Evaluate the extent (severity) of the bleeding and assess hemodynamic stability.
Evaluate the extent (severity) of the bleeding and assess hemodynamic stability. Locate the site of the bleeding:
Locate the site of the bleeding:Hx
 Meds (ASA, steroids, “blood thinners,” NSAIDs)
Meds (ASA, steroids, “blood thinners,” NSAIDs) Prior GI or vascular surgery
Prior GI or vascular surgery H/o GI dx or bleeding
H/o GI dx or bleeding Smoking
Smoking Alcohol intake (gastritis, esophageal varices)
Alcohol intake (gastritis, esophageal varices) Sx of PUD
Sx of PUD Associated diseases (CAD, diabetes, HTN, hematologic disorders, renal failure)
Associated diseases (CAD, diabetes, HTN, hematologic disorders, renal failure) Protracted retching and vomiting (consider gastric or gastroesophageal tear [Mallory-Weiss syndrome])
Protracted retching and vomiting (consider gastric or gastroesophageal tear [Mallory-Weiss syndrome]) Weight loss, anorexia (consider carcinoma)
Weight loss, anorexia (consider carcinoma) Color and character of stool (i.e., hematochezia or melena, constipation or diarrhea)
Color and character of stool (i.e., hematochezia or melena, constipation or diarrhea) Presence or absence of hematemesis
Presence or absence of hematemesisPE
 VS: tachycardia, hypotension, postural changes (orthostatic hypotension). A pulse ↑ >20 bpm or a postural ↑ in systolic BP >10 to 15 mm Hg indicates blood loss >1 L.
VS: tachycardia, hypotension, postural changes (orthostatic hypotension). A pulse ↑ >20 bpm or a postural ↑ in systolic BP >10 to 15 mm Hg indicates blood loss >1 L. Pts taking β-adrenergic blockers may not demonstrate significant tachycardia w/volume depletion.
Pts taking β-adrenergic blockers may not demonstrate significant tachycardia w/volume depletion. Cardiorespiratory exam: murmurs (↑ incidence of angiodysplasia in pts w/AS), pulmonary rales, JVD to determine rapidity of volume replacement
Cardiorespiratory exam: murmurs (↑ incidence of angiodysplasia in pts w/AS), pulmonary rales, JVD to determine rapidity of volume replacement Abd exam:
Abd exam: DRE: Check for masses, strictures, hemorrhoids; test stool for occult blood and inspect it for abnormalities (tarry, blood streaked, bright red, mahogany color).
DRE: Check for masses, strictures, hemorrhoids; test stool for occult blood and inspect it for abnormalities (tarry, blood streaked, bright red, mahogany color). Skin: Check for jaundice (liver disease), ecchymoses (coagulation abnormality), cutaneous telangiectasia (Rendu-Osler-Weber disease), buccal pigmentation (Peutz-Jeghers syndrome), and other mucocutaneous changes (Ehlers-Danlos syndrome).
Skin: Check for jaundice (liver disease), ecchymoses (coagulation abnormality), cutaneous telangiectasia (Rendu-Osler-Weber disease), buccal pigmentation (Peutz-Jeghers syndrome), and other mucocutaneous changes (Ehlers-Danlos syndrome). Look for evidence of metastatic disease (cachexia, firm nodular liver).
Look for evidence of metastatic disease (cachexia, firm nodular liver). If the pt is not experiencing hematemesis and endoscopy is not immediately available, an NG tube may be placed for gastric lavage while awaiting endoscopy to determine whether the bleeding is emanating from the UGI tract (presence of bright red blood clots or coffee-ground–like guaiac (+) aspirate); however, the sensitivity and specificity of this process are limited. A (−) aspirate does not r/o upper GI bleeding because it could have subsided or the pt could be bleeding from the duodenal bulb w/o reflux into the stomach. Lavage w/500 mL of NS. Failure to clear blood w/gastric lavage indicates persistent bleeding and the need for more urgent endoscopy.
If the pt is not experiencing hematemesis and endoscopy is not immediately available, an NG tube may be placed for gastric lavage while awaiting endoscopy to determine whether the bleeding is emanating from the UGI tract (presence of bright red blood clots or coffee-ground–like guaiac (+) aspirate); however, the sensitivity and specificity of this process are limited. A (−) aspirate does not r/o upper GI bleeding because it could have subsided or the pt could be bleeding from the duodenal bulb w/o reflux into the stomach. Lavage w/500 mL of NS. Failure to clear blood w/gastric lavage indicates persistent bleeding and the need for more urgent endoscopy.Initial Management
 Stabilize the pt: Insert two large-bore (18-gauge) IV catheters and administer lactated Ringer’s solution or NS; the rate of volume replacement is based on the estimated blood loss, clinical condition, and h/o CVD, including CHF.
Stabilize the pt: Insert two large-bore (18-gauge) IV catheters and administer lactated Ringer’s solution or NS; the rate of volume replacement is based on the estimated blood loss, clinical condition, and h/o CVD, including CHF. Type and crossmatch for 2 to 8 U of PRBCs, depending on the estimated blood loss, and transfuse as necessary. Aim for Hct >30 for elderly pts w/multiple comorbid conditions and ≥20 for young, healthy individuals.
Type and crossmatch for 2 to 8 U of PRBCs, depending on the estimated blood loss, and transfuse as necessary. Aim for Hct >30 for elderly pts w/multiple comorbid conditions and ≥20 for young, healthy individuals. Initial labs:
Initial labs: ECG: R/o myocardial ischemia secondary to severe anemia in patients with risk factors.
ECG: R/o myocardial ischemia secondary to severe anemia in patients with risk factors.Endoscopic EzZvaluation
 EGD is indicated when blood or guaiac (+) coffee ground–like material is obtained from the NG aspirate or if lower endoscopic findings are (−). It should be performed urgently in hemodynamically unstable pts or those found to still be actively bleeding by NG lavage or in those requiring blood transfusion. Otherwise, it should ideally be performed within 24 hr of the hospital admission. In addition, if a therapeutic procedure (e.g., bipolar heater probe, laser cauterization, injection scleroRx, or band ligation) is considered, endoscopy should be done on an emergency basis.
EGD is indicated when blood or guaiac (+) coffee ground–like material is obtained from the NG aspirate or if lower endoscopic findings are (−). It should be performed urgently in hemodynamically unstable pts or those found to still be actively bleeding by NG lavage or in those requiring blood transfusion. Otherwise, it should ideally be performed within 24 hr of the hospital admission. In addition, if a therapeutic procedure (e.g., bipolar heater probe, laser cauterization, injection scleroRx, or band ligation) is considered, endoscopy should be done on an emergency basis. Colonoscopy should be performed initially if lower GI bleeding is suspected, generally within 24 hr of hospital admission after adequate bowel preparation.
Colonoscopy should be performed initially if lower GI bleeding is suspected, generally within 24 hr of hospital admission after adequate bowel preparation.Imaging
 Arteriography can identify briskly bleeding sources. Overall diagnostic sensitivity of arteriography is 41%. Mesenteric arteriography is useful to identify bleeding from AV malformations.
Arteriography can identify briskly bleeding sources. Overall diagnostic sensitivity of arteriography is 41%. Mesenteric arteriography is useful to identify bleeding from AV malformations. Radionuclide scans may be used before angiography to determine which pts are bleeding sufficiently to make (+) angiographic result more likely. Bleeding at rates as low as 0.1 mL/min can be detected by radionuclide scans. A (+) “immediate blush” is a good indication for urgent angiography, whereas a (−) “delayed blush” is an indication for observation and elective colonoscopy.
Radionuclide scans may be used before angiography to determine which pts are bleeding sufficiently to make (+) angiographic result more likely. Bleeding at rates as low as 0.1 mL/min can be detected by radionuclide scans. A (+) “immediate blush” is a good indication for urgent angiography, whereas a (−) “delayed blush” is an indication for observation and elective colonoscopy. Technetium-99m (99mTc) pertechnetate scan (Meckel scan) selectively tags acid-secreting cells (gastric mucosa); it is used most often for unexplained bleeding in infants and young adults.
Technetium-99m (99mTc) pertechnetate scan (Meckel scan) selectively tags acid-secreting cells (gastric mucosa); it is used most often for unexplained bleeding in infants and young adults. 99mTc-sulfur colloid scan is very sensitive in detecting lesions w/low bleeding rates; its major drawbacks are as follows:
99mTc-sulfur colloid scan is very sensitive in detecting lesions w/low bleeding rates; its major drawbacks are as follows: 99mTc-labeled RBC scan: Its major advantage over the sulfur colloid scan is its long duration; it is useful for intermittent bleeding because the pt can be monitored for GI bleeding for 24 to 48 hr. Its disadvantage is that it has a high false-localization rate.
99mTc-labeled RBC scan: Its major advantage over the sulfur colloid scan is its long duration; it is useful for intermittent bleeding because the pt can be monitored for GI bleeding for 24 to 48 hr. Its disadvantage is that it has a high false-localization rate. Selective angiography:
Selective angiography:Treatment
 Correct bleeding abnormalities by administering FFP or vitamin K if the pt has a coagulopathy and Plt if the pt is severely thrombocytopenic.
Correct bleeding abnormalities by administering FFP or vitamin K if the pt has a coagulopathy and Plt if the pt is severely thrombocytopenic. IV PPIs in cases of probable peptic ulcer or gastritis. After endoscopic Rx of bleeding peptic ulcers, IV PPIs ↓ the risk of recurrent bleeding ↑ pH, ↑ platelet function.
IV PPIs in cases of probable peptic ulcer or gastritis. After endoscopic Rx of bleeding peptic ulcers, IV PPIs ↓ the risk of recurrent bleeding ↑ pH, ↑ platelet function. Octreotide: IV bolus of 50 to 100 μg followed by IV infusion of 25 to 50 μg/hr is useful for acute variceal bleeding. Another useful agent is terlipressin.
Octreotide: IV bolus of 50 to 100 μg followed by IV infusion of 25 to 50 μg/hr is useful for acute variceal bleeding. Another useful agent is terlipressin. Endoscopy:
Endoscopy: Balloon tamponade is indicated for severe bleeding from esophageal varices if octreotide or other endoscopic Rx modalities are ineffective.
Balloon tamponade is indicated for severe bleeding from esophageal varices if octreotide or other endoscopic Rx modalities are ineffective. Radiologic modalities include localized infusion of vasopressin, autologous clots, or foreign coagulating substances (e.g., Gelfoam) in the bleeding vessel during or after arteriography.
Radiologic modalities include localized infusion of vasopressin, autologous clots, or foreign coagulating substances (e.g., Gelfoam) in the bleeding vessel during or after arteriography. Surgery is indicated at the onset of dx of aortoduodenal fistula, but it is not suggested as the initial Rx in cases of other causes of GI bleeding until a definitive dx is made and other noninvasive modalities are tried. Surgical approach may be necessary in the following situations:
Surgery is indicated at the onset of dx of aortoduodenal fistula, but it is not suggested as the initial Rx in cases of other causes of GI bleeding until a definitive dx is made and other noninvasive modalities are tried. Surgical approach may be necessary in the following situations:B. Disorders of the Esophagus
1. Dysphagia
a. Oropharyngeal Dysphagia
 Inability to move food from oropharynx via UES → esophagus
Inability to move food from oropharynx via UES → esophagus Drooling, postnasal regurgitation, difficulty initiating swallowing, sialorrhea, sensation of food stuck in the neck, coughing/choking during swallowing, dysphonia, and dysarthria
Drooling, postnasal regurgitation, difficulty initiating swallowing, sialorrhea, sensation of food stuck in the neck, coughing/choking during swallowing, dysphonia, and dysarthriaDiagnosis
 First test = modified barium swallow videofluoroscopy, then fiberoptic flexible nasopharyngeal laryngoscopy
First test = modified barium swallow videofluoroscopy, then fiberoptic flexible nasopharyngeal laryngoscopyb. Esophageal Dysphagia
 Inability to move food from esophagus → stomach
Inability to move food from esophagus → stomach Dysphagia to solids suggests mechanical obstruction.
Dysphagia to solids suggests mechanical obstruction. Neuromuscular causes result in dysphagia to both solids and liquids.
Neuromuscular causes result in dysphagia to both solids and liquids. Sx intermittent in pts with esophageal dysphagia from benign causes of structural obstruction or diffuse esophageal spasm; sx progressive in pts with peptic stricture, esophageal carcinoma, scleroderma, and achalasia
Sx intermittent in pts with esophageal dysphagia from benign causes of structural obstruction or diffuse esophageal spasm; sx progressive in pts with peptic stricture, esophageal carcinoma, scleroderma, and achalasia Luminal diameter >18 to 20 mm (rarely sx); diameter <13 mm (sx)
Luminal diameter >18 to 20 mm (rarely sx); diameter <13 mm (sx)Diagnosis
 Esophageal dysphagia: first test = barium esophagography, then EGD
Esophageal dysphagia: first test = barium esophagography, then EGDTreatment
 Goal is airway protection and nutrition maintenance.
Goal is airway protection and nutrition maintenance. Consider consultation with ENT, head and neck surgeon, radiologist, speech pathologist, physical therapist, dietitian, gastroenterologist, physical medicine and rehabilitation specialist, dentist, neurologist, etc., because nursing home pts with oropharyngeal dysphagia and hx of aspiration have 45% mortality rate over 1 yr
Consider consultation with ENT, head and neck surgeon, radiologist, speech pathologist, physical therapist, dietitian, gastroenterologist, physical medicine and rehabilitation specialist, dentist, neurologist, etc., because nursing home pts with oropharyngeal dysphagia and hx of aspiration have 45% mortality rate over 1 yr2. Esophageal Motility Disorders
 Table 6-1 compares esophageal motor disorders.
Table 6-1 compares esophageal motor disorders.TABLE 6-1
Esophageal Motor Disorders
| Achalasia | Scleroderma | Diffuse Esophageal Spasm | |
| Symptoms | Dysphagia Regurgitation of nonacidic material |
Gastroesophageal reflux disease Dysphagia |
Substernal chest pain (angina-like) Dysphagia with pain |
| Radiographic appearance | Dilated, fluid-filled esophagus Distal bird-beak stricture |
Aperistaltic esophagus Free reflux Peptic stricture |
Simultaneous noncoordinated contractions |
| Manometric Findings | |||
| Lower esophageal sphincter | High resting pressure Incomplete or abnormal relaxation with swallow |
Low resting pressure | Normal pressure |
| Body | Low-amplitude, simultaneous contractions after swallowing | Low-amplitude peristaltic contractions or no peristalsis | Some peristalsis Diffuse and simultaneous nonperistaltic contractions, occasionally high amplitude |

From Andreoli, T E, Benjamin IJ, Griggs RC, Wing EJ: Andreoli and Carpenter’s Cecil Essentials of Medicine, 8th ed. Philadelphia, Saunders, 2010.
3. GERD
 Motility disorder caused by the reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus
Motility disorder caused by the reflux of gastric contents into the esophagusEtiology
 Incompetent LES
Incompetent LES Medications ↓ LES pressure (CCBs, β-blockers, theophylline, anti-AChs)
Medications ↓ LES pressure (CCBs, β-blockers, theophylline, anti-AChs) Foods ↓ LES pressure (chocolate, yellow onions, peppermint)
Foods ↓ LES pressure (chocolate, yellow onions, peppermint) Tobacco abuse, alcohol, coffee
Tobacco abuse, alcohol, coffee Pregnancy
Pregnancy Gastric acid hypersecretion
Gastric acid hypersecretion Hiatal hernia (present in 70% w/GERD ); however, most w/hiatal hernia asx
Hiatal hernia (present in 70% w/GERD ); however, most w/hiatal hernia asxDiagnosis
H&P
 Heartburn, dysphagia, sour taste, regurgitation of gastric contents into mouth, chronic cough/bronchospasm, chest pain, laryngitis, early satiety, abd fullness and bloating w/belching, dental erosions in children
Heartburn, dysphagia, sour taste, regurgitation of gastric contents into mouth, chronic cough/bronchospasm, chest pain, laryngitis, early satiety, abd fullness and bloating w/belching, dental erosions in childrenAdditional Testing
 EGD = document type/extent tissue damage; r/o potential malignancy (Barrett’s esophagus)
EGD = document type/extent tissue damage; r/o potential malignancy (Barrett’s esophagus) 24-hr esophageal pH monitoring: generally not done; useful in atypical manifestations of GERD (chest pain and chronic cough)
24-hr esophageal pH monitoring: generally not done; useful in atypical manifestations of GERD (chest pain and chronic cough) Esophageal manometry: useful in refractory reflux pt w/surgical Rx planned
Esophageal manometry: useful in refractory reflux pt w/surgical Rx planned Upper GI series: identify ulcerations/strictures; may miss mucosal abnormalities. Only one third of pts w/GERD have radiographic signs of esophagitis.
Upper GI series: identify ulcerations/strictures; may miss mucosal abnormalities. Only one third of pts w/GERD have radiographic signs of esophagitis.Treatment
 Lifestyle change (wt loss, ↓ fat intake)/avoidance of exacerbating factors: EtOH, tobacco, citrus/tomato–based products, caffeine, β-blockers, CCBs, α-agonists, theophylline
Lifestyle change (wt loss, ↓ fat intake)/avoidance of exacerbating factors: EtOH, tobacco, citrus/tomato–based products, caffeine, β-blockers, CCBs, α-agonists, theophylline ↑ Head of bed 4 to 8 in. Avoid lying supine directly after late/large meals.
↑ Head of bed 4 to 8 in. Avoid lying supine directly after late/large meals. Avoid wearing clothing that is tight around the waist.
Avoid wearing clothing that is tight around the waist. PPIs: preferred Rx (H2 blockers less effective)
PPIs: preferred Rx (H2 blockers less effective) Antacids: relief of mild sx; ineffective in severe cases
Antacids: relief of mild sx; ineffective in severe cases Prokinetic agents (metoclopramide): indicated if PPIs not fully effective. May be used in combination Rx; however, side effects limit use.
Prokinetic agents (metoclopramide): indicated if PPIs not fully effective. May be used in combination Rx; however, side effects limit use. Nissen fundoplication (refractory cases)
Nissen fundoplication (refractory cases) Endoscopic radiofrequency heating of GE-jxn (Stretta procedure): pts unresponsive to traditional Rx
Endoscopic radiofrequency heating of GE-jxn (Stretta procedure): pts unresponsive to traditional Rx4. Barrett’s Esophagus
 Squamous lining of lower esophagus replaced by intestinalized metaplastic columnar epithelium; predisposing to neoplasia
Squamous lining of lower esophagus replaced by intestinalized metaplastic columnar epithelium; predisposing to neoplasiaH&P
Diagnosis
 EGD with biopsy
EGD with biopsyTreatment
 Control GERD sx; maintain healed mucosa via PPI
Control GERD sx; maintain healed mucosa via PPIMonitoring
 Relative risk of adenocarcinoma is 11.3 compared with general population.
Relative risk of adenocarcinoma is 11.3 compared with general population. Pts should undergo surveillance EGD and systematic four-quadrant biopsy at intervals determined by the presence and grade of dysplasia.
Pts should undergo surveillance EGD and systematic four-quadrant biopsy at intervals determined by the presence and grade of dysplasia. Pts who have had two consecutive EGDs showing no dysplasia should have follow-up every 3 to 5 yr.
Pts who have had two consecutive EGDs showing no dysplasia should have follow-up every 3 to 5 yr. Pts with low-grade dysplasia should have extensive mucosal sampling within 6 mo and follow-up every 6 to 12 mo.
Pts with low-grade dysplasia should have extensive mucosal sampling within 6 mo and follow-up every 6 to 12 mo. Pts with high-grade dysplasia should have expert confirmation and extensive mucosal sampling. High-grade dysplasia with visible mucosal irregularities should be removed by endoscopic mucosal resection.
Pts with high-grade dysplasia should have expert confirmation and extensive mucosal sampling. High-grade dysplasia with visible mucosal irregularities should be removed by endoscopic mucosal resection. Consider intensive surveillance every 3 mo for patients with focal high-grade dysplasia. Patients with multifocal high-grade dysplasia or carcinoma should be considered for resection or ablation if not an operative candidate.
Consider intensive surveillance every 3 mo for patients with focal high-grade dysplasia. Patients with multifocal high-grade dysplasia or carcinoma should be considered for resection or ablation if not an operative candidate.5. Esophageal Tumors
 15% in proximal third esophagus, 50% in middle third, 35% in lower third
15% in proximal third esophagus, 50% in middle third, 35% in lower third Risk factors: EtOH, smoking, achalasia (7× > risk), chronic GERD, HPV (types 16, 18), obesity/hiatal hernia/low-vitamin high-fat diet, ingested carcinogens (nitrates, smoked opiates, fungal toxins [pickled vegetables], betel nut chewing), mucosal damage (long-term exposure tea >70° C, lye ingestion), radiation-induced stricture
Risk factors: EtOH, smoking, achalasia (7× > risk), chronic GERD, HPV (types 16, 18), obesity/hiatal hernia/low-vitamin high-fat diet, ingested carcinogens (nitrates, smoked opiates, fungal toxins [pickled vegetables], betel nut chewing), mucosal damage (long-term exposure tea >70° C, lye ingestion), radiation-induced strictureH&P
 Dysphagia (74%): initially with solid foods; gradually → semisolids/liquids
Dysphagia (74%): initially with solid foods; gradually → semisolids/liquids Unintentional weight loss; losing >10% of body mass = poor outcome
Unintentional weight loss; losing >10% of body mass = poor outcome Hoarseness (recurrent laryngeal nerve involvement)
Hoarseness (recurrent laryngeal nerve involvement) Cervical adenopathy; usually supraclavicular lymph nodes
Cervical adenopathy; usually supraclavicular lymph nodesDiagnosis
 EGD
EGD Endoscopic U/S: locoregional staging (depth of invasion/lymph assessment)
Endoscopic U/S: locoregional staging (depth of invasion/lymph assessment) Chest/abd CT and/or integrated CT-PET scans (tumor spread for preop staging)
Chest/abd CT and/or integrated CT-PET scans (tumor spread for preop staging) Staging laparoscopy may alter Rx plans (20%-30% cases) by more accurately staging regional lymph nodes/detecting occult peritoneal mets.
Staging laparoscopy may alter Rx plans (20%-30% cases) by more accurately staging regional lymph nodes/detecting occult peritoneal mets.Treatment
 Surgical resection of squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma of lower esophageal third indicated for local, resectable disease in the absence of widespread mets detected by CT-PET. Gastric pull-through/colonic interposition is typically used to provide luminal continuity.
Surgical resection of squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma of lower esophageal third indicated for local, resectable disease in the absence of widespread mets detected by CT-PET. Gastric pull-through/colonic interposition is typically used to provide luminal continuity. Squamous cell carcinoma is more radiosensitive than adenocarcinoma; used as palliative monoRx of obstructive sx in unresectable/advanced cases.
Squamous cell carcinoma is more radiosensitive than adenocarcinoma; used as palliative monoRx of obstructive sx in unresectable/advanced cases. Palliative radiation Rx for bone mets
Palliative radiation Rx for bone mets Preoperative chemoradioRx + surgery in late stage I (T2,3N0), stage II or III ↑ tumoricidal effects
Preoperative chemoradioRx + surgery in late stage I (T2,3N0), stage II or III ↑ tumoricidal effects 5-yr survival 13% (37.3% [local], 18.4% [regional], 3.1% [distant] disease)
5-yr survival 13% (37.3% [local], 18.4% [regional], 3.1% [distant] disease)C. Disorders of Stomach and Duodenum
1. Peptic Ulcer Disease
Etiology/Epidemiology
 H. pylori infection (70%-90% duodenal ulcers)
H. pylori infection (70%-90% duodenal ulcers) NSAIDs (40%-50% gastric ulcers)
NSAIDs (40%-50% gastric ulcers) Cigarette smoking, EtOH
Cigarette smoking, EtOH Neoplasia: gastrinoma (ZE syndrome), carcinoid, mastocytosis
Neoplasia: gastrinoma (ZE syndrome), carcinoid, mastocytosisDiagnosis
 EGD (preferred), UGI barium studies
EGD (preferred), UGI barium studiesTreatment
 Lifestyle change: d/c smoking/EtOH.
Lifestyle change: d/c smoking/EtOH. Add PPI to ↓ acid secretions.
