31 Evoked potentials
Sensory Evoked Potentials
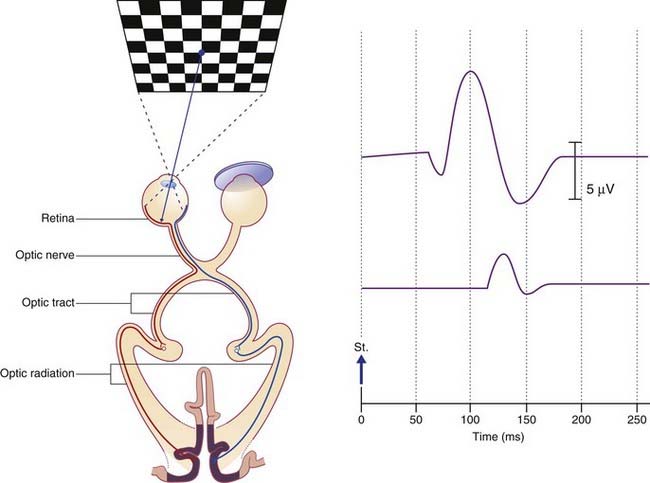
Visual evoked potentials
The wave peak of interest is called P100. In healthy subjects it is a positive deflection 100 ms poststimulus (Figure 31.1). In the clinical example shown, taken from a patient with a presumptive diagnosis of multiple sclerosis, the normal P100 wave from the right-eye test indicated that both optic tracts and both optic radiations were clear. The P100 wave from the left eye was both delayed and of reduced amplitude, suggesting presence of one or more plaques of myelin degeneration in the left optic nerve. (Note: On screen and in printouts, it is now customary for the waveforms to be ‘flipped’, with positive responses registering as upward deflections.)
Brainstem auditory evoked potentials
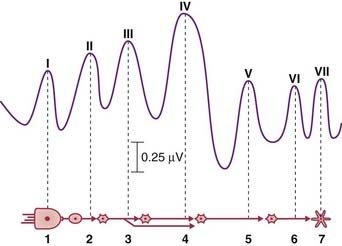
A sequence of seven averaged-out waves (I–VII) constitutes the BAER (brainstem auditory evoked response). They are accounted for in the caption to Figure 31.2.
Somatosensory evoked potentials
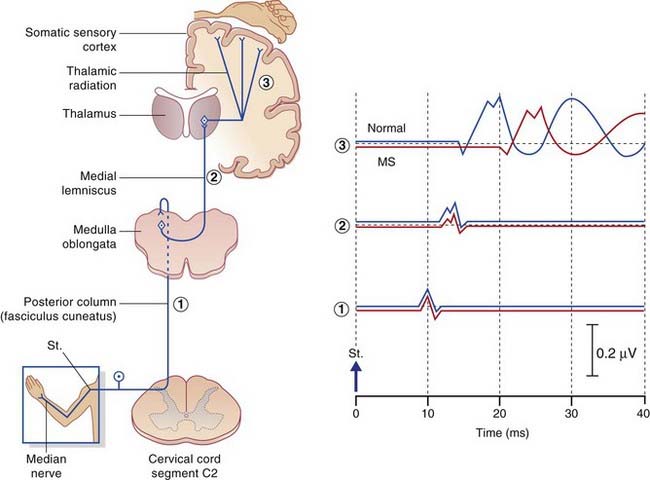
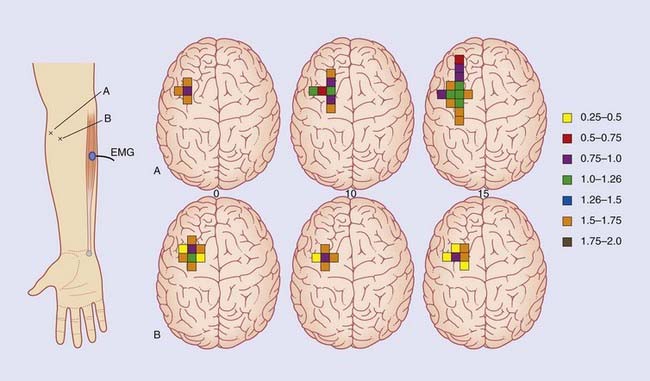
The nerve of choice for stimulation in the upper limb is the median at the wrist, in the lower limb the common peroneal at the knee. Repetitive electrical pulses are delivered to the nerve through a surface or needle electrode. The larger myelinated fibers are stimulated. Computer averaging is required to distinguish the stimulated responses from background noise, notably within the CNS. In the example shown in Figure 31.3, impulse traffic along the median nerve is detected by a sequence of active electrodes attached to the skin for the purpose of recording speed and amplitude of nerve conduction in sequential segments. as follows:
In the various peripheral neuropathies mentioned in Chapter 9 the first segment (wrist to brachial plexus) reveals slowing, usually with a reduction of amplitude. The second segment (brachial plexus to nucleus gracilis) may be affected in the first few milliseconds of its time course as a result of posterior nerve root compression by osteophytes in patients with cervical spondylosis. A little later, the curve may be affected by posterior column disease (Ch. 15). Abnormality in the third segment (contralateral medial lemniscus) is found in 9 out of 10 patients suffering from MS in the presence of sensory symptoms, and in 6 out of 10 in the absence of sensory symptoms.
