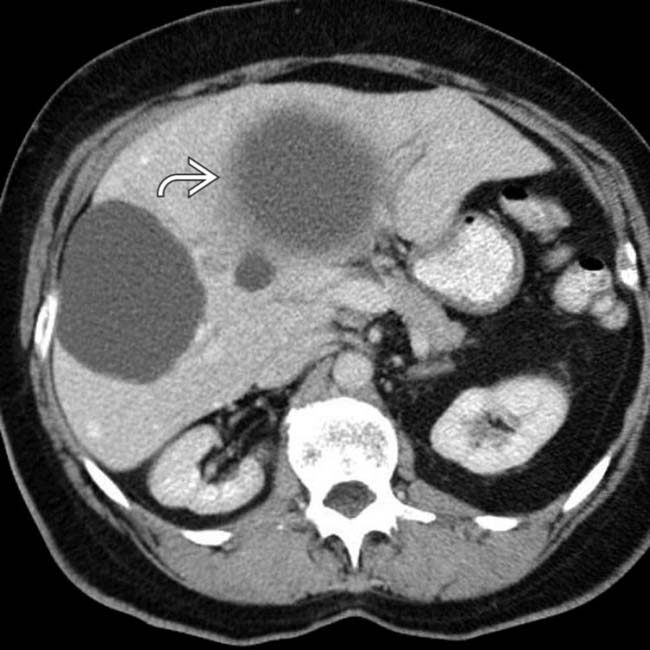
 , but this is due to partial volume averaging (as shown on the coronal reformatted images).
, but this is due to partial volume averaging (as shown on the coronal reformatted images).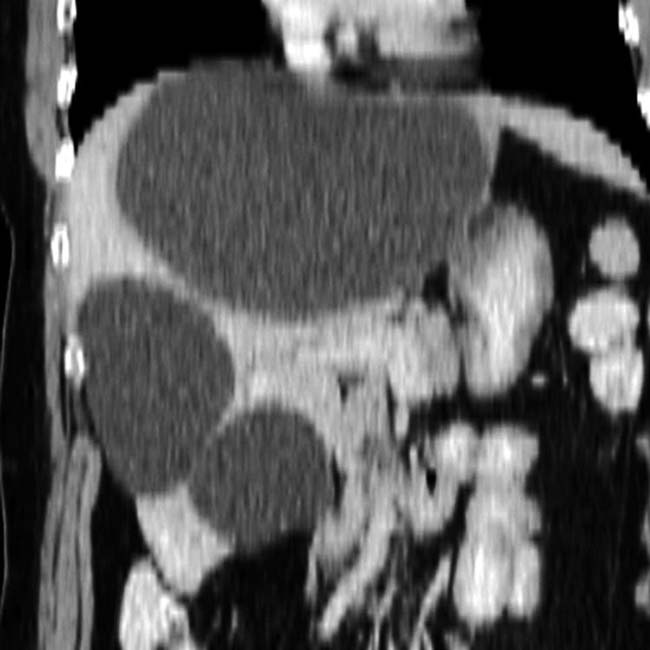
 .
.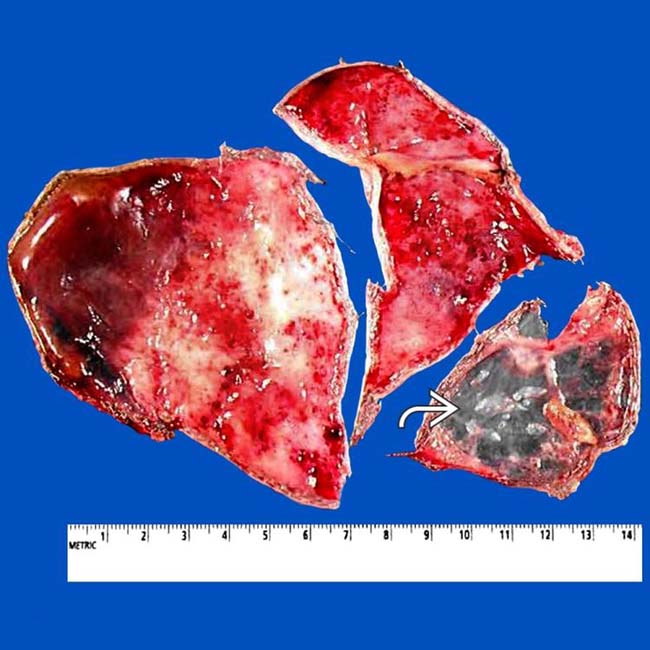
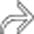 of the excised cyst.
of the excised cyst.
