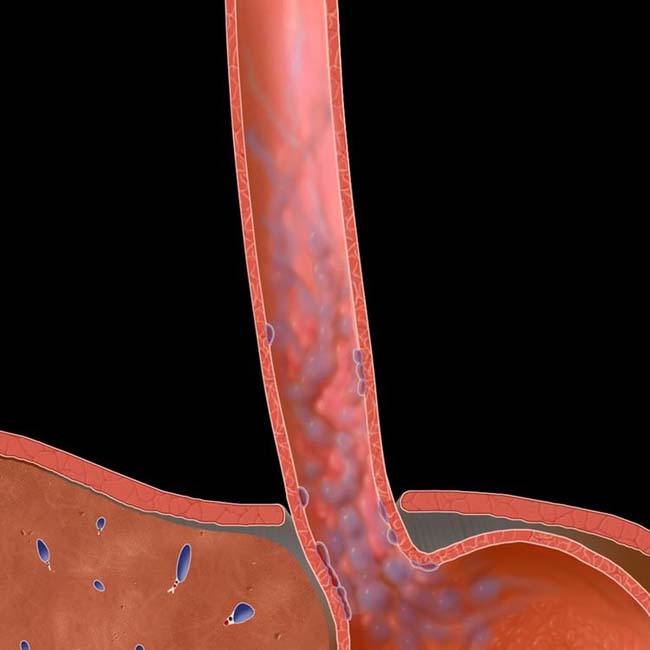
Distal 1/3 or 1/2 of esophagus
• Downhill varices: Obstruction of SVC → downward venous flow via esophageal collaterals to portal vein and inferior vena cava (IVC)
• Fluoroscopy: Tortuous, serpiginous, longitudinal radiolucent filling defects in collapsed or partially collapsed esophagus
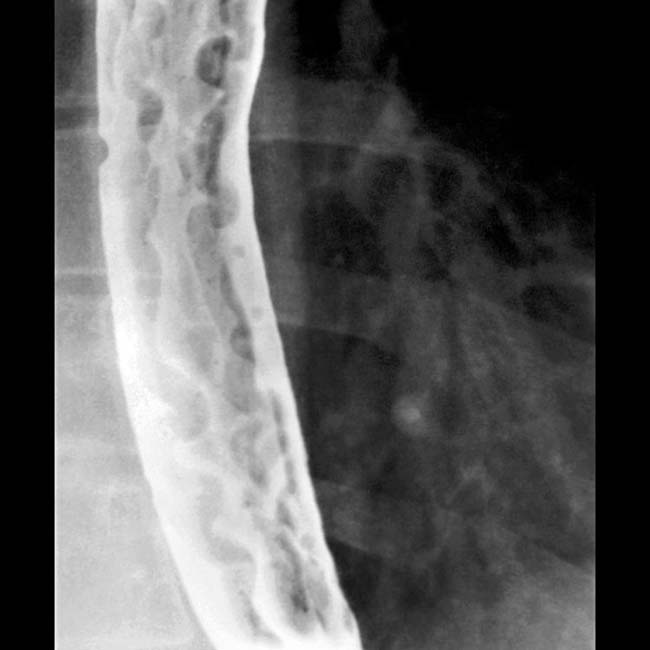
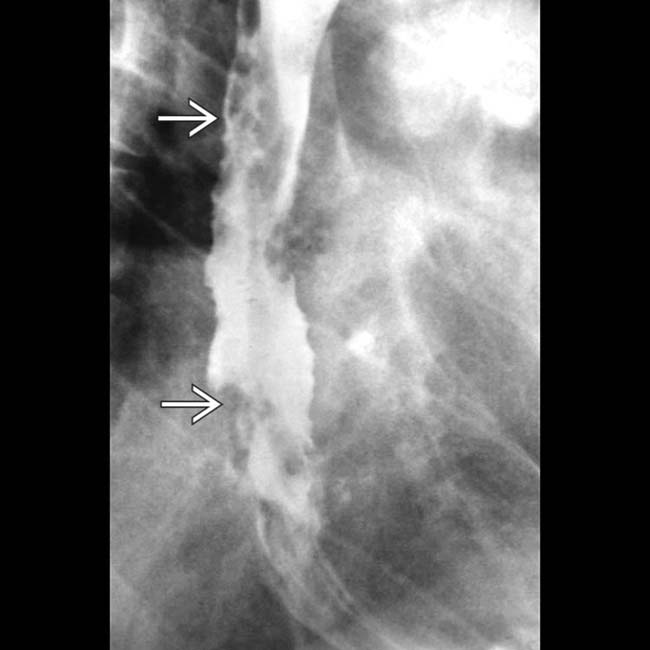
 in the esophageal wall and lumen. The fixed nature of these mimics the appearance of the “varicoid” morphology of some esophageal carcinomas.