Add PPI to ↓ acid secretions.TABLE 6-2
Overview of Antibiotics Used for Helicobacter Pylori Eradication
| Drug Class | Drug | Triple Therapy∗ Dose | Quadruple Therapy† Dose | Sequential Therapy‡ Dose |
| Acid suppression | Proton pump inhibitor | 20-40 mg bid§ | 20-40 mg bid§ | 20-40 mg bid§ |
| Standard antimicrobials | Bismuth compound|| | 2 tablets bid | 2 tablets bid | |
| Amoxicillin | 1 g bid | 1 g bid | ||
| Metronidazole¶ | 500 mg bid | 500 mg tid | 500 mg bid | |
| Clarithromycin | 500 mg bid | 500 mg bid | ||
| Tetracycline | 500 mg qid | |||
| Salvage antimicrobials | Levofloxacin | 300 mg bid | 300 mg bid | |
| Rifabutin | 150 mg bid | |||
| Furazolidone | 100 mg bid | |||
| Doxycycline | 100 mg bid | |||
| Nitazoxanide | 1 g bid |

∗ Triple therapy consists of a proton pump inhibitor or bismuth compound, together with two of the listed antibiotics, usually given for 7-14 days.
† Quadruple therapy consists of a proton pump inhibitor plus either the combination of a bismuth compound, metronidazole, and tetracycline given for 4-10 days, or the combination of levofloxacin, doxycycline, and nitazoxanide for 10 days.
‡ Sequential therapy consists of 10 days of proton pump inhibitor treatment, plus amoxicillin during days 1-5 and a combination of clarithromycin and an imidazole (when available, tinidazole; otherwise, metronidazole) during days 6-10.
§ Proton pump inhibitor dose equivalent to omeprazole 20 mg bid.
|| Bismuth subsalicylate or subcitrate.
¶ An alternative is tinidazole 500 mg bid.
From Goldman L, Schafer AI (eds): Goldman’s Cecil Medicine, 24th ed. Philadelphia, Saunders, Elsevier, 2012.
2. Gastroparesis
 Sx impaired gastric emptying in absence of mechanical obstruction
Sx impaired gastric emptying in absence of mechanical obstructionDifferential Diagnosis and Clinical Pearls
 Diabetes mellitus gastroparesis (HBA1c, fasting glucose)
Diabetes mellitus gastroparesis (HBA1c, fasting glucose) Gastric surgery
Gastric surgery Pregnancy
Pregnancy Hypothyroidism (TSH)
Hypothyroidism (TSH) Cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome (hx of use; hx of relief of N/V with hot baths/showers)
Cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome (hx of use; hx of relief of N/V with hot baths/showers) Rumination syndrome (hx of passive regurgitation of pleasant tasting food w/o nausea)
Rumination syndrome (hx of passive regurgitation of pleasant tasting food w/o nausea)Management
 Prokinetic agents (e.g., metoclopramide)
Prokinetic agents (e.g., metoclopramide) Refractory cases (↑ risk malnutrition), gastroduodenal manometry to distinguish myopathic from neuropathic process
Refractory cases (↑ risk malnutrition), gastroduodenal manometry to distinguish myopathic from neuropathic process3. Gastric Cancer
 Adenocarcinoma; mostly antral (35%)
Adenocarcinoma; mostly antral (35%) Male-to-female ratio 3:2
Male-to-female ratio 3:2 Familiar diffuse gastric cancer (autosomal dominant, mutation E-cadherin gene CDH1 = cancer at young age)
Familiar diffuse gastric cancer (autosomal dominant, mutation E-cadherin gene CDH1 = cancer at young age)Physical Exam and Labs
 Wt loss (70%-80%), N/V (20%-40%), dysphagia (20%)
Wt loss (70%-80%), N/V (20%-40%), dysphagia (20%) Dyspepsia (unrelieved by antacids, worse w/food), epigastric/abd mass (40%)
Dyspepsia (unrelieved by antacids, worse w/food), epigastric/abd mass (40%) Microcytic anemia, hemoccult (+) stools
Microcytic anemia, hemoccult (+) stools Hypoalbuminemia
HypoalbuminemiaDiagnosis
 Upper endoscopy with biopsy (staging via abd CT scan ± lymph node dissection)
Upper endoscopy with biopsy (staging via abd CT scan ± lymph node dissection)D. Disorders of the Pancreas
1. Acute Pancreatitis
 Inflammatory process w/intrapancreatic enzyme activation possibly also involving peripancreatic tissue/remote organ systems
Inflammatory process w/intrapancreatic enzyme activation possibly also involving peripancreatic tissue/remote organ systemsEtiology
 >90% of cases: biliary tract disease (calculi or sludge) or EtOH
>90% of cases: biliary tract disease (calculi or sludge) or EtOH Drugs: thiazides, furosemide, corticosteroids, tetracycline, estrogens, valproic acid, metronidazole, azathioprine, methyldopa, pentamidine, ethacrynic acid, procainamide, sulindac, nitrofurantoin, ACEIs, danazol, cimetidine, piroxicam, gold, ranitidine, sulfasalazine, isoniazid, acetaminophen, cisplatin, opiates, erythromycin
Drugs: thiazides, furosemide, corticosteroids, tetracycline, estrogens, valproic acid, metronidazole, azathioprine, methyldopa, pentamidine, ethacrynic acid, procainamide, sulindac, nitrofurantoin, ACEIs, danazol, cimetidine, piroxicam, gold, ranitidine, sulfasalazine, isoniazid, acetaminophen, cisplatin, opiates, erythromycin Abd trauma, surgery, ERCP, viral infections, PUD, pancreas divisum (congenital failure to fuse of dorsal or ventral pancreas), pregnancy, vascular (vasculitis, ischemic), hypolipoproteinemia (types I, IV, and V), hypercalcemia, pancreatic carcinoma (primary/mets), renal failure, hereditary pancreatitis, occupational exposure (methanol, cobalt, zinc, mercuric chloride, creosol, lead, organophosphates, chlorinated naphthalenes)
Abd trauma, surgery, ERCP, viral infections, PUD, pancreas divisum (congenital failure to fuse of dorsal or ventral pancreas), pregnancy, vascular (vasculitis, ischemic), hypolipoproteinemia (types I, IV, and V), hypercalcemia, pancreatic carcinoma (primary/mets), renal failure, hereditary pancreatitis, occupational exposure (methanol, cobalt, zinc, mercuric chloride, creosol, lead, organophosphates, chlorinated naphthalenes) Others: scorpion bite, obstruction at ampulla region (neoplasm, duodenal diverticula, Crohn’s disease), hypotensive shock, autoimmune pancreatitis
Others: scorpion bite, obstruction at ampulla region (neoplasm, duodenal diverticula, Crohn’s disease), hypotensive shock, autoimmune pancreatitisScoring System
 Table 6-3 describes various scoring systems to assess severity of acute pancreatitis.
Table 6-3 describes various scoring systems to assess severity of acute pancreatitis.TABLE 6-3
Scoring Systems to Assess Severity of Acute Pancreatitis
| System | Criteria |
| Ranson | At admission Age >55 yr WBC >16,000/μL Glucose >200 mg/dL LDH >350 IU/L AST >250 IU/L Within next 48 hr Decrease in hematocrit by >10% Estimated fluid sequestration of >6 L Serum calcium <8.0 mg/dL Pao2 <60 mm Hg BUN increase >5 mg/dL after hydration Base deficit >4 mmol/L |
| APACHE-II | Multiple clinical and laboratory factors. Calculator available at www.mdcalc.com/apache-ii-score-for-icu-mortality |
| BISAP | BUN >25 mg/dL Impaired mental status Presence of SIRS Age >60 yr Pleural effusion |
| CT | A: Normal pancreas B: Focal or diffuse enlargement of pancreas C: Grade B plus pancreatic and/or peripancreatic inflammation D: Grade C plus a single fluid collection E: Grade C plus two or more fluid collections or gas in pancreas |
| CT severity index | CT grade A = 0 B = 1 C = 2 D = 3 E = 4 Plus necrosis grade No necrosis = 0 <30% necrosis = 2 30-50% necrosis = 4 >50% necrosis = 6 |
APACHE-II, Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II; BISAP, bedside index of severity in acute pancreatitis.
From Goldman L, Schafer AI (eds): Goldman’s Cecil Medicine, 24th ed. Philadelphia, Saunders, Elsevier, 2012.
“Severe Acute Pancreatitis”
Diagnosis
H&P
 Fever, epigastric tenderness/guarding; sudden severe pain (peak intensity 10-30 min; lasting several hr w/o relief)
Fever, epigastric tenderness/guarding; sudden severe pain (peak intensity 10-30 min; lasting several hr w/o relief) Hypoactive bowel sounds (secondary to ileus)
Hypoactive bowel sounds (secondary to ileus) Tachycardia, shock (secondary to ↓ intravascular volume)
Tachycardia, shock (secondary to ↓ intravascular volume) Confusion (secondary to metabolic disturbances)
Confusion (secondary to metabolic disturbances) ↓ Breath sounds (atelectasis, pleural effusions, ARDS)
↓ Breath sounds (atelectasis, pleural effusions, ARDS) Jaundice (secondary to obstruction or compression of biliary tract)
Jaundice (secondary to obstruction or compression of biliary tract) Ascites (secondary to tear in pancreatic duct, leaking pseudocyst)
Ascites (secondary to tear in pancreatic duct, leaking pseudocyst) Palpable abd mass (pseudocyst, phlegmon, abscess, carcinoma)
Palpable abd mass (pseudocyst, phlegmon, abscess, carcinoma) Hypocalcemia (Chvostek’s sign, Trousseau’s sign)
Hypocalcemia (Chvostek’s sign, Trousseau’s sign) Intra-abd bleeding (hemorrhagic pancreatitis):
Intra-abd bleeding (hemorrhagic pancreatitis): Tender SC nodules (SC fat necrosis)
Tender SC nodules (SC fat necrosis)Labs
 ↑ Serum amylase (initial 3-5 days), ↑ serum lipase, ↑ serum trypsin
↑ Serum amylase (initial 3-5 days), ↑ serum lipase, ↑ serum trypsin Rapid urinary trypsinogen-2; useful screening test in pts w/abd pain; (−) dipstick r/o acute pancreatitis w/high degree of probability; (+) test result indicates need for further evaluation.
Rapid urinary trypsinogen-2; useful screening test in pts w/abd pain; (−) dipstick r/o acute pancreatitis w/high degree of probability; (+) test result indicates need for further evaluation. CBC: leukocytosis; ↑ Hct (secondary to hemoconcentration); ↓ Hct may indicate hemorrhage/hemolysis.
CBC: leukocytosis; ↑ Hct (secondary to hemoconcentration); ↓ Hct may indicate hemorrhage/hemolysis. ↑ BUN (secondary to dehydration)
↑ BUN (secondary to dehydration) ↑ Serum glucose; in previously nl pt correlates w/pancreatic malfunction
↑ Serum glucose; in previously nl pt correlates w/pancreatic malfunction ↑ AST/LDH (tissue necrosis); ↑ bili/alk phos (CBD obstruction); ≥3 ↑ ALT = biliary pancreatitis (95% probability)
↑ AST/LDH (tissue necrosis); ↑ bili/alk phos (CBD obstruction); ≥3 ↑ ALT = biliary pancreatitis (95% probability) ↓ Serum Ca (saponification, precipitation, and ↓ PTH response)
↓ Serum Ca (saponification, precipitation, and ↓ PTH response) ABGs: Pao2 may be ↓ secondary to ARDS, pleural effusions; pH may be ↓ secondary to lactic acidosis, respiratory acidosis, and renal insufficiency.
ABGs: Pao2 may be ↓ secondary to ARDS, pleural effusions; pH may be ↓ secondary to lactic acidosis, respiratory acidosis, and renal insufficiency. Serum electrolytes: K+ may be ↑ secondary to acidosis/renal insufficiency; Na+ may be ↑ secondary to dehydration.
Serum electrolytes: K+ may be ↑ secondary to acidosis/renal insufficiency; Na+ may be ↑ secondary to dehydration.Imaging
 Abd plain film: r/o perforated viscus; may reveal localized ileus (sentinel loop), pancreatic calcifications (chronic pancreatitis), blurring of left psoas shadow, dilation of transverse colon, calcified gallstones
Abd plain film: r/o perforated viscus; may reveal localized ileus (sentinel loop), pancreatic calcifications (chronic pancreatitis), blurring of left psoas shadow, dilation of transverse colon, calcified gallstones CXR: elevation of one or both diaphragms, pleural effusions, basilar infiltrates, platelike atelectasis
CXR: elevation of one or both diaphragms, pleural effusions, basilar infiltrates, platelike atelectasis Abd U/S: gallstones (sensitivity 60%-70%), pancreatic pseudocysts; limited in presence of distended bowel loops overlying pancreas
Abd U/S: gallstones (sensitivity 60%-70%), pancreatic pseudocysts; limited in presence of distended bowel loops overlying pancreas CT abd: superior to U/S in dx extent; also able dx pseudocysts (well-defined area surrounded by high-density capsule); GI fistulation or infection of a pseudocyst (gas within pseudocyst)
CT abd: superior to U/S in dx extent; also able dx pseudocysts (well-defined area surrounded by high-density capsule); GI fistulation or infection of a pseudocyst (gas within pseudocyst) Contrast-enhanced CT (pancreatic necrosis): severity graded by CT scan (see Table 6-3)
Contrast-enhanced CT (pancreatic necrosis): severity graded by CT scan (see Table 6-3) MRCP: useful if surgical procedure not anticipated
MRCP: useful if surgical procedure not anticipated ERCP: avoided during acute stage, unless to remove impacted stone
ERCP: avoided during acute stage, unless to remove impacted stoneTreatment
General Measures
 Maintain intravascular volume (vigorous IV hydration).
Maintain intravascular volume (vigorous IV hydration). NPO until clinically improved, stable, and hungry; enteral feedings preferred to TPN; PN necessary if unable to tolerate enteral/adequate infusion rate cannot be reached within 2 to 4 days.
NPO until clinically improved, stable, and hungry; enteral feedings preferred to TPN; PN necessary if unable to tolerate enteral/adequate infusion rate cannot be reached within 2 to 4 days. NG suction is used to decompress abd in pts w/ileus.
NG suction is used to decompress abd in pts w/ileus. Control pain with IV morphine or fentanyl.
Control pain with IV morphine or fentanyl.Specific Measures
 Pancreatic/peripancreatic infection in 40% to 70% pts w/pancreatic necrosis; prophylactic IV abx (5-7 days) justified if septicemia, pancreatic abscess, or pancreatitis secondary to biliary calculi. Cover Bacteroides fragilis/anaerobes (cefotetan, metronidazole, clindamycin, + AG) and enterococcus (ampicillin).
Pancreatic/peripancreatic infection in 40% to 70% pts w/pancreatic necrosis; prophylactic IV abx (5-7 days) justified if septicemia, pancreatic abscess, or pancreatitis secondary to biliary calculi. Cover Bacteroides fragilis/anaerobes (cefotetan, metronidazole, clindamycin, + AG) and enterococcus (ampicillin). Surgical Rx indicated: gallstone-induced pancreatitis (cholecystectomy when acute phase subsides), perforated peptic ulcer, excision/drainage necrotic/infected foci w/placement of wide-bore drains for continuous postop irrigation
Surgical Rx indicated: gallstone-induced pancreatitis (cholecystectomy when acute phase subsides), perforated peptic ulcer, excision/drainage necrotic/infected foci w/placement of wide-bore drains for continuous postop irrigationComplications
 Pseudocyst (dx: CT scan or U/S) Rx: CT scan or U/S-guided percutaneous drainage w/pigtail catheter for continuous drainage (↑ recurrence rate); conservative approach to reevaluate (w/CT scan or U/S) after 6 to 7 wk and surgically drain if no ↓ in size. Pseudocysts <5 cm generally reabsorbed w/o intervention; those >5 cm require surgery after wall maturation.
Pseudocyst (dx: CT scan or U/S) Rx: CT scan or U/S-guided percutaneous drainage w/pigtail catheter for continuous drainage (↑ recurrence rate); conservative approach to reevaluate (w/CT scan or U/S) after 6 to 7 wk and surgically drain if no ↓ in size. Pseudocysts <5 cm generally reabsorbed w/o intervention; those >5 cm require surgery after wall maturation. Phlegmon (dx: CT scan or U/S) Rx: supportive care
Phlegmon (dx: CT scan or U/S) Rx: supportive care Pancreatic abscess (dx: CT scan-retroperitoneal bubbles, Gram staining and cultures of fluid from percutaneous biopsy) Rx: surgical/catheter drainage + IV abx (imipenem-cilastatin)
Pancreatic abscess (dx: CT scan-retroperitoneal bubbles, Gram staining and cultures of fluid from percutaneous biopsy) Rx: surgical/catheter drainage + IV abx (imipenem-cilastatin) Pancreatic ascites (dx: paracentesis-amylase/lipase level in fluid, ERCP) Rx: surgery if exudative/does not resolve spontaneously
Pancreatic ascites (dx: paracentesis-amylase/lipase level in fluid, ERCP) Rx: surgery if exudative/does not resolve spontaneously GI bleeding: via EtOH gastritis, varices, stress ulcer, or DIC
GI bleeding: via EtOH gastritis, varices, stress ulcer, or DIC Renal failure: via hypovolemia (oliguria or anuria), cortical or tubular necrosis (shock, DIC), or thrombosis of renal artery or vein
Renal failure: via hypovolemia (oliguria or anuria), cortical or tubular necrosis (shock, DIC), or thrombosis of renal artery or vein Hypoxia: via ARDS, pleural effusion, or atelectasis
Hypoxia: via ARDS, pleural effusion, or atelectasis2. Chronic Pancreatitis
 Recurrent/persistent inflammatory process characterized by chronic pain and pancreatic exocrine/endocrine insufficiency
Recurrent/persistent inflammatory process characterized by chronic pain and pancreatic exocrine/endocrine insufficiencyEtiology
 Chronic EtOH, obstruction (ampullary stenosis, tumor, trauma, pancreas divisum, annular pancreas), hereditary pancreatitis, severe malnutrition, untreated hyperparathyroidism (hypercalcemia), mutations of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene (TF genotype)
Chronic EtOH, obstruction (ampullary stenosis, tumor, trauma, pancreas divisum, annular pancreas), hereditary pancreatitis, severe malnutrition, untreated hyperparathyroidism (hypercalcemia), mutations of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene (TF genotype) Autoimmune (sclerosing) pancreatitis (5% cases): manifests w/jaundice (63%) + abd pain (35%). CT = diffusely enlarged pancreas, enhanced peripheral rim of hypoattenuation “halo,” and low-attenuation mass in head of pancreas. Labs = ↑ serum IgG4, serum Ig or γ -globulin level, + antilactoferrin Ab, anti–carbonic anhydrase II level, ASMA, or ANA.
Autoimmune (sclerosing) pancreatitis (5% cases): manifests w/jaundice (63%) + abd pain (35%). CT = diffusely enlarged pancreas, enhanced peripheral rim of hypoattenuation “halo,” and low-attenuation mass in head of pancreas. Labs = ↑ serum IgG4, serum Ig or γ -globulin level, + antilactoferrin Ab, anti–carbonic anhydrase II level, ASMA, or ANA.Diagnosis
H&P
 Persistent/recurrent epigastric + LUQ pain, may radiate to the back
Persistent/recurrent epigastric + LUQ pain, may radiate to the back Tenderness over the pancreas, muscle guarding
Tenderness over the pancreas, muscle guarding Significant weight loss, epigastric mass (10%), jaundice (5%-10%)
Significant weight loss, epigastric mass (10%), jaundice (5%-10%) Bulky/greasy, foul-smelling stools
Bulky/greasy, foul-smelling stoolsLabs
 ↑/Nl serum amylase and lipase
↑/Nl serum amylase and lipase ↑ Glucose, bili, alk phos, glycosuria
↑ Glucose, bili, alk phos, glycosuria 72-hr fecal fat determination (rarely performed) = excess fecal fat. Fecal elastase test requires 20 g of stool.
72-hr fecal fat determination (rarely performed) = excess fecal fat. Fecal elastase test requires 20 g of stool. Secretin stimulation test (dx pancreatic exocrine insufficiency)
Secretin stimulation test (dx pancreatic exocrine insufficiency) Lipid panel: ↑↑ TGs can cause pancreatitis.
Lipid panel: ↑↑ TGs can cause pancreatitis. Serum Ca: hyperparathyroidism (rare cause of chronic pancreatitis)
Serum Ca: hyperparathyroidism (rare cause of chronic pancreatitis) ↑ Serum IgG4 (sclerosing pancreatitis and autoimmune pancreatitis)
↑ Serum IgG4 (sclerosing pancreatitis and autoimmune pancreatitis) ↑ Serum Ig or γ-globulin level, antilactoferrin Ab, anti–carbonic anhydrase II level, ASMA, or ANA in autoimmune pancreatitis
↑ Serum Ig or γ-globulin level, antilactoferrin Ab, anti–carbonic anhydrase II level, ASMA, or ANA in autoimmune pancreatitisImaging
 Plain abd radiographs: may reveal pancreatic calcifications (95% spec)
Plain abd radiographs: may reveal pancreatic calcifications (95% spec) U/S abd: duct dilation, pseudocyst, calcification, presence of ascites
U/S abd: duct dilation, pseudocyst, calcification, presence of ascites Contrast-enhanced abd CT scan: calcifications, evaluate ductal dilation, r/o pancreatic cancer
Contrast-enhanced abd CT scan: calcifications, evaluate ductal dilation, r/o pancreatic cancer EUS (97% sens, 60% spec)
EUS (97% sens, 60% spec) FNAB combined w/EUS = preferred evaluation of modality to r/o malignant cystic/mass lesions
FNAB combined w/EUS = preferred evaluation of modality to r/o malignant cystic/mass lesionsTreatment
 Steatorrhea Rx w/pancreatic supplements (e.g., pancrease, pancrelipase [Creon] PRN on basis of steatorrhea/weight loss)
Steatorrhea Rx w/pancreatic supplements (e.g., pancrease, pancrelipase [Creon] PRN on basis of steatorrhea/weight loss) Glucocorticoids (autoimmune pancreatitis)
Glucocorticoids (autoimmune pancreatitis) Surgical intervention if duct obstruction
Surgical intervention if duct obstruction Transduodenal sphincteroplasty/pancreaticojejunostomy if intractable pain
Transduodenal sphincteroplasty/pancreaticojejunostomy if intractable painClinical Pearls
 50% of pts die within 10 yr of chronic pancreatitis or malignant neoplasm.
50% of pts die within 10 yr of chronic pancreatitis or malignant neoplasm.3. Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma
Risk Factors
 Smoking, chronic EtOH, genetics (5%-10% pts have family hx), dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors, incretin mimetics
Smoking, chronic EtOH, genetics (5%-10% pts have family hx), dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors, incretin mimeticsDiagnosis
 Labs: ↑ alk phos, bili, amylase
Labs: ↑ alk phos, bili, amylaseH&P
 Jaundice, abd pain (dull upper abd pain/vague abd discomfort), wt loss
Jaundice, abd pain (dull upper abd pain/vague abd discomfort), wt lossImaging
 Multidetector helical CT with IV contrast (imaging procedure of choice)
Multidetector helical CT with IV contrast (imaging procedure of choice) Endoscopic ultrasonography: useful if no identifiable mass on CT + ↑ clinical suspicion
Endoscopic ultrasonography: useful if no identifiable mass on CT + ↑ clinical suspicionTreatment
Surgery
 Curative cephalic pancreatoduodenectomy (Whipple’s procedure) in 10% to 20% pts whose lesion <5 cm, solitary, and without metastases. Surgical mortality rate is 5%.
