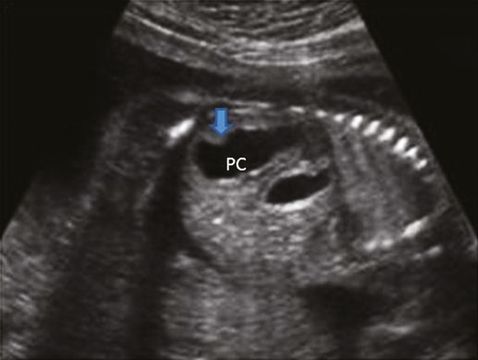
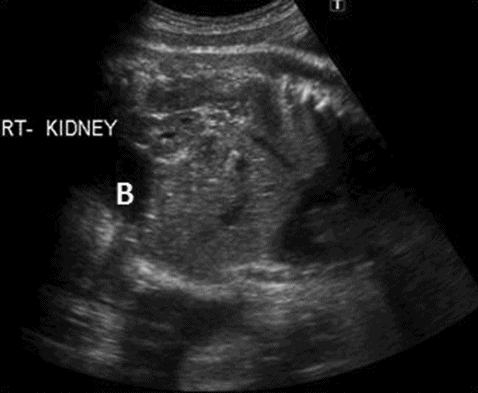
Transverse scan through fetal pelvis showing bladder (B) surrounded by right and left umbilical arteries (LUA and RUA).
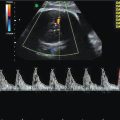
During the anomaly scan between 18–20 weeks, the kidneys are slightly hyperechoic in comparison with the surrounding bowels and paravertebral tissue. Two renal arteries can be easily demonstrated as originating from the aorta by color flow Doppler (Figure 12.2). The ureters, which are not usually visualized during the anomaly scan, measure 1 mm or less in diameter.
A systematic assessment of fetal kidneys, bladder and liquor volume will help in the detection of renal tract abnormalities.
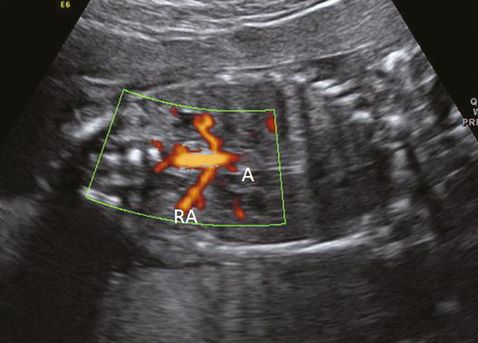
Coronal scan showing renal arteries (RA) originating from aorta (A) in color flow Doppler.
Renal agenesis
Failure of development and fusion of the ureteric bud with the metanephros is thought to be the result of renal agenesis. It can affect one or both kidneys. Unilateral renal agenesis is more common than bilateral with the incidence being 1 in 1,000 and 1 in 4,000 live births, respectively[7,8].
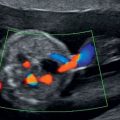
Diagnosis of unilateral renal agenesis is difficult unless a meticulous search is made of the renal fossa during the 18–20 weeks anomaly scan. In absence of renal tissue, fetal adrenal gland expands into the renal fossa mimicking the kidney. Furthermore, the liquor and bladder will also be normal. Demonstration of the unilateral absence of renal artery in color-flow Doppler will confirm the diagnosis of unilateral renal agenesis (Figure 12.3). The fetal pelvis should be checked carefully to rule out pelvic kidney. Similarly, normal size and shape of contralateral kidney will rule out crossed renal ectopi.
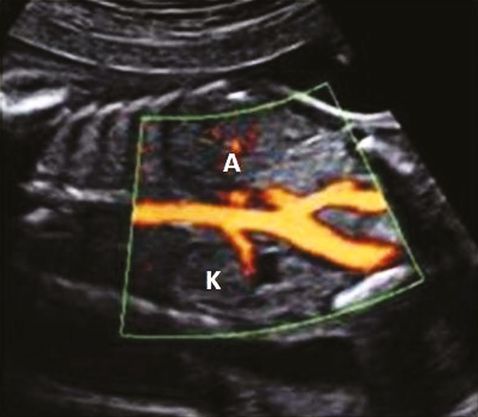
In contrast, there will be anhydramnios/severe oligohydramnios with absent bladder in bilateral renal agenesis. Lack of amniotic fluid and abnormal fetal position usually make the visualization of the renal fossa very difficult. Both renal arteries will be absent on color flow Doppler. Presence of normal liquor at 11–14 weeks scan does not preclude the diagnosis of bilateral renal agenesis as the kidneys do not become the major source of amniotic fluid until 14–16 weeks.