in the esophageal wall and lumen. The fixed nature of these mimics the appearance of the “varicoid” morphology of some esophageal carcinomas.IMAGING
General Features
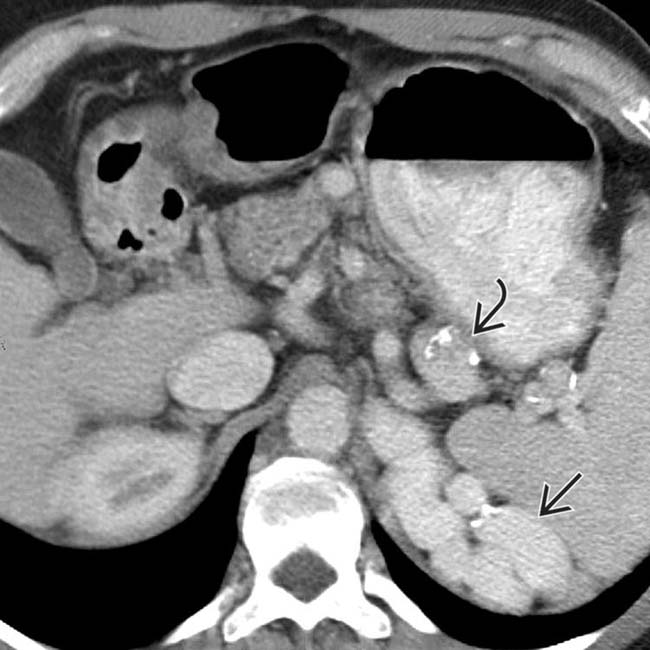
 and calcification present
and calcification present  in the walls of some varices that might be mistaken for arterial aneurysms.
in the walls of some varices that might be mistaken for arterial aneurysms.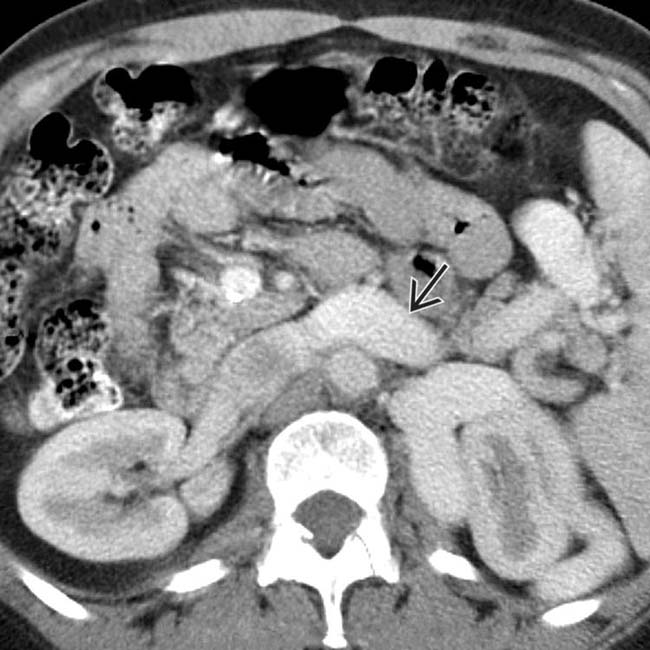
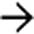 . Spontaneous or surgically created shunts help to decompress esophageal varices but increase the incidence of encephalopathy and portal vein thrombosis, making subsequent liver transplantation difficult or impossible.
