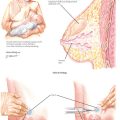
Chapter 71 Female Circumcision
INTRODUCTION
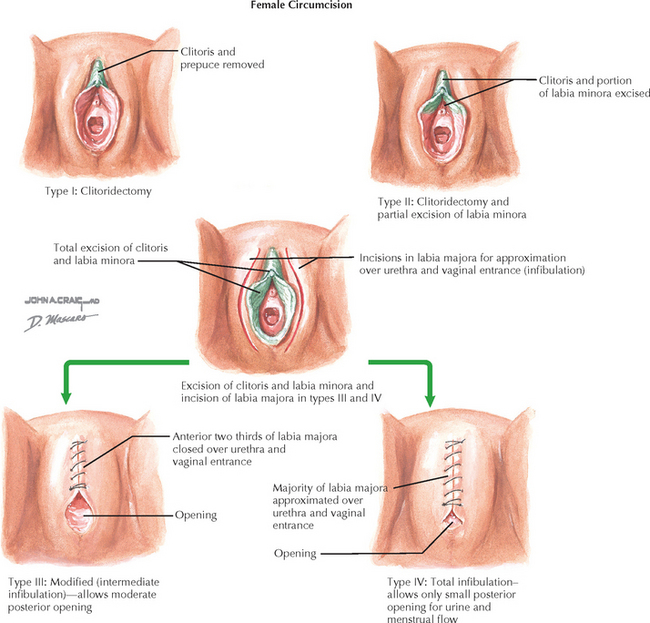
Other forms of female genital mutilation include the following:
ETIOLOGY AND PATHOGENESIS
CLINICAL CHARACTERISTICS
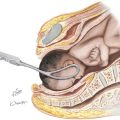
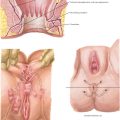
MANAGEMENT AND THERAPY
FOLLOW-UP
MISCELLANEOUS
Elmusharaf S, Elhadi N, Almroth L. Reliability of self reported form of female genital mutilation and WHO classification: cross sectional study. BMJ. 2006;333:124. Epub 2006 Jun 27
WHO study group on female genital mutilation and obstetric outcome, Banks E, Meirik O, Farley T, et al. Female genital mutilation and obstetric outcome: WHO collaborative prospective study in six African countries. Lancet. 2006;367:1835.
Adams KM, Gardiner LD, Assefi N. Healthcare challenges from the developing world: post-immigration refugee medicine. BMJ. 2004;328:1548.
Aziz FA. Gynecologic and obstetric complications of female circumcision. J Gynaecol Obstet. 1980;17:560.
Baker CA, Gilson GJ, Vill MD, Curet LB. Female circumcision: obstetric issues. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1993;169:1616.
Council on Scientific Affairs, American Medical Association. Female genital mutilation. JAMA. 1995;274:1714.
Cuntner LP. Female genital mutilation. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 1985;40:437.
Khaled K, Vause S. Genital mutilation: a continued abuse. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1996;103:86.
Lentz GM. Rape, incest, and domestic violence. In: Katz VL, Lentz GM, Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, editors. Comprehensive Gynecology. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Mosby/Elsevier; 2007:207.
Toubia N. Female circumcision as a public health issue. N Engl J Med. 1994;331:712.
World Health Organization. Female genital mutilation. Fact sheet 241. Available at: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs241/en/l, 2000. Accessed June 7, 2007.