CHAPTER 3 HEAD AND NECK PATHOLOGY
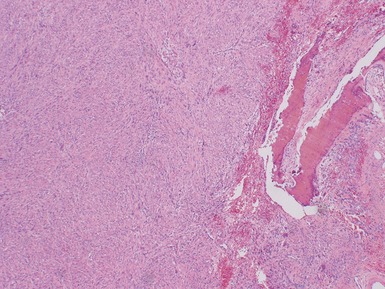
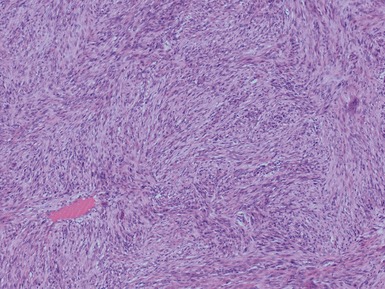
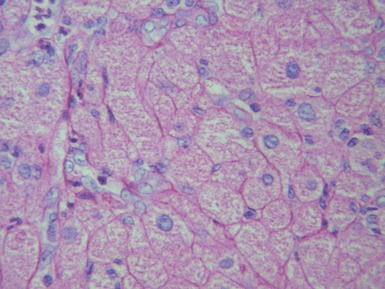
MALIGNANT PERIPHERAL NERVE SHEATH TUMOR
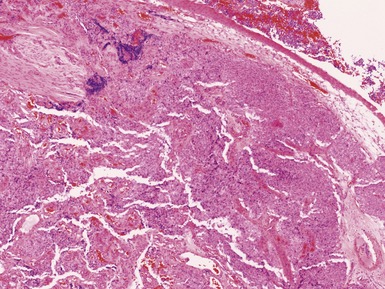
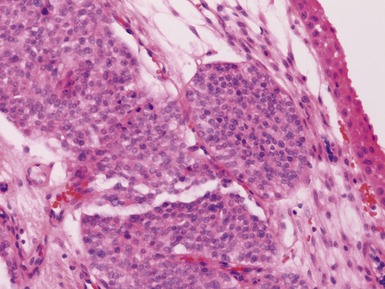
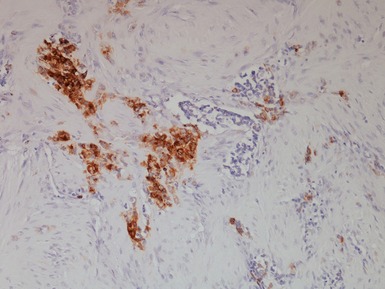
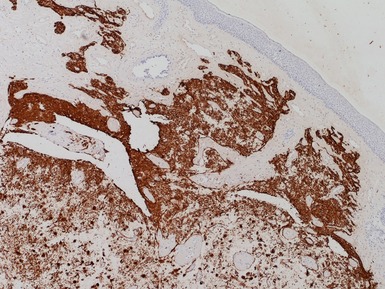
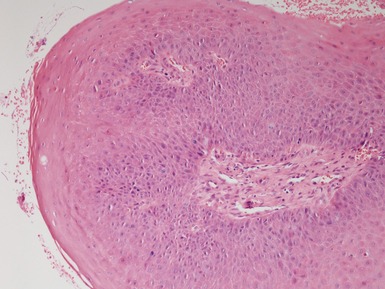
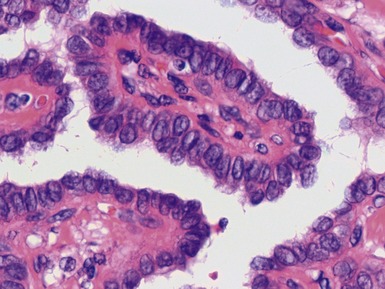
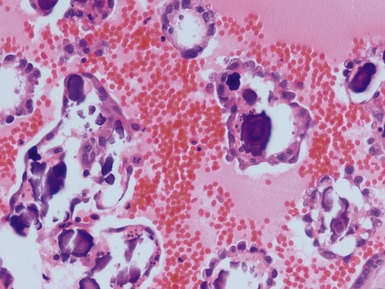
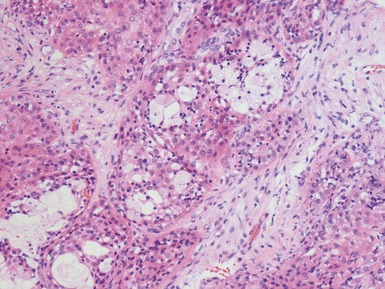
OLFACTORY NEUROBLASTOMA (ESTHESIONEUROBLASTOMA)
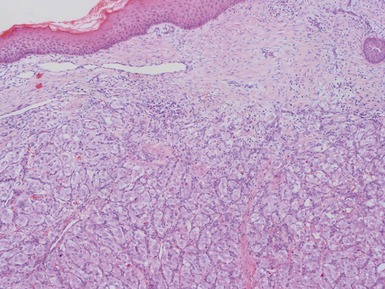
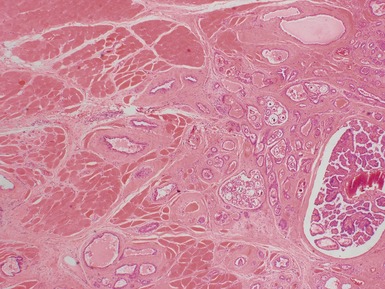
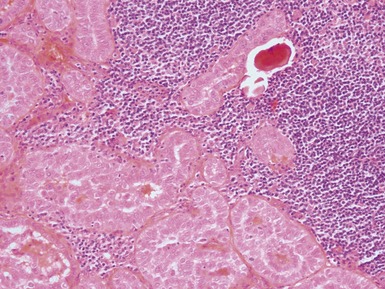
MELANOTIC NEUROECTODERMAL TUMOR OF INFANCY
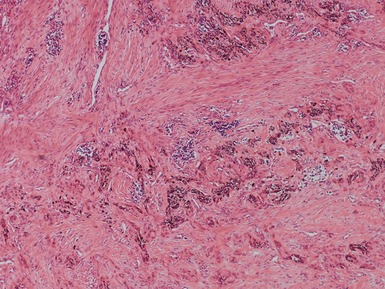