Bilateral renal agenesis should be differentiated from other renal diseases, particularly bilateral multicystic dyspalstic kidney or infantile polycystic kidney. Severe early onset intrauterine growth restriction and spontaneous rupture of membranes need to be excluded before confirming the diagnosis.
Renal agenesis may occur as an isolated anomaly or as a part of genetic syndrome. As a consequence of anhydramnios, a fetus with bilateral renal agenesis will be associated with Potter’s facies, limb deformities and pulmonary hypoplasia. Major structural anomalies such as cardiac and VATER (vertebral, anal, tracheoesophageal, renal) abnormalities could be associated in about 1 in 4 cases[9].
Bilateral renal agenesis is a lethal abnormality and babies usually die soon after birth or in the early neonatal period due to pulmonary hypoplasia. Termination of pregnancy is an option that should be offered to the parents following a diagnosis. Unilateral renal agenesis is associated with normal prognosis, but babies will need a follow-up renal scan in the neonatal period to exclude any abnormality of contralateral kidney. Parents need to be aware that the recurrence risk of bilateral renal agenesis in future pregnancy is around 3–6%[10].
Pelvic kidney
This is the most common location of an ectopic kidney with an overall incidence of 1 in 700 live births[11], and is due to the failure in the ascension of the definitive kidney to the lumbar region in the first trimester of pregnancy.
A midtrimester scan will reveal that the renal fossa is occupied by the adrenal gland and absence of renal artery on the affected side, mimicking renal agenesis. Careful scanning of the fetal pelvis will show presence of the kidney lying above the bladder (Figure 12.4).
Right pelvic kidney located above and lateral to bladder (B).
This condition is usually not associated with any other anomalies and has a very good prognosis if isolated.
Renal cystic disease
Cystic diseases of the kidney are of varied etiology. Based on etiological factors, they are classified into four different groups.
Two inheritable conditions are:
(1) infantile polycystic kidney (autosomal recessive or Potter type I)
(2) adult polycystic renal disease (autosomal dominant or Potter Type III).
Two developmental or acquired disorders are:
(3) multicystic dysplastic kidney (Potter type II)
(4) obstructive cystic disease (Potter type IV).
Infantile polycystic kidney: Potter type I
This is an autosomal recessive disease with an incidence of 1 in 40,000 to 50,000 live births[12]. Sonographic features of bilateral symmetrically enlarged hyper-echogenic kidney with small or absent bladder and oligohydramnios/anhydramnios are suggestive of Potter type I disease. This condition is also associated with hepatic fibrosis. The renal appearances are similar to adult polycystic kidney (Potter type III), but the presence of reduced/absent liquor will differentiate it from Potter type III disease.
Prognosis is very poor when diagnosed in utero. Although commonly diagnosed after 24 weeks of gestation, diagnosis as early as the end of the first trimester has also been reported[13]. In general, the earlier the prenatal manifestation of the disease, the poorer the prognosis. An option of termination of pregnancy can be offered to the parents, particularly if there is history of an affected sibling.
Multicystic dysplastic kidney: Potter type II
Multicystic dyspalstic kidney results from incomplete union of the metanephros to the branching ureteric bud leading to dilatation of the collecting tubules, which is a sporadic condition. The affected kidney appears enlarged with multiple noncommunicating cysts of different sizes. Usually, there is little or no renal parenchyma and the dyspalstic areas are echogenic (Figure 12.5). It is commonly seen in males with an overall incidence of 1 in 3,000 live births. In the majority of cases, it affects only one kidney, but bilateral disease can be seen in up to 23% of cases[14]. Contralateral kidney may have other abnormalities such as vesicoureteric reflux, renal hypoplasia and pelviureteric junction obstruction. Extra renal abnormalities including cardiac, gastrointestinal and central nervous system abnormalities may be seen.
