CHAPTER 14 GASTROINTESTINAL PATHOLOGY
ESOPHAGUS
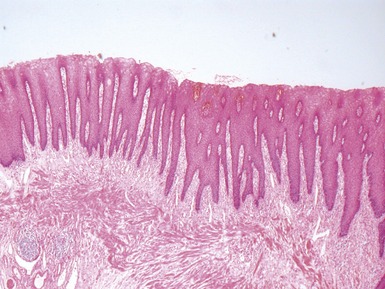
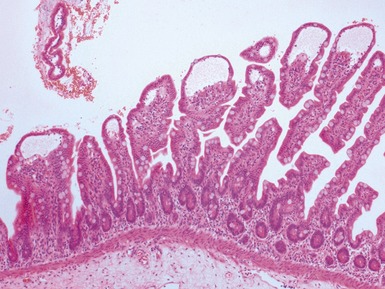
HISTOLOGICAL VARIANTS OF NORMAL ESOPHAGUS
ESOPHAGEAL ATRESIA AND TRACHEO-ESOPHAGEAL FISTULA
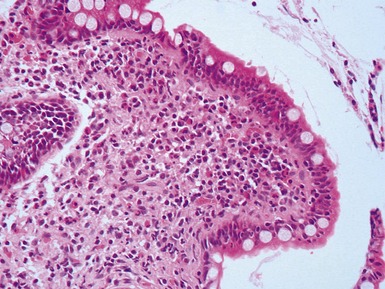
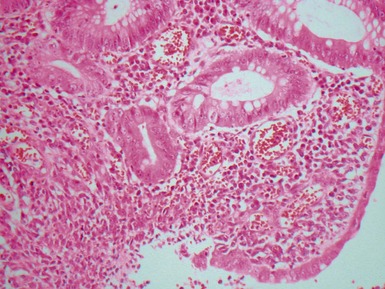
Histopathological features (Dutta, Mathur, Bhatnagar 2000)
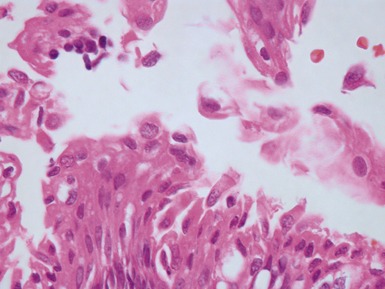
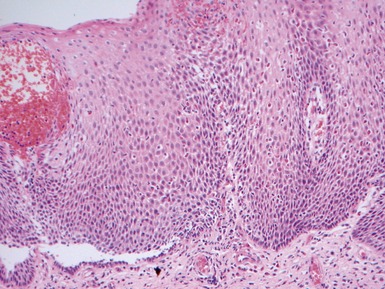
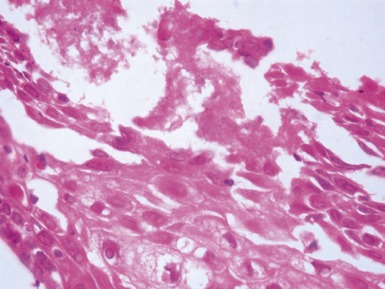
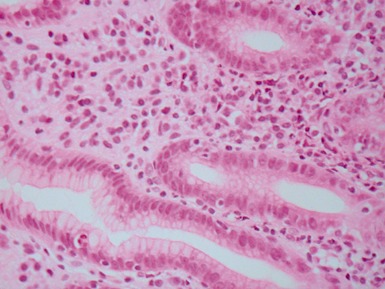
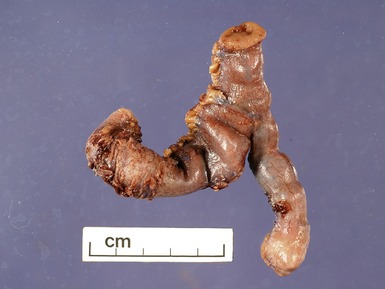
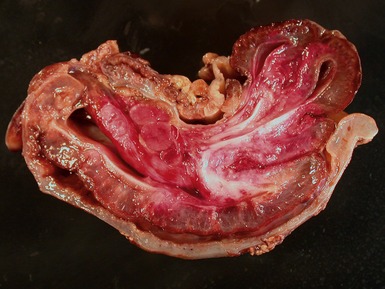
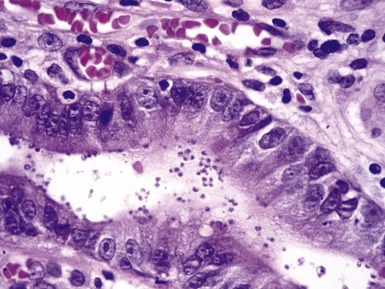
