Chapter 14 Foreign Bodies in Children
Gastrointestinal Foreign Bodies
4 What are the common esophageal sites for lodgment of foreign bodies?
Most esophageal foreign bodies (60–70%) lodge at the level of the thoracic inlet at the cricopharyngeus muscle (Fig. 14-1). The other sites of lodgment include the lower esophageal sphincter and the level of the aortic arch. Patients with histories of congenital esophageal abnormalities or acquired strictures have objects (usually meaty foodstuffs) that impact at the area of anatomic narrowing.
McGahren ED: Esophageal foreign bodies. Pediatr Rev 20:129–133, 1999.
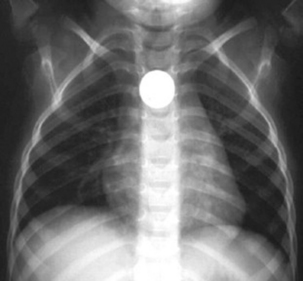
6 For a patient with a quarter in the stomach, how much time should be allowed for passage out of the stomach?
7 For an ingested coin that is in the stomach or beyond, should the family check the stool to ensure safe passage?
11 Can you promote passage of an impacted blunt esophageal foreign body with medication or otherwise?
14 Should sharp foreign bodies be removed from the stomach?
Key Points: Foreign Bodies in the Gastrointestinal Tract
1 Impacted esophageal disc batteries should be removed emergently.
2 Impacted esophageal coins may pass spontaneously.
3 An x-ray is recommended to determine the location of a swallowed coin.
4 Small, sharp objects (nails, screws, tacks, and staples) generally pass from the stomach without complications.
Aspirated Foreign Bodies
15 Classically, children with foreign bodies lodged in a bronchus or smaller airway have cough, decreased breath sounds, and new-onset wheezes. How often is this clinical constellation present?
19 How are the signs and symptoms of an aspirated foreign body different from those of other respiratory conditions?
22 A teenage boy presents to the ED after a choking episode while drinking beer. He reports that he removed the pull-tab of a beer can and placed it inside the can. Then he believes he may have swallowed or aspirated the pull-tab while gulping beer. What study is best to determine the location of the pull-tab?
Foreign Bodies in the Ear and Nose
23 What are the symptoms of a nasal foreign body?
Baker MD: Foreign bodies of the ears and nose in childhood. Pediatr Emerg Care 3:67–70, 1987.
24 What methods are available to remove nasal foreign bodies?
 Test the balloon (get a feel for how big with how much air or saline); deflate and lubricate (with lidocaine jelly) the catheter.
Test the balloon (get a feel for how big with how much air or saline); deflate and lubricate (with lidocaine jelly) the catheter.
 Pass the catheter to the posterior nasopharynx with the balloon deflated (usually it passes inferior to the foreign body).
Pass the catheter to the posterior nasopharynx with the balloon deflated (usually it passes inferior to the foreign body).
 Inflate the balloon a small amount.
Inflate the balloon a small amount.
 Pull the balloon/catheter back out of the nose.
Pull the balloon/catheter back out of the nose.
 Note that the foreign body will come out just prior to the balloon.
Note that the foreign body will come out just prior to the balloon.
 If this technique is unsuccessful, repeat with increased balloon size.
If this technique is unsuccessful, repeat with increased balloon size.
25 What methods are available to remove ear foreign bodies?
Baker MD: Foreign bodies of the ears and nose in childhood. Pediatr Emerg Care 3:67–70, 1987.