Fungal infections
Fungal infection in humans is common and mainly due to two groups of fungi:
These are usually confined to the stratum corneum, but deep mycoses invade other tissues (p. 61). Pityriasis versicolor, due to the yeast Malassezia (previously Pityrosporum ovale) is described on page 42.
Dermatophyte infections
Thirty species are pathogenic in humans. Zoophilic species (transmitted to humans from animals), e.g. Trichophyton verrucosum (Fig. 1), produce more inflammation than anthropophilic (human only) species.
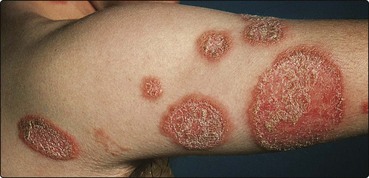
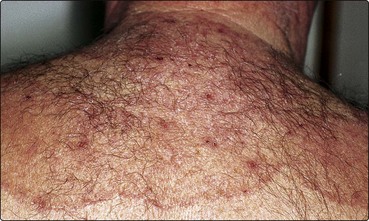
Fig. 1 Tinea corporis.
The infection is due to animal ringworm (T. verrucosum) and shows intense inflammation.
Pathology
Dermatophytes inhabit keratin as branching hyphae, identifiable on microscopy. Skin scrapings, placed on a slide with 10% aqueous potassium hydroxide (to separate the keratinocytes) and a coverslip, are examined microscopically for hyphae (p. 20). The dermatophyte is identified by culturing the scrapings on medium (e.g. Sabouraud’s) for 3 weeks.
Clinical presentation
 Tinea corporis (trunk and limbs). Single or multiple plaques, with scaling and erythema especially at the edges, characterize this presentation. The lesions enlarge slowly, with central clearing, leaving a ring pattern, hence ‘ringworm’ (Figs 1 and 2). Pustules or vesicles may be seen.
Tinea corporis (trunk and limbs). Single or multiple plaques, with scaling and erythema especially at the edges, characterize this presentation. The lesions enlarge slowly, with central clearing, leaving a ring pattern, hence ‘ringworm’ (Figs 1 and 2). Pustules or vesicles may be seen.
 Tinea cruris (groin). This is more common in men and is often seen in athletes (‘jock itch’), who may also have tinea pedis. It spreads to the upper thigh but rarely involves the scrotum. The advancing edge may be scaly, pustular or vesicular. Causative organisms are shown in Table 1.
Tinea cruris (groin). This is more common in men and is often seen in athletes (‘jock itch’), who may also have tinea pedis. It spreads to the upper thigh but rarely involves the scrotum. The advancing edge may be scaly, pustular or vesicular. Causative organisms are shown in Table 1.
 Tinea incognito. Fungal infection can be modified in appearance and spread by the anti-inflammatory effect of a topical steroid.
Tinea incognito. Fungal infection can be modified in appearance and spread by the anti-inflammatory effect of a topical steroid.
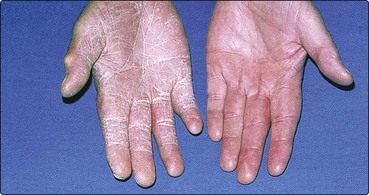
 Tinea manuum (hand). Typically, this appears as a unilateral, diffuse powdery scaling of the palm (Fig. 3). Trichophyton rubrum is often the cause. Tinea pedis may coexist.
Tinea manuum (hand). Typically, this appears as a unilateral, diffuse powdery scaling of the palm (Fig. 3). Trichophyton rubrum is often the cause. Tinea pedis may coexist.
 Tinea capitis (scalp/hair). See pages 66 and 114.
Tinea capitis (scalp/hair). See pages 66 and 114.
Table 1 Superficial mycoses: causative organisms and differential diagnosis
| Area | Commonest organism | Differential diagnosis |
|---|---|---|
| Body/limbs (corporis) | T. verrucosum, M. canis, T. rubrum | Discoid eczema, psoriasis, pityriasis rosea |
| Feet (pedis) | T. rubrum, T. interdigitale, E. floccosum | Contact dermatitis, psoriasis, pompholyx, erythrasma |
| Groin (cruris) | T. rubrum, E. floccosum, T. interdigitale | Intertrigo, candidiasis, erythrasma |
| Hand (manuum) | T. rubrum | Chronic eczema, psoriasis, granuloma annulare |
| Nail (unguium) | T. rubrum, T. interdigitale | Psoriasis, trauma, candidiasis |
| Scalp (capitis) | M. canis, M. audouinii, T. tonsurans, T. schoenleinii | Alopecia areata, psoriasis, seborrhoeic eczema, furunculosis |
Athlete’s foot (p. 114) is common in adults (especially young men), rare in children and predisposed to by communal washing, swimming baths, occlusive footwear and hot weather. Itchy interdigital maceration, usually of the fourth/fifth toeweb space, is most frequent, but diffuse ‘moccasin’ involvement is seen. Recurrent vesicles also occur, sometimes with pompholyx as an id reaction. The commonest organisms are T. rubrum, T. mentagrophytes var. interdigitale and Epidermophyton floccosum.