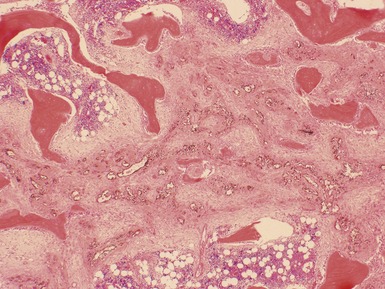
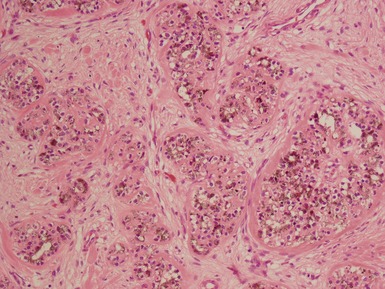
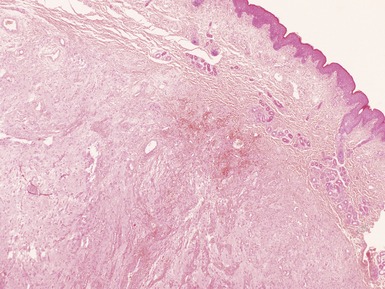
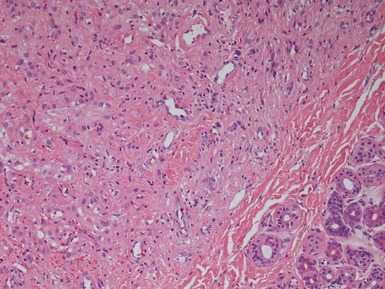
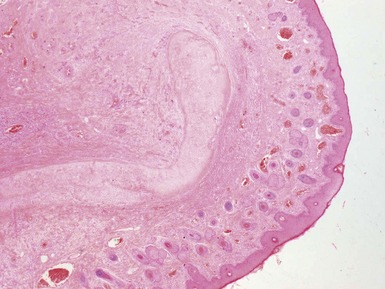
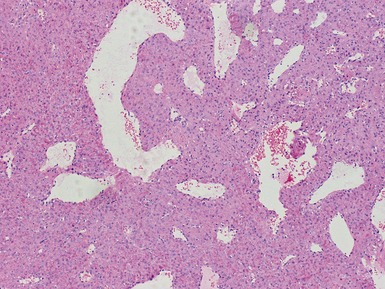
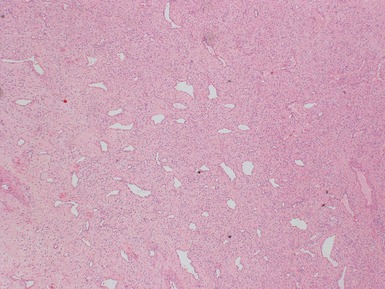
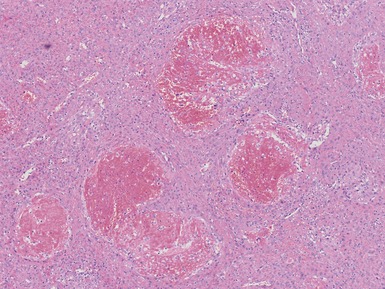
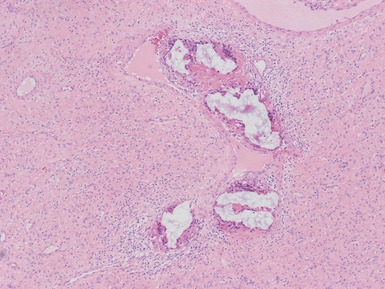
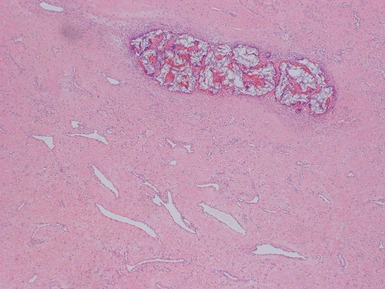
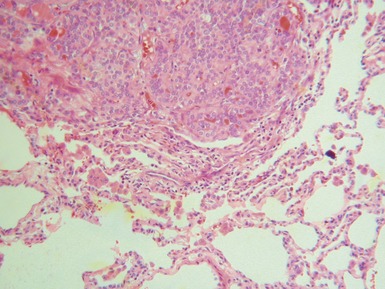
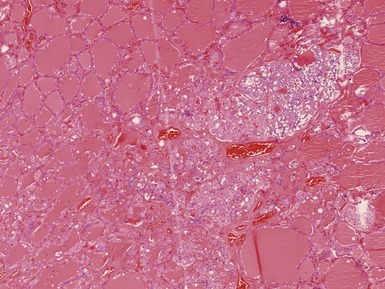
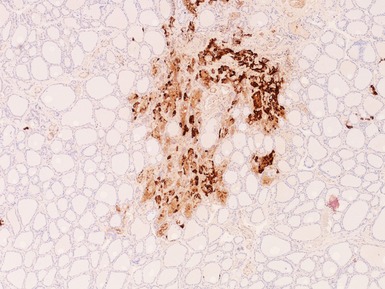
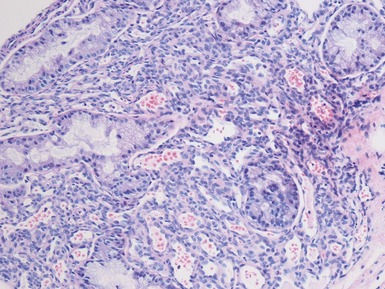
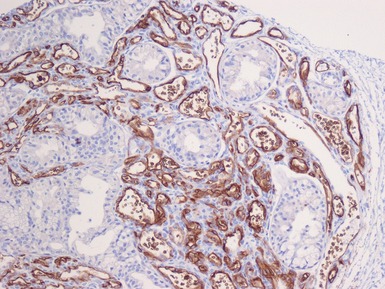
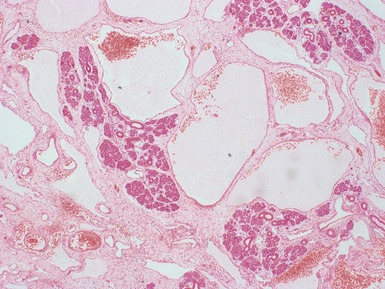
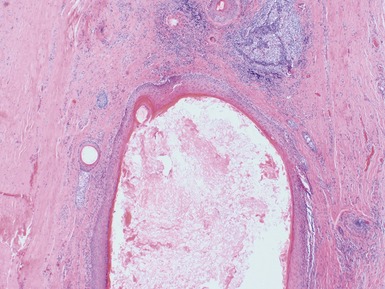
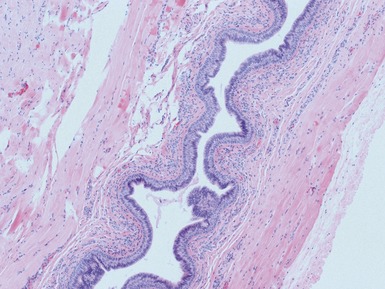