Curative cephalic pancreatoduodenectomy (Whipple’s procedure) in 10% to 20% pts whose lesion <5 cm, solitary, and without metastases. Surgical mortality rate is 5%. Palliative surgery (for biliary decompression/diversion)
Palliative surgery (for biliary decompression/diversion) Palliative therapeutic ERCP with stents
Palliative therapeutic ERCP with stents Celiac plexus block = pain relief in 80% to 90% of cases
Celiac plexus block = pain relief in 80% to 90% of casesChemoRx
 Gemcitabine given alone or + platinum agent (erlotinib or fluoropyrimidine)
Gemcitabine given alone or + platinum agent (erlotinib or fluoropyrimidine) Combination consisting oxaliplatin, irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin (Folfirinox)
Combination consisting oxaliplatin, irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin (Folfirinox)Radiation
 External-beam radiation for palliation of pain
External-beam radiation for palliation of pain4. Neuroendocrine Pancreatic Neoplasms
a. Gastrinoma
 ZE syndrome: hypergastrinemic state via pancreatic/extrapancreatic non–β islet cell tumor (gastrinoma) resulting in peptic ulcer disease
ZE syndrome: hypergastrinemic state via pancreatic/extrapancreatic non–β islet cell tumor (gastrinoma) resulting in peptic ulcer disease 2/3 gastrinomas (sporadic), 60% assoc (MEN-1; AD including hyperparathyroidism, pituitary tumors)
2/3 gastrinomas (sporadic), 60% assoc (MEN-1; AD including hyperparathyroidism, pituitary tumors) 60% gastrinomas = malignant (mets to liver, regional lymph nodes)
60% gastrinomas = malignant (mets to liver, regional lymph nodes) Neuroendocrine tumors = 1.3% of all cases of pancreatic cancer
Neuroendocrine tumors = 1.3% of all cases of pancreatic cancerDiagnosis
 Gastric acid secretion: serum gastrin level (fasting) >1000 pg/mL
Gastric acid secretion: serum gastrin level (fasting) >1000 pg/mL Provocative gastrin level tests:
Provocative gastrin level tests: Gastrinoma localization via arteriography, abd U/S or CT scan or MRI
Gastrinoma localization via arteriography, abd U/S or CT scan or MRIH&P
 95% sx of peptic ulcer, 60% sx related to GERD, 33% diarrhea, steatorrhea
95% sx of peptic ulcer, 60% sx related to GERD, 33% diarrhea, steatorrheaTreatment
 Surgical resection; total gastrectomy/vagotomy (palliative in some pts)
Surgical resection; total gastrectomy/vagotomy (palliative in some pts) Medical Rx: PPIs, somatostatin or octreotide, chemo (mets)
Medical Rx: PPIs, somatostatin or octreotide, chemo (mets)b Insulinoma
Diagnosis
H&P
 Sx typically in AM before meal; fasting hypoglycemia versus reactive hypoglycemia (which is not commonly associated w/insulinoma)
Sx typically in AM before meal; fasting hypoglycemia versus reactive hypoglycemia (which is not commonly associated w/insulinoma)Labs
 Overnight fasting blood sugar level + simultaneous plasma insulin, proinsulin, and/or C peptide level will establish existence of fasting organic hypoglycemia in 60% of pts.
Overnight fasting blood sugar level + simultaneous plasma insulin, proinsulin, and/or C peptide level will establish existence of fasting organic hypoglycemia in 60% of pts. Plasma proinsulin, C-peptide, antibodies to insulin, and plasma sulfonylurea levels to r/o factitious insulin use/hypoglycemic agents/autoantibodies against the insulin receptor or insulin. Refer to Table 5-5 in Chapter 5.
Plasma proinsulin, C-peptide, antibodies to insulin, and plasma sulfonylurea levels to r/o factitious insulin use/hypoglycemic agents/autoantibodies against the insulin receptor or insulin. Refer to Table 5-5 in Chapter 5.Imaging
 Abdominal CT scan or MRI
Abdominal CT scan or MRI Octreotide scan
Octreotide scanTreatment
 Enucleation of single insulinoma
Enucleation of single insulinoma Partial pancreatectomy for multiple adenomas
Partial pancreatectomy for multiple adenomasE. Disorders of Small and Large Bowel
1. Diarrhea
 ↑ Frequency (>200 g/24 hr) of stool w/ ↓ consistency compared with baseline; if lasting >3 wk = chronic diarrhea
↑ Frequency (>200 g/24 hr) of stool w/ ↓ consistency compared with baseline; if lasting >3 wk = chronic diarrheaDiagnosis
Hx
 Travel hx (traveler’s diarrhea)
Travel hx (traveler’s diarrhea) Short duration (1-3 days) assoc w/mild sx usually viral (rotavirus, Norwalk virus); >3 wk probably not bacterial or viral
Short duration (1-3 days) assoc w/mild sx usually viral (rotavirus, Norwalk virus); >3 wk probably not bacterial or viral Nocturnal diarrhea (common w/diabetic neuropathy)
Nocturnal diarrhea (common w/diabetic neuropathy) Onset within minutes: scombroid poisoning (tuna, mahi-mahi, mackerel) (N/V, flushing, diarrhea)
Onset within minutes: scombroid poisoning (tuna, mahi-mahi, mackerel) (N/V, flushing, diarrhea) Onset within hr: toxins (Staphylococcus aureus, toxigenic Escherichia coli, Clostridium perfringens, Bacillus cereus, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, [barracuda, grouper, red snapper: ciguatera toxin, causing paresthesia, weakness])
Onset within hr: toxins (Staphylococcus aureus, toxigenic Escherichia coli, Clostridium perfringens, Bacillus cereus, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, [barracuda, grouper, red snapper: ciguatera toxin, causing paresthesia, weakness]) Diarrhea secondary to Salmonella, Shigella, Campylobacter, Yersinia = longer incubation period.
Diarrhea secondary to Salmonella, Shigella, Campylobacter, Yersinia = longer incubation period. Stress: “functional” diarrhea, IBS
Stress: “functional” diarrhea, IBS Diarrhea alternating w/constipation: IBS
Diarrhea alternating w/constipation: IBS Foods containing sorbitol/mannitol (osmotic diarrhea), fried rice (B. cereus), undercooked hamburger (E. coli 157:H7), poultry, eggs (Campylobacter, Salmonella, S. aureus), diarrhea after dairy ingestion (lactose intolerance)
Foods containing sorbitol/mannitol (osmotic diarrhea), fried rice (B. cereus), undercooked hamburger (E. coli 157:H7), poultry, eggs (Campylobacter, Salmonella, S. aureus), diarrhea after dairy ingestion (lactose intolerance) Shellfish ingestion (Norwalk virus, Vibrio cholerae, Vibrio mimicus, V. parahaemolyticus, Plesiomonas shigelloides)
Shellfish ingestion (Norwalk virus, Vibrio cholerae, Vibrio mimicus, V. parahaemolyticus, Plesiomonas shigelloides) Long-distance runners (bloody diarrhea secondary to bowel ischemia)
Long-distance runners (bloody diarrhea secondary to bowel ischemia) Daycare centers (rotavirus, Giardia, Salmonella, Shigella, Cryptosporidium, Campylobacter)
Daycare centers (rotavirus, Giardia, Salmonella, Shigella, Cryptosporidium, Campylobacter) Medications: (common agents: Mg-containing antacids, misoprostol, PPIs, methylxanthines [caffeine, theophylline], laxatives, lactulose, colchicine, antiarrhythmic agents (quinidine, digitalis, propranolol), metformin, thyroxine). Abx-induced pseudomembranous colitis should be suspected in any pt receiving abx: (+) Clostridium difficile toxin w/the stool assay, cytotoxin test.
Medications: (common agents: Mg-containing antacids, misoprostol, PPIs, methylxanthines [caffeine, theophylline], laxatives, lactulose, colchicine, antiarrhythmic agents (quinidine, digitalis, propranolol), metformin, thyroxine). Abx-induced pseudomembranous colitis should be suspected in any pt receiving abx: (+) Clostridium difficile toxin w/the stool assay, cytotoxin test. Sexual habits: male homosexuals ↑ incidence of (Giardia, E. histolytica, Cryptosporidium, Salmonella, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Campylobacter).
Sexual habits: male homosexuals ↑ incidence of (Giardia, E. histolytica, Cryptosporidium, Salmonella, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Campylobacter). Relevant medical hx
Relevant medical hx Associated sx
Associated sx Characteristics of the stool (from pt’s hx)
Characteristics of the stool (from pt’s hx)PE
 Rectal fistulas, RLQ abd mass (Crohn’s disease)
Rectal fistulas, RLQ abd mass (Crohn’s disease) Arthritis, iritis, uveitis, erythema nodosum (IBD)
Arthritis, iritis, uveitis, erythema nodosum (IBD) Abd masses (neoplasms of colon, pancreas, or liver; diverticular abscess [LLQ mass], IBD)
Abd masses (neoplasms of colon, pancreas, or liver; diverticular abscess [LLQ mass], IBD) Flushing, bronchospasm (carcinoid syndrome)
Flushing, bronchospasm (carcinoid syndrome) Buccal pigmentation (Peutz-Jeghers syndrome)
Buccal pigmentation (Peutz-Jeghers syndrome) Pigmentation (Addison’s disease)
Pigmentation (Addison’s disease) Ammoniac/urinary breath odor (renal failure)
Ammoniac/urinary breath odor (renal failure) Ecchymosis (vitamin K deficiency secondary to malabsorption, fat-soluble vitamins, celiac)
Ecchymosis (vitamin K deficiency secondary to malabsorption, fat-soluble vitamins, celiac) Fever (IBD, infectious diarrhea, lymphoma)
Fever (IBD, infectious diarrhea, lymphoma) Goiter, tremor, tachycardia (hyperthyroidism)
Goiter, tremor, tachycardia (hyperthyroidism) Lymphadenopathy (neoplasm, lymphoma, tuberculosis, AIDS, Whipple’s disease)
Lymphadenopathy (neoplasm, lymphoma, tuberculosis, AIDS, Whipple’s disease) Macroglossia (amyloidosis)
Macroglossia (amyloidosis) Kaposi’s sarcoma (AIDS)
Kaposi’s sarcoma (AIDS)Initial Evaluation
 Labs (may not be necessary in pts not appearing ill/dehydrated)
Labs (may not be necessary in pts not appearing ill/dehydrated) Abd x-rays indicated if abd pain or evidence of obstruction (r/o toxic megacolon, bowel ischemia; pancreatic calcifications = pancreatic insufficiency)
Abd x-rays indicated if abd pain or evidence of obstruction (r/o toxic megacolon, bowel ischemia; pancreatic calcifications = pancreatic insufficiency)Treatment
 NPO, IV hydration, electrolyte abnl correction, d/c possible causative agents (antacids containing Mg, abx)
NPO, IV hydration, electrolyte abnl correction, d/c possible causative agents (antacids containing Mg, abx) Antiperistaltic agents (diphenoxylate) used w/caution in pts suspected of IBD or infectious diarrhea; loperamide/bismuth subsalicylate helpful in mild cases
Antiperistaltic agents (diphenoxylate) used w/caution in pts suspected of IBD or infectious diarrhea; loperamide/bismuth subsalicylate helpful in mild cases Persistent diarrhea + bacterial/parasitic organism ID, start abx:
Persistent diarrhea + bacterial/parasitic organism ID, start abx: IBS Rx: psyllium (fiber products) + ↓ caffeine, chocolate, EtOH, stress; antispasmodics (dicyclomine, hyoscyamine) if resistant cases
IBS Rx: psyllium (fiber products) + ↓ caffeine, chocolate, EtOH, stress; antispasmodics (dicyclomine, hyoscyamine) if resistant casesEvaluation of Pt w/Chronic or Recurrent Diarrhea
Etiology
 Drug induced (including laxative abuse), IBS, lactose intolerance, IBD, malabsorption (mucosal/pancreatic insufficiency, bacterial overgrowth), parasitic infections (giardiasis, amebiasis), functional diarrhea, postsurgical (partial gastrectomy, ileal resection, cholecystectomy)
Drug induced (including laxative abuse), IBS, lactose intolerance, IBD, malabsorption (mucosal/pancreatic insufficiency, bacterial overgrowth), parasitic infections (giardiasis, amebiasis), functional diarrhea, postsurgical (partial gastrectomy, ileal resection, cholecystectomy) Endocrine disturbances: DM (↓ sympathetic input to the gut), hyperthyroidism, Addison’s disease, gastrinoma (ZE syndrome), VIPoma (pancreatic cholera), carcinoid tumors (serotonin), medullary thyroid carcinoma (calcitonin)
Endocrine disturbances: DM (↓ sympathetic input to the gut), hyperthyroidism, Addison’s disease, gastrinoma (ZE syndrome), VIPoma (pancreatic cholera), carcinoid tumors (serotonin), medullary thyroid carcinoma (calcitonin) Pelvic irradiation, colonic carcinoma (villous adenoma)
Pelvic irradiation, colonic carcinoma (villous adenoma) Collagenous colitis (middle-aged woman, nl endoscopy, subepithelial acellular collagen band on sigmoid bx or right colon; sx resolution w/sulfasalazine alone or steroid combination)
Collagenous colitis (middle-aged woman, nl endoscopy, subepithelial acellular collagen band on sigmoid bx or right colon; sx resolution w/sulfasalazine alone or steroid combination) Lymphocytic colitis (lymphocytic infiltration w/o collagen band)
Lymphocytic colitis (lymphocytic infiltration w/o collagen band)Diagnosis
 H&P/initial labs same as new-onset diarrhea; additional labs:
H&P/initial labs same as new-onset diarrhea; additional labs: Secretory diarrhea from impaired absorption/excessive secretion of electrolytes via enteric infection, neoplasms of exocrine pancreas (VIP, GIP, secretin, glucagon), bile salt enteropathy, villous adenoma, IBD, carcinoid tumor, celiac, cathartic agent ingestion
Secretory diarrhea from impaired absorption/excessive secretion of electrolytes via enteric infection, neoplasms of exocrine pancreas (VIP, GIP, secretin, glucagon), bile salt enteropathy, villous adenoma, IBD, carcinoid tumor, celiac, cathartic agent ingestion Osmotic diarrhea from impaired water absorption secondary to osmotic effect of nonabsorbable intraluminal molecules via lactose and other disaccharide excess, pancreatic insufficiency, lactulose/sorbitol/sodium sulfate/antacid induced, postop (gastrojejunostomy, vagotomy, pyloroplasty, intestinal resection)
Osmotic diarrhea from impaired water absorption secondary to osmotic effect of nonabsorbable intraluminal molecules via lactose and other disaccharide excess, pancreatic insufficiency, lactulose/sorbitol/sodium sulfate/antacid induced, postop (gastrojejunostomy, vagotomy, pyloroplasty, intestinal resection) Dx “osmotic gap” in stool analysis = measured osmolality –2([Na+] + [K+])
Dx “osmotic gap” in stool analysis = measured osmolality –2([Na+] + [K+]) Difference between calculated and actual Osm >50 = osmotic diarrhea
Difference between calculated and actual Osm >50 = osmotic diarrhea2. Constipation
 DDx: metabolic (hypercalcemia, DM, pregnancy, hypothyroidism), structural (colorectal cancer, strictures, hernias, adhesions, endometriosis, rectocele, diverticular disease, volvulus, intussusception, IBD, hematoma of bowel wall secondary to trauma or anticoagulants), drug induced (opiates, anti-Ach, iron, CCB, antipsychotics, antacids w/aluminum, verapamil), neurologic/psychological (IBS, anorexia, depression, MS), neonatal (Hirschsprung’s disease, meconium ileus, atresia), insufficient bulk in diet, travel, old age, spinal cord injury
DDx: metabolic (hypercalcemia, DM, pregnancy, hypothyroidism), structural (colorectal cancer, strictures, hernias, adhesions, endometriosis, rectocele, diverticular disease, volvulus, intussusception, IBD, hematoma of bowel wall secondary to trauma or anticoagulants), drug induced (opiates, anti-Ach, iron, CCB, antipsychotics, antacids w/aluminum, verapamil), neurologic/psychological (IBS, anorexia, depression, MS), neonatal (Hirschsprung’s disease, meconium ileus, atresia), insufficient bulk in diet, travel, old age, spinal cord injuryTreatment
 Fiber (25-30 g/day) and fluid intake essential
Fiber (25-30 g/day) and fluid intake essential Physiologic testing (DRE, anorectal manometry, rectal balloon expulsion colonic transit) provides insight/possible indication for MR defecography
Physiologic testing (DRE, anorectal manometry, rectal balloon expulsion colonic transit) provides insight/possible indication for MR defecography Pts >50 yr old or have alarm sx (wt loss, rectal bleeding, change in bowel habits, FHx colon cancer) should undergo colonoscopy
Pts >50 yr old or have alarm sx (wt loss, rectal bleeding, change in bowel habits, FHx colon cancer) should undergo colonoscopy3. Malabsorption
Differential Diagnosis
 Celiac disease (diarrhea, bloating, wt loss)
Celiac disease (diarrhea, bloating, wt loss) Lactose malabsorption (osmotic diarrhea, bloating, excess flatus)
Lactose malabsorption (osmotic diarrhea, bloating, excess flatus) Short-bowel syndrome (<200 cm of small bowel, nl 600 cm) from Crohn’s disease, ischemia, volvulus, desmoid tumors, trauma
Short-bowel syndrome (<200 cm of small bowel, nl 600 cm) from Crohn’s disease, ischemia, volvulus, desmoid tumors, trauma Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth: bacterial overgrowth from change in colonic flora via dysmotility (scleroderma, amyloidosis), altered secretion/anatomy
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth: bacterial overgrowth from change in colonic flora via dysmotility (scleroderma, amyloidosis), altered secretion/anatomy4. Celiac Disease
 Chronic disease characterized by malabsorption and diarrhea precipitated by ingestion of food products containing gluten. Celiac sprue is considered an autoimmune-type disease, with TTG suggested as a major autoantigen. It results from an inappropriate T-cell–mediated immune response against ingested gluten in genetically predisposed individuals who carry either HLA-DQ2 or HLA-DQ8 genes. There is sensitivity to gliadin, a protein fraction of gluten found in wheat, rye, and barley. In patients with celiac disease, immune responses to gliadin fractions promote an inflammatory reaction, mainly in the upper small intestine, manifested by infiltration of the lamina propria and the epithelium with chronic inflammatory cells and villous atrophy.
Chronic disease characterized by malabsorption and diarrhea precipitated by ingestion of food products containing gluten. Celiac sprue is considered an autoimmune-type disease, with TTG suggested as a major autoantigen. It results from an inappropriate T-cell–mediated immune response against ingested gluten in genetically predisposed individuals who carry either HLA-DQ2 or HLA-DQ8 genes. There is sensitivity to gliadin, a protein fraction of gluten found in wheat, rye, and barley. In patients with celiac disease, immune responses to gliadin fractions promote an inflammatory reaction, mainly in the upper small intestine, manifested by infiltration of the lamina propria and the epithelium with chronic inflammatory cells and villous atrophy.Diagnosis
H&P
 Weight loss, pallor (from anemia), dyspepsia, short stature, and failure to thrive in children and infants
Weight loss, pallor (from anemia), dyspepsia, short stature, and failure to thrive in children and infants Weight loss, fatigue, pallor, and diarrhea in adults
Weight loss, fatigue, pallor, and diarrhea in adults Angular cheilitis, aphthous ulcers, atopic dermatitis, and dermatitis herpetiformis frequently associated w/celiac disease
Angular cheilitis, aphthous ulcers, atopic dermatitis, and dermatitis herpetiformis frequently associated w/celiac diseaseLabs
 IgA TTG antibody by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (TTG test) is the best screening serologic test for celiac disease.
IgA TTG antibody by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (TTG test) is the best screening serologic test for celiac disease. Iron deficiency anemia (microcytic anemia, ↓ ferritin level)
Iron deficiency anemia (microcytic anemia, ↓ ferritin level) Folic acid deficiency
Folic acid deficiency Serum IfA (small % of patients are IfA deficient)
Serum IfA (small % of patients are IfA deficient) Vitamin B12 deficiency, ↓ Mg, ↓ Ca
Vitamin B12 deficiency, ↓ Mg, ↓ CaTreatment
 Gluten-free diet (avoidance of wheat, rye, and barley). Safe grains (gluten free) include rice, corn, oats, buckwheat, millet, amaranth, quinoa.
Gluten-free diet (avoidance of wheat, rye, and barley). Safe grains (gluten free) include rice, corn, oats, buckwheat, millet, amaranth, quinoa. Correct nutritional deficiencies w/iron, folic acid, Ca, vitamin B12 as needed.
Correct nutritional deficiencies w/iron, folic acid, Ca, vitamin B12 as needed. Prednisone 20-60 mg qd gradually tapered is useful in refractory cases.
Prednisone 20-60 mg qd gradually tapered is useful in refractory cases.Clinical Pearls
 Celiac disease should be considered in pts w/unexplained metabolic bone disease or hypocalcemia, especially because GI sx may be absent or mild. Clinicians should also consider testing children and young adults for celiac disease if unexplained weight loss, abd pain or distention, and chronic diarrhea are present.
Celiac disease should be considered in pts w/unexplained metabolic bone disease or hypocalcemia, especially because GI sx may be absent or mild. Clinicians should also consider testing children and young adults for celiac disease if unexplained weight loss, abd pain or distention, and chronic diarrhea are present. Pts w/celiac disease have an overall risk of cancer that is almost 2× that in the general population: risk of adenocarcinoma of the small intestine and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, especially of T-cell type and primarily localized in the gut.
Pts w/celiac disease have an overall risk of cancer that is almost 2× that in the general population: risk of adenocarcinoma of the small intestine and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, especially of T-cell type and primarily localized in the gut. Screening for celiac disease is recommended in first-degree relatives. It should also be considered in type 1 DM and autoimmune disorders such as PBC, primary sclerosing cholangitis, autoimmune hepatitis, IBD, thyroid disease (hypothyroidism occurs in up to 15% of patients with celiac disease), SLE, RA, and Sjögren’s syndrome because of the increased risk of celiac disease in these populations. Screening persons with Down’s syndrome or Turner’s syndrome for celiac disease has also been recommended.
Screening for celiac disease is recommended in first-degree relatives. It should also be considered in type 1 DM and autoimmune disorders such as PBC, primary sclerosing cholangitis, autoimmune hepatitis, IBD, thyroid disease (hypothyroidism occurs in up to 15% of patients with celiac disease), SLE, RA, and Sjögren’s syndrome because of the increased risk of celiac disease in these populations. Screening persons with Down’s syndrome or Turner’s syndrome for celiac disease has also been recommended.5. Inflammatory Bowel Disease
a. Crohn’s Disease
 Inflammatory disease most commonly involving the terminal ileum. Table 6-4 compares Crohn’s disease with ulcerative colitis.
Inflammatory disease most commonly involving the terminal ileum. Table 6-4 compares Crohn’s disease with ulcerative colitis.TABLE 6-4
Differentiating Features of Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn’s Disease
| Ulcerative Colitis | Crohn’s Disease | |
| Site of involvement | Involves only colon Rectum almost always involved |
Any area of the gastrointestinal tract Rectum usually spared |
| Pattern of involvement | Continuous | Skip lesions |
| Diarrhea | Bloody | Usually nonbloody |
| Severe abdominal pain | Rare | Frequent |
| Perianal disease | No | In 30% of patients |
| Fistula | No | Yes |
| Endoscopic findings | Erythematous and friable Superficial ulceration | Aphthoid and deep ulcers Cobblestoning |
| Radiologic findings | Tubular appearance resulting from loss of haustral folds | String sign of terminal ileum RLQ mass, fistulas, abscesses |
| Histologic features | Mucosa only Crypt abscesses |
Transmural Crypt abscesses, granulomas (about 30%) |
| Smoking | Protective | Worsens course |
| Serology | p-ANCA more common | ASCA more common |
From Andreoli, T E, Benjamin IJ, Griggs RC, Wing EJ: Andreoli and Carpenter’s Cecil Essentials of Medicine, 8th ed. Philadelphia, Saunders, 2010.