Motor Evoked Potentials
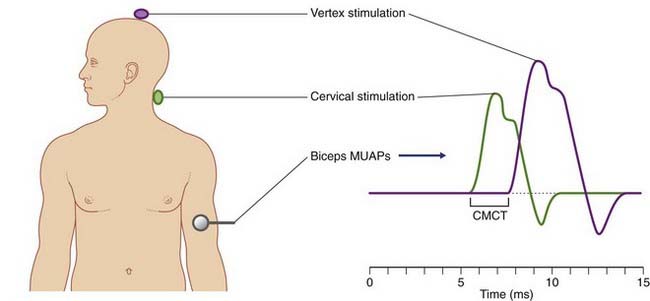
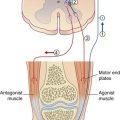
Motor evoked potentials are motor unit action potentials (MUAPs) detected in surface EMG recordings following controlled excitation of the corticospinal tract. The technique was mentioned in Chapter 18 because it revealed that the pyramidal tract pathway to sternomastoid spinal motor neurons is essentially crossed, rather than being ipsilateral as previously thought. The most frequent objective is to determine central motor conduction time along the corticospinal tract. The procedure is both safe and painless. It uses a subtraction approach comparable in principle to that used to determine peripheral nerve conduction times (Figure 31.3).
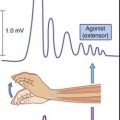
The procedure is known as transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS). Figure 31.4 illustrates the concept in action. Stimulation is by means of a magnet in the form of a circular coil about 10 cm in diameter. To stimulate the pyramidal cells of the corticospinal tract supplying left anterior horn motor neurons, the magnet is hand held a little to the right side of the vertex and the patient maintains the selected limb muscle (biceps brachii in this example) in a state of slight contraction. A few very brief (200 ms) currents are pulsed at an intensity comfortably above the threshold required to elicit a twitch. The patient feels only a small ‘tap’ sensation on the scalp. The procedure is then repeated with the magnet touching the skin of the neck overlying the spine of vertebra C5, again eliciting a ‘tap’ sensation. It is generally agreed that the second pulse depolarizes the axons of anterior nerve roots exiting the vertebral canal.
Motor training
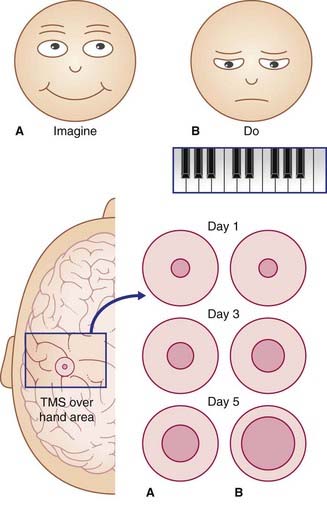
A remarkable degree of plasticity in the healthy motor cortex has been demonstrated by TMS studies. Figure 31.5 represents outcomes of five-finger piano-playing exercises. A small magnetic coil was used over the scalp to locate the modules primarily involved in flexion and extension of the fingers of the right hand. This small scalp area was marked in three sets of volunteers, and the baseline size was measured for each subject. Group A imagined doing the five-finger exercise for 2 hours per day for 5 days; Group B did the exercises for the same periods; Group C did not participate in any way prior to attempting the task once on day 5. As indicated in the figure, merely thinking about performance led to a major increase in the number of modules that activated the fingers when stimulated on days 3 and 5. Group B – the actual performers – showed the greatest increase of participating motor modules. The performance skills on day 5 were substantially better in Group B than Group A, and Group A’s performance was better than that of Group C.
There is general agreement that dramatic alterations such as those shown in this group experiment are best explained in terms of unmasking of pre-existing connections, as in the case of rapid expansion of the cortical sensory territory of one thalamocortical projection following experimental inactivation of a neighboring projection. The most likely mechanism of additional pyramidal cell recruitment appears to be one of disinhibition, probably by the premotor cortex, involving activation of sequential pairs of GABAergic neurons in the manner illustrated in Figure 6.2.
Finally, Box 31.1 includes an experiment in which TMS has been used to assess the supposed usefulness of acupuncture in improving motor performance.
Box 31.1 Acupuncture
Sensation
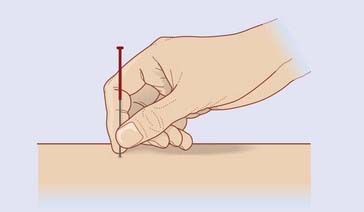
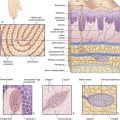
For relief of pain, fine (0.25 mm) needles are inserted bilaterally through appropriate acupoints, coming to rest among superficial muscle fibers underlying the subcutaneous fat (Figure 31.1.1). The needle is then briefly spun to excite Types II and III sensory nerve fibers in its immediate neighborhood. A subjective sense of numbness or heaviness in the acupoint area is usually reported.