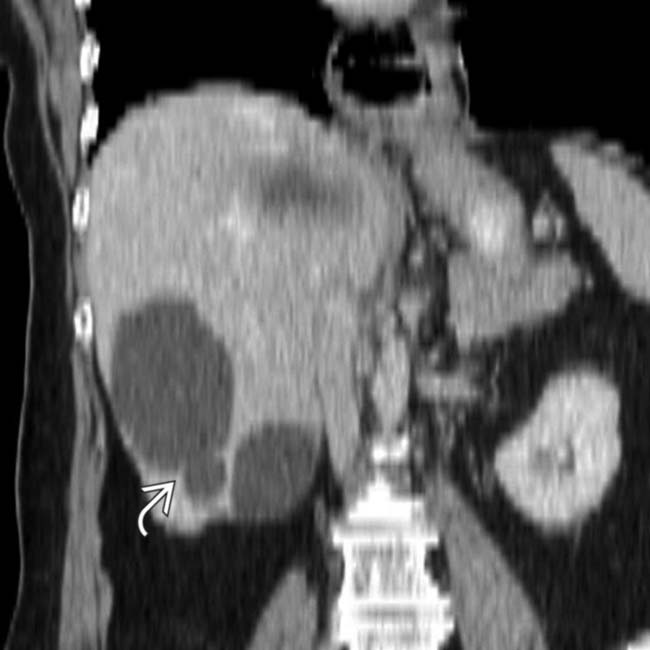
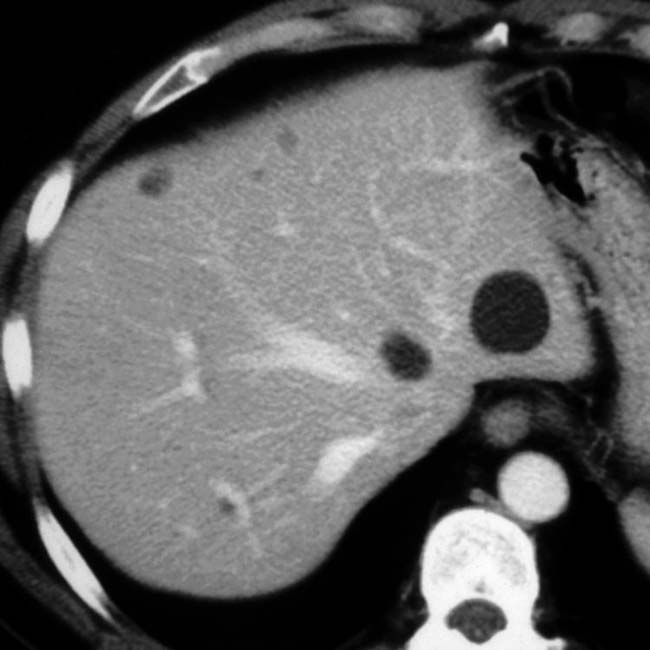
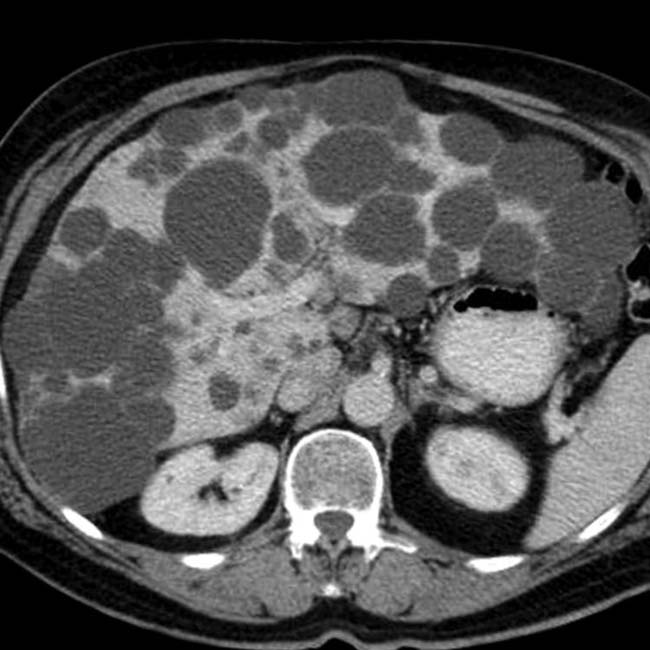
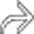 . Simple hepatic cysts are commonly multiple, and this is not necessarily evidence of autosomal dominant polycystic disease, which usually results in many more and larger cysts. Biliary hamartomas can also cause an appearance of multiple cysts, but these are rarely > 15 mm.
. Simple hepatic cysts are commonly multiple, and this is not necessarily evidence of autosomal dominant polycystic disease, which usually results in many more and larger cysts. Biliary hamartomas can also cause an appearance of multiple cysts, but these are rarely > 15 mm.
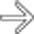 with a thin wall.
with a thin wall.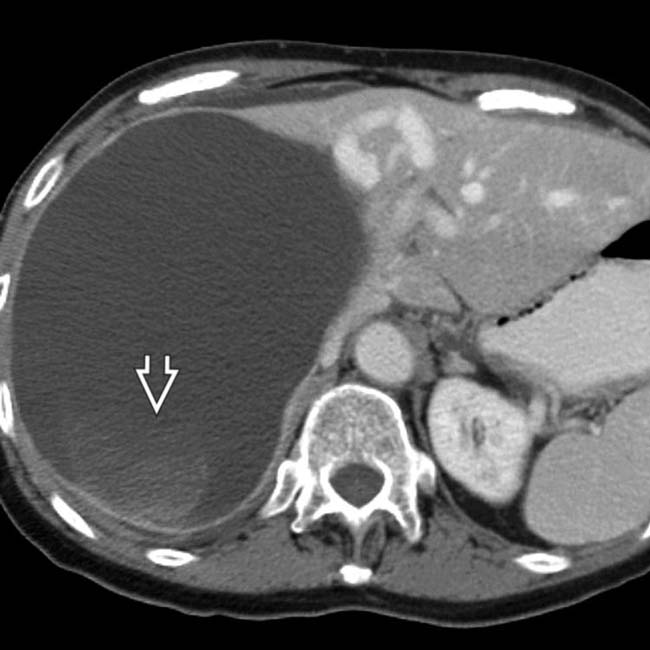
 within the cyst, suggestive of acute hemorrhage.