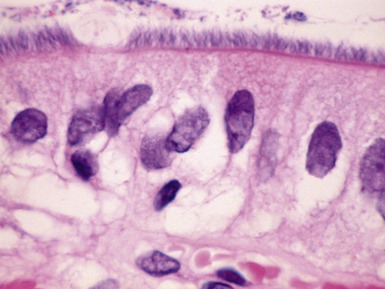
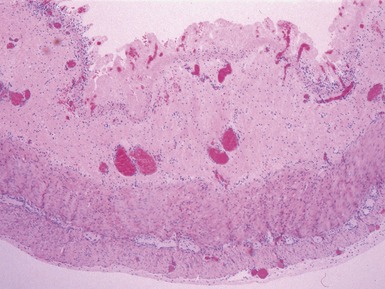
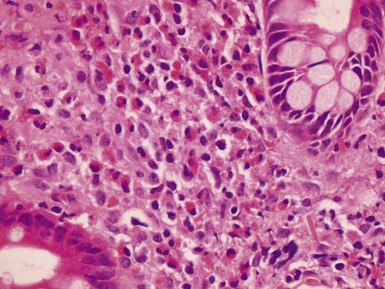
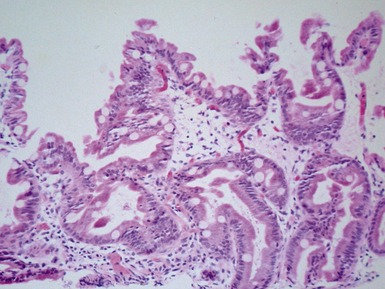
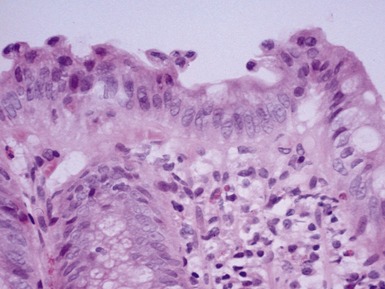
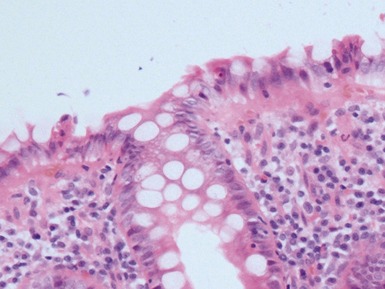
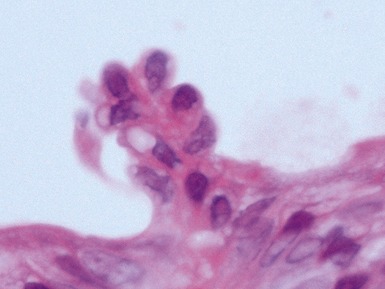
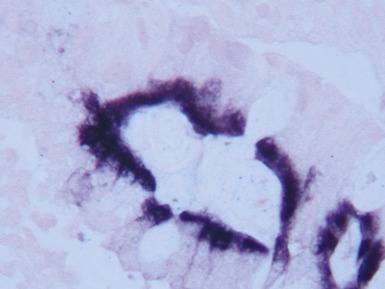
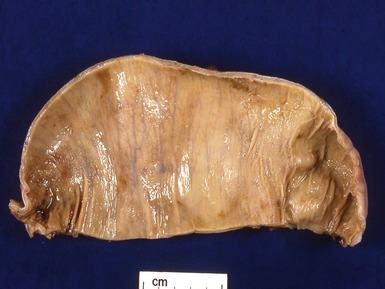
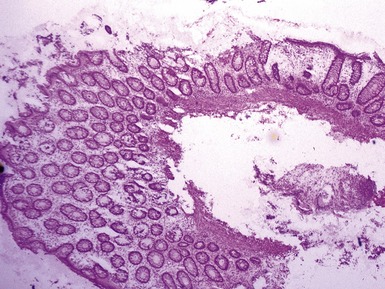
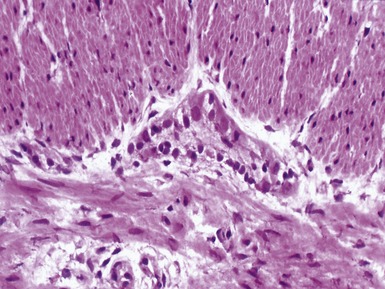
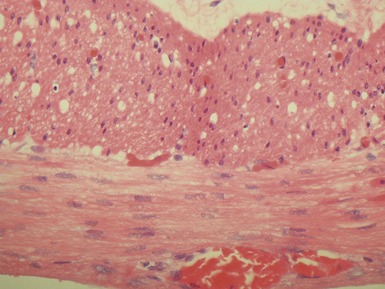
Fig 14.2 One-day-old girl with esophageal atresia and tracheo-esophageal fistula. The specimen is the tip of the proximal esophageal pouch. Photomicrograph of the specimen