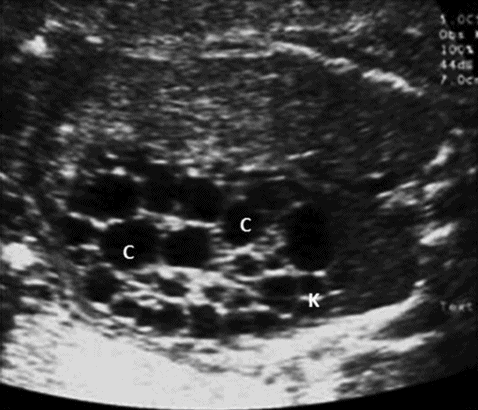
Multicystic dysplastic kidney. A sagittal scan showing kidney (K) with multiple cysts (C) with echogenic parenchyma.
Bilateral disease is associated with anhydramnios leading to pulmonary hypoplasia and neonatal death. Termination of pregnancy is an appropriate management option. The prognosis of unilateral disease is good provided the contralateral kidney maintains normal function and is managed conservatively. During the antenatal period, serial scans are performed to check the liquor volume, parenchyma of the normal kidney as well as the affected kidney. Renal scans are performed after delivery to confirm the diagnosis followed by micturating cystourethrogram (MCUG) and dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA) scans. The unilateral multicystic kidney usually atrophies in childhood and nephrectomy is rarely required.
Adult polycystic renal disease: Potter type III
Adult polycystic renal disease is an autosomal dominant disease with an incidence of 1 in 1,000 live births. The condition is most commonly caused by a mutation in the chromosome 16 and manifests as cystic dilatation of the nephrons of both kidneys, which are rarely seen in utero[15].
Prenatally, a symmetrically enlarged and echogenic kidney with presence of a normal bladder, normal or reduced liquor and family history will help in diagnosing this condition (Figure 12.6). It is important to scan the kidneys of parents if there is no known family history. The presence of two or more cysts in each kidney of either of the parents will confirm the diagnosis. Kidneys may look normal at the 20 weeks’ anomaly scan, so it is important to repeat the scan later in a pregnancy where there is a family history.
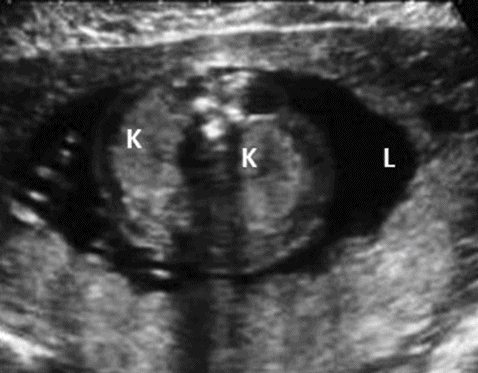
Adult polycystic kidney. A transverse scan showing bilateral enlarged echogenic kidneys (K) with normal liquor (L).
The most common associated abnormalities are cysts in the liver, spleen and pancreas, which are mainly seen in adults.
The prognosis of antenatally detected adult polycystic kidneys is difficult to determine. Presence or absence of a previously affected sibling and family history will help in counseling regarding the short- and long-term outlook of the baby. Around 43% of babies will die within first year of life in the absence of previous affected pregnancy [16]. Being an autosomal dominant condition, there is a 50% risk of recurrence in future pregnancy.
Obstructive cystic dysplasia: Potter type IV
Urinary tract obstruction in the first-trimester or early second-trimester pregnancy will lead to dysplastic lesion in the kidneys, which is a sporadic condition. It is very difficult to ascertain the actual incidence of this condition as only a minority of cases of urinary tract obstruction will progress to cystic dysplasia. An incidence of approximately 1 in 8,000 live births has been reported[17].