within the cyst, suggestive of acute hemorrhage.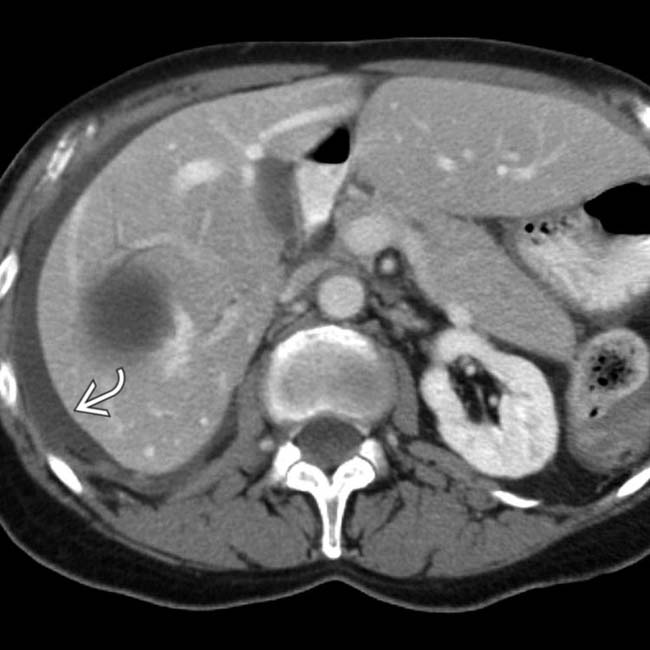
 that had an attenuation of about 15 HU, suggesting intraperitoneal rupture of the cyst. These findings were confirmed at surgery and the cyst was resected.
that had an attenuation of about 15 HU, suggesting intraperitoneal rupture of the cyst. These findings were confirmed at surgery and the cyst was resected.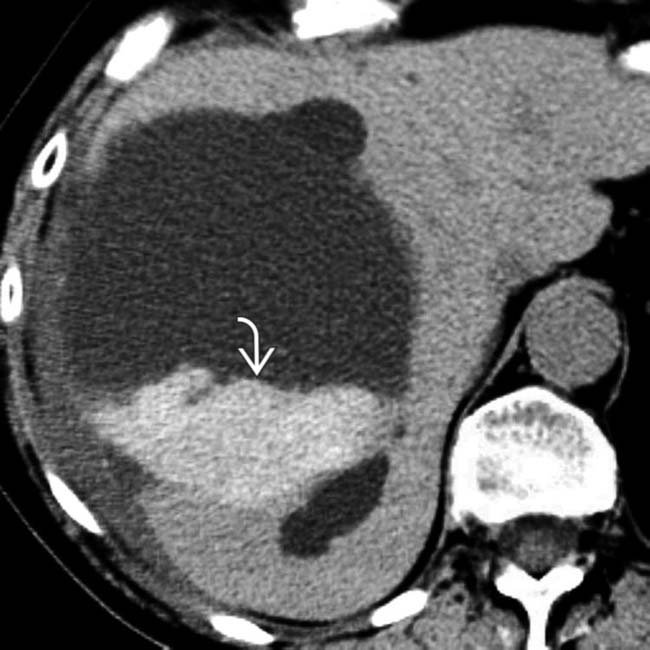
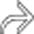 settling in a dependent position.
settling in a dependent position.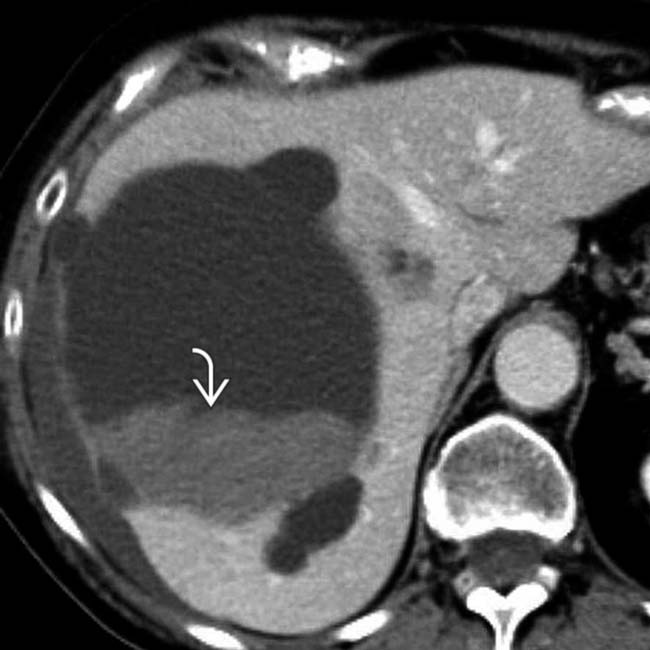
 within the cyst. Without the NECT for comparison, it would be easy to misinterpret the clot as a mural nodularity or tumor.
within the cyst. Without the NECT for comparison, it would be easy to misinterpret the clot as a mural nodularity or tumor.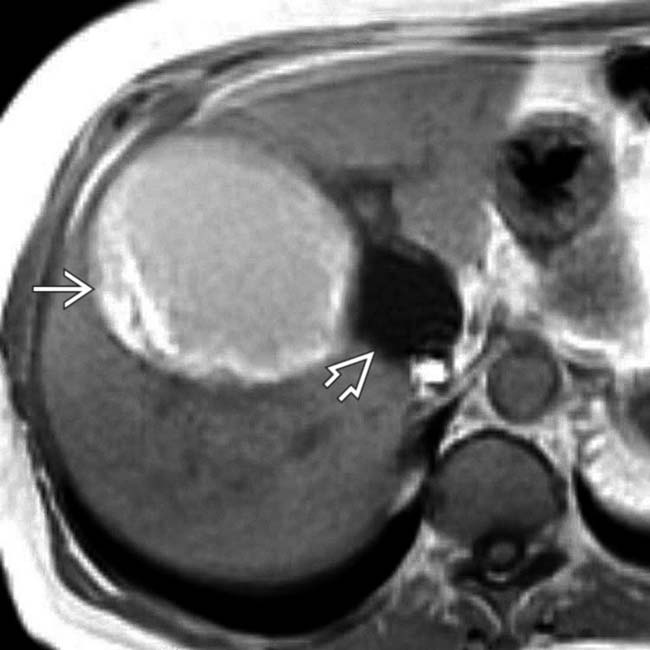
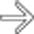 on T1WI, whereas the smaller cyst’s contents
on T1WI, whereas the smaller cyst’s contents  are low in signal.
are low in signal.