. Spontaneous or surgically created shunts help to decompress esophageal varices but increase the incidence of encephalopathy and portal vein thrombosis, making subsequent liver transplantation difficult or impossible.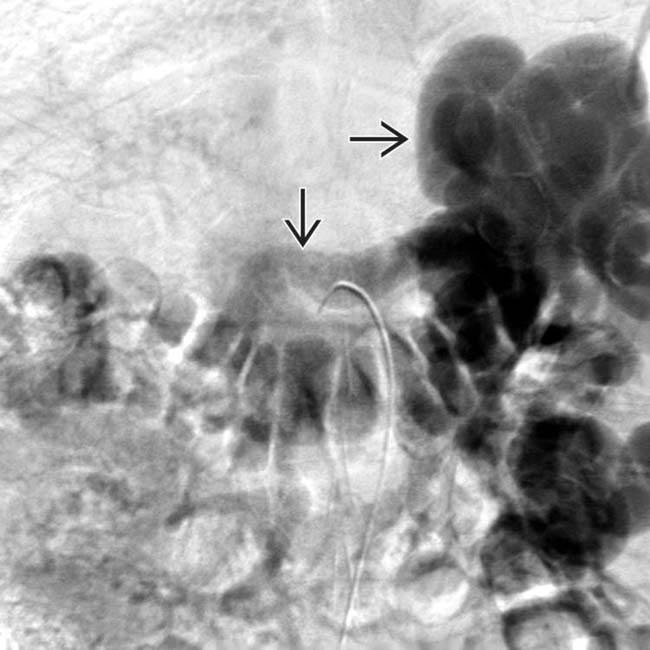
 but no portal vein flow.
but no portal vein flow.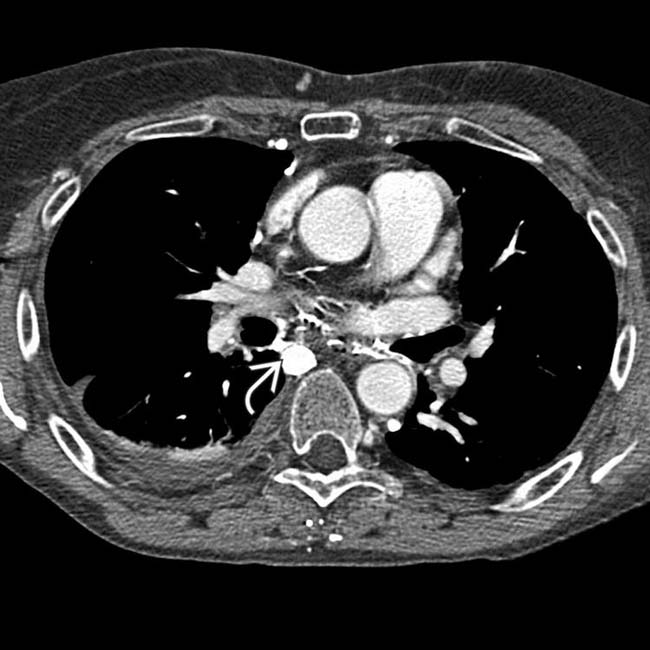
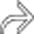 and various mediastinal collateral veins.
