132 Gout
Salient features
Examination
• Uric acid crystals are negatively birefringent, needle shaped and may be deposited in bursae and bone marrow. They are demonstrable in synovial fluid within leukocytes and free in the fluid during attacks of gouty arthritis. They react with nitric acid and ammonium hydroxide to give a purple colour (murexide test).
• Be prepared to discuss the differences between the clinical features of typical gout and gout in the elderly.
Questions
Advanced-level questions
What are the diagnostic criteria for acute gout?
• More than 1 attack of acute arthritis
• Maximum inflammation developed within 1 day
• Redness observed over joints
• First metatarsophalangeal joint painful and swollen
• Unilateral attack of first metatarsophalangeal joint
• Unilateral attack of tarsal joint
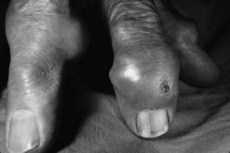
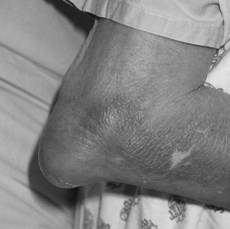
• Tophus (proven or suspected)
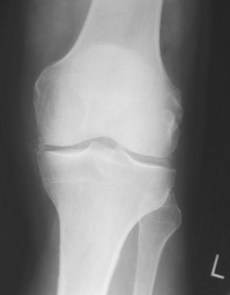
• Asymmetric swelling within a joint on radiograph
• Subcortical cysts without erosions on radiograph
• Monosodium urate monohydrate microcrystals in joint fluid during attack
• Culture of joint fluid negative for organisms during attack.
How would you determine whether a patient with elevated uric acid is an overproducer or an underexcretor?
An overproducer is one whose 24-hour urinary uric acid level >750 mg.
What is pseudogout?
Pseudogout is an acute arthritis resulting from the release of calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals (deposited in the bone and cartilage) into the synovial fluid (Fig. 132.3).