 , while the larger cyst’s contents are more heterogeneous with mural irregularity and debris evident
, while the larger cyst’s contents are more heterogeneous with mural irregularity and debris evident  . Aspiration of the larger cyst yielded hemorrhagic fluid with no sign of infection or neoplasm.
. Aspiration of the larger cyst yielded hemorrhagic fluid with no sign of infection or neoplasm.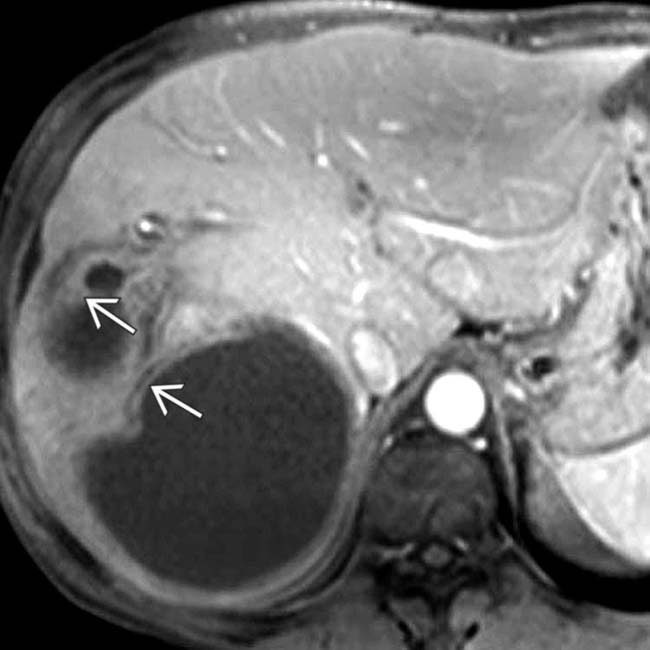
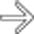 .
.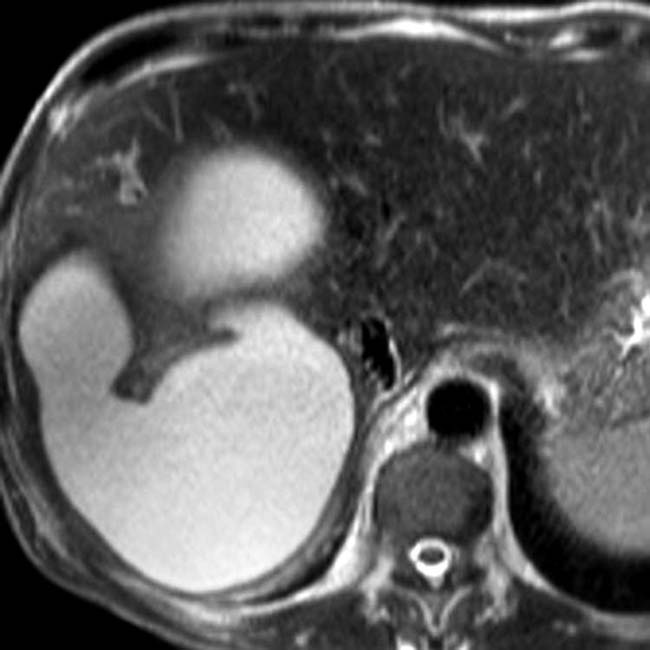
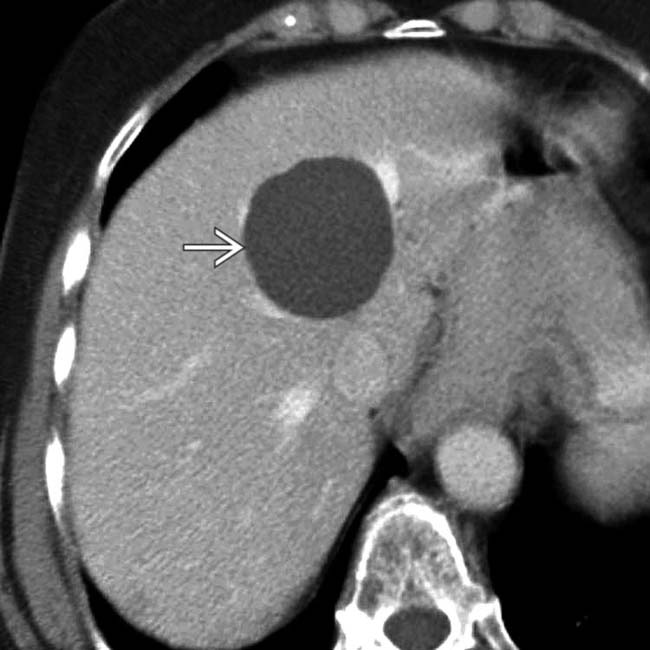
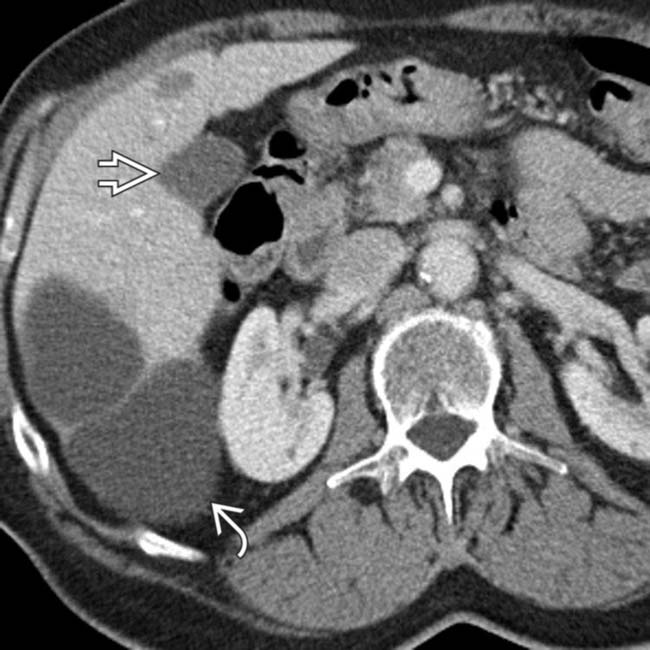
 , cystic hepatic mass
, cystic hepatic mass  with accentuated through-transmission
with accentuated through-transmission  .