Diagnosis
H&P
 Sx intermittent w/episodic remission:
Sx intermittent w/episodic remission:Labs
 ↓ Hgb/Hct (chronic blood loss, bone marrow inflammation, and vitamin B12 malabsorption)
↓ Hgb/Hct (chronic blood loss, bone marrow inflammation, and vitamin B12 malabsorption) ↓ K, Mg, Ca, alb in pts w/chronic diarrhea
↓ K, Mg, Ca, alb in pts w/chronic diarrhea Vitamin B12 and folate deficiency
Vitamin B12 and folate deficiency ↑ ESR, (+) ASCA, (−) ANCA
↑ ESR, (+) ASCA, (−) ANCAImaging
 Endoscopy: transmural asymmetric/discontinued disease w/deep longitudinal fissures (“cobblestone appearance via submusocal inflammation”), strictures, crypt distortion + inflammation, possible noncaseating granulomas + lymphoid aggregates on bx
Endoscopy: transmural asymmetric/discontinued disease w/deep longitudinal fissures (“cobblestone appearance via submusocal inflammation”), strictures, crypt distortion + inflammation, possible noncaseating granulomas + lymphoid aggregates on bx Barium imaging (rarely indicated): deep ulcerations (often longitudinal/transverse) and segmental lesions (skip lesions, strictures, fistulas); “thumbprinting” is common; “string sign” in terminal ileum
Barium imaging (rarely indicated): deep ulcerations (often longitudinal/transverse) and segmental lesions (skip lesions, strictures, fistulas); “thumbprinting” is common; “string sign” in terminal ileum CT abd: helpful in identifying abscesses/complications
CT abd: helpful in identifying abscesses/complications See Table 6-4.
See Table 6-4.Treatment
 Figure 6-1 describes a treatment algorithm for Crohn’s disease.
Figure 6-1 describes a treatment algorithm for Crohn’s disease.b. Ulcerative Colitis
Diagnosis
H&P
 Abd distention and tenderness
Abd distention and tenderness Bloody diarrhea, fever, evidence of dehydration
Bloody diarrhea, fever, evidence of dehydration Extraintestinal manifestations (25% pts): liver disease, sclerosing cholangitis, iritis, uveitis, episcleritis, arthritis, erythema nodosum, pyoderma gangrenosum, aphthous stomatitis
Extraintestinal manifestations (25% pts): liver disease, sclerosing cholangitis, iritis, uveitis, episcleritis, arthritis, erythema nodosum, pyoderma gangrenosum, aphthous stomatitisLabs
 Anemia, ↑ ESR
Anemia, ↑ ESR ↓ K, Mg, Ca, alb
↓ K, Mg, Ca, alb If persistent diarrhea: Consider stool exam O&P, stool culture, and testing for C. difficile toxin.
If persistent diarrhea: Consider stool exam O&P, stool culture, and testing for C. difficile toxin. (−) ASCA (anti-Saccharomyces cerevisiae Ab), (+) p-ANCA (>45% pts; p-ANCA assoc w/relative resistance to medical Rx)
(−) ASCA (anti-Saccharomyces cerevisiae Ab), (+) p-ANCA (>45% pts; p-ANCA assoc w/relative resistance to medical Rx)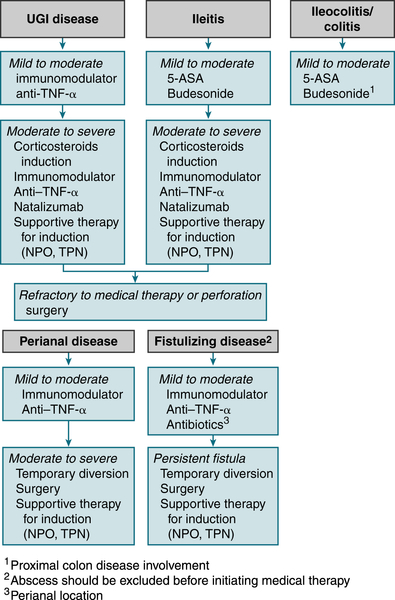
FIGURE 6-1 Crohn’s disease treatment algorithm. (From Goldman L, Schafer AI [eds]: Goldman’s Cecil Medicine, 24th ed. Philadelphia, Saunders, 2012.)
Imaging
 Generally not indicated; double-contrast barium enema w/small bowel follow-through used if colonic strictures prevent evaluation, may reveal continuous involvement (including rectum), pseudopolyps, ↓ mucosal pattern, and fine superficial ulcerations.
Generally not indicated; double-contrast barium enema w/small bowel follow-through used if colonic strictures prevent evaluation, may reveal continuous involvement (including rectum), pseudopolyps, ↓ mucosal pattern, and fine superficial ulcerations.Treatment
 Rx is based on disease activity. According to Hanauer and Sanborn, disease activity can be defined as follows:
Rx is based on disease activity. According to Hanauer and Sanborn, disease activity can be defined as follows: TPN in patients with advanced disease
TPN in patients with advanced disease Oral salicylates, such as mesalamine (Asacol, Rowasa)
Oral salicylates, such as mesalamine (Asacol, Rowasa) Corticosteroids have been the mainstay for treating moderate to severe active Crohn’s disease. Prednisone 40 to 60 mg/day is useful for acute exacerbation. Steroids are usually tapered over approximately 2 to 3 mo. Some patients require a low dose for a prolonged period of maintenance.
Corticosteroids have been the mainstay for treating moderate to severe active Crohn’s disease. Prednisone 40 to 60 mg/day is useful for acute exacerbation. Steroids are usually tapered over approximately 2 to 3 mo. Some patients require a low dose for a prolonged period of maintenance. Steroid analogues are locally active corticosteroids that target specific areas of inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract. Budesonide is available as a controlled-release formulation and is approved for mild to moderate active Crohn’s disease involving the ileum and/or ascending colon.
Steroid analogues are locally active corticosteroids that target specific areas of inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract. Budesonide is available as a controlled-release formulation and is approved for mild to moderate active Crohn’s disease involving the ileum and/or ascending colon. Immunosuppressants such as azathioprine 150 mg/day, methotrexate, or cyclosporine can be used for severe, progressive disease. In pts with Crohn’s disease who enter remission after treatment with methotrexate, a low dose of methotrexate maintains remission.
Immunosuppressants such as azathioprine 150 mg/day, methotrexate, or cyclosporine can be used for severe, progressive disease. In pts with Crohn’s disease who enter remission after treatment with methotrexate, a low dose of methotrexate maintains remission. Metronidazole 500 mg qid may be useful for colonic fistulas and treatment of mild to moderate active Crohn’s disease. Ciprofloxacin 1 g qd has also been found to be effective in decreasing disease activity.
Metronidazole 500 mg qid may be useful for colonic fistulas and treatment of mild to moderate active Crohn’s disease. Ciprofloxacin 1 g qd has also been found to be effective in decreasing disease activity. TNF inhibitors: Infliximab can induce clinical improvement in 80% of pts with Crohn’s disease refractory to other agents. It can be used in combination with other medications such as azathioprine in patients with severe Crohn’s disease. Adalimumab and certolizumab are also effective in inducing remissions and may be useful in adult patients with Crohn’s disease who cannot tolerate infliximab.
TNF inhibitors: Infliximab can induce clinical improvement in 80% of pts with Crohn’s disease refractory to other agents. It can be used in combination with other medications such as azathioprine in patients with severe Crohn’s disease. Adalimumab and certolizumab are also effective in inducing remissions and may be useful in adult patients with Crohn’s disease who cannot tolerate infliximab. Natalizumab effective in increasing the rate of remission and response in pts with active Crohn’s disease.
Natalizumab effective in increasing the rate of remission and response in pts with active Crohn’s disease. Hydrocortisone enema bid or tid is useful for proctitis.
Hydrocortisone enema bid or tid is useful for proctitis. Most patients who have anemia associated with Crohn’s disease respond to iron supplementation. ESAs are useful in patients with anemia refractory to treatment with iron and vitamins.
Most patients who have anemia associated with Crohn’s disease respond to iron supplementation. ESAs are useful in patients with anemia refractory to treatment with iron and vitamins.6. Microscopic Colitis
 Painless, watery diarrhea without bleeding via drugs/idiopathic
Painless, watery diarrhea without bleeding via drugs/idiopathic High likelihood (acarbose, ASA, PPIs, NSAIDs, ranitidine, sertraline, ticlopidine)
High likelihood (acarbose, ASA, PPIs, NSAIDs, ranitidine, sertraline, ticlopidine) Intermediate (carbamazepine, lisinopril, simvastatin, paroxetine, flutamide)
Intermediate (carbamazepine, lisinopril, simvastatin, paroxetine, flutamide)7. Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 Recurrent abd pain/discomfort ≥3 days/month in past 3 mo (with onset >6 mo prior) associated w/2/3 of the following:
Recurrent abd pain/discomfort ≥3 days/month in past 3 mo (with onset >6 mo prior) associated w/2/3 of the following: Risk factors: physical/sexual abuse, infectious gastroenteritis, somatization/psychological traits
Risk factors: physical/sexual abuse, infectious gastroenteritis, somatization/psychological traits Alarm sx (onset age >50 yr, anemia, nocturnal sx, wt loss, bleeding, FHx colon cancer) should prompt further testing tailored to the clinical scenario.
Alarm sx (onset age >50 yr, anemia, nocturnal sx, wt loss, bleeding, FHx colon cancer) should prompt further testing tailored to the clinical scenario. Rx: high-fiber diet and PO linaclotide if constipation IBS, SSRIs, loperamide if diarrheal IBS, behavioral + psychoRx
Rx: high-fiber diet and PO linaclotide if constipation IBS, SSRIs, loperamide if diarrheal IBS, behavioral + psychoRx8. Appendicitis
Etiology
 Obstruction of appendiceal lumen w/subsequent vascular congestion, inflammation, and edema; common causes of obstruction are
Obstruction of appendiceal lumen w/subsequent vascular congestion, inflammation, and edema; common causes of obstruction are Fecaliths: 30% to 35% of cases (most common in adults)
Fecaliths: 30% to 35% of cases (most common in adults) Foreign body: 4% (fruit seeds, pinworms, tapeworms, roundworms, calculi)
Foreign body: 4% (fruit seeds, pinworms, tapeworms, roundworms, calculi) Inflammation: 50% to 60% of cases (submucosal lymphoid hyperplasia [most common etiology in children, teens])
Inflammation: 50% to 60% of cases (submucosal lymphoid hyperplasia [most common etiology in children, teens]) Neoplasms: 1% (carcinoids, metastatic disease, carcinoma)
Neoplasms: 1% (carcinoids, metastatic disease, carcinoma)Diagnosis
H&P
 Abd pain: initially may be epigastric/periumbilical (50%) → localizing to RLQ within 12 to 18 hr. Pain can be found in back/right flank if retrocecal or malrotated appendix.
Abd pain: initially may be epigastric/periumbilical (50%) → localizing to RLQ within 12 to 18 hr. Pain can be found in back/right flank if retrocecal or malrotated appendix. (+) psoas sign: pain w/right thigh ext, low-grade fever: Temperature may be >38°C if appendiceal perforation.
(+) psoas sign: pain w/right thigh ext, low-grade fever: Temperature may be >38°C if appendiceal perforation. (+) obturator sign: pain w/internal rotation of flexed right thigh
(+) obturator sign: pain w/internal rotation of flexed right thigh (+) Rovsing’s sign: RLQ pain on palpation of the LLQ
(+) Rovsing’s sign: RLQ pain on palpation of the LLQ PE may reveal right-sided tenderness in pts w/pelvic appendix.
PE may reveal right-sided tenderness in pts w/pelvic appendix. Point of maximum tenderness = RLQ (McBurney’s point).
Point of maximum tenderness = RLQ (McBurney’s point). N/V, tachycardia, cutaneous hyperesthesias at the level of T12
N/V, tachycardia, cutaneous hyperesthesias at the level of T12Labs
Imaging
 CT abd/pelvis (sens >90%): distended appendix, periappendiceal inflammation, and thickened appendiceal wall
CT abd/pelvis (sens >90%): distended appendix, periappendiceal inflammation, and thickened appendiceal wall U/S (sens 75%-90%): useful in younger/pregnant women if dx unclear. Anl U/S should not deter surgery if H&P suggest appendicitis.
U/S (sens 75%-90%): useful in younger/pregnant women if dx unclear. Anl U/S should not deter surgery if H&P suggest appendicitis.Treatment
 Urgent appendectomy (laparoscopic or open), IV hydration/electrolyte replacement
Urgent appendectomy (laparoscopic or open), IV hydration/electrolyte replacement IV abx prophylaxis to cover gram(−) bacilli and anaerobes (ampicillin-sulbactam 3 g IV q6h or piperacillin-tazobactam 4.5 g IV q8h in adults)
IV abx prophylaxis to cover gram(−) bacilli and anaerobes (ampicillin-sulbactam 3 g IV q6h or piperacillin-tazobactam 4.5 g IV q8h in adults)Clinical Pearl
 Perforation is common (20% adult pts): sx perforation = pain >24 hr, leukocytosis >20,000/mm3, temp >102° F, palpable abd mass, and peritoneal findings
Perforation is common (20% adult pts): sx perforation = pain >24 hr, leukocytosis >20,000/mm3, temp >102° F, palpable abd mass, and peritoneal findings9. Diverticular Disease
Definitions
 Colonic diverticula: herniations of mucosa + submucosa through muscularis along the colon’s mesenteric border at anatomic weak point (site where vasa recta penetrates the muscle wall)
Colonic diverticula: herniations of mucosa + submucosa through muscularis along the colon’s mesenteric border at anatomic weak point (site where vasa recta penetrates the muscle wall) Diverticulosis: asx presence of multiple colonic diverticula
Diverticulosis: asx presence of multiple colonic diverticula Diverticulitis: inflammatory process/localized perforation of diverticula
Diverticulitis: inflammatory process/localized perforation of diverticulaDiagnosis
H&P
 Painful diverticular disease can manifest w/LLQ pain, relieved by defecation; location of pain may be anywhere in lower abd due to redundant sigmoid colon.
Painful diverticular disease can manifest w/LLQ pain, relieved by defecation; location of pain may be anywhere in lower abd due to redundant sigmoid colon. Diverticulitis can cause muscle spasm, guarding, and rebound tenderness predominantly affecting the LLQ.
Diverticulitis can cause muscle spasm, guarding, and rebound tenderness predominantly affecting the LLQ. Diverticular bleed: painless and stops spontaneously in 60% of pts; 70% occurs in right colon
Diverticular bleed: painless and stops spontaneously in 60% of pts; 70% occurs in right colonLabs
 WBC w/left shift: diverticulitis
WBC w/left shift: diverticulitis Microcytic anemia (chronic bleeding); MCV may be ↑ acute bleeding secondary to reticulocytosis.
Microcytic anemia (chronic bleeding); MCV may be ↑ acute bleeding secondary to reticulocytosis.Imaging
 CT of abd: (sens of 93%-97%, spec ∼100%) for diverticulitis. Typical findings = bowel wall thickening, fistulas, and abscess formation. May also reveal (appendicitis, tubo-ovarian abscess, Crohn’s disease) accounting for lower abd pain.
CT of abd: (sens of 93%-97%, spec ∼100%) for diverticulitis. Typical findings = bowel wall thickening, fistulas, and abscess formation. May also reveal (appendicitis, tubo-ovarian abscess, Crohn’s disease) accounting for lower abd pain. If bleeding suspected:
If bleeding suspected:Treatment
Diverticulosis
 ↑ Fiber intake + regular exercise
↑ Fiber intake + regular exerciseDiverticulitis
 Mild: Cipro 500 mg PO bid (aerobic colonic flora) + metronidazole 500 mg q6h (anaerobes) + liquid diet for 7 to 10 days
Mild: Cipro 500 mg PO bid (aerobic colonic flora) + metronidazole 500 mg q6h (anaerobes) + liquid diet for 7 to 10 days Severe: NPO + aggressive IV abx
Severe: NPO + aggressive IV abx Life-threatening: imipenem 500 mg IV q6h or meropenem 1 g IV q8h
Life-threatening: imipenem 500 mg IV q6h or meropenem 1 g IV q8h Surgical: resection of involved area + diverting colostomy w/reanastomosis performed when infection controlled
Surgical: resection of involved area + diverting colostomy w/reanastomosis performed when infection controlledDiverticular Hemorrhage
 Blood replacement/correction of volume and clotting abnl
Blood replacement/correction of volume and clotting abnl Colonoscopic Rx w/epinephrine injection and/or bipolar coagulation, may prevent recurrent bleeding and ↓ need for surgery.
Colonoscopic Rx w/epinephrine injection and/or bipolar coagulation, may prevent recurrent bleeding and ↓ need for surgery.10. Small Bowel Obstruction
Etiology
 Adhesions from prior surgery (60%)
Adhesions from prior surgery (60%) Hernias (25%)
Hernias (25%) Malignant tumors (15%)
Malignant tumors (15%)Diagnosis
H&P
 Colicky abd pain, N/V, abd distention
Colicky abd pain, N/V, abd distention Failure to pass gas/feces
Failure to pass gas/feces Tachycardia, hypotension, dehydration, fever (if strangulation present)
Tachycardia, hypotension, dehydration, fever (if strangulation present) Distended abd, tenderness w/ or w/o palpable mass, hyperactive bowel sounds initially followed by ↓ bowel sounds late in obstruction
Distended abd, tenderness w/ or w/o palpable mass, hyperactive bowel sounds initially followed by ↓ bowel sounds late in obstructionLabs
 Electrolytes, BUN, Cr, ALT, amylase (generally not helpful)
Electrolytes, BUN, Cr, ALT, amylase (generally not helpful)Imaging
 Plain abd films: dilated loops of small intestine w/o evidence of colonic distention, air-fluid levels
Plain abd films: dilated loops of small intestine w/o evidence of colonic distention, air-fluid levels CT: sensitive for dx complete or high-grade obstruction (less sensitive for partial obstruction); may also ID cause (abscess, neoplasm).
CT: sensitive for dx complete or high-grade obstruction (less sensitive for partial obstruction); may also ID cause (abscess, neoplasm). Barium studies: enteroclysis (PO insertion of a tube into the duodenum and instillation of air and barium) may be useful for low-grade or intermittent obstruction.
Barium studies: enteroclysis (PO insertion of a tube into the duodenum and instillation of air and barium) may be useful for low-grade or intermittent obstruction.Treatment
 IV fluid resuscitation, NG suction to empty stomach
IV fluid resuscitation, NG suction to empty stomach Prophylactic broad-spectrum abx
Prophylactic broad-spectrum abx Operative management
Operative management11. Adynamic Ileus
 Abdominal trauma
Abdominal trauma Infection (retroperitoneal, pelvic, intrathoracic)
Infection (retroperitoneal, pelvic, intrathoracic) Laparotomy
Laparotomy Metabolic disease (hypokalemia)
Metabolic disease (hypokalemia) Renal colic
Renal colic Skeletal injury (rib fracture, vertebral fracture)
Skeletal injury (rib fracture, vertebral fracture) Medications (e.g., narcotics)
Medications (e.g., narcotics)12. Ischemic Bowel Disease
a. Mesenteric Ischemia
 Sudden-onset intestinal hypoperfusion via emboli, a/v thrombosis, or vasoconstriction (low-flow states)
Sudden-onset intestinal hypoperfusion via emboli, a/v thrombosis, or vasoconstriction (low-flow states)Etiology
 Mesenteric arterial embolism: usually LA, LV, or cardiac valves (superior mesenteric artery)
Mesenteric arterial embolism: usually LA, LV, or cardiac valves (superior mesenteric artery) Mesenteric arterial thrombosis: hx progressive atherosclerotic stenoses, w/superimposed abd trauma or infection
Mesenteric arterial thrombosis: hx progressive atherosclerotic stenoses, w/superimposed abd trauma or infection Mesenteric venous thrombosis: hypercoagulable states, blunt trauma, abd infection, portal HTN, pancreatitis, and portal malignancy
Mesenteric venous thrombosis: hypercoagulable states, blunt trauma, abd infection, portal HTN, pancreatitis, and portal malignancy Nonocclusive mesenteric ischemia: atherosclerotic vascular disease, pt treated w/drugs ↓ intestinal perfusion (recent cardiac surgery/dialysis); cocaine use
Nonocclusive mesenteric ischemia: atherosclerotic vascular disease, pt treated w/drugs ↓ intestinal perfusion (recent cardiac surgery/dialysis); cocaine useDiagnosis
H&P
 Rapid onset of severe periumbilical pain out of proportion to PE findings
Rapid onset of severe periumbilical pain out of proportion to PE findings N/V
N/V Initial abd exam may be nl, w/no rebound or guarding, or show minimal distention or occult blood (+) stool.
Initial abd exam may be nl, w/no rebound or guarding, or show minimal distention or occult blood (+) stool. Later in course, may present w/gross distention, absent bowel sounds + peritoneal signs (in elderly change in mental status).
Later in course, may present w/gross distention, absent bowel sounds + peritoneal signs (in elderly change in mental status).Labs
 Nonspecific (early); later may reveal leukocytosis, acidosis, and ↑ Hct (hemoconcentration).
Nonspecific (early); later may reveal leukocytosis, acidosis, and ↑ Hct (hemoconcentration). Protein C/S, AT III, FV Leiden (? hypercoagulable state)
Protein C/S, AT III, FV Leiden (? hypercoagulable state)Imaging
 Mesenteric angiography (gold standard)
Mesenteric angiography (gold standard) Doppler U/S evaluation of intestinal blood flow: often limited by air-filled loops of bowel
Doppler U/S evaluation of intestinal blood flow: often limited by air-filled loops of bowel CT scan: nonspecific. Portal venous/intramural gas possible if development of gangrene. CT more useful if mesenteric vein thrombosis causing acute mesenteric ischemia (90% sens).
CT scan: nonspecific. Portal venous/intramural gas possible if development of gangrene. CT more useful if mesenteric vein thrombosis causing acute mesenteric ischemia (90% sens).Treatment
 Rapid blood flow restoration before infarction; correct acidosis, broad-spectrum abx, NG tube decompression
Rapid blood flow restoration before infarction; correct acidosis, broad-spectrum abx, NG tube decompression If peritonitis: laparotomy + infarcted bowel resection
If peritonitis: laparotomy + infarcted bowel resection SMA embolus: embolectomy. Depending on location/degree of occlusion, surgical revascularization, intra-arterial thrombolytic infusion or vasodilators, or systemic anticoagulation may be considered.
SMA embolus: embolectomy. Depending on location/degree of occlusion, surgical revascularization, intra-arterial thrombolytic infusion or vasodilators, or systemic anticoagulation may be considered. SMA thrombosis: emergent surgical revascularization
SMA thrombosis: emergent surgical revascularization Mesenteric venous thrombosis: if peritoneal sx (laparotomy + infarcted bowel resection), if no peritoneal sx (anticoagulate-heparin)
Mesenteric venous thrombosis: if peritoneal sx (laparotomy + infarcted bowel resection), if no peritoneal sx (anticoagulate-heparin)b. Mesenteric Thrombosis
 Thrombotic occlusion of the mesenteric venous system involving major trunks or smaller branches and leading to intestinal infarction in its acute form
Thrombotic occlusion of the mesenteric venous system involving major trunks or smaller branches and leading to intestinal infarction in its acute formEtiology
 Hypercoagulable states
Hypercoagulable states Portal HTN
Portal HTN Inflammation (pancreatitis, peritonitis [appendicitis, diverticulitis, perforated viscus], IBD, pelvic/intra-abd abscess)
Inflammation (pancreatitis, peritonitis [appendicitis, diverticulitis, perforated viscus], IBD, pelvic/intra-abd abscess) Intra-abd cancer
Intra-abd cancer Postop state or trauma
Postop state or trauma Thrombosis may begin in small mesenteric branches (e.g., in hypercoagulable states) and propagate to the major venous mesenteric trunks or begin in large veins (e.g., in cirrhosis, intra-abd cancer, surgery) and extend distally. If collateral drainage is inadequate, the intestine becomes congested, edematous, cyanotic, and hemorrhagic and eventually may infarct.