demonstrating the pouch comprising the usual elements of esophageal wall. The mucosa shows some ciliated epithelium. Unusually, no striated muscle was present in the muscular coat.
GASTRO-ESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE
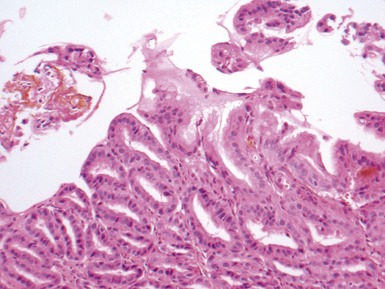
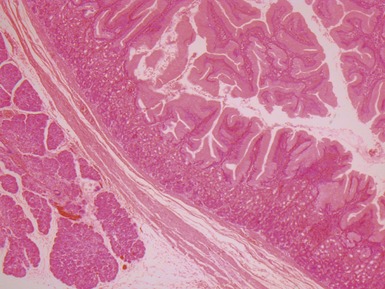
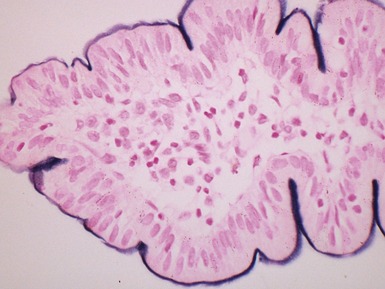
COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL LINED ESOPHAGUS (CELE)
INFECTIVE ESOPHAGITIS
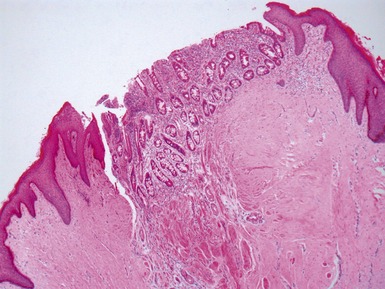
CROHN’S DISEASE OF THE ESOPHAGUS
STOMACH
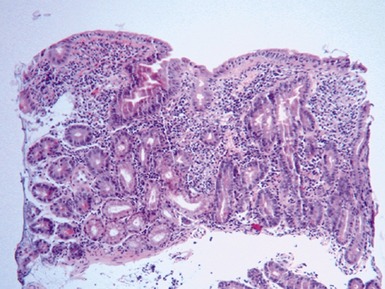
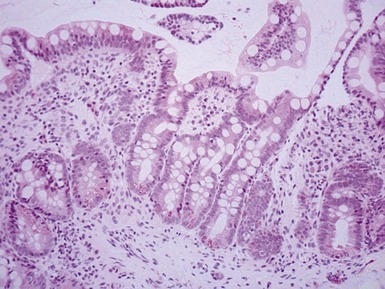