.
 . It was not evident whether the most caudal cystic lesion
. It was not evident whether the most caudal cystic lesion  was an additional cyst or part of the largest septate cyst.
was an additional cyst or part of the largest septate cyst.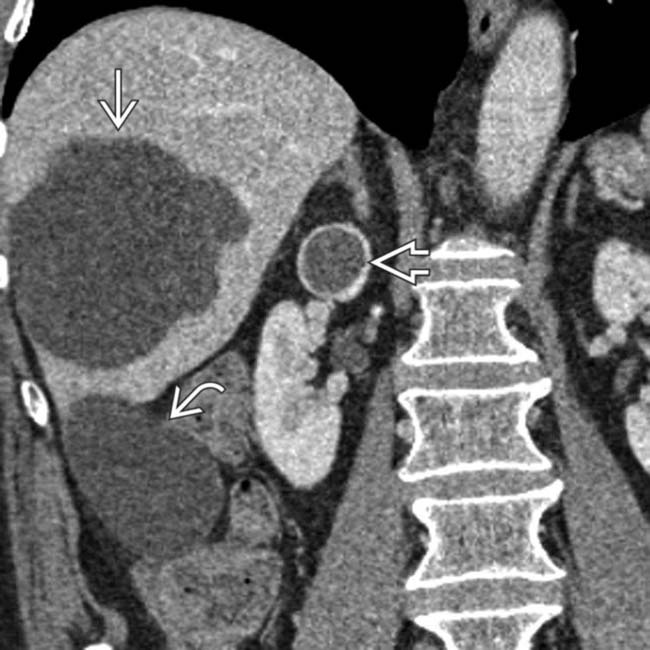
 and other smaller cysts
and other smaller cysts  . Note the renal cyst with a calcified wall
. Note the renal cyst with a calcified wall  , presumably on the basis of prior hemorrhage or infection.
, presumably on the basis of prior hemorrhage or infection.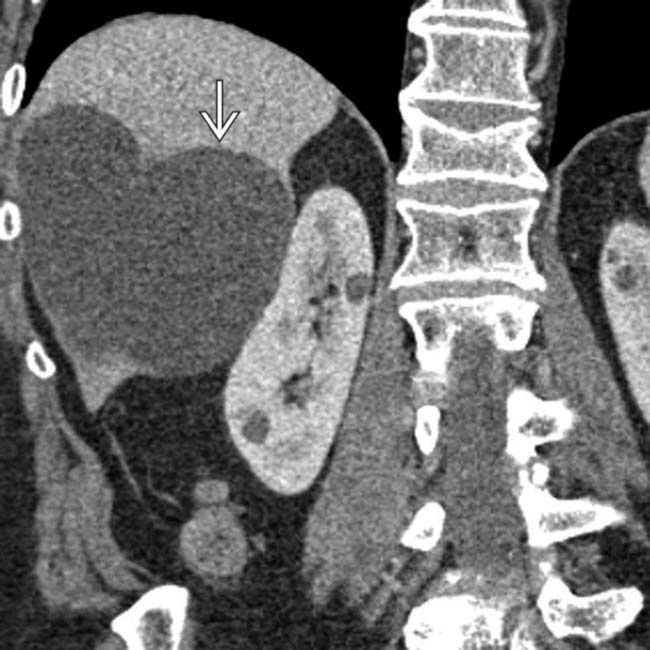
 and numerous renal cysts. By imaging criteria alone, the large lesion identified by US and CT could not be differentiated from a biliary cystadenoma. However, cystadenomas are usually solitary and occur almost exclusively in women, whereas this patient is a man.
and numerous renal cysts. By imaging criteria alone, the large lesion identified by US and CT could not be differentiated from a biliary cystadenoma. However, cystadenomas are usually solitary and occur almost exclusively in women, whereas this patient is a man.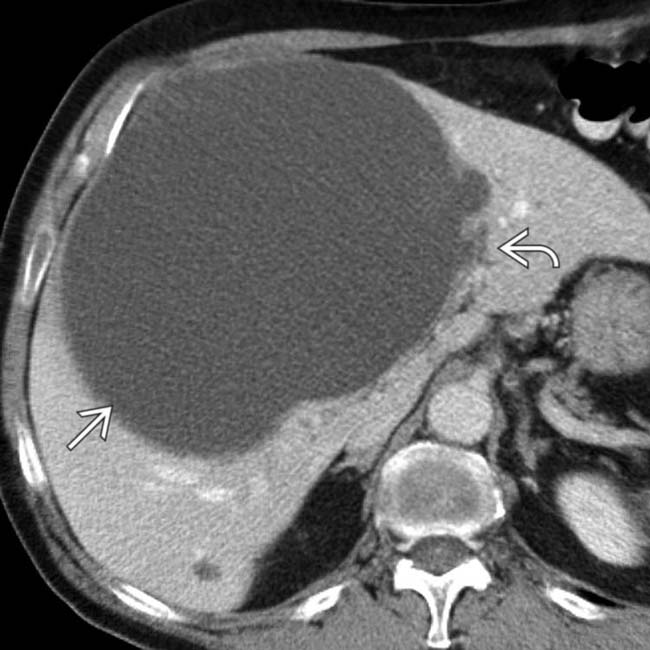
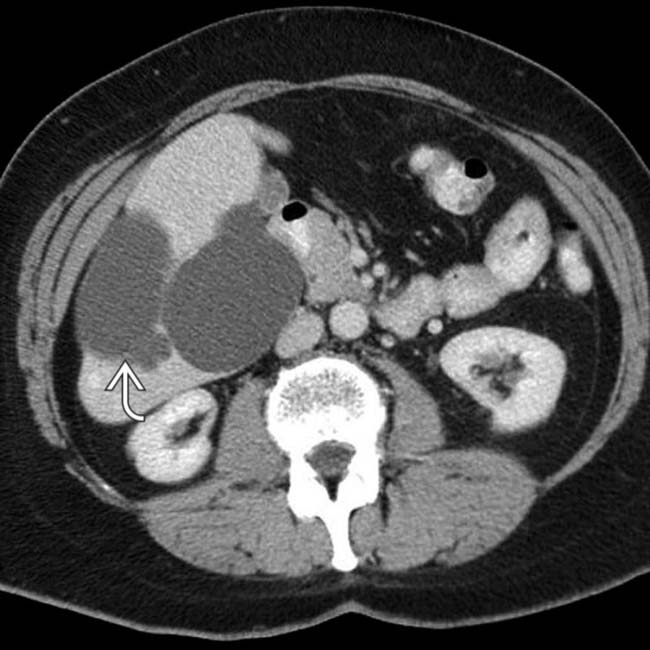
 is almost 15 cm in diameter and displaces hepatic vessels. Bile ducts within the left lobe are dilated
is almost 15 cm in diameter and displaces hepatic vessels. Bile ducts within the left lobe are dilated  due to extrinsic compression of the left main duct.
