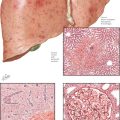
Chapter 210 HELLP Syndrome
INTRODUCTION
ETIOLOGY AND PATHOGENESIS
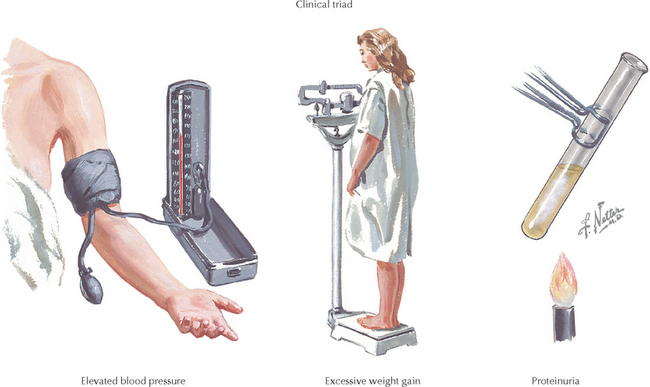
CLINICAL CHARACTERISTICS
DIAGNOSTIC APPROACH
Differential Diagnosis
Workup and Evaluation
MANAGEMENT AND THERAPY
Nonpharmacologic
Drug(s) of Choice
FOLLOW-UP
Barrilleaux PS, Martin JNJr, Klauser CK, et al. Postpartum intravenous dexamethasone for severely preeclamptic patients without hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, low platelets (HELLP) syndrome: a randomized trial. Obstet Gynecol. 2005;105:843.
Fonseca JE, Mendez F, Catano C, Arias F. Dexamethasone treatment does not improve the outcome of women with HELLP syndrome: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2005;193:1591.
Ganzevoort W, Rep A, Bonsel GJ, et al. PETRA Investigators: A randomised controlled trial comparing two temporising management strategies, one with and one without plasma volume expansion, for severe and early onset pre-eclampsia. BJOG. 2005;112:1358.
Isler CM, Barrilleaux PS, Magann EF, et al. A prospective, randomized trial comparing the efficacy of dexamethasone and betamethasone for the treatment of antepartum HELLP (hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelet count) syndrome. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2001;184:1332.
Matchaba P, Moodley J. Corticosteroids for HELLP syndrome in pregnancy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004. CD002076.
Thangaratinam S, Ismail KM, Sharp S, et alTests in Prediction of Pre-eclampsia Severity Review Group. Accuracy of serum uric acid in predicting complications of pre-eclampsia: a systematic review. BJOG. 2006;113:369.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Thrombocytopenia in pregnancy. ACOG Practice Bulletin 6. Washington, DC: ACOG, 1999.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Chronic hypertension in pregnancy. ACOG Practice Bulletin 29. Obstet Gynecol. 2001;98:177.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Diagnosis and management of preeclampsia and eclampsia. ACOG Practice Bulletin 33. Obstet Gynecol. 2002;99:159.
Clenney TL, Viera AJ. Corticosteroids for HELLP (haemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, low platelets) syndrome. BMJ. 2004;329:270.
Geary M. The HELLP syndrome. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1997;104:8871.
Martin JNJr, Rose CH, Briery CM. Understanding and managing HELLP syndrome: the integral role of aggressive glucocorticoids for mother and child. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2006;195:914. Epub 2006 May 2
O’Brien JM, Milligan DA, Barton JR. Impact of high-dose corticosteroid therapy for patients with HELLP (hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelet count) syndrome. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2000;183:921.