Histopathological features (Figs 3.6–3.11)
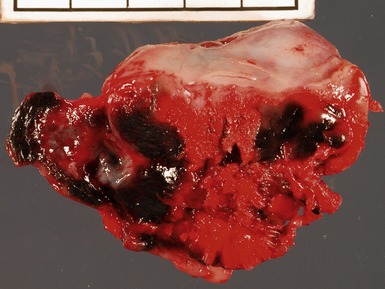
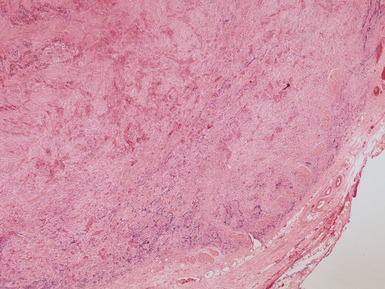
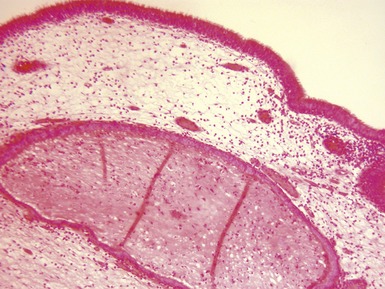
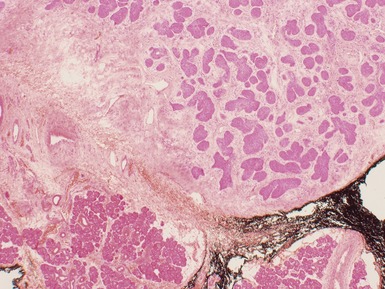
Fig 3.6 Photograph of a case of melanotic neuroectodermal tumor of infancy, demonstrating an intraosseous lesion with areas of black (melanin) pigmentation seen on macroscopic examination.
ECTOMESENCHYMOMA
NASAL GLIAL HETEROTOPIA
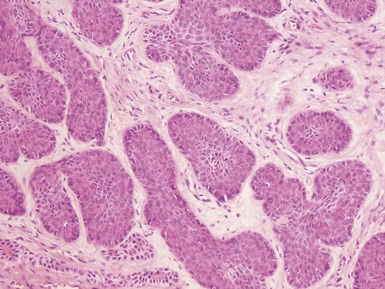
NASOPHARYNGEAL CARCINOMA
NASAL / CHOANAL POLYPS
HAIRY POLYP OF THE NASOPHARYNX
(JUVENILE) NASOPHARYNGEAL ANGIOFIBROMA
Histopathological features (Figs 3.17–3.21)
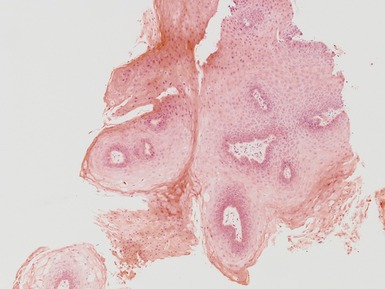
JUVENILE LARYNGEAL PAPILLOMATOSIS
Clinical features
LARYNGEAL GRANULAR CELL TUMOUR