Thrombosis may begin in small mesenteric branches (e.g., in hypercoagulable states) and propagate to the major venous mesenteric trunks or begin in large veins (e.g., in cirrhosis, intra-abd cancer, surgery) and extend distally. If collateral drainage is inadequate, the intestine becomes congested, edematous, cyanotic, and hemorrhagic and eventually may infarct.Diagnosis
H&P
 Sx: abd pain (90%), typically out of proportion to the physical findings; N/V (50%), GI bleeding (50% occult, 15% gross)
Sx: abd pain (90%), typically out of proportion to the physical findings; N/V (50%), GI bleeding (50% occult, 15% gross) Early: abd tenderness/distention, ↓ bowel sounds
Early: abd tenderness/distention, ↓ bowel sounds Later: guarding and rebound tenderness, fever, and septic shock
Later: guarding and rebound tenderness, fever, and septic shockLabs
 CBC (leukocytosis), electrolytes (metabolic acidosis [lactic] indicates bowel infarction), amylase
CBC (leukocytosis), electrolytes (metabolic acidosis [lactic] indicates bowel infarction), amylase Hypercoagulable state evaluation: PT, PTT, protein C/S, factor V Leiden, antithrombin III
Hypercoagulable state evaluation: PT, PTT, protein C/S, factor V Leiden, antithrombin IIIImaging
 Abd CT (diagnostic in 90%): bowel wall thickening, venous dilation, venous thrombus
Abd CT (diagnostic in 90%): bowel wall thickening, venous dilation, venous thrombusTreatment
 Anticoagulation or thrombolytic Rx
Anticoagulation or thrombolytic Rx Laparotomy if intestinal infarction is suspected
Laparotomy if intestinal infarction is suspected13. Colorectal Neoplasia
a. Colorectal Carcinoma
 Descending colon (40%-42%), rectosigmoid and rectum (30%-33%), cecum and ascending colon (25%-30%), transverse colon (10%-13%)
Descending colon (40%-42%), rectosigmoid and rectum (30%-33%), cecum and ascending colon (25%-30%), transverse colon (10%-13%)Etiology
 CRC arises via mutations in microsatellite/chromosomal instability, in germline mutations (basis of inherited syndromes), and in accumulation of somatic mutations in cells (basis of sporadic colon cancer).
CRC arises via mutations in microsatellite/chromosomal instability, in germline mutations (basis of inherited syndromes), and in accumulation of somatic mutations in cells (basis of sporadic colon cancer). Classification and staging
Classification and stagingDiagnosis
H&P
 Presentation initially nonspecific (weight loss, anorexia, malaise)
Presentation initially nonspecific (weight loss, anorexia, malaise) Right-sided sx:
Right-sided sx: Left-sided sx:
Left-sided sx:Labs
 + Fecal occult blood test
+ Fecal occult blood test Microcytic anemia
Microcytic anemia ↑ Plasma CEA (poor screening test for CRC as may be ↑ in pts w/ [smoking, IBD, alcoholic liver disease]); normal CEA level does not r/o CRC; main use is to monitor CRC recurrence.
↑ Plasma CEA (poor screening test for CRC as may be ↑ in pts w/ [smoking, IBD, alcoholic liver disease]); normal CEA level does not r/o CRC; main use is to monitor CRC recurrence. LFTs
LFTsImaging
 Colonoscopy w/bx (primary assessment tool)
Colonoscopy w/bx (primary assessment tool) Virtual colonoscopy (sens/spec detection of polyps >10 mm = 70%-96%, 72%-96%, respectively)
Virtual colonoscopy (sens/spec detection of polyps >10 mm = 70%-96%, 72%-96%, respectively) CT of abd, pelvis, chest (preoperative staging)
CT of abd, pelvis, chest (preoperative staging) PET scan: accurate in detection of CRC + distant mets; combined PET/CT optimal (colonography) can provide whole-body tumor staging in a single session.
PET scan: accurate in detection of CRC + distant mets; combined PET/CT optimal (colonography) can provide whole-body tumor staging in a single session.Treatment
 Surgical resection: 70% resectable for cure at presentation; 45% of pts are cured by primary resection.
Surgical resection: 70% resectable for cure at presentation; 45% of pts are cured by primary resection. Rx mainstay = fluorouracil; addition of leucovorin (folinic acid) enhances fluorouracil effect
Rx mainstay = fluorouracil; addition of leucovorin (folinic acid) enhances fluorouracil effect Radiation Rx = useful adjunct to fluorouracil + leucovorin (stage II or III rectal cancers)
Radiation Rx = useful adjunct to fluorouracil + leucovorin (stage II or III rectal cancers) For pts w/standard-risk stage III tumors (e.g., involvement of 1-3 regional lymph nodes), both fluorouracil alone and fluorouracil w/oxaliplatin are reasonable choices. Capecitabine is an alternative to IV fluorouracil as adjuvant Rx for stage III CRC.
For pts w/standard-risk stage III tumors (e.g., involvement of 1-3 regional lymph nodes), both fluorouracil alone and fluorouracil w/oxaliplatin are reasonable choices. Capecitabine is an alternative to IV fluorouracil as adjuvant Rx for stage III CRC. Irinotecan can be used to treat metastatic CRC refractory to other drugs.
Irinotecan can be used to treat metastatic CRC refractory to other drugs. Oxaliplatin, a third-generation platinum derivative, can be used in combination w/fluorouracil and leucovorin for pts w/metastatic CRC whose disease has recurred or progressed despite Rx w/fluorouracil and leucovorin + irinotecan. Fluorouracil + oxaliplatin should be considered for high-risk pts w/stage III cancers (e.g., >3 involved regional nodes [N2] or tumor invasion beyond the serosa [T4 lesion]).
Oxaliplatin, a third-generation platinum derivative, can be used in combination w/fluorouracil and leucovorin for pts w/metastatic CRC whose disease has recurred or progressed despite Rx w/fluorouracil and leucovorin + irinotecan. Fluorouracil + oxaliplatin should be considered for high-risk pts w/stage III cancers (e.g., >3 involved regional nodes [N2] or tumor invasion beyond the serosa [T4 lesion]). The monoclonal Abs cetuximab, panitumumab, and bevacizumab can be used for advanced CRC.
The monoclonal Abs cetuximab, panitumumab, and bevacizumab can be used for advanced CRC. The liver is generally the initial and most common site of CRC mets. Resection of mets limited to the liver is curative in more than 30% of selected pts. In pts who undergo resection of liver mets, postoperative Rx w/a combination of hepatic arterial infusion of floxuridine and IV fluorouracil improves the outcome at 2 yr.
The liver is generally the initial and most common site of CRC mets. Resection of mets limited to the liver is curative in more than 30% of selected pts. In pts who undergo resection of liver mets, postoperative Rx w/a combination of hepatic arterial infusion of floxuridine and IV fluorouracil improves the outcome at 2 yr.F. Disorders of the Liver
1. Approach to the PT with Abnormal Liver Enzymes
 Table 6-7 describes typical liver test patterns in hepatocellular necrosis and biliary obstruction.
Table 6-7 describes typical liver test patterns in hepatocellular necrosis and biliary obstruction.2. Viral Hepatitis
a. Hepatitis A
 Infection by HAV (27-nm, nonenveloped, icosahedral, [+]-stranded RNA virus) transmitted interpersonally via fecal-oral route (contact w/poorly purified food/water); IV transmission rare; vertical transmission also reported.
Infection by HAV (27-nm, nonenveloped, icosahedral, [+]-stranded RNA virus) transmitted interpersonally via fecal-oral route (contact w/poorly purified food/water); IV transmission rare; vertical transmission also reported.TABLE 6-5
Colorectal Cancer (CRC) Screening and Surveillance Recommendations∗
| Indication | Recommendations |
| Average risk | Beginning at age 50 yr: colonoscopy every 10 yr, CT colonography every 5 yr Flexible sigmoidoscopy every 5 yr Double-contrast barium enema every 5 yr (stool blood testing annually or stool DNA testing acceptable but not preferred) |
| One or two first-degree relatives with CRC at any age or adenoma at age <60 yr | Colonoscopy every 5 yr beginning at age 40 yr, or 10 yr younger than earliest diagnosis, whichever comes first |
| Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer | Genetic counseling and screening† Colonoscopy every 1 to 2 years beginning at age 25 yr and then yearly after age 40 yr‡ |
| Familial adenomatous polyposis and variants | Genetic counseling and testing† Flexible sigmoidoscopy yearly beginning at puberty‡ |
| Personal history of CRC | Colonoscopy within 1 yr of curative resection; repeat at 3 yr and then every 5 yr if normal |
| Personal history of colorectal adenoma Inflammatory bowel disease |
Colonoscopy every 3 to 5 yr after removal of all index polyps Colonoscopy every 1 to 2 yr beginning after 8 yr of pancolitis or after 15 yr if only left-sided disease |
∗ Recommendations proposed by the American Cancer Society and U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer; recommendations for average-risk patients also endorsed by the American College of Radiology.
† Whenever possible, affected relatives should be tested first because of potential false-negative results.
‡ Screening recommendation for individuals with positive or indeterminate tests, as well as for those who refuse genetic testing.
From Andreoli, T E, Benjamin IJ, Griggs RC, Wing EJ: Andreoli and Carpenter’s Cecil Essentials of Medicine, 8th ed. Philadelphia, Saunders, 2010.
TABLE 6-6
Hereditary Colorectal Cancer Syndromes
| Type | Trait | Gastric | Small Bowel | Colon | Histology | GI Malignancy | Extraintestinal |
| Familial polyposis | AD | <5% | <5% | 100% | Adenoma | 100% | — |
| Gardner | AD | 5% | 5% | 100% | Adenoma | 100% | Osteoma, others∗ |
| Peutz-Jeghers | AD | 25% | 95% | 30% | Hamartoma | Rare | Perioral pigmentation |
| Juvenile polyposis | AD | — | — | 100% | Inflammatory | ? | — |
| Turcot | AR | — | — | 100% | Adenoma | 100% | Glioma |
| Cronkhite-Canada | Nonhereditary | 100% | 50% | 100% | Inflammatory | None | Ectodermal changes |
| Cowden† | AD | — | — | — | Hamartoma | None | Oral papilloma‡ |
| Ruvalcaba-Myhre† | AD | Yes | Yes | Yes | Hamartoma | None | Macrocephaly, penile macules, mental retardation, SC lipomas |
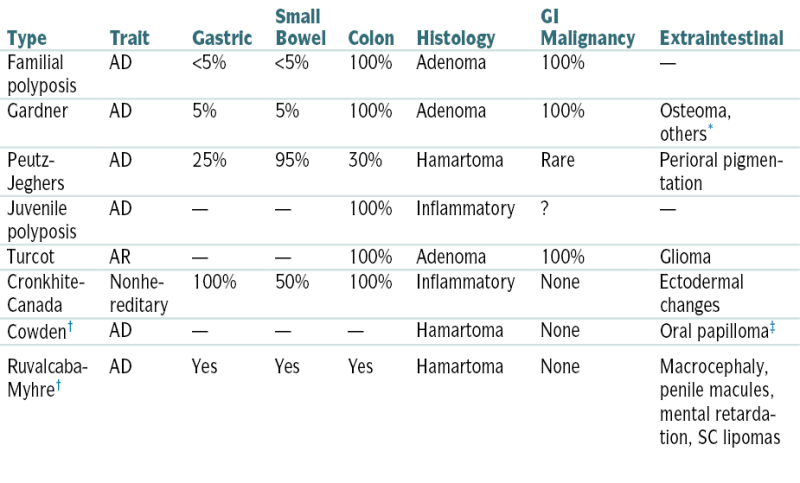
∗ Soft tissue tumors, sarcomas, ampullary carcinoma, ovarian carcinoma.
† Extremely rare.
‡ Gingival hyperplasia, breast cancer, thyroid cancer.
From Weissleder R, Wittenberg J, Harisinghani M, Chen JW: Primer of Diagnostic Imaging, 5th ed. St. Louis, Mosby, 2011.
Diagnosis
H&P
 Infection w/HAV may have acute or subacute presentation, icteric or anicteric. Severity of illness ↑ w/age (90% infections in children <5 yr may be subclinical).
Infection w/HAV may have acute or subacute presentation, icteric or anicteric. Severity of illness ↑ w/age (90% infections in children <5 yr may be subclinical). A preicteric, prodromal phase (1-14 days); 15% no prodrome. Sx onset usually abrupt and may include anorexia, malaise, N/V, fever, headache, abd pain, chills, myalgias, arthralgias, URI sx, constipation, diarrhea, pruritus, urticaria (less common).
A preicteric, prodromal phase (1-14 days); 15% no prodrome. Sx onset usually abrupt and may include anorexia, malaise, N/V, fever, headache, abd pain, chills, myalgias, arthralgias, URI sx, constipation, diarrhea, pruritus, urticaria (less common). Jaundice (>70%); icteric phase is preceded by dark urine.
Jaundice (>70%); icteric phase is preceded by dark urine.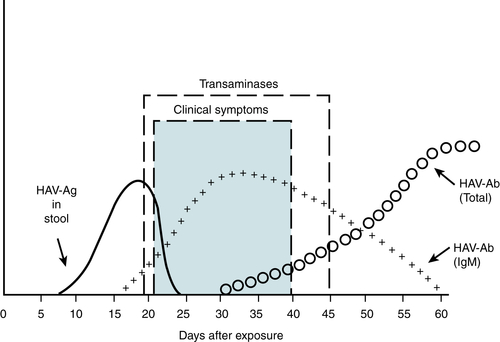
FIGURE 6-2 Serologic test in hepatitis A virus infection. (From Goldberger E: Treatment of Cardiac Emergencies, 5th ed. St. Louis, Mosby, 1990.)
TABLE 6-7
Typical Liver Test Patterns
| Test | Hepatocellular Necrosis | Biliary Obstruction | |||||
| Toxic or Ischemic | Viral | Alcohol | Chronic Complete | Chronic Partial | Acute Complete (first 24 hr) | Infiltration (Chronic) | |
| Aminotransferases | 50-100× | 5-50× | 2-5× | 1-5× | 1-5× | 1-50× | 1-3× |
| Alkaline phosphatase | 1-3× | 1-3× | 1-10× | 2-20× | 2-10× | May be nl | 1-20× |
| Bilirubin | 1-5× | 1-30× | 1-30× | 1-30× | 1-5× | Usually nl | 1-5× |
| PT | Prolonged in severe cases, unresponsive to vitamin K | May be prolonged, responsive to vitamin K | Usually nl | Usually nl | Usually nl | ||
| Albumin | Nl in acute illness, may be ↓ in chronic illness | Usually nl, but may be ↓ in biliary cirrhosis | Usually nl | Usually nl | |||
| Typical disorders | Acetaminophen toxicity, shock liver | Acute hepatitis A or B | Alcoholic hepatitis | Pancreatic carcinoma | Sclerosing cholangitis | Choledocholithiasis | Primary or metastatic carcinoma, Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare infection |
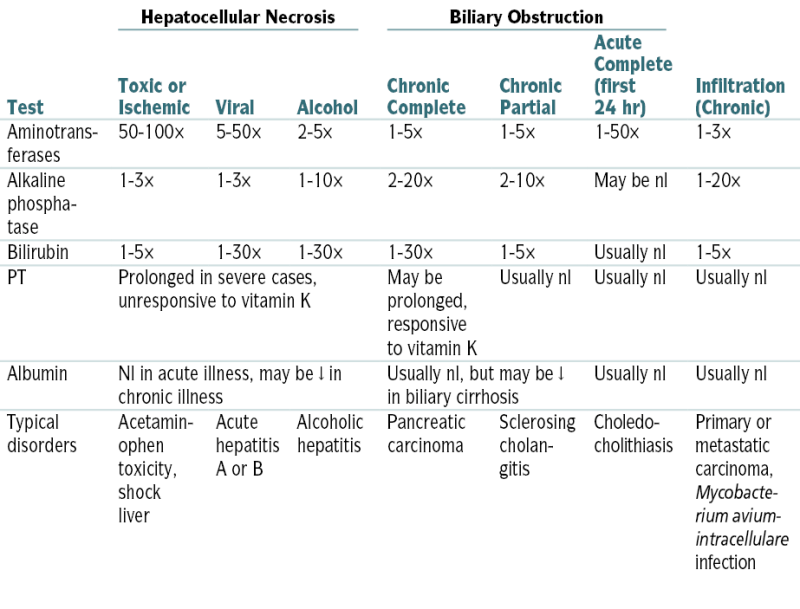
Labs (Fig. 6-2)
 Dx confirmed by IgM anti-HAV; detectable in almost all infected pts at presentation and remains (+) for 3 to 6 mo.
Dx confirmed by IgM anti-HAV; detectable in almost all infected pts at presentation and remains (+) for 3 to 6 mo. 4× ↑ titer of total Ab (IgM + IgG) to HAV confirms acute infection.
4× ↑ titer of total Ab (IgM + IgG) to HAV confirms acute infection. HAV detection in stool and body fluids by EM
HAV detection in stool and body fluids by EM HAV RNA detection in stool, body fluids, serum, and liver tissue
HAV RNA detection in stool, body fluids, serum, and liver tissue ↑ ALT AST (usually >8× nl in acute infection)
↑ ALT AST (usually >8× nl in acute infection) ↑ Bili (usually 5-15× nl)
↑ Bili (usually 5-15× nl) Alk phos minimally ↑ but higher level in cholestasis
Alk phos minimally ↑ but higher level in cholestasis Alb and PT generally nl; if ↑ may herald hepatic necrosis
Alb and PT generally nl; if ↑ may herald hepatic necrosisTreatment
 Self-limited (supportive care; activity as tolerated)
Self-limited (supportive care; activity as tolerated) Advise to avoid alcohol and hepatotoxic drugs
Advise to avoid alcohol and hepatotoxic drugs Pts w/fulminant hepatitis may require hospitalization/assessment for liver transplantation.
Pts w/fulminant hepatitis may require hospitalization/assessment for liver transplantation.Clinical Pearls
 Reported to public health authorities
Reported to public health authorities Common illness in internationally traveled/developing countries; preexposure prophylaxis if travel to endemic area (IG 0.02-0.06 mL/kg IM); Lower dose = effective up to 3 mo; higher dose = effective up to 5 mo.
Common illness in internationally traveled/developing countries; preexposure prophylaxis if travel to endemic area (IG 0.02-0.06 mL/kg IM); Lower dose = effective up to 3 mo; higher dose = effective up to 5 mo. Postexposure prophylaxis (IG 0.02 mL/kg given IM) if exposure within 2 wk + no previous vaccination; high-risk pts, may vaccinate with immunoglobulin
Postexposure prophylaxis (IG 0.02 mL/kg given IM) if exposure within 2 wk + no previous vaccination; high-risk pts, may vaccinate with immunoglobulin Inactivated vaccines HAVRIX or VAQTA safe/immunogenic in adults/children >12 mo w/protective Ab levels reached 94% to 100% 1 mo combined HepA/HepB vaccine TWINRIX also available
Inactivated vaccines HAVRIX or VAQTA safe/immunogenic in adults/children >12 mo w/protective Ab levels reached 94% to 100% 1 mo combined HepA/HepB vaccine TWINRIX also availableb. Hepatitis B
 Infection by HBV (42-nm hepadnavirus w/an outer surface coat [HBsAg], inner nucleocapsid core [HBcAg; HBeAg], DNA polymerase, and partially double-stranded DNA genome) with transmission via parenteral (needle use, tattooing, piercing, acupuncture, blood transfusion, hemodialysis, sexual contact) and perinatal routes
Infection by HBV (42-nm hepadnavirus w/an outer surface coat [HBsAg], inner nucleocapsid core [HBcAg; HBeAg], DNA polymerase, and partially double-stranded DNA genome) with transmission via parenteral (needle use, tattooing, piercing, acupuncture, blood transfusion, hemodialysis, sexual contact) and perinatal routesDiagnosis
H&P
 Often nonspecific sx, malaise
Often nonspecific sx, malaise Prodrome:
Prodrome:Labs (Fig. 6-3)
 Acute HBV infection is best confirmed by IgM HBcAb in acute or early convalescent serum or by HB DNA.
Acute HBV infection is best confirmed by IgM HBcAb in acute or early convalescent serum or by HB DNA. HBsAg and IgG-HBcAb during acute jaundice are strongly suggestive of remote HBV infection and another etiology for current illness.
HBsAg and IgG-HBcAb during acute jaundice are strongly suggestive of remote HBV infection and another etiology for current illness. HBsAb alone is suggestive of immunization response.
HBsAb alone is suggestive of immunization response. W/recovery, HBeAg is rapidly replaced by HBeAb in 2 to 3 mo, and HBsAg is replaced by HBsAb in 5 to 6 mo.
W/recovery, HBeAg is rapidly replaced by HBeAb in 2 to 3 mo, and HBsAg is replaced by HBsAb in 5 to 6 mo. In chronic HBV, HBsAg and HBeAg are persistent w/o corresponding Ab.
In chronic HBV, HBsAg and HBeAg are persistent w/o corresponding Ab. In chronic carrier state, HBsAg is persistent, but HBeAg is replaced by HBeAb.
In chronic carrier state, HBsAg is persistent, but HBeAg is replaced by HBeAb. HBcAb develops in all outcomes.
HBcAb develops in all outcomes. HBeAg correlation w/highest infectivity; appearance of HBeAb heralds recovery.
HBeAg correlation w/highest infectivity; appearance of HBeAb heralds recovery. LFTs:
LFTs: Alb and PT: generally nl; if abnl, possible harbinger of impending hepatic necrosis (fulminant hepatitis)
Alb and PT: generally nl; if abnl, possible harbinger of impending hepatic necrosis (fulminant hepatitis) WBC and ESR: generally nl or mildly ↑
WBC and ESR: generally nl or mildly ↑Imaging
 U/S to r/o obstructive jaundice
U/S to r/o obstructive jaundiceTreatment
Acute Hepatitis B
 90% of adults spontaneously clear infection; avoid hepatic metabolized drugs; IV hydration if severe vomiting
90% of adults spontaneously clear infection; avoid hepatic metabolized drugs; IV hydration if severe vomiting Hospitalization if pt risk dehydration via poor PO intake, PT ↑, bili level >15 to 20 μg/dL, or if hepatic failure
Hospitalization if pt risk dehydration via poor PO intake, PT ↑, bili level >15 to 20 μg/dL, or if hepatic failure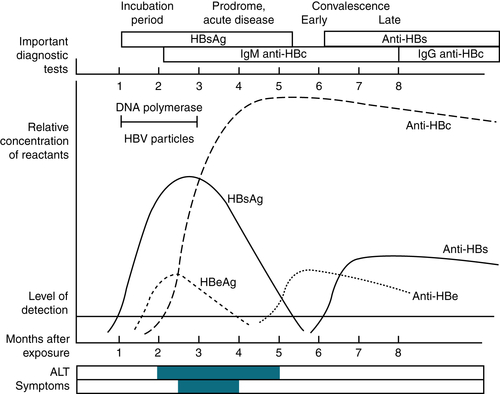
FIGURE 6-3 Serologic and clinical patterns observed during acute hepatitis B virus infection. Patients in whom the hepatitis B infection does not resolve (chronic carrier state) will demonstrate persistence of HBsAg and will not have an elevation of anti-HBs. (From Ravel R: Clinical Laboratory Medicine, 6th ed. St. Louis, Mosby, 1995.)
Chronic Hepatitis B
 Rx: determined by e antigen status and viral qualification
Rx: determined by e antigen status and viral qualification Documented cirrhosis [(+) or (−) HBeAg] with
Documented cirrhosis [(+) or (−) HBeAg] withClinical Pearls
 Virus and HBsAg are present in high titers in blood for 1 to 7 wk before jaundice and for a variable time thereafter.
Virus and HBsAg are present in high titers in blood for 1 to 7 wk before jaundice and for a variable time thereafter. Transmission is possible during entire period of HBsAg (and especially during HBeAg) in serum.
Transmission is possible during entire period of HBsAg (and especially during HBeAg) in serum. Prevention after exposure:
Prevention after exposure: Preventive Rx w/lamivudine for pts who test (+) for HBsAg and are undergoing chemoRx may ↑ the risk for HBV reactivation and HBV-associated morbidity and mortality.
Preventive Rx w/lamivudine for pts who test (+) for HBsAg and are undergoing chemoRx may ↑ the risk for HBV reactivation and HBV-associated morbidity and mortality.c. Hepatitis C
 Infection via HCV (single-stranded RNA flavivirus) is mostly via the parenteral route (IV drug use 60% new cases, 20%-50% chronic cases). Occupational needle stick exposure from an HCV(+) source has a seroconversion rate of 1.8% (range, 0%-7%).
Infection via HCV (single-stranded RNA flavivirus) is mostly via the parenteral route (IV drug use 60% new cases, 20%-50% chronic cases). Occupational needle stick exposure from an HCV(+) source has a seroconversion rate of 1.8% (range, 0%-7%).Diagnosis
H&P
 Sx usually develop 7 to 8 wk after infection (2-26 wk), but 70% to 80% of cases are subclinical.