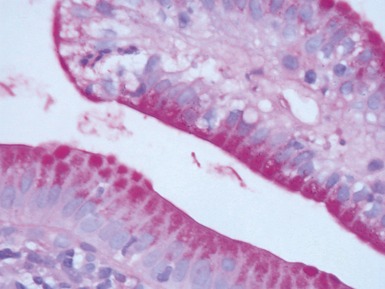
GASTRITIS
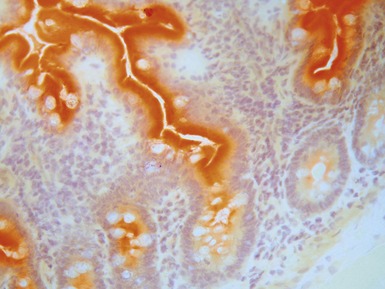
Helicobacter pylori gastritis
Crohn’s disease associated gastritis
Lymphocytic gastritis
SMALL INTESTINE
INTESTINAL ATRESIA
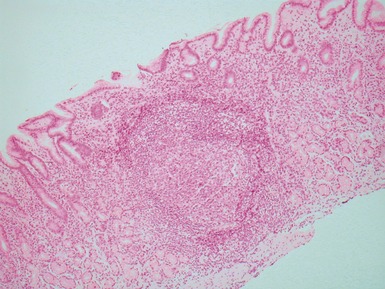
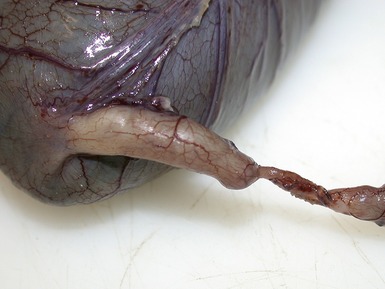
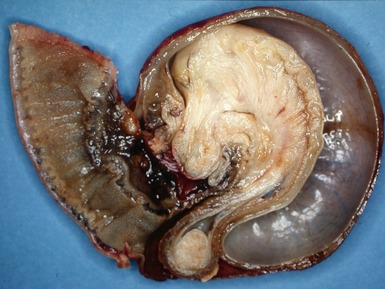
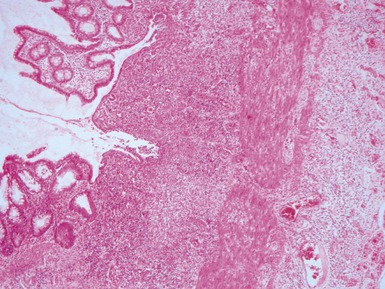
MECKEL’S DIVERTICULUM
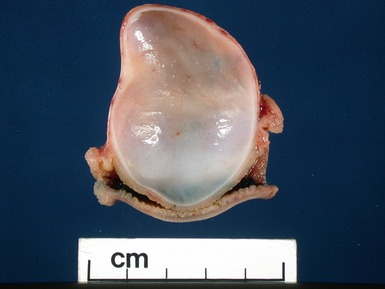
DUPLICATION CYSTS
INTUSSUSCEPTION
VOLVULUS
MECONIUM ILEUS
Histopathological features
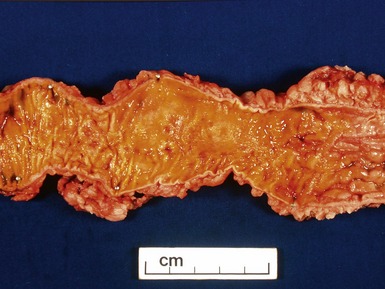
CROHN’S DISEASE
INTESTINAL INFECTIONS
Cryptosporidiosis
Astrovirus
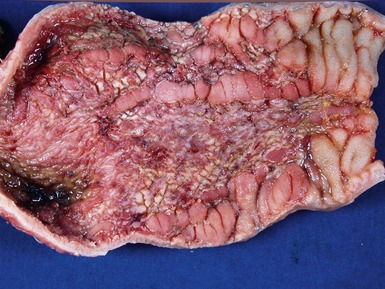