A range of other tumors may also rarely affect the larynx (see other sections) (Fig 3.24)
THYROID DISORDERS
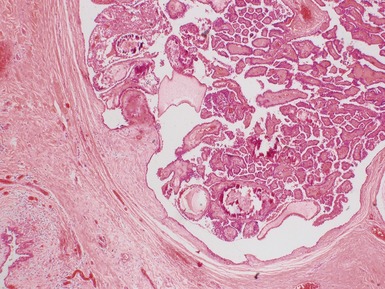
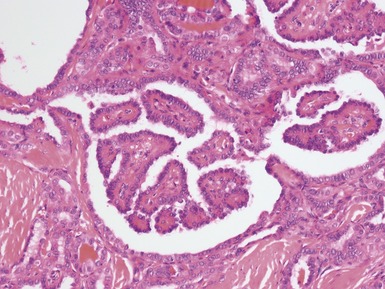
PAPILLARY CARCINOMA OF THYROID
Histopathological features (Figs 3.25–3.31)
FOLLICULAR CARCINOMA OF THYROID
MEDULLARY THYROID CARCINOMA
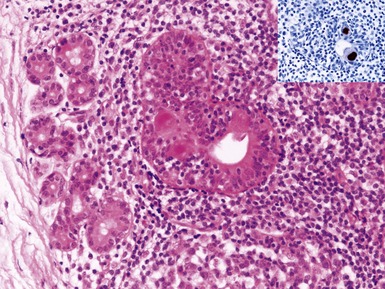
Histopathological features (Figs 3.32, 3.33)
THYROID C-CELL HYPERPLASIA
ORAL LESIONS
SALIVARY GLAND TUMORS
ODONTOGENIC TUMORS
Histopathological features
MISCELLANEOUS LESIONS
DERMOID CYST (Fig 3.42)
BRANCHIAL CLEFT REMNANTS (Fig 3.43)
Abraham SC, Montgomery EA, Giardiello FM, Wu TT. Frequent beta-catenin mutations in juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibromas. Am J Pathol. 2001;158:1073-1078.