The condition can be unilateral or bilateral. Unilateral disease is most commonly due to pelviureteric or vesicoureteric junction obstruction. Presence of duplex kidneys with associated ureterocele can lead to unilateral obstructive disease. Bilateral disease is mainly caused by posterior urethral vale or urethral atresia.
Sonographic features of small echogenic kidney containing peripheral cortical cysts along with other evidence of obstruction are suggestive of obstructive cystic dysplasia. Bilateral diseases are associated with bilateral hydronephrosis, hydroureter, a large thick-walled bladder and oligo- or anhydramnios. In a duplex system, dysplasia can affect only the upper moiety of the kidney. Normal echogenicity of the renal cortex does not always exclude dyspepsia so a serial assessment of the renal cortex is essential.
This condition can be associated with other abnormalities, such as vertebral, anorectal atresia, cardiac abnormalities, tracheoesophageal fistula and limb abnormalities (VACTERL).
Prognosis is very poor in a bilateral disease and an option of termination pregnancy should be discussed with the parents. In the absence of other abnormalities and contralateral renal disease, the prognosis of unilateral disease is good and it can be managed conservatively.
Renal obstruction
Urinary tract obstruction in the midtrimester of pregnancy will manifest as renal pelvic dilatation or hydronephrosis. There are controversies regarding the cutoff value of anteroposterior (AP) diameter of the renal pelvis, above which it should be considered abnormal. An AP diameter of above 15mm (severe) at 20 weeks gestation is associated with about 50% reduction in the mean differential renal function and 30% reduction is seen when the diameter is between 10 and 15 mm (moderate)[18]. A mild renal pelvic dilatation (AP diameter of 5–8 mm) is not associated with significant reduction of renal function but can be associated with vesicoureteric reflux in up to 12% of cases. The UK National Health Service Fetal Anomaly Screening Programme (FASP) recommends a follow-up scan in third trimester for renal pelvic dilatation of more than 7 mm at 18–20 weeks.
The common causes of renal pelvic dilatation or hydronephrosis are pelviureteric junction (PUJ) obstruction, vesicoureteric junction (VUJ) obstruction, vesicoureteric reflux, posterior urethral valve and duplex renal system, with or without ureterocele.
Pelviureteric junction obstruction
PUJ obstruction is the most common urinary tract abnormality, which is unilateral in 90% of cases. This condition is seen commonly in males with an overall incidence of 1 in 2,000 live births.
The presence of unilateral dilatation of the renal pelvis without dilatation of the bladder and ureter in the midtrimester scan will lead to the suspicion of PUJ obstruction. Severe obstruction will cause calyceal dilatation with thinning of the renal cortex (Figure 12.7). Evidence of cortical dysplasia in the form of increased echogenicity or small cortical cyst can be seen in severe disease. Liquor volume is usually normal. It is essential to assess the contralateral kidney to rule out bilateral disease or other associated renal abnormality, such as renal agenesis, multicystic dysplastic kidney, which can be seen in about 25% cases[19]. Bilateral disease needs to be differentiated from VUJ obstruction, vesicoureteric reflux and bladder neck obstruction. Bilateral renal pelvis dilatation in the absence of ureteric dilatation will make a strong case of PUJ obstruction.
It is very important to organize a follow-up scan in the third trimester following suspicion of PUJ obstruction at 20 weeks to assess the severity of the disease, liquor volume and contralateral kidney. A neonatologist should be informed and the baby will need prophylactic antibiotics. A follow-up renal scan during the neonatal period, an MCUG and DMSA scan will be helpful to confirm the antenatal diagnosis and severity of the disease. Although the majority of cases are managed conservatively, severe disease with poor differential renal function will need surgical correction to prevent further renal cortical damage.
Severity of renal pelvic dilatation during antenatal period correlates well with the degree of renal impairment. In general, the prognosis is good. Due to the sporadic nature of the condition, the risk of recurrence in any future pregnancy is low.
Vesicoureteric junction obstruction
VUJ obstruction constitutes about 10% of all antenatally detected significant renal tract abnormalities[20]. Similar to PUJ obstruction, this condition is more common in males. It is bilateral in about 25% of cases.