due to extrinsic compression of the left main duct.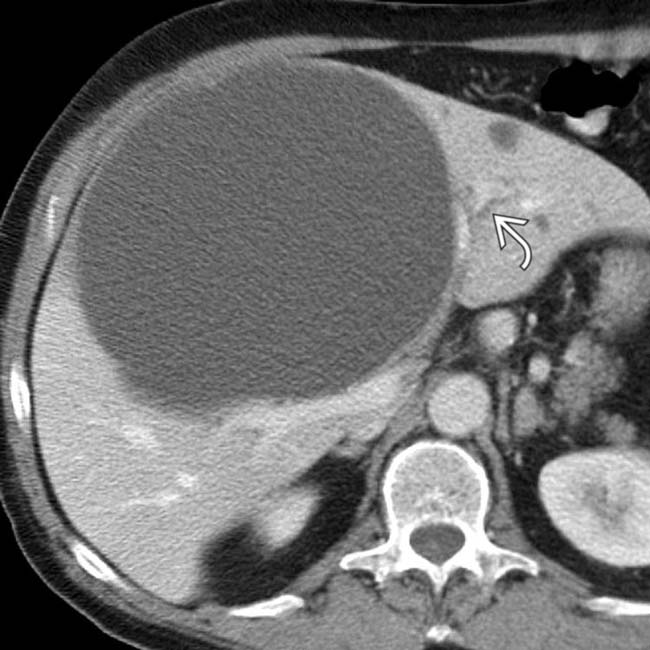
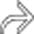 . The mass was resected and confirmed as a simple hepatic cyst.
. The mass was resected and confirmed as a simple hepatic cyst.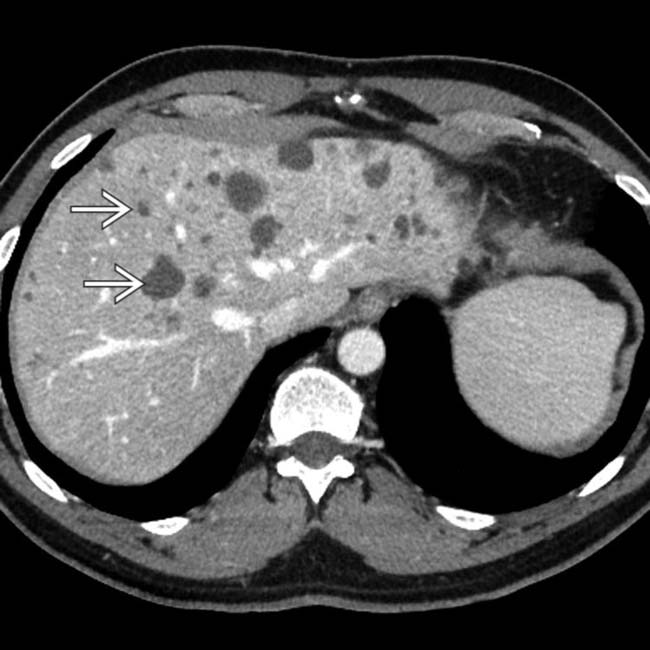
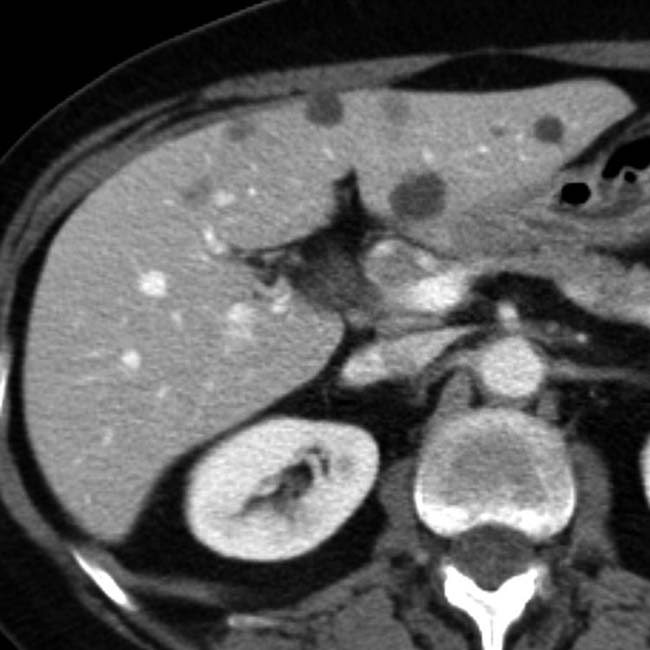
 throughout the liver, ranging in size from 2-15 mm. Close attention shows that the lesions are often not perfectly spherical and many have visible nodular enhancement within their walls.