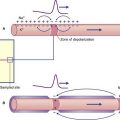
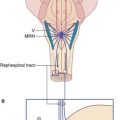
The accepted explanation of the rapid pain relief produced by this form of stimulation is release of enkephalin by (a) spinal antinociception via the segmental reflex mentioned in ‘rubbing the sore spot’ combined with (b) supraspinal antinociception via spinoreticular activation of the PAG–MRN–RST–Enk pathway shown in Figure 24.8. Pain relief is not achieved if the subject has received a prior injection of the opiate antagonist naloxone.
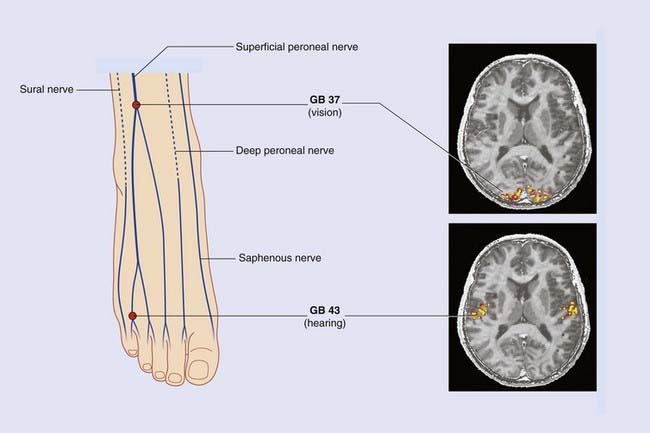
With availability of fMRI as a research tool, attention is being focused on the effects of acupuncture on higher-level sensory functions. Figure 31.1.2 is composite, reproducing the remarkable results of two quite separate experiments. In each volunteer, needling was performed bilaterally, one acupoint being traditional for relief of disorders of vision, the other for disorders of hearing. Areas of increased cortical blood flow closely resemble those associated with retinal/cochlear activation. Surprisingly, the volunteers did not report visual/auditory hallucinations. And an obvious question persists concerning the mysteriously specific anatomical pathways from the acupoints to the appropriate areas of cortex.
Movement
Movement disorders also have tradional therapeutic acupoints. One of these acupoints, on the lateral side of the proximal forearm, has been selected for low-frequency (1 Hz) electroacupuncture in the experiment illustrated in Figure Box 31.1.3.
Chen K. Neuroanatomical basis of acupuncture treatment for some common illnesses. Acupuncture in medicine. 2009;27:61-64.
Gruccu G, Aminoff MJ, Curio G, et al. Recommendations for the clinical use of somatosensory-evoked potentials. Clin Neurophysiol. 2008:1705-1719.
Lo YL, Cui SL. Acupuncture and the modulation of cortical excitability. Neuroreport. 2003;14:1229-1231.
Lo YL, Cui SL, Fook-Chong S. The effect of acupuncture on motor cortex excitability and plasticity. Neurosci Lett. 2005;384:385-389.
Olssen C-J, Jonnson B, Nyberg L. Learning by doing and learning by thinking: an fMRI study of combining motor and mental training. Front Hum Neurosci. 2008;2:5-12.
Pomeranz P, Berman B. Scientific basis of acupuncture. In: Stux G, Berman B, Pomeranz B, editors. Basics of acupuncture. ed 5. Berlin: Springer; 2003:52-86.
Stux G, Berman B, Pomeraz B. Basics of acupuncture, ed 5. Berlin: Springer-Verlag; 1997.
Tageshige C. Mechanisms of acupuncture analgesia produced by low frequency electrical stimulation of aupuncture points. In: Stux G, Hammerschlag R, editors. Clinical acupuncture: scientific basis. Berlin: Springer; 2003:29-50.
Yan B, Li K, Xu J, et al. Acupoint-specific fMRI patterns in human brain. Neurosci Lett. 2005;383:236-240.
Adams RD, Victor M. Principles of neurology, ed 5. New York: McGraw-Hill; 1993.
Cho Z, Na C, Wong E, Lee S, Hong I. Investigation of acupuncture using fMRI. In: Litscher G, Cho Z, editors. Computer-controlled acupuncture. Berlin: Pabst; 2000:45-64.
Maccabee PJ, Amassian VE, Ziemann U, Wassermann E, Deletis V. Emerging applications in neuromagnetic stimulation. In: Levin KH, Lüders HO, editors. Comprehensive clinical neurology. Philadelphia: Saunders; 2000:325-347.
Misulis KE, Fakhoury T. Spehlman’s evoked potential primer, ed 3. Boston: Butterworth-Heinemann; 2000.
Pascual-Leone A, Dang N, Cohen LG. Modulation of muscle responses evoked by transcranial magnetic stimulation during the acquisition of new motor skills. J Neurophysiol. 1995;74:1037-1045.
Tata MS, Ward LM. Spatial attention modulates activity in a posterior “where” pathway. Neuropsychologia. 2005;43:509-516.
Walsh P, Kane N, Butler S. The clinical role of evoked potentials. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2005;76:ii16-ii22.