and various mediastinal collateral veins.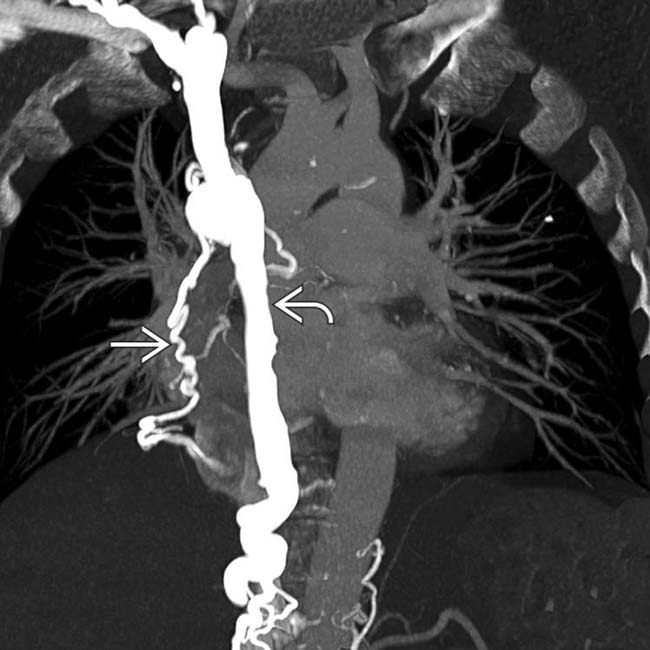
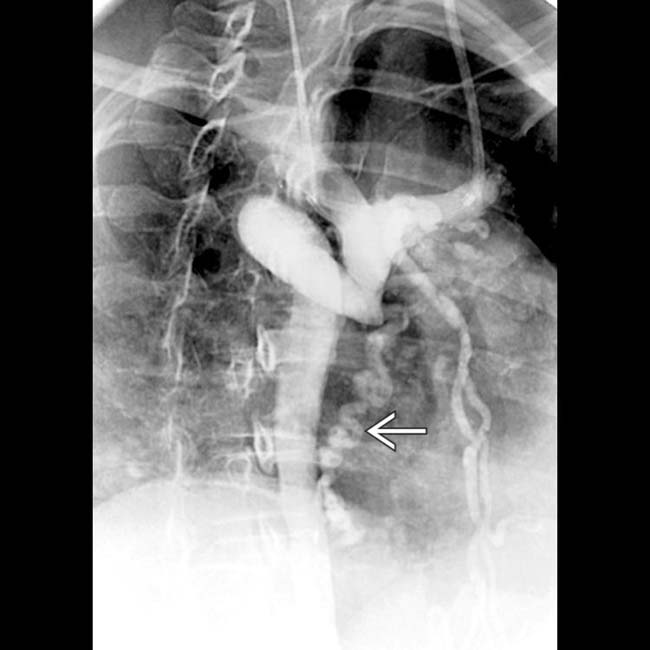
 and mediastinal collateral veins
and mediastinal collateral veins  . The collaterals are carrying flow from tributaries of the SVC into abdominal circulation to be returned to the heart via the inferior vena cava (IVC). These are sometimes referred to as “downhill varices.”
. The collaterals are carrying flow from tributaries of the SVC into abdominal circulation to be returned to the heart via the inferior vena cava (IVC). These are sometimes referred to as “downhill varices.”











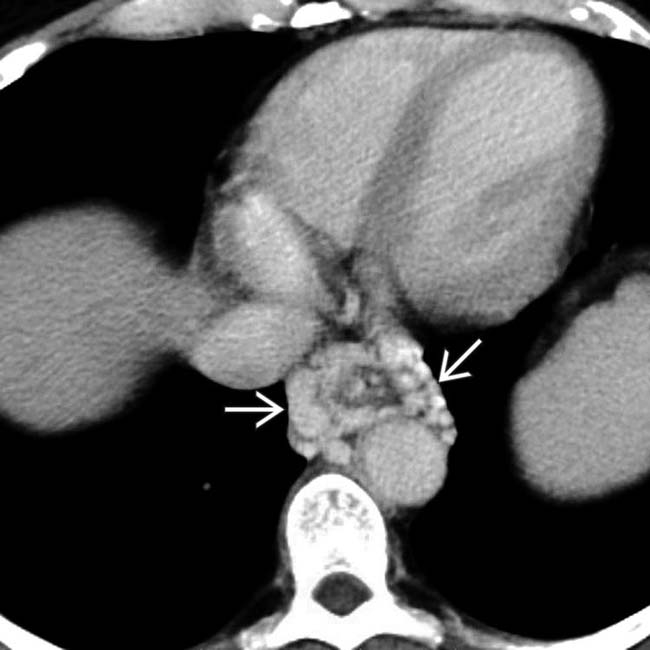
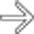 .
.




















