NEONATAL NECROTIZING ENTEROCOLITIS
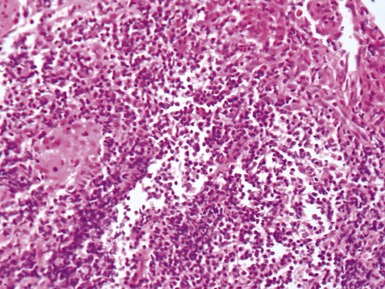
Histopathological features
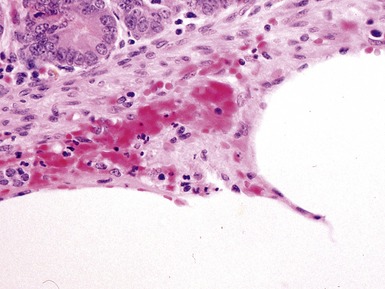
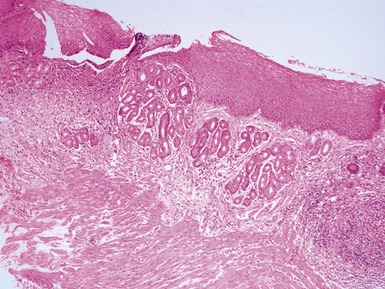
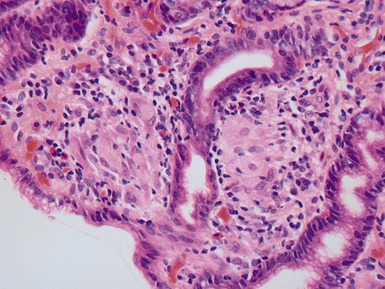
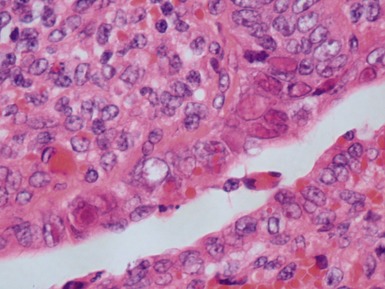
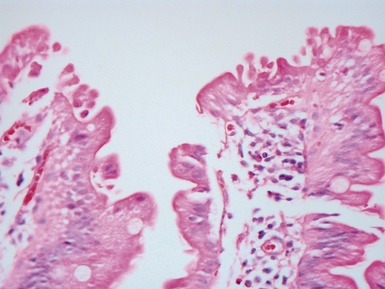
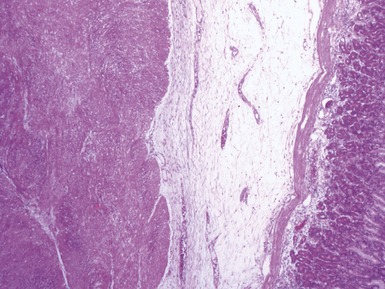
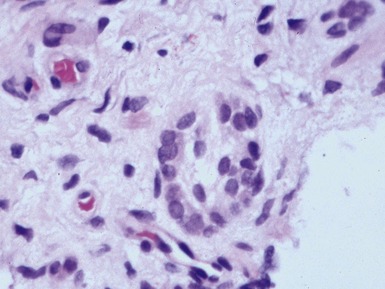
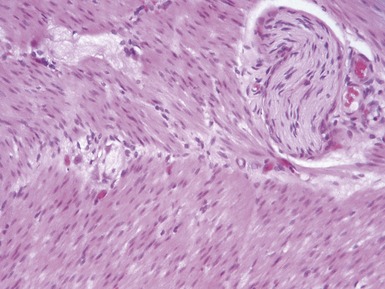
Fig 14.52 Necrotizing enterocolitis. Photomicrograph at a higher power of the same lesion as in Fig 14.51 demonstrating the edge of one of the gas-filled areas. There is hemorrhage and a neutrophil polymorph infiltrate.