Sx usually develop 7 to 8 wk after infection (2-26 wk), but 70% to 80% of cases are subclinical. 10% to 20% report acute illness w/jaundice and nonspecific sx (abd pain, anorexia, malaise).
10% to 20% report acute illness w/jaundice and nonspecific sx (abd pain, anorexia, malaise). After acute infection, 15% to 25% have complete resolution (absence of HCV RNA in serum, nl ALT).
After acute infection, 15% to 25% have complete resolution (absence of HCV RNA in serum, nl ALT). Progression to chronic infection is common (50%-84%); 74% to 86% have persistent viremia; spontaneous clearance of viremia in chronic infection is rare. 60% to 70% of pts will have persistent or fluctuating ALT levels; 30% to 40% w/chronic infection have nl ALT levels.
Progression to chronic infection is common (50%-84%); 74% to 86% have persistent viremia; spontaneous clearance of viremia in chronic infection is rare. 60% to 70% of pts will have persistent or fluctuating ALT levels; 30% to 40% w/chronic infection have nl ALT levels. 15% to 20% of those w/chronic HCV will develop cirrhosis during a period of 20 to 30 yr; in most others, chronic infection leads to hepatitis and varying degrees of fibrosis.
15% to 20% of those w/chronic HCV will develop cirrhosis during a period of 20 to 30 yr; in most others, chronic infection leads to hepatitis and varying degrees of fibrosis. 0.4% to 2.5% of pts w/chronic infection develop HCC.
0.4% to 2.5% of pts w/chronic infection develop HCC. 25% of pts w/chronic infection continue to have an asymptomatic course w/nl LFTs and benign histology.
25% of pts w/chronic infection continue to have an asymptomatic course w/nl LFTs and benign histology. In chronic HCV infection, extrahepatic sequelae include a variety of immunologic and lymphoproliferative disorders (e.g., cryoglobulinemia, membranoproliferative GN, and possibly Sjögren’s syndrome, autoimmune thyroiditis, polyarteritis nodosa, aplastic anemia, lichen planus, porphyria cutanea tarda, B-cell lymphoma, others).
In chronic HCV infection, extrahepatic sequelae include a variety of immunologic and lymphoproliferative disorders (e.g., cryoglobulinemia, membranoproliferative GN, and possibly Sjögren’s syndrome, autoimmune thyroiditis, polyarteritis nodosa, aplastic anemia, lichen planus, porphyria cutanea tarda, B-cell lymphoma, others).Labs (Fig. 6-4)
 Dx is often by exclusion because it takes 6 wk to 12 mo to develop anti-HCV Ab (70% + by 6 wk, 90% + by 6 mo).
Dx is often by exclusion because it takes 6 wk to 12 mo to develop anti-HCV Ab (70% + by 6 wk, 90% + by 6 mo). Diagnostic tests include serologic assays for Abs and molecular tests for viral particles.
Diagnostic tests include serologic assays for Abs and molecular tests for viral particles. Enzyme immunoassay is the test for anti-HCV Ab:
Enzyme immunoassay is the test for anti-HCV Ab: Recombinant immunoblot is used to confirm + enzyme immunoassays: recommended only in low-risk settings
Recombinant immunoblot is used to confirm + enzyme immunoassays: recommended only in low-risk settings Qualitative and quantitative HCV RNA tests using PCR:
Qualitative and quantitative HCV RNA tests using PCR: Viral genotyping can distinguish among genotypes 1, 2, 3, and 4, which is helpful in choosing Rx; most of these tests use PCR. (Genotypes 1, 2, 3, and 4 predominate in the United States and Europe [1 is especially common in North America].)
Viral genotyping can distinguish among genotypes 1, 2, 3, and 4, which is helpful in choosing Rx; most of these tests use PCR. (Genotypes 1, 2, 3, and 4 predominate in the United States and Europe [1 is especially common in North America].)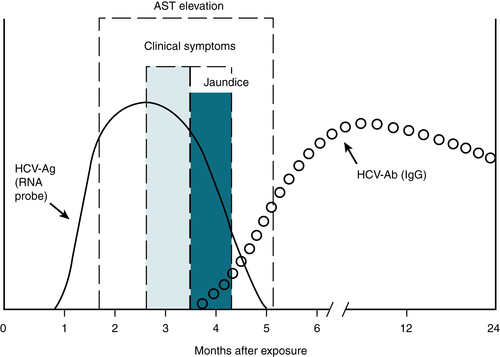
FIGURE 6-4 Hepatitis C virus antigen and antibody. (From Hollinger FB, Dienstag JL. In Murray PR, et al [eds]: Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 6th ed. Washington, DC, American Society for Microbiology, 1995.)
 LFTs:
LFTs:Imaging
 U/S is useful to r/o obstructive jaundice and to evaluate rapid liver size ↓ during fulminant hepatitis or mass in HCC.
U/S is useful to r/o obstructive jaundice and to evaluate rapid liver size ↓ during fulminant hepatitis or mass in HCC.Treatment
Acute Hepatitis C
 HCV PCR detected within 13 days (antibody in >36 days)
HCV PCR detected within 13 days (antibody in >36 days) If clear HCV viral load via PCR within 3 to 4 mo (no Rx-supportive care)
If clear HCV viral load via PCR within 3 to 4 mo (no Rx-supportive care)Chronic Hepatitis C (persistent HCV viral load)
 Rx duration depends on HCV RNA level:
Rx duration depends on HCV RNA level: Null: no ↓ of 2log10 by wk 12
Null: no ↓ of 2log10 by wk 12 Partial: 2log10 ↓ by wk12 but detectable by wk 24
Partial: 2log10 ↓ by wk12 but detectable by wk 24 Nonresponsive: HCV RNA not cleared by wk 24
Nonresponsive: HCV RNA not cleared by wk 24 Early Virologic Response (EVR): >2log10 ↓ by wk 12, undetectable by wk 24
Early Virologic Response (EVR): >2log10 ↓ by wk 12, undetectable by wk 24 Complete EVR: undetectable by wk 12 and 24, but not at wk 4
Complete EVR: undetectable by wk 12 and 24, but not at wk 4 Rapid Virologic Response (RVR): undetectable by wk 4, no change during Rx
Rapid Virologic Response (RVR): undetectable by wk 4, no change during Rx Extended Virologic Response (eRVR): undetectable by wk 4 (telaprevir) or wk 8 (boceprevir) and wks 12 and 24
Extended Virologic Response (eRVR): undetectable by wk 4 (telaprevir) or wk 8 (boceprevir) and wks 12 and 24 Relapse: undetectable at Rx end, but detectable within 24 wk s/p Rx
Relapse: undetectable at Rx end, but detectable within 24 wk s/p Rx Sustained Virologic Response (SVR): cure; undetectable s/p 24 wk Rx
Sustained Virologic Response (SVR): cure; undetectable s/p 24 wk Rx Rx options depend on Genotype:
Rx options depend on Genotype: When Rx HIV-HCV dually infected pt, monitor interactions between direct-acting antivirals (DAAs) and antiretroviral drugs. Rx duration will likely be the full 48 wk.
When Rx HIV-HCV dually infected pt, monitor interactions between direct-acting antivirals (DAAs) and antiretroviral drugs. Rx duration will likely be the full 48 wk. Liver transplantation: May be only option if HCV-related deteriorating cirrhosis exists.
Liver transplantation: May be only option if HCV-related deteriorating cirrhosis exists.d. Hepatitis D
 Incomplete virus requiring presence of HBV for replication; thus, resolution of HBV infection will result in resolution of HDV infection.
Incomplete virus requiring presence of HBV for replication; thus, resolution of HBV infection will result in resolution of HDV infection.e. Hepatitis E
 Similar to HAV (enteric transmission, acute infection only)
Similar to HAV (enteric transmission, acute infection only) Despite low overall mortality, infection during third trimester mortality rate ≥25%
Despite low overall mortality, infection during third trimester mortality rate ≥25% Prevention via good hygiene; avoid dirty water/poorly cooked food.
Prevention via good hygiene; avoid dirty water/poorly cooked food.3. Autoimmune Hepatitis
Diagnosis
H&P
 Can manifest asymptomatically → fulminant hepatic failure; most commonly fatigue, pruritus, jaundice, hepatomegaly/splenomegaly
Can manifest asymptomatically → fulminant hepatic failure; most commonly fatigue, pruritus, jaundice, hepatomegaly/splenomegalyTABLE 6-8
Simplified Diagnostic Criteria for Autoimmune Hepatitis
| Variable | Cutoff | Points | Cutoff | Points |
| ANA or SMA | ≥1:40 | 1 | ≥1:80 | 2 |
| LKM | ≥1:40 | 2 | ||
| SLA | Positive | 2 | ||
| IgG | ≥ULN | 1 | ≥1.1 × ULN | 2 |
| Histology | Compatible with AIH | 1 | Typical of AIH | 2 |
| Absence of viral hepatitis | Yes | 2 | ||
| Maximum number of points for all antibodies = 2, total = 8. | ||||
| Probable AIH ≥6 points, definite AIH ≥7 points. | ||||
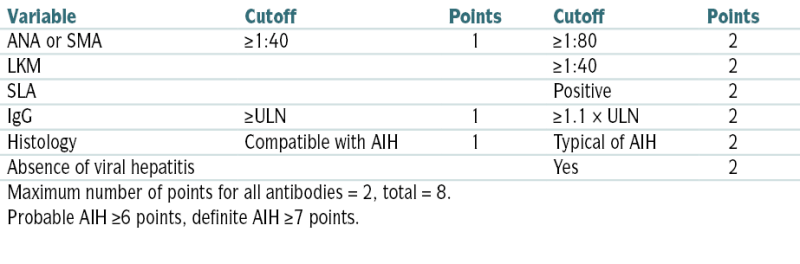
AIH, Autoimmune hepatitis; LKM, liver/kidney microsomes; SLA, soluble liver antigen; SMA, smooth muscle antibody; ULN, upper limit of normal.
From Ferri F: Ferri’s Clinical Advisor: 5 Books in 1. 2013 edition. Philadelphia, Mosby, 2012.
 Autoimmune findings: arthritis, xerostomia, keratoconjunctivitis, cutaneous vasculitis, and erythema nodosum
Autoimmune findings: arthritis, xerostomia, keratoconjunctivitis, cutaneous vasculitis, and erythema nodosumLabs
 ↑ ALT and AST (both 2-10× nl)
↑ ALT and AST (both 2-10× nl) Women 4× > risk than men
Women 4× > risk than men Bili and alk phos moderately ↑/nl
Bili and alk phos moderately ↑/nl ↑ γ-Globulin (>2.0 g/dL)
↑ γ-Globulin (>2.0 g/dL) Serum ANA + anti–smooth muscle Ab (64% cases); if (−), p-ANCA helpful
Serum ANA + anti–smooth muscle Ab (64% cases); if (−), p-ANCA helpful Liver bx = interface hepatitis (lymphoplasmacytic inflammatory infiltrate extending from portal tract → lobule)
Liver bx = interface hepatitis (lymphoplasmacytic inflammatory infiltrate extending from portal tract → lobule) Table 6-8 describes simplified diagnostic criteria for autoimmune hepatitis.
Table 6-8 describes simplified diagnostic criteria for autoimmune hepatitis.Imaging
 U/S of liver and biliary tree: r/o obstruction or hepatic mass
U/S of liver and biliary tree: r/o obstruction or hepatic massIndications for Treatment
 AST >10× nl
AST >10× nl AST >5× nl, w/↑ γ-globulin 2× nl
AST >5× nl, w/↑ γ-globulin 2× nl Fever, N/V, jaundice
Fever, N/V, jaundice Histologic features of bridging necrosis or multiacinar necrosis
Histologic features of bridging necrosis or multiacinar necrosisTreatment
 Prednisone 60 mg PO/day or (prednisone 30 mg + azathioprine 50 mg PO/day); both achieve remission in 80% pts w/combo Rx = less steroid SE
Prednisone 60 mg PO/day or (prednisone 30 mg + azathioprine 50 mg PO/day); both achieve remission in 80% pts w/combo Rx = less steroid SE Taper based on lab response striving for minimum dose needed for maintenance Rx (same regimen 12-18 mo) to ↑ remission rate.
Taper based on lab response striving for minimum dose needed for maintenance Rx (same regimen 12-18 mo) to ↑ remission rate. If liver transplant necessary, 10-yr survival rate 75%
If liver transplant necessary, 10-yr survival rate 75%4. Cholestatic Liver Disease
a. Primary Biliary Cirrhosis (PBC)
Diagnosis
H&P
 Typical pt middle-aged female (50 yr); most asx but develop fatigue, pruritus, dry eyes/mouth over 10-yr period
Typical pt middle-aged female (50 yr); most asx but develop fatigue, pruritus, dry eyes/mouth over 10-yr periodLabs
 (+) Antimitochondrial Ab titer >1:40 (if undetectable, need biopsy)
(+) Antimitochondrial Ab titer >1:40 (if undetectable, need biopsy) ↑ alk phos >1.5× nl (with nl total bili); ↑ AST/ALT <5× nl possible
↑ alk phos >1.5× nl (with nl total bili); ↑ AST/ALT <5× nl possible Histology: florid duct lesion (duct obliteration w/granuloma formation = pathognomic)
Histology: florid duct lesion (duct obliteration w/granuloma formation = pathognomic)Treatment
 Pruritus: cholestyramine (8-24 g qd), sertraline, rifampin
Pruritus: cholestyramine (8-24 g qd), sertraline, rifampin Hyperlipidemia/malabsorption of fat-soluble vitamins via cholestasis: statin Rx + wt loss and vitamin (especially vitamin D) replacement
Hyperlipidemia/malabsorption of fat-soluble vitamins via cholestasis: statin Rx + wt loss and vitamin (especially vitamin D) replacement Asymptomatic stage: Follow LFTs q3-4 mo; if alk phos and/or AST >1.5× nl start ursodeoxycholic acid 12 to 15 mg/kg/day (UDCA).
Asymptomatic stage: Follow LFTs q3-4 mo; if alk phos and/or AST >1.5× nl start ursodeoxycholic acid 12 to 15 mg/kg/day (UDCA). Liver transplant is only definitive Rx.
Liver transplant is only definitive Rx.b. Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC)
Diagnosis
H&P
 Mean age 40 yr; 60% men (most asymptomatic, but may have pruritus, abd pain, jaundice)
Mean age 40 yr; 60% men (most asymptomatic, but may have pruritus, abd pain, jaundice)Labs/Imaging
 ↑ Alk phos (3-10× nl); ↑ ALT/AST (2-3× nl); (+) ANA, smooth muscle abs (20%-50%)
↑ Alk phos (3-10× nl); ↑ ALT/AST (2-3× nl); (+) ANA, smooth muscle abs (20%-50%) “Beads on a string” (segmental bile duct fibrosis w/saccular dilatation of nl areas)
“Beads on a string” (segmental bile duct fibrosis w/saccular dilatation of nl areas) Cholangiography: MRCP (gold standard); if obstruction, ERCP
Cholangiography: MRCP (gold standard); if obstruction, ERCP Liver bx: periductal fibrosis, fibro-obliterative cholangiopathy
Liver bx: periductal fibrosis, fibro-obliterative cholangiopathyStaging
 See Table 6-9.
See Table 6-9.TABLE 6-9
Staging of Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
| Stage | Description |
| I: Portal | Portal edema, inflammation, ductal proliferation; abnormalities do not extend beyond the limiting plate |
| II: Periportal | Periportal fibrosis with or without inflammation extending beyond the limiting plate |
| III: Septal | Septal fibrosis, bridging necrosis, or both |
| IV: Cirrhotic | Biliary cirrhosis |
From: Cameron AM: Current Surgical Therapy, 10th ed. Philadelphia, Saunders, 2011.
Treatment
 Sx relief; liver transplantation
Sx relief; liver transplantation5. Complications of Liver Disease
a. Cirrhosis
 Defined histologically as the presence of fibrosis/regenerative nodules in the liver
Defined histologically as the presence of fibrosis/regenerative nodules in the liverEtiology
 EtOH abuse, secondary to biliary cirrhosis/obstruction of the CBD (stone, stricture, pancreatitis, neoplasm, sclerosing cholangitis), drugs (acetaminophen, INH, MTX, methyldopa), hepatic congestion (CHF, constrictive pericarditis, tricuspid insufficiency, hepatic vein thrombosis, vena cava obstruction), PBC, PSC, chronic hepB/C, Wilson’s disease, α1-antitrypsin deficiency, infiltrative diseases (amyloidosis, glycogen storage diseases, hemochromatosis), jejunoileal bypass, parasitic infections (schistosomiasis), idiopathic portal HTN, congenital hepatic fibrosis, systemic mastocytosis, autoimmune hepatitis, hepatic steatosis, IBD
EtOH abuse, secondary to biliary cirrhosis/obstruction of the CBD (stone, stricture, pancreatitis, neoplasm, sclerosing cholangitis), drugs (acetaminophen, INH, MTX, methyldopa), hepatic congestion (CHF, constrictive pericarditis, tricuspid insufficiency, hepatic vein thrombosis, vena cava obstruction), PBC, PSC, chronic hepB/C, Wilson’s disease, α1-antitrypsin deficiency, infiltrative diseases (amyloidosis, glycogen storage diseases, hemochromatosis), jejunoileal bypass, parasitic infections (schistosomiasis), idiopathic portal HTN, congenital hepatic fibrosis, systemic mastocytosis, autoimmune hepatitis, hepatic steatosis, IBDDiagnosis
H&P
 Jaundice; spider angiomas; ecchymosis; gynecomastia in men; small, nodular liver; ascites; hemorrhoids; testicular atrophy
Jaundice; spider angiomas; ecchymosis; gynecomastia in men; small, nodular liver; ascites; hemorrhoids; testicular atrophyLabs
 Alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis: mild ↑ ALT, AST, usually <500 IU; AST > ALT (ratio >2:3)
Alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis: mild ↑ ALT, AST, usually <500 IU; AST > ALT (ratio >2:3) Extrahepatic obstruction: moderate ↑ ALT/AST to levels <500 IU
Extrahepatic obstruction: moderate ↑ ALT/AST to levels <500 IU Viral, toxic, or ischemic hepatitis: ↑↑ (>500 IU) ALT, AST
Viral, toxic, or ischemic hepatitis: ↑↑ (>500 IU) ALT, AST ↑ Alk phos: extrahepatic obstruction, PBC, and PSC
↑ Alk phos: extrahepatic obstruction, PBC, and PSC ↑ Serum LDH: liver mets, hepatitis, cirrhosis, extrahepatic obstruction, congestive hepatomegaly
↑ Serum LDH: liver mets, hepatitis, cirrhosis, extrahepatic obstruction, congestive hepatomegaly ↑ Serum GGTP: alcoholic liver disease, PBC, PSC
↑ Serum GGTP: alcoholic liver disease, PBC, PSC ↑ Serum bili + urinary bili: hepatitis, hepatocellular jaundice, biliary obstruction
↑ Serum bili + urinary bili: hepatitis, hepatocellular jaundice, biliary obstruction ↓ Serum alb: significant liver disease
↓ Serum alb: significant liver disease ↑ PT: severe liver damage and poor prognosis
↑ PT: severe liver damage and poor prognosis (+) HBsAg: acute or chronic hepatitis B
(+) HBsAg: acute or chronic hepatitis B (+) Antimitochondrial Abs: PBC, chronic hepatitis
(+) Antimitochondrial Abs: PBC, chronic hepatitis ↑ Serum copper, ↓ ceruloplasmin: Wilson’s disease
↑ Serum copper, ↓ ceruloplasmin: Wilson’s disease ↓ α1-Globulins (α1-antitrypsin deficiency), ↑ IgA (alcoholic cirrhosis), ↑ IgM (PBC), ↑ IgG (chronic hepatitis, cryptogenic cirrhosis)
↓ α1-Globulins (α1-antitrypsin deficiency), ↑ IgA (alcoholic cirrhosis), ↑ IgM (PBC), ↑ IgG (chronic hepatitis, cryptogenic cirrhosis) ↑ Serum ferritin, ↑ transferrin saturation: hemochromatosis
↑ Serum ferritin, ↑ transferrin saturation: hemochromatosis ↑ Blood ammonia: hepatocellular dysfunction
↑ Blood ammonia: hepatocellular dysfunction (+) ANA: autoimmune hepatitis
(+) ANA: autoimmune hepatitisImaging
 U/S: detection of gallstones and dilation of CBDs
U/S: detection of gallstones and dilation of CBDs CT abd: detection of mass lesions in liver/pancreas; hepatic fat content; identification of idiopathic hemochromatosis; early dx of Budd-Chiari syndrome, dilation of intrahepatic bile ducts; and detection of varices and splenomegaly
CT abd: detection of mass lesions in liver/pancreas; hepatic fat content; identification of idiopathic hemochromatosis; early dx of Budd-Chiari syndrome, dilation of intrahepatic bile ducts; and detection of varices and splenomegaly Percutaneous liver bx: evaluation of hepatic filling defects; dx of hepatocellular disease or hepatomegaly; evaluation of persistently abnl LFTs; and dx of hemochromatosis, PBC, Wilson’s disease, glycogen storage diseases, chronic hepatitis, autoimmune hepatitis, infiltrative diseases, alcoholic liver disease, drug-induced liver disease, and primary or secondary carcinoma
Percutaneous liver bx: evaluation of hepatic filling defects; dx of hepatocellular disease or hepatomegaly; evaluation of persistently abnl LFTs; and dx of hemochromatosis, PBC, Wilson’s disease, glycogen storage diseases, chronic hepatitis, autoimmune hepatitis, infiltrative diseases, alcoholic liver disease, drug-induced liver disease, and primary or secondary carcinoma Scoring system: Table 6-10
Scoring system: Table 6-10Treatment
 Variable w/etiology. Figure 6-5 summarizes the management of compensated and decompensated cirrhosis.
Variable w/etiology. Figure 6-5 summarizes the management of compensated and decompensated cirrhosis. Liver transplantation: indicated in otherwise healthy pts (age <65 yr) w/sclerosing cholangitis, chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, or PBC, w/prognostic information suggesting <20% chance of survival w/o transplantation. Contraindications to liver transplantation are AIDS, most metastatic malignant neoplasms, active substance abuse, uncontrolled sepsis, and uncontrolled cardiac or pulmonary disease.
Liver transplantation: indicated in otherwise healthy pts (age <65 yr) w/sclerosing cholangitis, chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, or PBC, w/prognostic information suggesting <20% chance of survival w/o transplantation. Contraindications to liver transplantation are AIDS, most metastatic malignant neoplasms, active substance abuse, uncontrolled sepsis, and uncontrolled cardiac or pulmonary disease.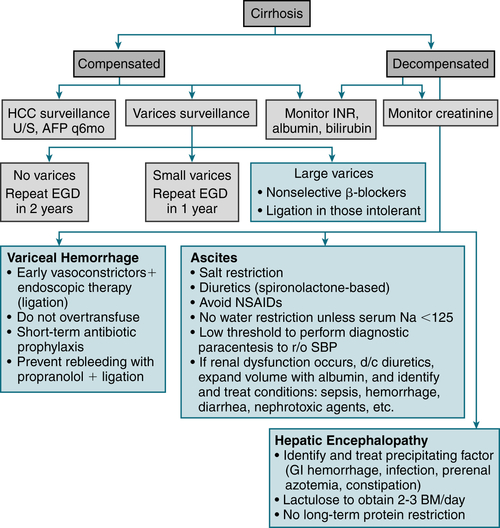
FIGURE 6-5 Summary of the management of compensated and decompensated cirrhosis. (From Goldman L, Schafer AI [eds]: Goldman’s Cecil Medicine, 24th ed. Philadelphia, Saunders, 2012.)
