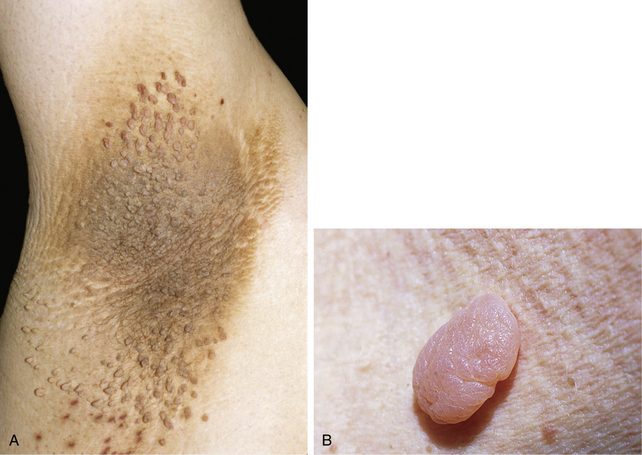
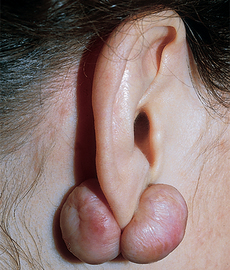
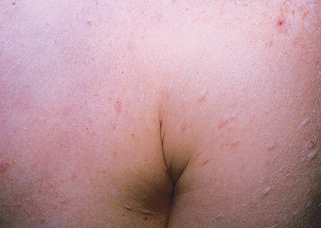
Chapter 43 Fibrous tumors of the skin
Demir S, Demir Y: Acrochordon and impaired carbohydrate metabolism, Acta Diabetol 39:57–59, 2002.
Table 43-2. Clinical Features That Distinguish Hypertrophic Scars from Keloids
| HYPERTROPHIC SCAR | KELOID |
|---|---|
| Any age group, especially children | Adolescents and young adults |
| All racial and ethnic groups | Blacks and Asians > Caucasians |
| No familial tendency | Familial tendency |
| Limited to sites of trauma | Sites of trauma or spontaneous |
| Onset within 2 months | Onset within 1 year |
| Any anatomic site | High-risk anatomic site |
| Dome-shaped lesions | Dome-shaped, exophytic, or crablike extensions |
| Confined to site of trauma | Extends into normal skin |
| Improved by corrective surgery | Often worsened by surgery |
| Spontaneous regression | No spontaneous regression |
Heymann WR: Infantile digital fibromatosis, J Am Acad Dermatol 59:122–123, 2008.
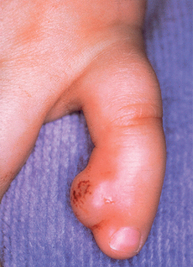
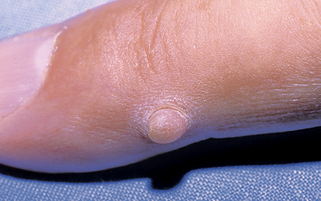
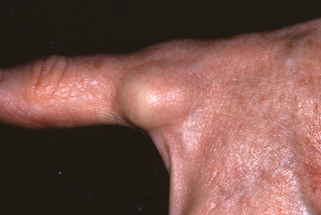
Figure 43-5. Infantile digital fibroma. Firm skin-colored nodule with focal hemorrhage on the finger of an infant.
(Courtesy of the Fitzsimons Army Medical Center teaching files.)
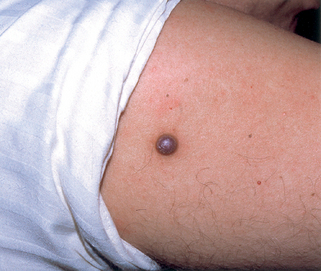
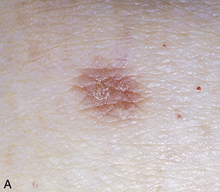
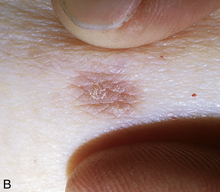
Microscopically, most dermatofibromas are composed primarily of fibroblasts that produce abundant collagen. Within some, but not all, dermatofibromas, there are often cellular areas composed of cells with round nuclei that phagocytize lipid or hemosiderin. Multinucleated giant cells may also be present. Dermatofibromas that phagocytize abundant hemosiderin molecules are sometimes referred to as hemosiderotic dermatofibromas or sclerosing hemangiomas (Fig. 43-6).
Key Points: Fibrohistiocytic Tumors