throughout the liver, ranging in size from 2-15 mm. Close attention shows that the lesions are often not perfectly spherical and many have visible nodular enhancement within their walls.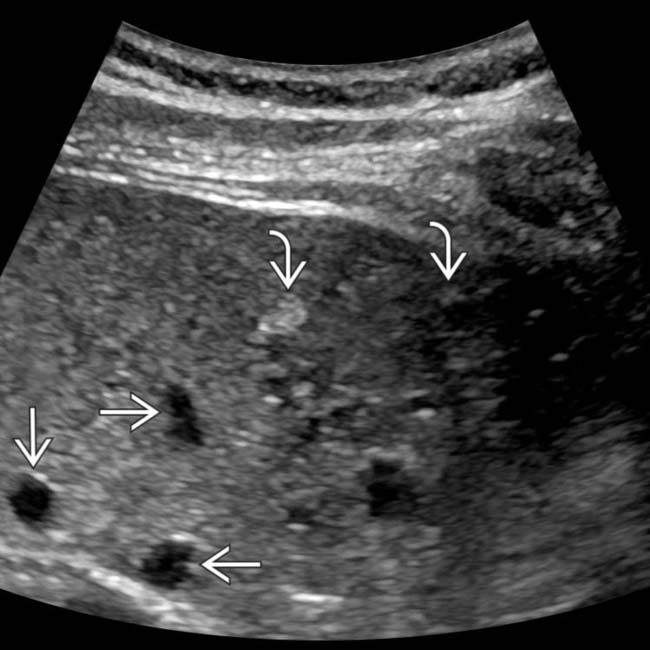
 whereas the smaller lesions were actually hyperechoic
whereas the smaller lesions were actually hyperechoic  to background liver. This is the classic appearance of biliary hamartomas.
to background liver. This is the classic appearance of biliary hamartomas.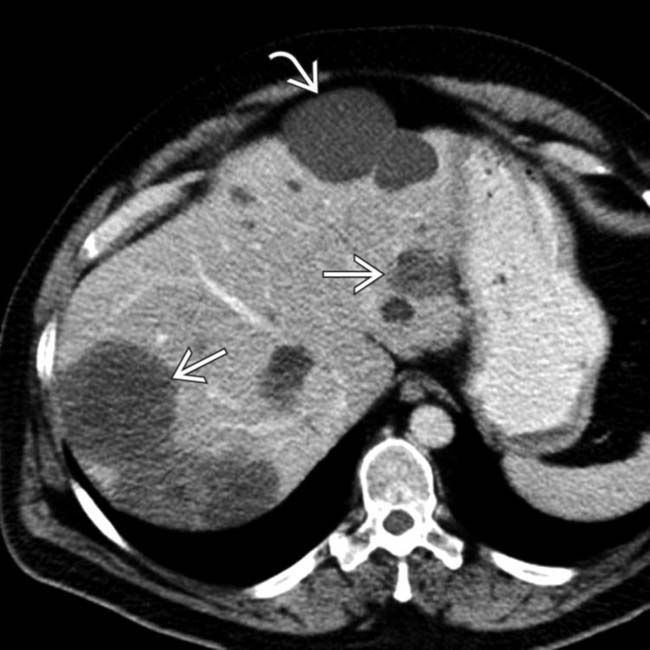
 are water density and homogeneous whereas multiple foci of tumor
are water density and homogeneous whereas multiple foci of tumor  are heterogeneous and enhancing compared with NECT images.
are heterogeneous and enhancing compared with NECT images.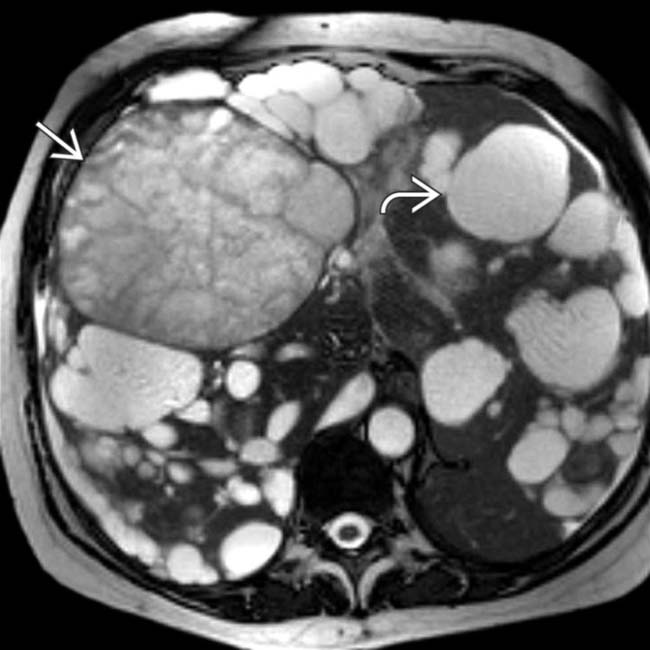
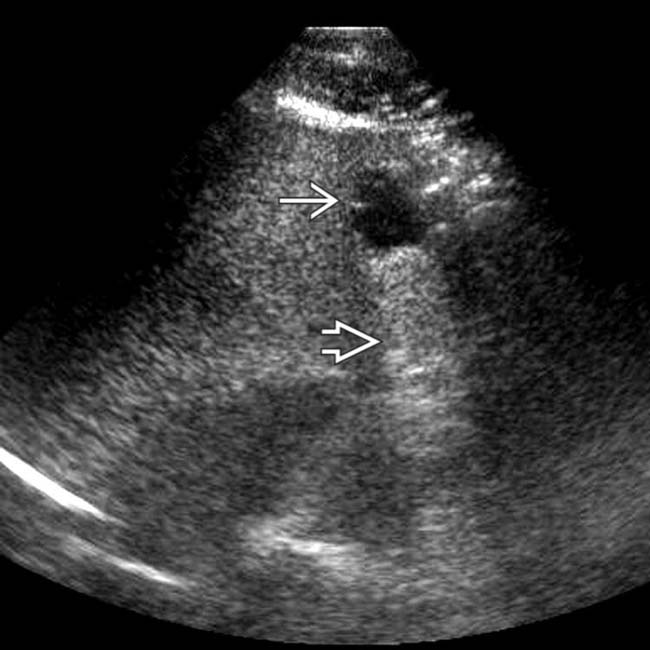
 and are the result of internal hemorrhage. Others have simple fluid
and are the result of internal hemorrhage. Others have simple fluid  .