TABLE 6-10
The Two Most Commonly Used Scoring Systems in Cirrhosis
| 1. Child-Turcotte-Pugh (CTP) Score (Range, 5-15) | |||
| Parameters | Points Ascribed | ||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| Ascites | None | Grade 1-2 (or easy to treat) | Grade 3-4 (or refractory) |
| Hepatic encephalopathy | None | Grade 1-2 (or induced by a precipitant) | Grade 3-4 (or spontaneous) |
| Bilirubin (mg/dL) | <2 | 2-3 | >3 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | >3.5 | 2.8-3.5 | <2.8 |
| PT (seconds > control) or INR | <4 | 4-6 | >6 |
| <1.7 | 1.7-2.3 | >2.3 | |
| CTP classification: Child A: score of 5-6; Child B: score of 7-9; Child C: score of 10-15 | |||
| 2. Model of End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) Score (Range, 6-40) | |||
| [0.957 × LN (creatinine in mg/dL) + 0.378 × LN (bilirubin in mg/dL) + 1.12 × LN (INR) + 0.643] × 10 | |||
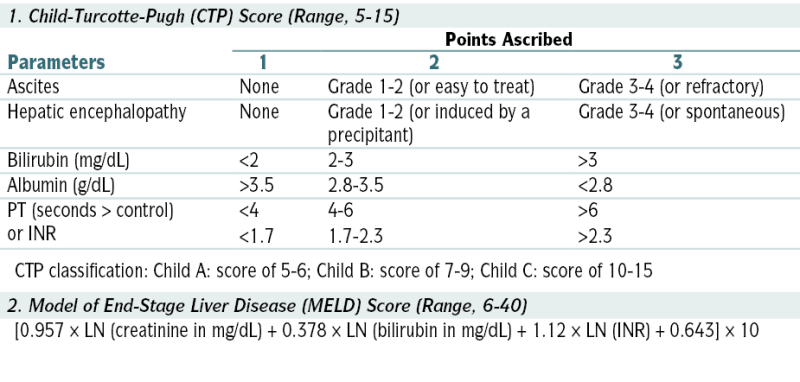
From Goldman L, Schafer AI (eds): Goldman’s Cecil Medicine, 24th ed. Philadelphia, Saunders, 2012.
 Rx of complications of portal HTN (ascites, esophagogastric varices, hepatic encephalopathy, and HRS)
Rx of complications of portal HTN (ascites, esophagogastric varices, hepatic encephalopathy, and HRS)b. Ascites/Paracentesis
Paracentesis
Indications
 Ascites of undetermined etiology
Ascites of undetermined etiology Evaluation for possible peritonitis
Evaluation for possible peritonitis Relief of abd pain and discomfort caused by tense ascites
Relief of abd pain and discomfort caused by tense ascites Relief of dyspnea caused by ↑ diaphragm (from ascites)
Relief of dyspnea caused by ↑ diaphragm (from ascites) Evaluation of possible intra-abd hemorrhage in a pt w/blunt abd trauma
Evaluation of possible intra-abd hemorrhage in a pt w/blunt abd trauma Institution of peritoneal dialysis
Institution of peritoneal dialysisContraindications
 Bleeding disorders, thrombocytopenia (relative contraindication)
Bleeding disorders, thrombocytopenia (relative contraindication) Bowel distention
Bowel distention Infection or surgical scars at the site of needle entry
Infection or surgical scars at the site of needle entry Acute abdomen
Acute abdomen Distended bladder that cannot be emptied w/Foley catheter
Distended bladder that cannot be emptied w/Foley catheterProcedure
Interpretation of Results
 Peritoneal effusion, like pleural effusion, can be subdivided into exudative or transudative on the basis of its characteristics (Fig. 6-6).
Peritoneal effusion, like pleural effusion, can be subdivided into exudative or transudative on the basis of its characteristics (Fig. 6-6). The serum-ascites alb gradient (SAAG) (serum alb level–ascitic fluid alb level) correlates directly w/portal pressure and can also be used to classify ascites (Table 6-11). Pts w/gradients of ≥1.1 g/dL or higher have ascites secondary to portal HTN, and those w/gradients <1.1 g/dL do not; the accuracy of this method is >95%.
The serum-ascites alb gradient (SAAG) (serum alb level–ascitic fluid alb level) correlates directly w/portal pressure and can also be used to classify ascites (Table 6-11). Pts w/gradients of ≥1.1 g/dL or higher have ascites secondary to portal HTN, and those w/gradients <1.1 g/dL do not; the accuracy of this method is >95%.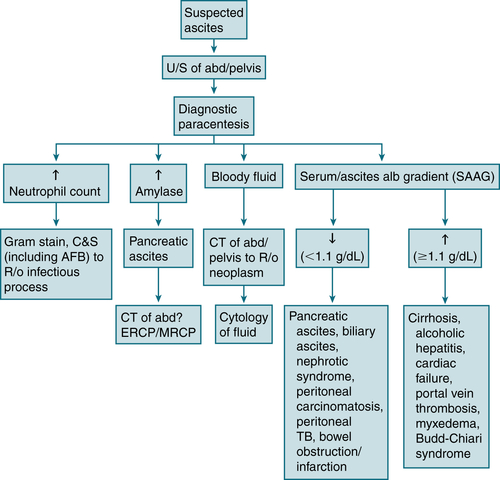
FIGURE 6-6 Diagnostic algorithm for ascites. (From Ferri FF: Ferri’s Best Test: A Practical Guide to Clinical Laboratory Medicine and Diagnostic Imaging, 2nd ed. Philadelphia, Mosby, 2010.)
TABLE 6-11
Causes of Ascites Based on Normal or Diseased Peritoneum and Serum-to-Ascites Albumin Gradient (SAAG)
| Normal Peritoneum | |
| Portal Hypertension (SAAG >1.1 g/dL) | Hypoalbuminemia (SAAG <1.1 g/dL) |
| Hepatic congestion | Nephrotic syndrome |
| Congestive heart failure | Protein-losing enteropathy |
| Constrictive pericarditis | Severe malnutrition with anasarca |
| Tricuspid insufficiency | |
| Budd-Chiari syndrome | |
| Liver disease | Miscellaneous Conditions (SAAG <1.1 g/dL) |
| Cirrhosis | Chylous ascites |
| Alcoholic hepatitis | Pancreatic ascites |
| Fulminant hepatic failure | Bile ascites |
| Massive hepatic metastases | Nephrogenic ascites |
| Urine ascites | |
| Ovarian disease | |
| Diseased Peritoneum (SAAG <1.1 g/dL) | |
| Infections | Other Rare Conditions |
| Bacterial peritonitis | Familial Mediterranean fever |
| Tuberculous peritonitis | Vasculitis |
| Fungal peritonitis | Granulomatous peritonitis |
| HIV-associated peritonitis | Eosinophilic peritonitis |
| Malignant Conditions | |
| Peritoneal carcinomatosis | |
| Primary mesothelioma | |
| Pseudomyxoma peritonei | |
| Hepatocellular carcinoma | |
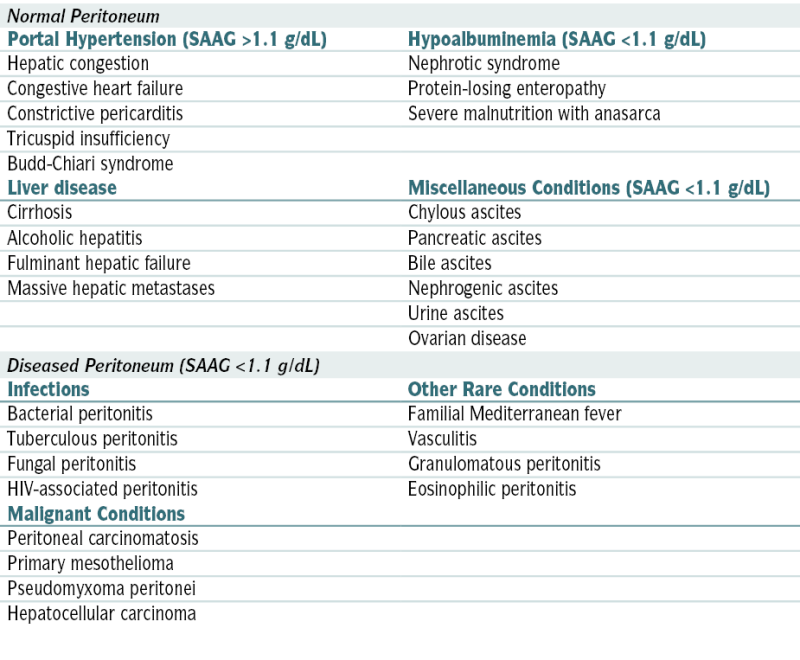
From Vincent JL, Abraham E, Moore FA, et al (eds): Textbook of Critical Care, 6th ed. Philadelphia, Saunders, 2011.
Complications
 Persistent leakage of ascitic fluid
Persistent leakage of ascitic fluid Hypotension and shock
Hypotension and shock Bleeding
Bleeding Perforated bowel
Perforated bowel Abscess formation in area of puncture site
Abscess formation in area of puncture sitec. Varices
 Dilated submucosal veins via portal vein HTN (>10-12 mm Hg), functioning as a shunt between portal and systemic venous circulation; result in severe upper GI hemorrhage (25%-40% cirrhotic pts)
Dilated submucosal veins via portal vein HTN (>10-12 mm Hg), functioning as a shunt between portal and systemic venous circulation; result in severe upper GI hemorrhage (25%-40% cirrhotic pts)Diagnosis
 EGD (Esophagography with barium noninvasive option)
EGD (Esophagography with barium noninvasive option)Labs and W/up
 Anemia (blood loss, nutritional deficiencies, alcohol myelosuppression)
Anemia (blood loss, nutritional deficiencies, alcohol myelosuppression) Thrombocytopenia (hypersplenism, alcohol myelosuppression)
Thrombocytopenia (hypersplenism, alcohol myelosuppression) BUN: often ↑ in setting of upper GI bleeding
BUN: often ↑ in setting of upper GI bleeding Cr: often ↑ by hypovolemia, monitor for hepatorenal syndrome
Cr: often ↑ by hypovolemia, monitor for hepatorenal syndrome Na+: dilutional hyponatremia
Na+: dilutional hyponatremia Heme (+) stools (type/crossmatch: in preparation for blood transfusion)
Heme (+) stools (type/crossmatch: in preparation for blood transfusion) INR/PT and PTT: may be ↑ in liver disease or impairment
INR/PT and PTT: may be ↑ in liver disease or impairment LFTs: ALT/AST may be nl in cirrhotic pts because of fibrosis, ↑ alk phos, direct hyperbilirubinemia possible if cholestatic liver disease
LFTs: ALT/AST may be nl in cirrhotic pts because of fibrosis, ↑ alk phos, direct hyperbilirubinemia possible if cholestatic liver disease Serum alb: Severe liver disease results in hypoalbuminemia.
Serum alb: Severe liver disease results in hypoalbuminemia.Treatment
 Hemorrhage: acute hemodynamic resuscitation (pRBC transfusion, correct coagulopathy/thrombocytopenia), SBP prophylaxis (ceftriaxone or norfloxacin), octreotide 2 to 5 days in conjunction with endoscopic Rx
Hemorrhage: acute hemodynamic resuscitation (pRBC transfusion, correct coagulopathy/thrombocytopenia), SBP prophylaxis (ceftriaxone or norfloxacin), octreotide 2 to 5 days in conjunction with endoscopic Rx Ligation (if ↑ risk hemorrhage: Child Pugh B/C or red wale markings on EGD)
Ligation (if ↑ risk hemorrhage: Child Pugh B/C or red wale markings on EGD) Follow-up surveillance EGD 1 to 3 mo s/p obliteration, then q6-12mo indefinitely
Follow-up surveillance EGD 1 to 3 mo s/p obliteration, then q6-12mo indefinitely Primary prophylaxis: nonselective β-blockers (propranolol 20 mg bid or nadolol 40 mg daily)
Primary prophylaxis: nonselective β-blockers (propranolol 20 mg bid or nadolol 40 mg daily)d. Portal Hypertension
 Portal vein pressure >10 mm Hg
Portal vein pressure >10 mm HgEtiology
 ↑ Resistance to flow (portal/splenic/hepatic vein thrombosis, cirrhosis, schistosomiasis)
↑ Resistance to flow (portal/splenic/hepatic vein thrombosis, cirrhosis, schistosomiasis) ↑ Portal blood flow (splanchnic arterial vasodilation, arterial-portal venous fistulae)
↑ Portal blood flow (splanchnic arterial vasodilation, arterial-portal venous fistulae)Imaging
 Duplex-Doppler U/S (CT/MRI/MRA scanning if results unclear)
Duplex-Doppler U/S (CT/MRI/MRA scanning if results unclear)Treatment
 ↓ HTN directly, minimize volume overload, correct underlying disorders, and prevent complications (most notably SBP and variceal bleeding).
↓ HTN directly, minimize volume overload, correct underlying disorders, and prevent complications (most notably SBP and variceal bleeding).e. Hepatic Encephalopathy (HE)
 Cognitive disturbance via hepatic insufficiency and portosystemic shunting
Cognitive disturbance via hepatic insufficiency and portosystemic shuntingEtiology
 Precipitating factors in pts w/underlying cirrhosis (UGI bleeding, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, analgesic and sedative drugs, sepsis, alkalosis, dietary protein), acute fulminant viral hepatitis, drugs and toxins (INH, acetaminophen-Reye’s syndrome, diclofenac, statins, methyldopa, loratadine, propylthiouracil, lisinopril, labetalol, halothane, carbon tetrachloride, erythromycin, nitrofurantoin, troglitazone), shock or sepsis, fatty liver of pregnancy, metastatic carcinoma, HCC, other (autoimmune hepatitis, ischemic veno-occlusive disease, sclerosing cholangitis, heat stroke, amebic abscesses)
Precipitating factors in pts w/underlying cirrhosis (UGI bleeding, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, analgesic and sedative drugs, sepsis, alkalosis, dietary protein), acute fulminant viral hepatitis, drugs and toxins (INH, acetaminophen-Reye’s syndrome, diclofenac, statins, methyldopa, loratadine, propylthiouracil, lisinopril, labetalol, halothane, carbon tetrachloride, erythromycin, nitrofurantoin, troglitazone), shock or sepsis, fatty liver of pregnancy, metastatic carcinoma, HCC, other (autoimmune hepatitis, ischemic veno-occlusive disease, sclerosing cholangitis, heat stroke, amebic abscesses)Diagnosis
 Requires r/o other causes (medications, metabolic disorders, infectious diseases, intracranial lesions/events). Clinical stages of hepatic encephalopathy are described in Table 6-12. The West Haven criteria is noted here.
Requires r/o other causes (medications, metabolic disorders, infectious diseases, intracranial lesions/events). Clinical stages of hepatic encephalopathy are described in Table 6-12. The West Haven criteria is noted here.West Haven Criteria for Classification of Hepatic Encephalopathy
 Stage 0: nl cognitive function/no abnl detected
Stage 0: nl cognitive function/no abnl detected Stage 1: lack of awareness, euphoria/anxiety, ↓ attention/concentration
Stage 1: lack of awareness, euphoria/anxiety, ↓ attention/concentration Stage 2: lethargy/apathy, altered personality, inappropriate behavior, time disorientation
Stage 2: lethargy/apathy, altered personality, inappropriate behavior, time disorientation Stage 3: somnolence to semistupor, confusion, gross disorientation, bizarre behavior
Stage 3: somnolence to semistupor, confusion, gross disorientation, bizarre behaviorTABLE 6-12
Clinical Stages of Hepatic Encephalopathy
| Stage | Asterixis E | EEG Changes | Clinical Manifestations |
| I (prodrome) | Slight | Minimal | Mild intellectual impairment, disturbed sleep-wake cycle |
| II (impending) | Easily elicited | Usually generalized | Drowsiness, confusion, coma/inappropriate behavior, disorientation, mood swings |
| III (stupor) | Present if patient cooperative | Grossly abnormal slowing of rhythm | Drowsy, unresponsive to verbal commands, markedly confused, delirious, hyperreflexia, positive Babinski’s sign |
| IV (coma) | Usually absent | Appearance of delta waves, decreased amplitudes | Unconscious, decerebrate or decorticate response to pain present (stage IVA) or absent (stage IVB) |
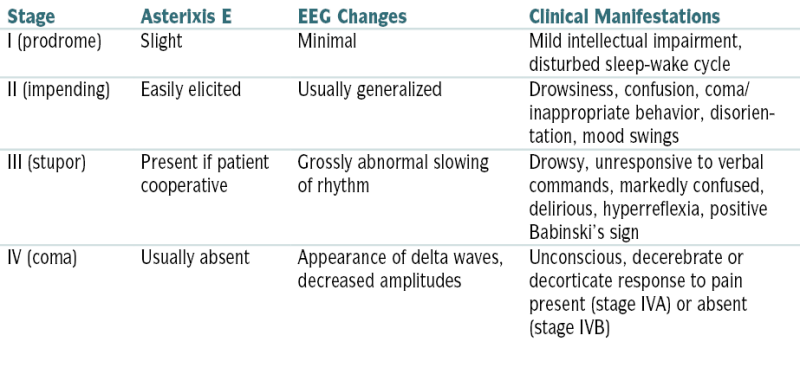
From Fuhrman BP, Zimmerman JJ, Carcillo JA, Clark RS, et al (eds): Pediatric Critical Care, 4th ed. Philadelphia, Saunders, 2011.
 Stage 4: Coma, unable to test mental state
Stage 4: Coma, unable to test mental statePE
 Variable w/the stage and may reveal the following abnormalities:
Variable w/the stage and may reveal the following abnormalities:Labs
 ALT, AST, bili, alk phos, glucose, Ca, electrolytes, BUN, Cr, alb
ALT, AST, bili, alk phos, glucose, Ca, electrolytes, BUN, Cr, alb CBC, Plt count, PT, PTT
CBC, Plt count, PT, PTT Serum/urine toxicology screen (suspected medication/illegal drug use)
Serum/urine toxicology screen (suspected medication/illegal drug use) Blood/urine cultures, U/A
Blood/urine cultures, U/A Venous ammonia level (no correlation w/stage HE but helpful in initial evaluation)
Venous ammonia level (no correlation w/stage HE but helpful in initial evaluation) ABGs
ABGsTreatment
 Identification and Rx of precipitating factors
Identification and Rx of precipitating factors Restriction of protein intake (30-40 g/day) to ↓ toxic protein metabolites
Restriction of protein intake (30-40 g/day) to ↓ toxic protein metabolites ↓ Colonic ammonia production:
↓ Colonic ammonia production: Rx of cerebral edema: Cerebral edema is often present in pts w/acute liver failure, and it accounts for nearly 50% of deaths. Monitoring of ICP by epidural, intraparenchymal, or subdural transducers and Rx of cerebral edema w/mannitol (100-200 mL of 20% solution [0.3-0.4 g/kg of BW]) given by rapid IV infusion is helpful in selected pts (e.g., potential transplantation pts). Dexamethasone and hyperventilation (useful in head injury) are of little value in treating cerebral edema from liver failure.
Rx of cerebral edema: Cerebral edema is often present in pts w/acute liver failure, and it accounts for nearly 50% of deaths. Monitoring of ICP by epidural, intraparenchymal, or subdural transducers and Rx of cerebral edema w/mannitol (100-200 mL of 20% solution [0.3-0.4 g/kg of BW]) given by rapid IV infusion is helpful in selected pts (e.g., potential transplantation pts). Dexamethasone and hyperventilation (useful in head injury) are of little value in treating cerebral edema from liver failure.f. Hepatorenal Syndrome (HRS)
 Type 1: progressive renal function impairment (doubling of initial serum Cr >2.5 mg/dL or 50% reduction initial 24-hr CrCl to <20 mL/min in <2 wk)
Type 1: progressive renal function impairment (doubling of initial serum Cr >2.5 mg/dL or 50% reduction initial 24-hr CrCl to <20 mL/min in <2 wk) Type 2: stable/slowly progressive renal function impairment (assoc w/refractory ascites)
Type 2: stable/slowly progressive renal function impairment (assoc w/refractory ascites)Etiology
 HRS may occur after significant ↓ effective blood volume (paracentesis, GI bleeding, diuretics) or in absence of any precipitating factors.
HRS may occur after significant ↓ effective blood volume (paracentesis, GI bleeding, diuretics) or in absence of any precipitating factors.Diagnosis
 Serum Cr >1.5 mg/dL; with no improvement (↓ ≤1.5 mg/dL) after 2 days diuretic withdrawal + albumin volume expansion
Serum Cr >1.5 mg/dL; with no improvement (↓ ≤1.5 mg/dL) after 2 days diuretic withdrawal + albumin volume expansion Absence of shock, infection, fluid loss, or current Rx w/nephrotoxic drugs
Absence of shock, infection, fluid loss, or current Rx w/nephrotoxic drugs Absence of proteinuria (<500 mg/day) or hematuria (<50 RBC/hpf)
Absence of proteinuria (<500 mg/day) or hematuria (<50 RBC/hpf) Absence of U/S evidence of obstructive uropathy/parenchymal renal disease
Absence of U/S evidence of obstructive uropathy/parenchymal renal disease Urinary Na <10 mmol/L
Urinary Na <10 mmol/LTreatment
 Volume challenge (↑ MAP) then large-volume paracentesis (↑ CO, ↓ renal venous pressure) recommended to distinguish HRS from prerenal azotemia in pts w/FeNa <1% [if prerenal azotemia the ↑ renal perfusion pressure/renal blood flow results in prompt diuresis]; volume challenge can be accomplished by 100 g albumin in 500 mL isotonic saline.
Volume challenge (↑ MAP) then large-volume paracentesis (↑ CO, ↓ renal venous pressure) recommended to distinguish HRS from prerenal azotemia in pts w/FeNa <1% [if prerenal azotemia the ↑ renal perfusion pressure/renal blood flow results in prompt diuresis]; volume challenge can be accomplished by 100 g albumin in 500 mL isotonic saline. Vasopressin analogues may ↑ renal perfusion by reversing splanchnic vasodilation (hallmark HRS); IV NE + albumin and furosemide may also be effective.
Vasopressin analogues may ↑ renal perfusion by reversing splanchnic vasodilation (hallmark HRS); IV NE + albumin and furosemide may also be effective. Rx w/vasoconstrictors 5 to 15 days in attempt to ↓ serum Cr to <1.5 mg/dL:
Rx w/vasoconstrictors 5 to 15 days in attempt to ↓ serum Cr to <1.5 mg/dL: Liver transplantation (most effective Rx) may be indicated pts (<65 yr) w/sclerosing cholangitis, chronic hepatitis w/cirrhosis, or PBC. Contraindications include AIDS, metastatic disease, substance abuse, uncontrolled sepsis, and uncontrolled cardiac/pulmonary disease.
Liver transplantation (most effective Rx) may be indicated pts (<65 yr) w/sclerosing cholangitis, chronic hepatitis w/cirrhosis, or PBC. Contraindications include AIDS, metastatic disease, substance abuse, uncontrolled sepsis, and uncontrolled cardiac/pulmonary disease.g. Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis
Management and Treatment
 Third-generation cephalosporin given until culture report finalized
Third-generation cephalosporin given until culture report finalized If SBP + hepatorenal syndrome, concomitant IV alb ↑ survival rate
If SBP + hepatorenal syndrome, concomitant IV alb ↑ survival rate Repeat paracentesis (48 hr) should reveal ↓ PMN count, will be ↑ if secondary peritonitis
Repeat paracentesis (48 hr) should reveal ↓ PMN count, will be ↑ if secondary peritonitis Rx secondary peritonitis with norfloxacin (TMP-SMX if fluoroquinolone allergy)
Rx secondary peritonitis with norfloxacin (TMP-SMX if fluoroquinolone allergy) Prophylaxis with norfloxacin warranted if low-protein ascitic fluid <1 g/dL (10 g/L)
Prophylaxis with norfloxacin warranted if low-protein ascitic fluid <1 g/dL (10 g/L)h. Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
Diagnosis
H&P
 33% asx at dx; Abd pain may be initial presentation.
33% asx at dx; Abd pain may be initial presentation. Sx underlying cirrhosis often present; new ascites, encephalopathy, jaundice/bleeding, paraneoplastic syndromes (hypoglycemia, erythrocytosis, hypercalcemia, severe diarrhea) may be present.
Sx underlying cirrhosis often present; new ascites, encephalopathy, jaundice/bleeding, paraneoplastic syndromes (hypoglycemia, erythrocytosis, hypercalcemia, severe diarrhea) may be present.Labs
 ↑ LFTs
↑ LFTs ↑ AFP 70% pts (sens 40%-65%; spec 80%-94%)
↑ AFP 70% pts (sens 40%-65%; spec 80%-94%) Paraneoplastic syndromes associated w/HCC may cause hypercalcemia, hypoglycemia, and polycythemia.