FOOD ALLERGY
PRIMARY INTESTINAL FAILURE / NEONATAL-INFANTILE ENTEROPATHIES
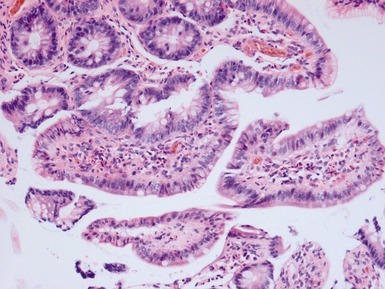
CELIAC DISEASE (GLUTEN SENSITIVE ENTEROPATHY)
Clinical features (Fasano et al 2008)
Histopathological features
Differential diagnosis and diagnostic pitfalls
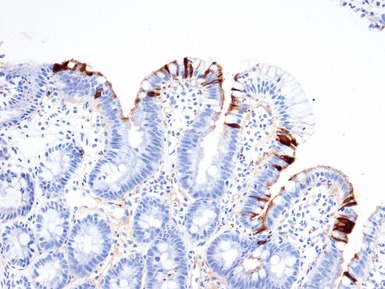
TUFTING ENTEROPATHY
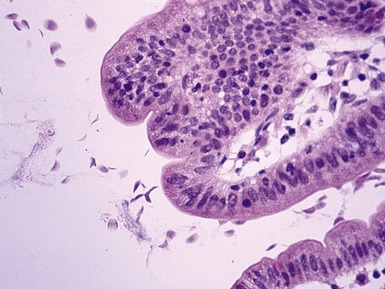
Histopathological features
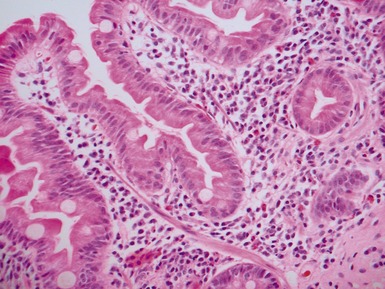
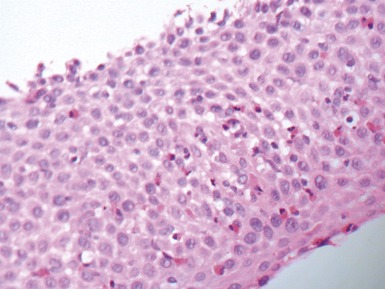
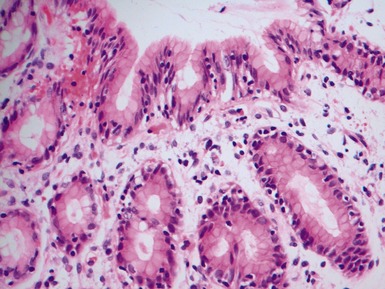
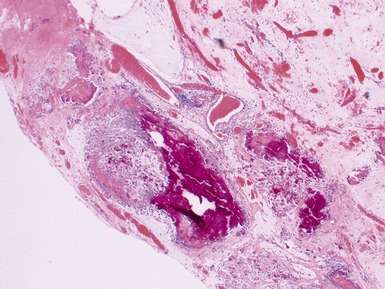
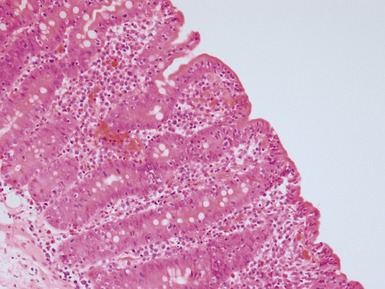
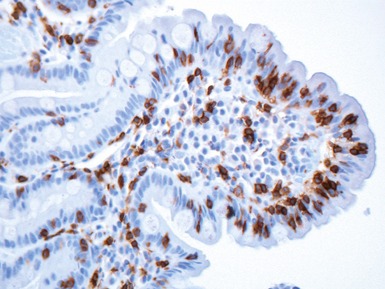
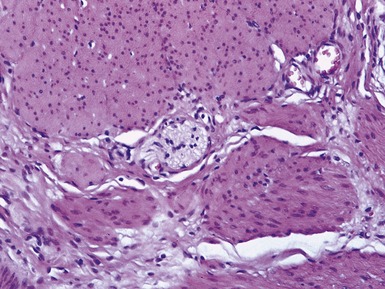
Fig 14.60 Tufting enteropathy inflammation. Photomicrograph demonstrating partial villous atrophy and an acute and chronic inflammatory cell infiltrate in the mucosa. No tufts are present in this field. The degree of inflammation present is very variable, but some degree is usually present.