A diagnosis of VUJ obstruction should be considered when there is sonographic evidence of unilateral or bilateral renal pelvic dilatation along with dilated ureter (Figure 12.8). Dilated sonolucent ureter can be differentiated from the bowels, which show a low level of echos. In a unilateral disease, the bladder and liquor volume are usually normal but may be reduced in bilateral disease. Similar to any other renal tract abnormality, it is important to assess the contralateral kidney, which may be affected with VUJ obstruction, muticystic dysplatic kidney or renal agenesis. It is very difficult to differentiate a bilateral VUJ obstruction from vesicoureteric reflux antenatally. MCUG after delivery will differentiate between these two conditions. An obstruction caused by a ureterocele in a duplex kidney will have similar features as unilateral VUJ obstruction but the presence of a ureterocele within the bladder and dilatation of the upper moiety will differentiate it from a VUJ obstruction.
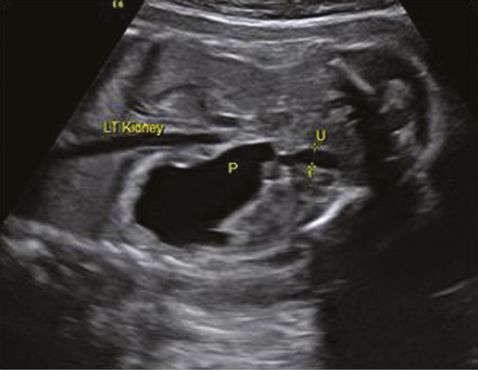
Coronal section through left kidney showing hydronephrosis (P) and dilated ureter (U).
A follow-up scan in the third trimester should be arranged to assess liquor volume and severity of the condition. During the neonatal period, the baby will need prophylactic antibiotics until further investigations rule out vesicoureteric reflux. Renal function can be assessed by a DMSA scan. The majority of the babies are managed conservatively with a good outcome. In cases of severe disease with deteriorating renal function, ureteric reimplantation will be required.
The recurrence in any future pregnancy is very low.
Bladder outlet obstruction
Bladder outlet obstruction could be due to posterior urethral valve or urethral atresia.
Posterior urethral valve
This condition only affects males with an overall incidence of 1 in 5,000 to 8,000. The presence of a membranous tissue within the posterior urethra leads to bladder neck obstruction.
A second-trimester scan will show evidence of a distended, thick-walled bladder with dilated posterior urethra (Figure 12.9). There will be oligohydramnios or anhydramnios along with hydroureter and hydronephrosis. In cases of incomplete obstruction, the liquor volume and bladder may look normal at the 20 weeks’ scan. The condition should be differentiated from urethral atresia, severe bilateral vesicoureteric reflux and megacystis-microcolon syndrome.
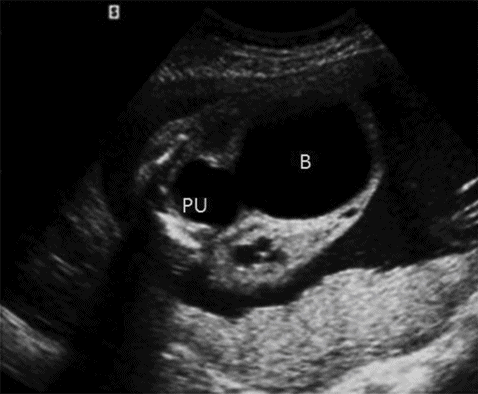
It is important to rule out chromosomal anomaly in cases of posterior urethral valve, which is seen in about 8% of cases. Other associated structural anomalies are cardiac anomalies, anal atresia and VATER syndrome.
Prognosis depends on the severity of the disease and gestational age of diagnosis. Diagnosis before 24 weeks, oligohydramnios, hydroureter and hydronephrosis, along with echogenic/cystic renal cortex, indicate very poor prognosis[21]. About 44% of the babies who survive the early neonatal period will develop end-stage renal failure by the age of 4–5 years.