Bar-Sela G, Ben Arush MW, Sabo E, Kuten A, Minkov I, Ben-Izhak O. Pediatric nasopharyngeal carcinoma: better prognosis and increased c-Kit expression as compared to adults. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2005;45:291-297.
Bar-Sela G, Kaplan-Cohen V, Ilan N, Vlodavsky I, Ben-Izhak O. Heparanase expression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma inversely correlates with patient survival. Histopathol. 2006;49:188-193.
Braham H, Trimeche M, Ziadi S, et al. CD10 expression by fusiform stromal cells in nasopharyngeal carcinoma correlates with tumor progression. Virchows Arch. 2006;449:220-224.
Brandwein M, Al-Naeif NS, Manwani D, et al. Sialoblastoma: clinicopathological/immunohistochemical study. Am J Surg Pathol. 1999;23:342-348.
Cannon T, Zanation AM, Lai V, Weissler MC. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma in young patients: a systematic review of racial demographics. Laryngoscope. 2006;116:1021-1026.
Chang SS, Halushka M, Meer JV, Goins M, Francis HW. Nasopharyngeal hairy polyp with recurrence in the middle ear. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2007;72:261-264.
Floris G, Debiec-Rychter M, Wozniak A, et al. Malignant ectomesenchymoma: genetic profile reflects rhabdomyosarcomatous differentiation. Diagn Mol Pathol. 2007;16:243-248.
Fowler DJ, Chisholm J, Roebuck D, Newman L, Malone M, Sebire NJ. Melanotic neuroectodermal tumor of infancy: clinical, radiological, and pathological features. Fetal Pediatr Pathol. 2006;25:59-72.
Friedrich RE, Hartmann M, Mautner VF. Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors (MPNST) in NF1-affected children. Anticancer Res. 2007;27:1957-1960.
Hirose T, Scheithauer BW, Sano T. Perineurial malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST): a clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical, and ultrastructural study of seven cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1998;22:1368-1378.
Hwang HC, Mills SE, Patterson K, Gown AM. Expression of androgen receptors in nasopharyngeal angiofibroma: an immunohistochemical study of 24 cases. Mod Pathol. 1998;11:1122-1126.
Kazahaya K, Potsic WP. Congenital cholesteatoma. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2004;12:398-403.
Kieff DA, Curtin HD, Limb CJ, Nadol JB. A hairy polyp presenting as a middle ear mass in a pediatric patient. Am J Otolaryngol. 1998;19:228-231.
Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK, Lovell MA, Donson AM, et al. Molecular array analyses of 51 pediatric tumors shows overlap between malignant intracranial ectomesenchymoma and MPNST but not medulloblastoma or atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumor. Acta Neuropathol. 2007;113:695-703.
Kumar S, Perlman E, Pack S, et al. Absence of EWS/FLI1 fusion in olfactory neuroblastomas indicates these tumors do not belong to the Ewing’s sarcoma family. Hum Pathol. 1999;30:1356-1360.
Mouton SC, Rosenberg HS, Cohen MC, Drut R, Emms M, Kaschula RO. Malignant ectomesenchymoma in childhood. Pediatr Pathol Lab Med. 1996;16:607-624.
Penner CR, Thompson L. Nasal glial heterotopia: a clinicopathologic and immunophenotypic analysis of 10 cases with a review of the literature. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2003;7:354-359.
Saylam G, Yücel OT, Sungur A, Onerci M. Proliferation, angiogenesis and hormonal markers in juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2006;70:227-234.
Sebire NJ, Ramsay AD, Malone M, Risdon RA. Extensive post treatment ganglioneuromatous differentiation of rhabdomyosarcoma: malignant ectomesenchymoma in an infant. Pediatr Dev Pathol. 2003;6:94-96.
Védrine PO, Coffinet L, Temam S, et al. Mucoepidermoid carcinoma of salivary glands in the pediatric age group: 18 clinical cases, including 11 second malignant neoplasms. Head Neck. 2006;28:827-833.
Wiatrak BJ, Wiatrak DW, Broker TR, Lewis L. Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis: a longitudinal study comparing severity associated with human papilloma viral types 6 and 11 and other risk factors in a large pediatric population. Laryngoscope. 2004;114:1-23.