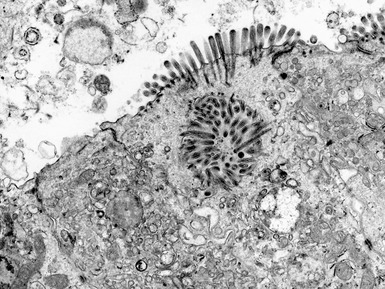
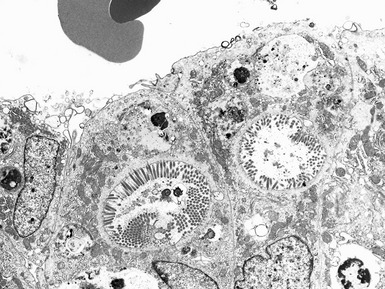
MICROVILLOUS INCLUSION DISEASE
DISSACHARIDASE ASSESSMENT OF JEJUNAL SPECIMENS
ABETALIPOPROTEINEMIA
PATHOLOGY OF INTESTINAL TRANSPLANTATION
GASTROINTESTINAL NEUROMUSCULAR / MOTILITY DISEASES
Introduction
Investigation of intestinal motility disorders
ACHALASIA OF ESOPHAGUS
HYPERTROPHIC PYLORIC STENOSIS
Differential diagnosis of infantile gastric outlet obstruction
HIRSCHSPRUNG’S DISEASE (HSCR)
Genetics
Clinical features
Histopathological features
Primary diagnosis on rectal suction biopsy
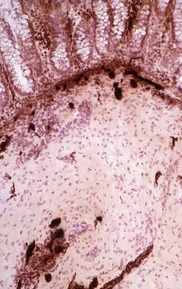
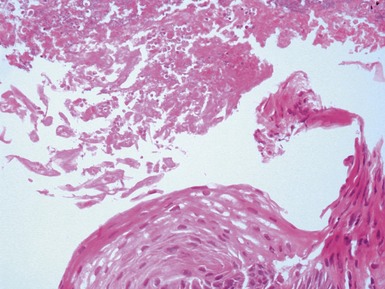
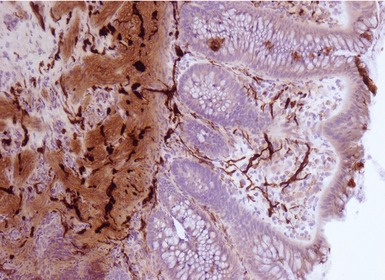
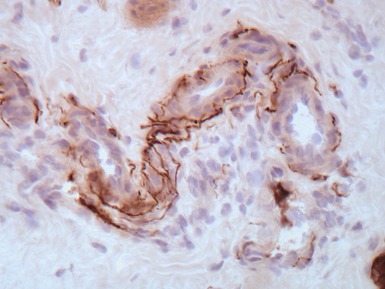
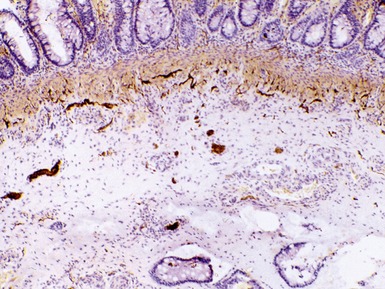
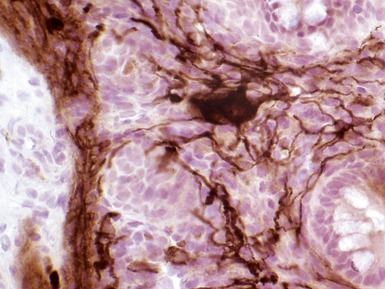
Fig 14.84 Photomicrograph of frozen section of normal rectal suction biopsy stained to display acetylcholinesterase activity demonstrating occasional fine nerves in the muscularis mucosae and lamina propria.