Antenatal management will depend upon the severity of the disease. Termination of pregnancy can be offered in the poor prognostic group; on the other hand, conservative management is appropriate where the liquor volume is normal and hydronephrosis remain stable. In utero insertion of the vesicoamniotic shunt to bypass the bladder obstruction is considered only in a few cases where there is progression of obstruction in the third trimester, and repeated vesicocentesis confirm preservation of renal function. There are controversies regarding the role of antenatal insertion of the shunt, and a multicenter randomized trial in the UK was closed early because of poor recruitment. It is important to discuss in a multidisciplinary team involving the fetal medicine consultant, neonatologist and pediatric urologist.
The recurrence risk in future pregnancy is low.
Urethral atresia
Urethral atresia results from incomplete canalization of distal urogenital sinus, which forms the proximal urethra. This is seen more commonly in males and may constitute up to 60% of all prenatal diagnosed bladder neck obstruction[22].
The presence of a distended bladder, severe oligohydramnios/anhydramnios, hydroureter and hydronephrosis are characteristics of urethral atresia. The condition is manifested early in the pregnancy (Figure 12.10). The absence of a dilated proximal urethra will differentiate this condition from posterior urethral valve.
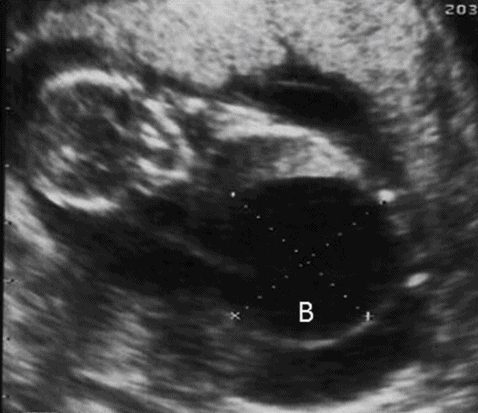
Chromosomal and other structural anomalies are associated in about two-thirds of the cases. It may be difficult to rule out structural anomalies due to the presence of anhydramnios.
Termination of pregnancy is an appropriate management option due to poor prognosis of the baby. The majority of the babies will die in the early neonatal period due to pulmonary hypoplasia.
The condition is sporadic with a very low risk of recurrence in future pregnancy.
Vesicoureteric reflux
Vesicoureteric reflux accounts for about 10% of all fetal hydronephrosis and about 20% of all prenatally detected significant renal abnormality[20]. About 30–50% of children who present with recurrent urinary tract infection will show some evidence of vesicoureteric reflux. In-utero reflux is thought to be caused by the distortion of VUJ by the high-voiding pressure.
Bilateral or unilateral dilatation of the renal pelvis may be the only feature of vesicoureteric reflux. In severe cases there will be associated ureteric dilatation and thin-walled distended bladder. A high grade of bilateral reflux can cause renal scarring in utero. Liquor volume is usually normal even in bilateral disease. Unilateral disease needs to be differentiated from unilateral PUJ or VUJ obstruction. Bladder neck obstruction needs to be considered in cases of bilateral disease with distended bladder. Confirmation of diagnosis is possible only after delivery by MCUG. In a unilateral condition, contralateral kidney should be checked for associated anomalies, such as PUJ obstruction, muticystic kidney, duplex kidney and renal agenesis.
A follow-up scan at the third trimester is essential to assess the severity of the disease and liquor volume. After delivery, the baby should have prophylactic antibiotics followed by a renal scan in the first week of life, and MCUG depending on the renal scan findings. In some cases, MCUG is considered in all neonates with antenatal diagnosis of renal pelvic dilatation irrespective of postnatal renal scan findings[23].
Vesicoureteric reflux can lead to renal scarring and reflux nephropathy if not treated appropriately. The majority (70%) of mild reflux can resolve spontaneously in the first few months of life, but spontaneous resolution is seen in around 40% of severe refluxes by 15 months of age[24].
Reflux disease is thought to be genetically linked as there is high risk of recurrence. Two-thirds of babies will be affected if the mother suffers from reflux and one-third of siblings of an affected child will have reflux[25].
Megacystis-microcolon-intestinal-hypoperistalsis syndrome
Megacystis-microcolon-intestinal-hypoperistalsis syndrome is an autosomal recessive condition more commonly seen in girls with a female-to-male ratio of 4 to1. Exact etiology is unknown but it manifests as a functional small bowel obstruction with nonobstructed distended urinary bladder.