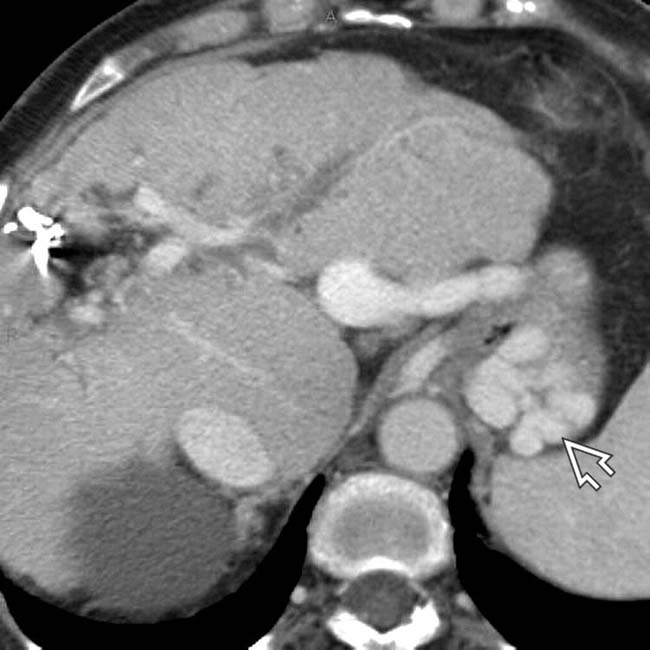
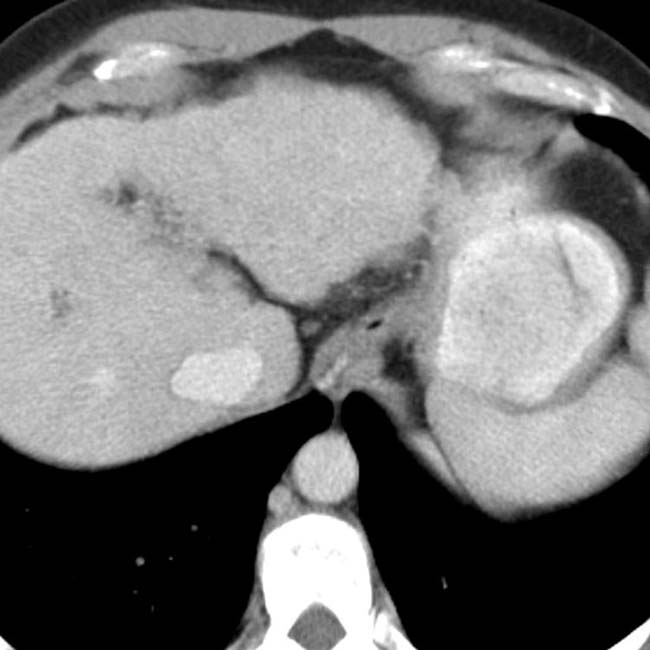
 in the gastric fundus wall.
in the gastric fundus wall.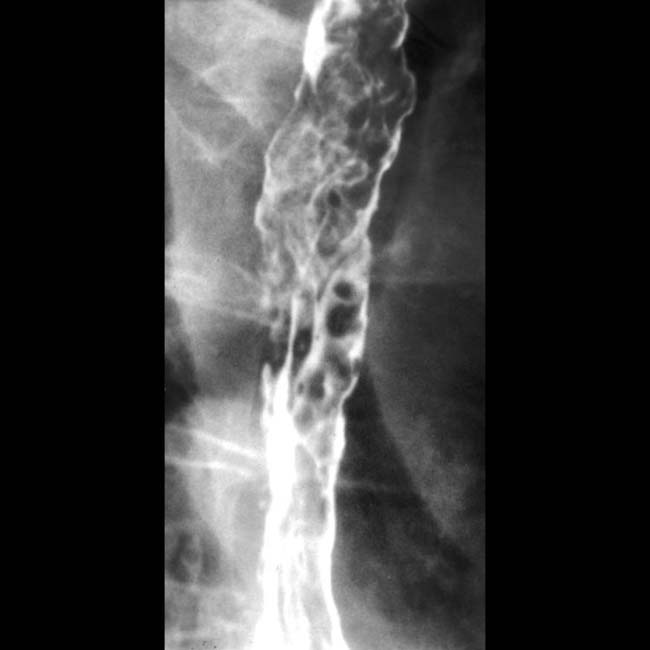
 in the periesophageal region are part of collateral venous drainage.
in the periesophageal region are part of collateral venous drainage.

