Chapter 7 Gynaecological Infections
Vaginal discharge and infection
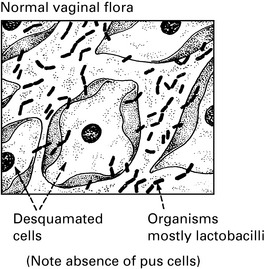
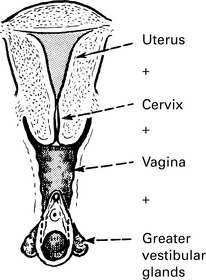
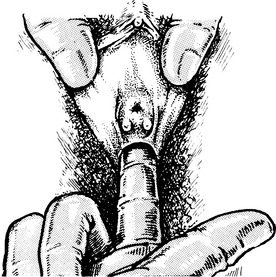
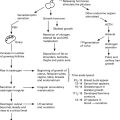
Source of vaginal discharge
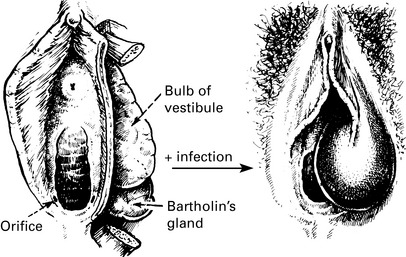
Vulva: Greater vestibular glands, glands of vulval skin.
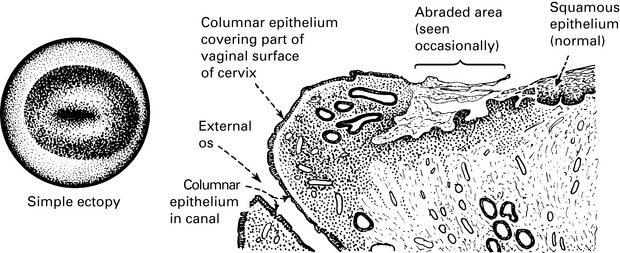
Cervix: Alkaline mucous secretion which becomes copious and watery during ovulation.
Complaints of vaginal discharge
Women will complain under the following conditions.
Examination
Vaginal discharge
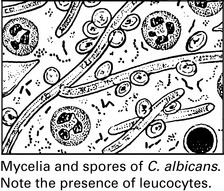
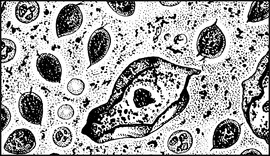
Candida albicans
Source of Infection
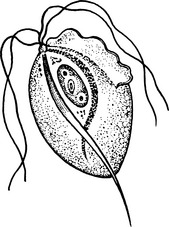
Vaginitis
Vulvovaginitis in children
With reference to the above points.
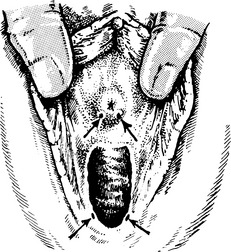
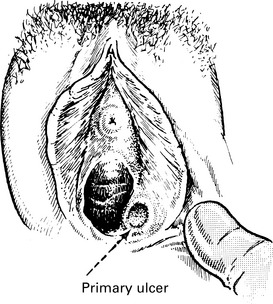
Genital herpes
Clinical findings
Infection of the neonate can lead to herpes encephalitis with a primary infection.
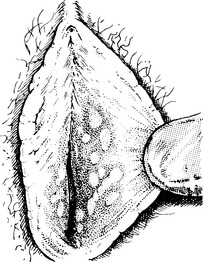
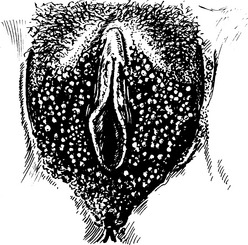
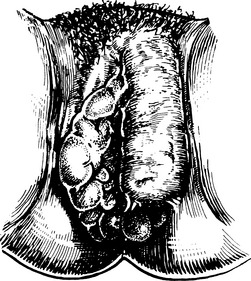
Genital warts
Differential diagnosis
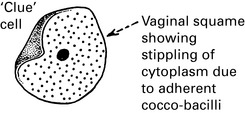
Bacterial infections
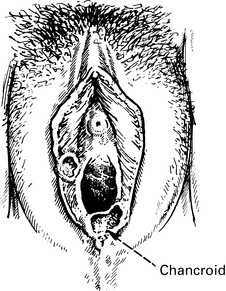
Tropical sexually transmitted infections
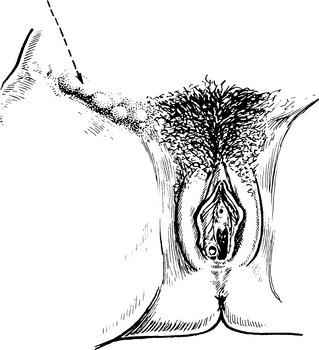
Lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV)
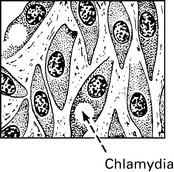
LGV is attributed to a strain of Chlamydia. This is rare in the developed countries.
