38. Gardner Syndrome
Definition
Gardner syndrome is a type of familial adenomatous polyposis that also has extracolonic manifestations, including intestinal polyposis, desmoids, osteomas, and epidermoid cysts. The disorder is inherited via an autosomal dominant pattern.
Incidence
The incidence of Gardner syndrome is about 1:7000 live births, of which 80% are of mendelian dominant inheritance and 20% are spontaneous mutations.
Etiology
Gardner syndrome develops as the result of five mutations:
1. Mutation of the APC gene
2. Loss of DNA methylation
3. RAS gene mutation on chromosome 12
4. Deletion of the colon cancer (DCC) gene on chromosome 18
5. TP53 gene mutation on chromosome 17
Signs and Symptoms
• Adrenal carcinoma
• Biliary duct carcinoma
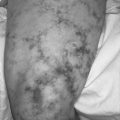
• Congenital hyperpigmentation of the retinal pigment epithelium
• Cushing syndrome
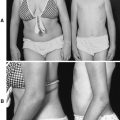
• Desmoid tumor
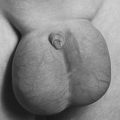
• Epidermal cysts
• Gastric carcinoma
• Hepatoblastoma
• Impacted teeth
• Multiple colonic polyps
• Multiple duodenal polyps
• Multiple gastric polyps
• Osteoma
• Osteosarcoma
• Periampullary carcinoma
• Root abnormalities
• Sebaceous cysts
• Skin fibromas
• Supernumerary teeth
• Thyroid carcinoma
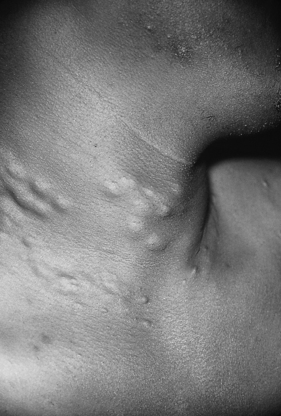 |
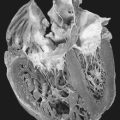
| Gardner Syndrome. Multiple epidermoid cysts are present in this patient with adenomatous colonic polyps. |
Medical Management
The most direct and appropriate treatment for Gardner syndrome is surgical colectomy because 65% of patients have carcinoma at the time of diagnosis.
Surgical Procedures for Gardner Syndrome
• Proctocolectomy with ileostomy
• Total colectomy with ileorectal anastomosis
• Proctocolectomy with ileal pouch anal anastomosis
Treatment Goals for Gardner Syndrome
• Treat or eliminate colorectal cancer risk
• Preserve/maintain continence and defecation abilities
• Preserve sexual organ innervation
• Reduce mortality and morbidity
Sulindac appears to produce rectal polyp regression for patients who have had total colectomy. Doxorubicin with dacarbazine also reduces polyps following colectomy.
Desmoid polyps of the abdominal wall or extra-abdominal manifestations of Gardner syndrome are best treated with sulindac, tamoxifen, or a combination of the two medications.
Complications
• Bowel obstruction
• CHRPE (congenital hypertrophy of retinal pigmented epithelium)
• Colon perforation
• Dental abnormalities
• Desmoid tumor
• Duodenal polyps
• Epidermoid cysts
• Gastric polyps
• Hemorrhage
• Hepatoblastoma
• Osteoma
• Thyroid cancer
Anesthesia Implications
A patient with Gardner syndrome may present with low hemoglobin concentrations and may also lose greater amounts of blood than typical for a given operation. The patient is more apt to require blood transfusion(s).
Dental abnormalities may produce jaw pain. Osteomas may develop in the mandible. Direct laryngoscopy must be undertaken with caution as well as gentleness to minimize airway trauma.
As with any extensive bowel/lower abdominal surgical procedure, fluid resuscitation is a critical issue. Preoperative bowel cleaning preparation combined with fluid intake restrictions can produce significant dehydration. The patient may then be falsely hemoconcentrated.
Thyroid cancer may cause significant alteration to the patient’s airway anatomy.
Hepatoblastoma, if present, may alter the metabolism of many anesthesia-related medications, from opioid analgesics to nondepolarizing muscle relaxants. Residual effects of any of these medications, singularly or in combination, may result in the need for postoperative ventilatory support.