.
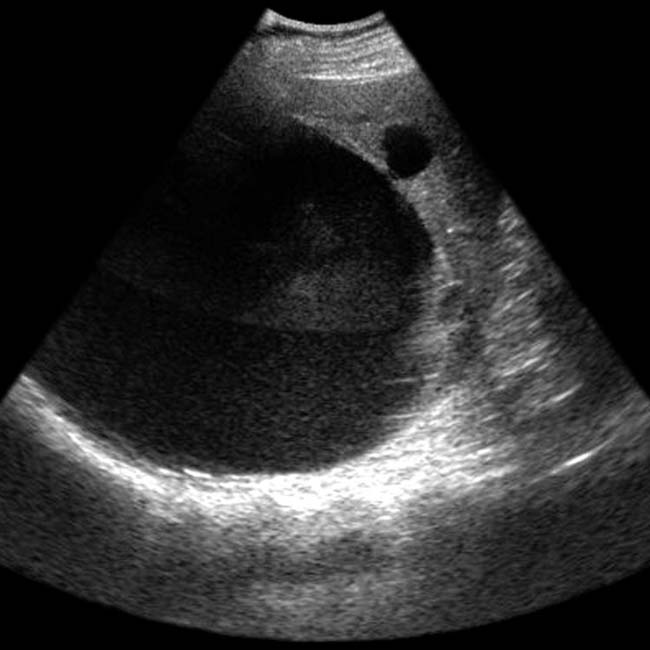
 with no visible wall. Note the through transmission of sound
with no visible wall. Note the through transmission of sound  .
.


























































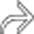 .
.
 with no discernible walls.
with no discernible walls.
 .
.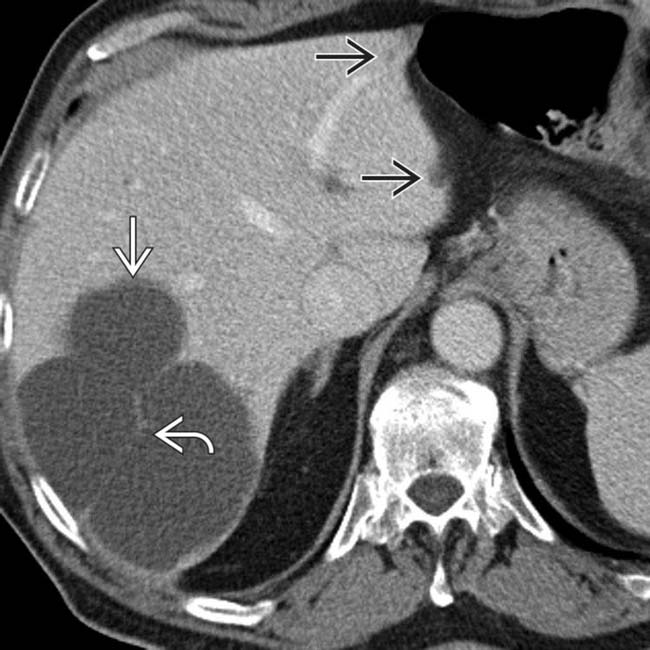
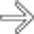
 cyst
cyst  , but also shows several smaller cysts
, but also shows several smaller cysts  .
.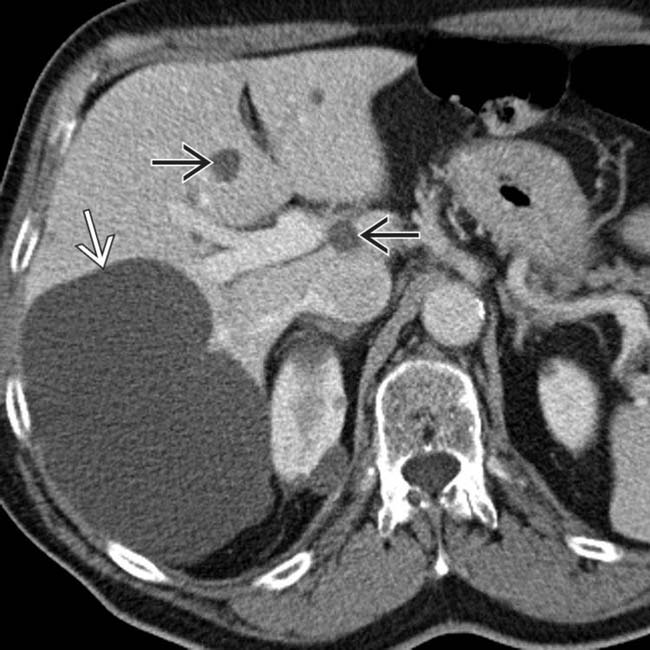
 and several smaller cysts
and several smaller cysts  .
.