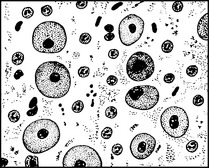
Gonorrhoea
Syphilis
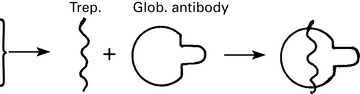
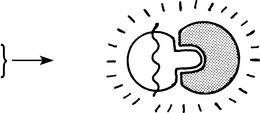
Diagnosis of syphilis
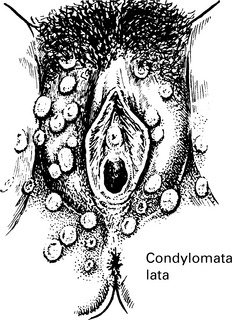
Signs and symptoms of syphilis
Diagnosis is by the demonstration of T. pallidum in the lesions and by serological tests.
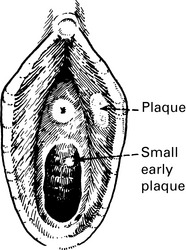
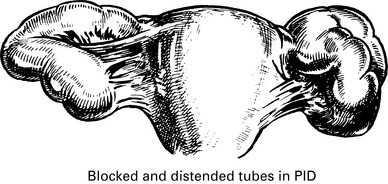
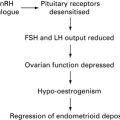
Pelvic inflammatory disease
Differential diagnosis
Pelvic inflammatory disease
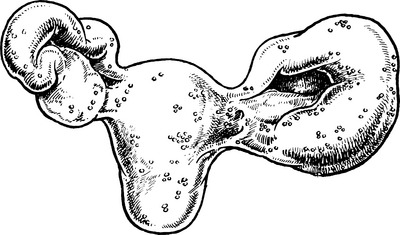
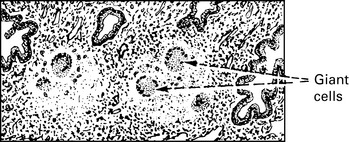
Genital tuberculosis
Diagnosis
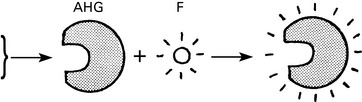
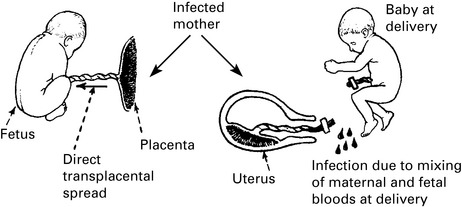
Human immunodeficiency virus
Transmission
The following are the main modes of transmission of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV):
Acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS)
Three conditions are particularly characteristic of the immunodeficiency state:
Intercurrent infections frequently found in aids patients
| Infective agents | Clinical results |
|---|---|
| Parasites | |
| Pneumocystis carinii | Pneumonia |
| Cryptosporidium | Severe diarrhoea |
| Strongyloides stercoralis | Severe diarrhoea |
| Toxoplasma gondii | Chorio-retinitis |
| Viruses | |
| Herpes | Pneumonia |
| J.C. virus | Leuco-encephalopathy |
| Bacteria | |
| Species usually causing minor lesions, e.g. skin spots | Septicaemia |
| Fungi | |
| Cryptococcus neoformans | Pneumonia, meningitis |