The differential diagnoses of superficial mycoses are shown Table 1. Microscopy and culture of skin scrapings are often helpful. Wood’s ultraviolet light examination is used for tinea capitis, especially for screening during outbreaks. Hair infected by Microsporum audouinii and M. canis fluoresces green, but Trichophyton tonsurans does not fluoresce.
Candida albicans infection
Clinical presentation
 Genital. Thrush commonly appears as an itchy, sore vulvovaginitis. White plaques adhere to inflamed mucous membranes, and a white vaginal discharge may occur. Males develop similar changes on the penis. It can be spread by sexual intercourse.
Genital. Thrush commonly appears as an itchy, sore vulvovaginitis. White plaques adhere to inflamed mucous membranes, and a white vaginal discharge may occur. Males develop similar changes on the penis. It can be spread by sexual intercourse.
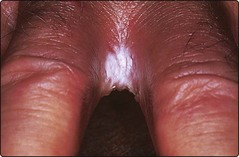
 Intertrigo. Superinfection with C. albicans, and often also with bacteria, gives a moist, glazed and macerated appearance to the submammary, axillary or inguinal body folds. The interdigital clefts are involved (Fig. 4) in wet workers who do not dry their hands properly.
Intertrigo. Superinfection with C. albicans, and often also with bacteria, gives a moist, glazed and macerated appearance to the submammary, axillary or inguinal body folds. The interdigital clefts are involved (Fig. 4) in wet workers who do not dry their hands properly.
 Mucocutaneous candidiasis. This rare, sometimes inherited disorder of immune deficiency starts in infancy. Chronic C. albicans intertrigo with nail and mouth infections is seen.
Mucocutaneous candidiasis. This rare, sometimes inherited disorder of immune deficiency starts in infancy. Chronic C. albicans intertrigo with nail and mouth infections is seen.
 Oral. White plaques adhere to an erythematous buccal mucosa. Broad-spectrum antibiotics, false teeth and poor oral hygiene predispose. Angular stomatitis may coexist.
Oral. White plaques adhere to an erythematous buccal mucosa. Broad-spectrum antibiotics, false teeth and poor oral hygiene predispose. Angular stomatitis may coexist.
 Systemic. Systemic candidiasis can occur in immunosuppressed patients. Red nodules are seen in the skin.
Systemic. Systemic candidiasis can occur in immunosuppressed patients. Red nodules are seen in the skin.
Management
Candida albicans infections must be differentiated from other conditions (Table 2). General measures are important. Body folds are separated and kept dry with dusting powder. Hands are dried carefully (p. 38) and oral hygiene improved. Systemic antibiotics may need to be stopped. Specific agents against Candida are used topically and systemically.
| Variant | Differential diagnosis |
|---|---|
| Genital | Psoriasis, lichen planus, lichen sclerosus |
| Intertrigo | Psoriasis, seborrhoeic dermatitis, bacterial secondary infection |
| Oral | Lichen planus, epithelial dysplasia |
| Paronychia | Bacterial infection, chronic eczema |
Systemic therapy
Fungal infections
 Dermatophytes infect the feet, groin, body, nails, hands and scalp. The commonest dermatophyte pathogens are Trichophyton rubrum, T. mentagrophytes var. interdigitale and Epidermophyton floccosum.
Dermatophytes infect the feet, groin, body, nails, hands and scalp. The commonest dermatophyte pathogens are Trichophyton rubrum, T. mentagrophytes var. interdigitale and Epidermophyton floccosum.
 Topical imidazoles and oral terbinafine or itraconazole are effective for most dermatophyte infections.
Topical imidazoles and oral terbinafine or itraconazole are effective for most dermatophyte infections.
 C. albicans produces opportunistic infection of the body folds, mouth, genitals and nail fold. These are predisposed to by humidity, obesity, diabetes and oral antibiotic therapy.
C. albicans produces opportunistic infection of the body folds, mouth, genitals and nail fold. These are predisposed to by humidity, obesity, diabetes and oral antibiotic therapy.