The antenatal scan will show a distended thick-walled bladder with bilateral hydronephrosis. The presence of normal or excessive liquor will differentiate it from posterior urethral valve. The past history of an affected sibling and a female baby are two important factors in diagnosing this condition.
The prognosis is very poor. Termination of pregnancy is an appropriate option, particularly when there is a family history.
Risk of recurrence is 25%.
Ureterocele
Stenosis of distal ureteric orifice leads to dilatation of the intravesical part of the ureter, which is known as ureterocele. It is commonly associated with a duplex renal system (Figure 12.11) in females, but in males it may develop from a normal kidney[2]. This condition is bilateral in about 10–15% of cases.
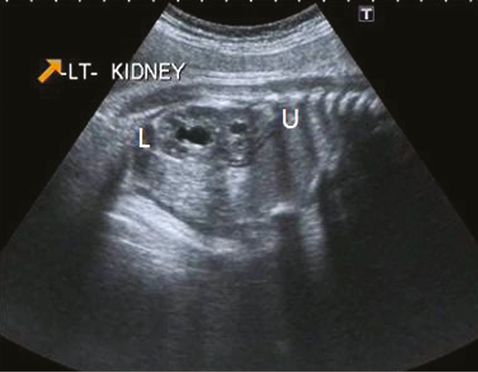
Duplex kidney. Sagittal scan showing upper and lower moiety (U and L) with two renal pelvis.
Ureterocele is commonly associated with dilated ureter and renal pelvis. In a duplex system, it is the upper moiety that is commonly affected. Sometimes a large ureterocele can obstruct the contralateral ureteric orifice leading to hydroureter and hydronephrosis of the opposite kidney. Rarely, it can obstruct the bladder neck. Liquor volume is usually normal in unilateral cases. Detection of ureterocele within the bladder is the confirmatory sign but is not always possible to visualize on the scan (Figure 12.12).
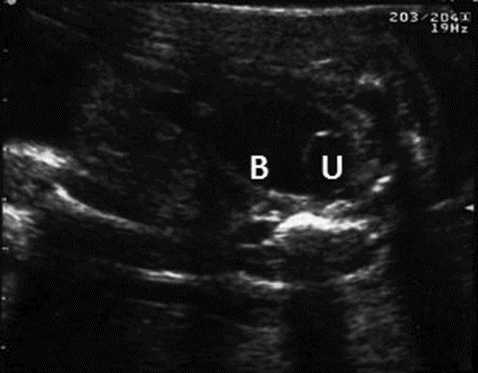
Scan through fetal pelvis showing ureterocele (U) within the bladder (B).
Vesicoureteric reflux is commonly associated with this condition and can affect the lower pole moiety. Prognosis is usually good. A follow-up scan in the third trimester is essential to assess the liquor volume and renal parenchyma of the affected kidney. Diagnosis is confirmed and renal function is assessed by neonatal renal scan, DMSA scan and MCUG. Cystoscopic puncture of the ureterocele is the treatment of choice.
The risk of recurrence in future pregnancy is low.
Cloacal exstrophy
Cloacal exstrophy is a sporadic condition with an incidence of 1 in 250,000 live births[26]. Rupture of the cloacal membrane before the completion of caudal growth of the urorectal septum will lead to this abnormality. It is usually manifested as bladder exstrophy, herniation of small and large bowels through the lower part of anterior abdominal wall and bifid phallus. An exomphalus and lumbosacral spina bifida are usually associated with this abnormality.
An absent bladder and an anterior abdominal wall defect below the umbilicus on the antenatal scan will lead to a strong suspicion of cloacal exstrophy. Liquor volume is usually normal but sometimes the condition can be associated with polyhydramnios. Associated abnormality can be seen in up to 85% of cases. Renal anomalies, such as unilateral renal agenesis, pelvic kidney and multicystic kidney, are the most common association.
Absence of bladder and defect below the umbilicus will differentiate this condition from exomphalus and gastroschisis.
Major surgical correction after delivery is required and an option of termination of pregnancy should be discussed with the parents following antenatal detection of cloacal exstrophy.