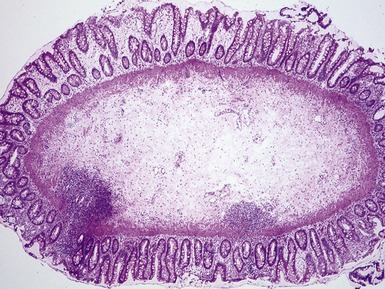
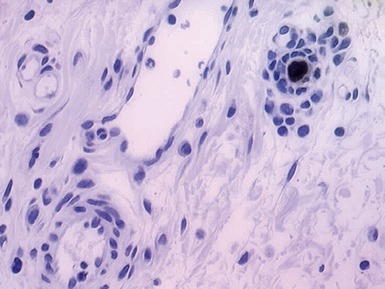
Fig 14.87 Photomicrograph of adequate rectal suction biopsy demonstrating large submucosal surface area.
Urgent
Differential diagnosis and diagnostic pitfalls
Identification of ganglion cells
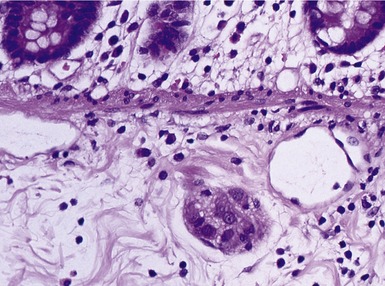
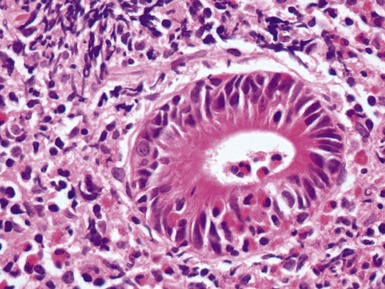
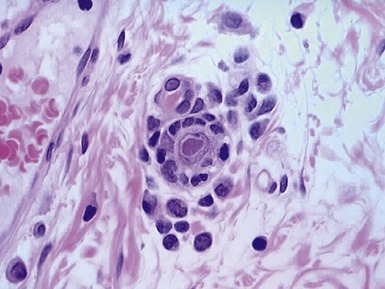
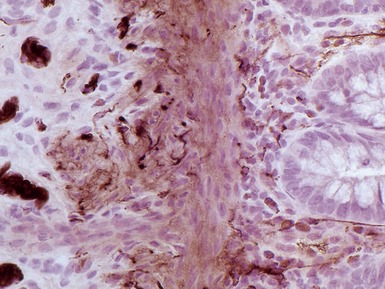
Fig 14.89 Photomicrograph of frozen section of rectal suction biopsy demonstrating normal submucosal ganglion cells. Note cluster of six cells with basophilic cytoplasm and prominent eccentric nucleus. Most do not show a nucleolus, a feature which is typical of neonatal specimens. Note also fine fibrillary neuropil and satellite cell nuclei.
Biopsy from physiological hypoganglionic zone 1–2 cm proximal to dentate line (‘low biopsy’; Fig 14.92)
Superficial biopsy (Fig 14.93)
Variability of AChE staining patterns
Short segment HSCR
Ultra-short segment HSCR (see also below: achalasia of internal anal sphincter)
Intestinal neuronal dysplasia (INDB)
Stains used in evaluation of rectal suction biopsies in other institutions
Reporting on frozen sections of intra-operative biopsies
Differential diagnosis and diagnostic pitfalls
Evaluation of resected bowel
 since neuronal population may have spiral architecture, despite intraoperative sections showing ganglionic bowel at one point, may occasionally reveal transitional zone
since neuronal population may have spiral architecture, despite intraoperative sections showing ganglionic bowel at one point, may occasionally reveal transitional zone