Paraneoplastic syndromes associated w/HCC may cause hypercalcemia, hypoglycemia, and polycythemia. HBV DNA level (>10,000 copies/mL) is a strong risk predictor of HCC independent of HBeAg, serum aminotransferase level, and liver cirrhosis.
HBV DNA level (>10,000 copies/mL) is a strong risk predictor of HCC independent of HBeAg, serum aminotransferase level, and liver cirrhosis.Imaging
 U/S (optimal for screening q6mo if ↑ risk), CT scan, or MRI
U/S (optimal for screening q6mo if ↑ risk), CT scan, or MRIStaging and Treatment
 According to the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer staging classification, Rx is determined according to stage.
According to the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer staging classification, Rx is determined according to stage. Early stage: Liver transplantation is the most effective Rx.
Early stage: Liver transplantation is the most effective Rx. Ablation (via radiofrequency, transarterial hepatic artery chemoembolization, percutaneous ethanol injection) can be used as bridge to transplantation.
Ablation (via radiofrequency, transarterial hepatic artery chemoembolization, percutaneous ethanol injection) can be used as bridge to transplantation. Nonresectable HCC: sorafenib
Nonresectable HCC: sorafenibi. Fulminant Hepatic Failure (FHF)
 Classification:
Classification: Etiologies: acetaminophen overdose (most common cause), infectious (HepA-E, HSV, CMV, EBV, PB19, varicella), drugs (INH, sulfa, NSAIDs, MDMA, cocaine), autoimmune hepatitis
Etiologies: acetaminophen overdose (most common cause), infectious (HepA-E, HSV, CMV, EBV, PB19, varicella), drugs (INH, sulfa, NSAIDs, MDMA, cocaine), autoimmune hepatitis Rx: Recognition should prompt immediate referral to liver transplantation center (1-yr survival 73%). Table 6-13 summarizes the management of fulminant hepatic failure.
Rx: Recognition should prompt immediate referral to liver transplantation center (1-yr survival 73%). Table 6-13 summarizes the management of fulminant hepatic failure.j. Liver Abscess
Etiology
 Pyogenic abscess: polymicrobial (streptococcal species [37%], E. coli [33%], Klebsiella pneumoniae [18%], Pseudomonas, Proteus, Bacteroides)
Pyogenic abscess: polymicrobial (streptococcal species [37%], E. coli [33%], Klebsiella pneumoniae [18%], Pseudomonas, Proteus, Bacteroides) Sources of pyogenic abscess: biliary disease w/cholangitis, gallbladder disease, diverticulitis, appendicitis, penetrating wounds, hematogenous
Sources of pyogenic abscess: biliary disease w/cholangitis, gallbladder disease, diverticulitis, appendicitis, penetrating wounds, hematogenous Amebic abscess: E. histolytica. Transmission is through fecal-oral contamination w/invasion of intestinal mucosa and portal system.
Amebic abscess: E. histolytica. Transmission is through fecal-oral contamination w/invasion of intestinal mucosa and portal system.TABLE 6-13
Management of Fulminant Hepatic Failure
From Fuhrman BP, Zimmerman JJ, Carcillo JA, Clark RS, et al (eds): Pediatric Critical Care, 4th ed. Philadelphia, Saunders, 2011.
Diagnosis
H&P
 RUQ abd pain, fever, nausea, cough w/pleuritic chest pain, anorexia, jaundice
RUQ abd pain, fever, nausea, cough w/pleuritic chest pain, anorexia, jaundiceLabs
 Leukocytosis, + blood cultures (50%), ↑ INR (70%), ↑ alk phos (>90%), ↑ ALT/AST (50%), + stool samples for E. histolytica (10%-15%). Serologic testing for E. histolytica does not differentiate acute from prior infection.
Leukocytosis, + blood cultures (50%), ↑ INR (70%), ↑ alk phos (>90%), ↑ ALT/AST (50%), + stool samples for E. histolytica (10%-15%). Serologic testing for E. histolytica does not differentiate acute from prior infection.Imaging
 Abdominal CT (imaging study of choice)
Abdominal CT (imaging study of choice) CXR is abnl in 50% of cases: ↑ right hemidiaphragm, pleural effusion, subdiaphragmatic air fluid levels.
CXR is abnl in 50% of cases: ↑ right hemidiaphragm, pleural effusion, subdiaphragmatic air fluid levels. U/S (80%-95% sensitivity)
U/S (80%-95% sensitivity) CT or U/S-guided aspiration (50% sterile) in suspected pyogenic abscess.
CT or U/S-guided aspiration (50% sterile) in suspected pyogenic abscess.Treatment
 Medical management (amebic liver abscess) versus percutaneous drainage under CT or U/S guidance + IV abx (pyogenic liver abscess)
Medical management (amebic liver abscess) versus percutaneous drainage under CT or U/S guidance + IV abx (pyogenic liver abscess) Empiric broad spectrum abx recommended until culture results available:
Empiric broad spectrum abx recommended until culture results available:6. Vascular Disorders of the Liver
a. Budd-Chiari Syndrome
 Primary BCS = endoluminal obstruction (thromboses/webs)
Primary BCS = endoluminal obstruction (thromboses/webs) Secondary BCS = obstruction from nonvascular invasion (malignant/parasitic masses) or extrinsic compression (tumor, abscess, cysts)
Secondary BCS = obstruction from nonvascular invasion (malignant/parasitic masses) or extrinsic compression (tumor, abscess, cysts)Etiology
 Hypercoagulable state and/or underlying risk factor for thromboses (80%), myeloproliferative disease (50%), Behçet’s disease, infection, malignancy (<5%), PNH, abd trauma, UC, celiac disease, dacarbazine
Hypercoagulable state and/or underlying risk factor for thromboses (80%), myeloproliferative disease (50%), Behçet’s disease, infection, malignancy (<5%), PNH, abd trauma, UC, celiac disease, dacarbazineDiagnosis
H&P
 Fulminant/acute (uncommon): severe RUQ abd pain, fever, N/V, jaundice, hepatomegaly, ascites, ↑ serum aminotransferases, ↓ coagulation factors, and encephalopathy. Early recognition and Rx are essential to survival.
Fulminant/acute (uncommon): severe RUQ abd pain, fever, N/V, jaundice, hepatomegaly, ascites, ↑ serum aminotransferases, ↓ coagulation factors, and encephalopathy. Early recognition and Rx are essential to survival. Subacute/chronic (more common): vague abd discomfort, gradual progression to hepatomegaly, portal HTN w/ or w/o cirrhosis; late-onset ascites, LE edema, esophageal varices, splenomegaly, coagulopathy, HRS; asx (15% cases)
Subacute/chronic (more common): vague abd discomfort, gradual progression to hepatomegaly, portal HTN w/ or w/o cirrhosis; late-onset ascites, LE edema, esophageal varices, splenomegaly, coagulopathy, HRS; asx (15% cases) Ascites protein content > 2.5 g/dL and SAAG ≥ 1.1 g/dL = BCS + cardiac disease
Ascites protein content > 2.5 g/dL and SAAG ≥ 1.1 g/dL = BCS + cardiac diseaseImaging
 Color and pulsed Doppler U/S: (sens >85%) first-line test
Color and pulsed Doppler U/S: (sens >85%) first-line test MRI w/gadolinium contrast (second-line test)
MRI w/gadolinium contrast (second-line test) Venography (gold standard); useful if difficult case or precise delineation of venous stenoses required
Venography (gold standard); useful if difficult case or precise delineation of venous stenoses requiredTreatment
 Lifelong anticoagulation INR 2 to 3 (LMWH → warfarin [Coumadin]) recommended for all
Lifelong anticoagulation INR 2 to 3 (LMWH → warfarin [Coumadin]) recommended for all OCPs contraindicated
OCPs contraindicated Hepatic vein/IVC angioplasty w/ or w/o stenting if refractory to anticoagulation
Hepatic vein/IVC angioplasty w/ or w/o stenting if refractory to anticoagulation If unresponsive to medical Rx, TIPS insertion recommended
If unresponsive to medical Rx, TIPS insertion recommended If unresponsive to TIPS, liver transplant indicated (5-yr survival 70%)
If unresponsive to TIPS, liver transplant indicated (5-yr survival 70%)b. Portal Vein Thrombosis
Etiology
 In adults: cirrhosis (common cause), hypercoagulable states, inflammatory diseases, complications of medical intervention: ambulatory dialysis, chemoembolization, liver transplantation, partial hepatectomy, scleroRx, splenectomy, TIPS, infections (appendicitis, diverticulitis, cholecystitis)
In adults: cirrhosis (common cause), hypercoagulable states, inflammatory diseases, complications of medical intervention: ambulatory dialysis, chemoembolization, liver transplantation, partial hepatectomy, scleroRx, splenectomy, TIPS, infections (appendicitis, diverticulitis, cholecystitis) In children: umbilical sepsis
In children: umbilical sepsisDiagnosis
H&P
 May result in portal HTN → esophageal/GI varices; upper GI hemorrhage (hematemesis or melena) can result from esophageal varices.
May result in portal HTN → esophageal/GI varices; upper GI hemorrhage (hematemesis or melena) can result from esophageal varices. If abd pain is present, mesenteric venous thrombosis should be suspected.
If abd pain is present, mesenteric venous thrombosis should be suspected.Imaging
 Abd U/S or MRI may show the portal vein thrombosis.
Abd U/S or MRI may show the portal vein thrombosis. Esophagogastroscopy (esophageal varices)
Esophagogastroscopy (esophageal varices)Treatment
 Anticoagulation
Anticoagulation Variceal scleroRx or banding
Variceal scleroRx or banding Surgical mesocaval or splenorenal shunt
Surgical mesocaval or splenorenal shunt7. Hepatic Cysts
 Simple cysts (uniform thin wall, no echoic structures) asx, usually occur more in women
Simple cysts (uniform thin wall, no echoic structures) asx, usually occur more in women Cysts <4 cm rarely of clinical significance
Cysts <4 cm rarely of clinical significance If sx (nausea/abd discomfort), r/o cystadenoma (irregularity/internal echoes) via U/S
If sx (nausea/abd discomfort), r/o cystadenoma (irregularity/internal echoes) via U/S Rx: Laparoscopic fenestration (simple needle aspiration assoc ↑ recurrence) if cystadenoma as malignant transformation to cystadenocarcinoma possible
Rx: Laparoscopic fenestration (simple needle aspiration assoc ↑ recurrence) if cystadenoma as malignant transformation to cystadenocarcinoma possible8. Hepatic Adenoma (HA)
 Sheets of benign hepatocytes without biliary structures/nonparenchymal liver cells
Sheets of benign hepatocytes without biliary structures/nonparenchymal liver cells Assoc with use of OCPs
Assoc with use of OCPs Rx: Resection of HA >5 cm or if pregnancy considered, discontinuation OCP with follow-up imaging if <5 cm
Rx: Resection of HA >5 cm or if pregnancy considered, discontinuation OCP with follow-up imaging if <5 cmG. Metabolic Liver Disease
1. Alcoholic Hepatitis
 Alcohol-induced liver disease: ranges from steatosis (fatty liver) → cirrhosis
Alcohol-induced liver disease: ranges from steatosis (fatty liver) → cirrhosisLabs
 ↑ AST (2-6× nl); [AST/ALT ratio 2:3 typical, AST >500/ALT >200 rare]
↑ AST (2-6× nl); [AST/ALT ratio 2:3 typical, AST >500/ALT >200 rare] Alk phos nl to ↑, bili nl to ↑↑↑, ↑ PT, ↓ GGT
Alk phos nl to ↑, bili nl to ↑↑↑, ↑ PT, ↓ GGT ↑ CRP, hypophosphatemia, hypomagnesia, CBC (possible leukocytosis w/bandemia or anemia)
↑ CRP, hypophosphatemia, hypomagnesia, CBC (possible leukocytosis w/bandemia or anemia) Carbohydrate-deficient transferring (CDT) = reliable marker chronic alcoholism
Carbohydrate-deficient transferring (CDT) = reliable marker chronic alcoholism Screen to r/o: HbsAg, anti-Hep C, ferritin/transferrin sat, AFP, liver biopsy if necessary
Screen to r/o: HbsAg, anti-Hep C, ferritin/transferrin sat, AFP, liver biopsy if necessaryImaging
 U/S (macrovascular steatosis, hepatocyte ballooning/necrosis, Mallory’s bodies, perivenular fibrosis, portal/lobular inflammation)
U/S (macrovascular steatosis, hepatocyte ballooning/necrosis, Mallory’s bodies, perivenular fibrosis, portal/lobular inflammation)Prognosis
 Maddrey discriminant function (MDF) score: 4.6× (prothrombin time [s] – control prothrombin time [s]) + total bili (mg/dL)
Maddrey discriminant function (MDF) score: 4.6× (prothrombin time [s] – control prothrombin time [s]) + total bili (mg/dL) MDF ≥32 (severe alcoholic hepatitis): short-term mortality risk 50%
MDF ≥32 (severe alcoholic hepatitis): short-term mortality risk 50% Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) score (prognostic index based on serum total bili, Cr, and INR): similar implications as MDF score
Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) score (prognostic index based on serum total bili, Cr, and INR): similar implications as MDF scoreTreatment
2. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Diagnosis
 Abdominal imaging via U/S, CT, MRI (reveal steatosis but not fibrosis)
Abdominal imaging via U/S, CT, MRI (reveal steatosis but not fibrosis) Liver biopsy (confirms NASH)
Liver biopsy (confirms NASH)Treatment
 Lifestyle change, wt loss; monitor LFTs q3-6mo; metformin currently investigational Rx
Lifestyle change, wt loss; monitor LFTs q3-6mo; metformin currently investigational Rx3. Hereditary Hemochromatosis
Diagnosis
H&P
 ↑ Skin pigmentation, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, hepatic tenderness, testicular atrophy (↓ libido 50% men), amenorrhea (25% women), alopecia, gynecomastia/ascites, fatigue, joint pain, new-onset diabetes, cardiomyopathy, arthropathy
↑ Skin pigmentation, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, hepatic tenderness, testicular atrophy (↓ libido 50% men), amenorrhea (25% women), alopecia, gynecomastia/ascites, fatigue, joint pain, new-onset diabetes, cardiomyopathy, arthropathyLabs
 Transferrin saturation (iron/TIBC) = best screening test; values >45% indicate need for further testing; values >52% in men and >50% in women suggest hemochromatosis. Serum ferritin is helpful but may be ↑ in inflammatory conditions or malignancy.
Transferrin saturation (iron/TIBC) = best screening test; values >45% indicate need for further testing; values >52% in men and >50% in women suggest hemochromatosis. Serum ferritin is helpful but may be ↑ in inflammatory conditions or malignancy. ↑ AST, ALT, alk phos
↑ AST, ALT, alk phos Hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia ↓ testosterone, LH, FSH
↓ testosterone, LH, FSH Measurement of hepatic iron index (hepatic iron concentration divided by age) in liver bx specimen can confirm dx.
Measurement of hepatic iron index (hepatic iron concentration divided by age) in liver bx specimen can confirm dx. Genetic testing (HFE genotyping for C282Y/H63D mutations) useful in pts w/liver disease + suspected iron overload (transferrin saturation >40%). Genetic testing should not be performed as part of initial routine evaluation for hereditary hemochromatosis. Once pt confirmed, first-degree relatives should also be screened. Figure 6-7 describes an algorithm for evaluation of possible hereditary hemochromatosis in a person with (−) family hx.
Genetic testing (HFE genotyping for C282Y/H63D mutations) useful in pts w/liver disease + suspected iron overload (transferrin saturation >40%). Genetic testing should not be performed as part of initial routine evaluation for hereditary hemochromatosis. Once pt confirmed, first-degree relatives should also be screened. Figure 6-7 describes an algorithm for evaluation of possible hereditary hemochromatosis in a person with (−) family hx.
FIGURE 6-7 Algorithm for elevation of possible hereditary hemochromatosis in a person with a negative family history. (From Goldman L, Schafer AI [eds]: Goldman’s Cecil Medicine, 24th ed. Philadelphia, Saunders, 2012.)
 Pts >40 yr old or serum ferritin level >1000 μg/L ↑ risk cirrhosis
Pts >40 yr old or serum ferritin level >1000 μg/L ↑ risk cirrhosisImaging
 CT or MRI of the liver: useful to r/o other causes + may show iron overload in the liver
CT or MRI of the liver: useful to r/o other causes + may show iron overload in the liverTreatment
 Weekly phlebotomies of 1 to 2 U of blood (each w/ ≈250 mg iron) should be continued until ferritin level <50 ng/mL and transferrin saturation <30%. Subsequent phlebotomies PRN to maintain a transferrin saturation <50% and a ferritin level <100 ng/mL.
Weekly phlebotomies of 1 to 2 U of blood (each w/ ≈250 mg iron) should be continued until ferritin level <50 ng/mL and transferrin saturation <30%. Subsequent phlebotomies PRN to maintain a transferrin saturation <50% and a ferritin level <100 ng/mL. Deferoxamine 0.5 to 1 g IM qd or 20 mg SC constant infusion (iron chelating agent) is generally reserved for pts w/severe hemochromatosis w/diffuse organ involvement (liver disease, heart disease) and when phlebotomy is not possible.
Deferoxamine 0.5 to 1 g IM qd or 20 mg SC constant infusion (iron chelating agent) is generally reserved for pts w/severe hemochromatosis w/diffuse organ involvement (liver disease, heart disease) and when phlebotomy is not possible.4. α1-Antitrypsin Deficiency
Diagnosis
 Serum α1-antitrypsin level, genetic analysis for mutation/allele involvement PFTs (obstructive pattern)
Serum α1-antitrypsin level, genetic analysis for mutation/allele involvement PFTs (obstructive pattern) CXR (emphysematous change at lung bases)
CXR (emphysematous change at lung bases) Chest CT (panacinar emphysema)
Chest CT (panacinar emphysema)H&P
 Early-onset, severe, lower-lobe predominant panacinar emphysema (± bronchiectasis)
Early-onset, severe, lower-lobe predominant panacinar emphysema (± bronchiectasis) Sx similar to “typical” COPD presentation (dyspnea, cough, sputum production)
Sx similar to “typical” COPD presentation (dyspnea, cough, sputum production) Liver involvement (neonatal cholestasis, cirrhosis, primary hepatocarcinoma)
Liver involvement (neonatal cholestasis, cirrhosis, primary hepatocarcinoma) Dermatologic manifestation (panniculitis) to 85% deficit in plasma α1-antitrypsin
Dermatologic manifestation (panniculitis) to 85% deficit in plasma α1-antitrypsinTreatment
 Manage acute exacerbations similar to “typical” COPD
Manage acute exacerbations similar to “typical” COPD Avoid smoking/factors that would worsen COPD
Avoid smoking/factors that would worsen COPD5. Wilson’s Disease
 Rare (1/30,000 newborns) autosomal recessive ↑ hepatic uptake and ↓ biliary excretion of copper
Rare (1/30,000 newborns) autosomal recessive ↑ hepatic uptake and ↓ biliary excretion of copperDiagnosis
 Usually pts < 45 yr old; ↓ ceruloplasmin, ↑ urinary copper excretion
Usually pts < 45 yr old; ↓ ceruloplasmin, ↑ urinary copper excretion ↑ LFTs
↑ LFTs Liver biopsy (excessive intrahepatic copper)
Liver biopsy (excessive intrahepatic copper) Kayser-Fleischer rings
Kayser-Fleischer rings Neuropsychiatric abnormalities (copper deposition in brain)
Neuropsychiatric abnormalities (copper deposition in brain)Treatment
 Chelating agents (trientine, penicillamine) and low-copper diet
Chelating agents (trientine, penicillamine) and low-copper dietH. Disorders of Gallbladder
1. Cholelithiasis
Epidemiology and Demographics
 Incidence ↑ with age (highest in 40s-50s)
Incidence ↑ with age (highest in 40s-50s) Female sex, pregnancy, FHx, obesity, ileal disease, OCPs, DM
Female sex, pregnancy, FHx, obesity, ileal disease, OCPs, DM 90% gallstones = cholesterol/mixed type, black-pigmented stones assoc with chronic hemolytic disease/cirrhosis, brown-pigmented stones assoc with biliary tract infection
90% gallstones = cholesterol/mixed type, black-pigmented stones assoc with chronic hemolytic disease/cirrhosis, brown-pigmented stones assoc with biliary tract infectionPhysical Exam and Clinical Findings
 (60%-80%) asx
(60%-80%) asx If biliary colic: episodic, cramping RUQ pain, may radiate to back/right shoulder
If biliary colic: episodic, cramping RUQ pain, may radiate to back/right shoulderDiagnosis
 Labs nl (unless obstruction: ↑ alk phos, ↑ bili)
Labs nl (unless obstruction: ↑ alk phos, ↑ bili) U/S; if unclear HIDA scan (90% accuracy)
U/S; if unclear HIDA scan (90% accuracy)Treatment
2. Acute Cholecystitis
 Inflammation of the gallbladder
Inflammation of the gallbladderEtiology
 Gallstones (>95% of cases), ischemic damage to the gallbladder, critically ill pt (acalculous cholecystitis), infectious agents (especially in AIDS pts [CMV, Cryptosporidium]), bile duct stricture, neoplasia
Gallstones (>95% of cases), ischemic damage to the gallbladder, critically ill pt (acalculous cholecystitis), infectious agents (especially in AIDS pts [CMV, Cryptosporidium]), bile duct stricture, neoplasiaDiagnosis
H&P
 Pain/tenderness of right hypochondrium/epigastrium; possibly radiating to infrascapular region. RUQ palpation elicits marked tenderness + stoppage of inspired breath (Murphy’s sign). Guarding, fever (33%), jaundice (25%-50%), palpable gallbladder (20%)
Pain/tenderness of right hypochondrium/epigastrium; possibly radiating to infrascapular region. RUQ palpation elicits marked tenderness + stoppage of inspired breath (Murphy’s sign). Guarding, fever (33%), jaundice (25%-50%), palpable gallbladder (20%) N/V (>70%), fever and chills (>25%), and ingestion of large, fatty meals before onset of pain in the epigastrium and RUQ
N/V (>70%), fever and chills (>25%), and ingestion of large, fatty meals before onset of pain in the epigastrium and RUQLabs
 Leukocytosis (12,000-20,000) >70% of pts, alk phos, ALT, AST, bili; bili elevation >4 mg/dL is unusual and suggests presence of choledocholithiasis.
Leukocytosis (12,000-20,000) >70% of pts, alk phos, ALT, AST, bili; bili elevation >4 mg/dL is unusual and suggests presence of choledocholithiasis.Imaging
 U/S of gallbladder: presence of stones, dilated gallbladder w/thickened wall and surrounding edema, fluid stranding
U/S of gallbladder: presence of stones, dilated gallbladder w/thickened wall and surrounding edema, fluid stranding HIDA scan: sensitivity and specificity >90% for acute cholecystitis. Test is reliable only when bili is <5 mg/dL. (+) Test = absence of gallbladder filling within 60 min after the administration of tracer.
HIDA scan: sensitivity and specificity >90% for acute cholecystitis. Test is reliable only when bili is <5 mg/dL. (+) Test = absence of gallbladder filling within 60 min after the administration of tracer. CT of abd: in cases of suspected abscess, neoplasm, or pancreatitis
CT of abd: in cases of suspected abscess, neoplasm, or pancreatitisTreatment
 Cholecystectomy
Cholecystectomy Conservative management w/IV fluids and abx (ampicillin-sulbactam 3 g IV q6h or piperacillin-tazobactam 4.5 g IV q8h) may be justified in some high-risk pts to convert an emergency procedure into an elective one w/lower mortality.
Conservative management w/IV fluids and abx (ampicillin-sulbactam 3 g IV q6h or piperacillin-tazobactam 4.5 g IV q8h) may be justified in some high-risk pts to convert an emergency procedure into an elective one w/lower mortality. ERCP w/sphincterectomy and stone extraction can be performed in conjunction w/laparoscopic cholecystectomy for pts w/choledocholithiasis; 7% to 15% of pts w/cholelithiasis also have stones in the CBD.
ERCP w/sphincterectomy and stone extraction can be performed in conjunction w/laparoscopic cholecystectomy for pts w/choledocholithiasis; 7% to 15% of pts w/cholelithiasis also have stones in the CBD.