Recurrence risk in future pregnancy is low.
Bladder exstrophy
Rupture of cloacal membrane after the completion of caudal growth of urorectal septum will cause bladder exstrophy. The condition is commonly seen in males with an overall incidence of 1 in 30,000 live births[27].
Ultrasonographic features of absent bladder, along with lower abdominal bulge, a small penis along with anteriorly displaced scrotum, normal liquor and kidneys, are suggestive of bladder exstrophy. Other anomalies are usually not associated with this condition, which differentiates it from cloacal exstrophy.
Long-term prognosis following surgical correction after delivery is generally good. The recurrence is less than 1%.
Ambiguous genitalia
It is a rare disorder caused either by chromosomal abnormality or by abnormal hormonal effect.
Female pseudohermaphroditism is due to either maternal ingestion of androgen or congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Excess androgen will cause clitoral enlargement of variable degree. The karyotype is 46,XX.
The abnormal response of external genitalia to testosterone or under production of testosterone in a genetically male fetus will lead to male pseudohermaphroditism. In this condition, a male fetus will have a blind vagina or micropenis with or without cryptorchidism.
Chromosomal defects such as mixed gonadal dysgenesis, pure gonadal dysgenesis and true hermaphroditism are the other causes of ambiguous genitalia.
It is hard to detect ambiguous genitalia during the antenatal period. A micropenis with undescended testes will have a similar ultrasound appearance to that of clitoromegaly with normal labia (Figure 12.13). Ultrasound features of male genitalia in a genetically female baby are suggestive of congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Diagnosis can be confirmed by estimating 17-hydroxyprogesterone levels in amniotic fluid. A follow-up scan in the latter half of pregnancy will be helpful to assess fetal genitalia but not accurate enough to assign a gender during the antenatal period. A final diagnosis should be made after a thorough neonatal assessment.
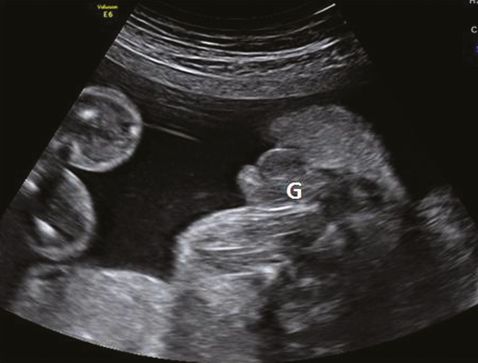
Section through the external genitalia (G) showing scrotum and micropenis in a genetically male fetus.
Ovarian cyst
Ovarian cysts are relatively common intra-abdominal cystic lesions in the female fetus. Ovarian cysts develop in response to high maternal hormones and resolve spontaneously after delivery. Sonographically, a unilocular/occasionally multilocular cystic structure below the kidney and beside the bladder in a female fetus will raise the suspicion of an ovarian cyst (Figure 12. 14). Absence of two umbilical arteries surrounding the cyst will differentiate it from the fetal bladder. Usually no intervention is required during antenatal period. Very rarely, a large ovarian cyst can cause pressure effects on other organs or obstructed labor. A transabdominal aspiration of the cyst is an appropriate option in those circumstances. A scan during the neonatal period will confirm the diagnosis and assess the size of the cyst.
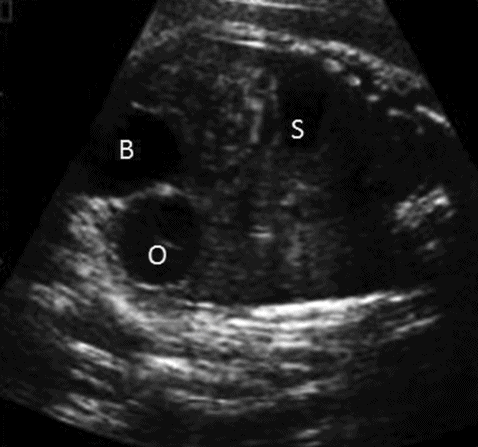
Coronal scan showing right ovarian cyst (O) located just above and lateral to bladder (B). Stomach (S) on the left side.