30. Epidermolysis Bullosa
Definition
Epidermolysis bullosa (EB) is a group of disorders that give rise to blister formation secondary to even the most minor mechanical trauma.
Incidence
In the United States the incidence of EB is about 50:1,000,000 live births. Internationally it varies according to country, e.g., Norway: 54:1,000,000; Japan: 7.8:1,000,000; Croatia: 9.6:1,000,000.
Etiology
The skin and oral mucosa are composed of several stratified squamous epithelial tissues that contain a basement membrane zone (BMZ). The BMZ itself is composed of specialized components. These components combine to make various complexes that anchor the BMZ. EB results from inherited defects in the BMZ and/or anchoring complexes, depending on the variant of EB.
Signs and Symptoms
• Anal stenosis
• Blisters (conjunctival, oral, genital mucosa)
• Corneal scarring
• Esophageal strictures and webs
• Flexion contractures
• Hyperhidrosis
• Palmoplantar hyperkeratosis
• Phimosis
• Scar-like papules on the trunk
• Urethral stenosis
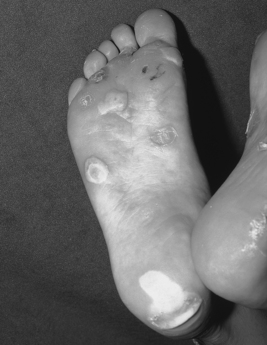 |
| Epidermolysis Bullosa. Epidermolysis bullosa simplex, Weber-Cockayne type. |
Medical Management
The chief concerns with EB are infection and wound healing. Large bullae can form from relatively minor trauma, producing large areas of denuded skin. These areas are generally moist and rich with substrate supportive of bacterial growth. The patient with EB is more susceptible to sepsis as a result.
Strict adherence to hand washing and asepsis are high priorities when dealing with the patient with EB. Any and all wounds must be carefully observed for slow healing or nonhealing.
Dysphagia commonly occurs in the patient with EB and can contribute to formation of esophageal lesions. Oral steroids are combined with phenytoin to reduce the dysphagia and potential for lesion formation.
Good oral hygiene is absolutely essential in the patient with EB. Nevertheless, the patient frequently develops dental caries as the result of enamel defects. Mild saline mouthwashes are recommended rather than those containing alcohol.
Surgical interventions specific to the patient with EB are sometimes required. For example, correction of mitten deformity of the hand(s), esophageal dilation, or squamous cell carcinoma excision may be needed. The patient with EB is susceptible to significant hemodynamic and metabolic alterations. However, intake and absorption may be altered as the result of oral, oropharyngeal, and/or gastrointestinal lesions.
The patient with EB may need physical therapy to combat formation of contractures. Because of the pain and scarring associated with this disease, the patient is more prone to reduced activity levels or frank inactivity, which can further contribute to contracture formation.
Complications
• Chronic blepharitis
• Cicatricial conjunctivitis
• Corneal erosions
• Corneal ulcerations/scarring
• Dysphagia
• Esophageal webbing/stricture/stenosis
• Eyelid lesions
• Obliteration of lacrimal ducts
• Pseudosyndactyly
• Squamous cell carcinoma
Anesthesia Implications
The patient with EB is often treated with corticosteroids. Therefore the patient should receive a perioperative dose of hydrocortisone.
The patient who has severe dysphagia may have compromised airway reflexes with the concomitant increased risk of aspiration during either induction and/or emergence.
There have been reports of patients with EB who have significant tracheal stenosis. A thorough noninvasive or minimally invasive airway evaluation should be completed preoperatively, especially if there is any history of airway compromise or demonstrated airway compromise symptoms.
The patient with EB is exquisitely sensitive to skin injury. Any manner of shear force can produce significant injury. Shearing force can be produced by a number of actions during anesthesia. Blood pressure cuff inflation/deflation produces shear forces and should only be placed on the patient after cast padding has been applied. The blood pressure cuff should be monitored to ensure proper function, because a malfunctioning blood pressure cuff that produces excessive and/or sustained inflation will also produce injury. Electrocardiography pads are in essence a form of tape and will produce injury. Tape removal in any form will produce shearing forces and cause injury where it is applied. Commercially available products for securing the endotracheal tube without tape should therefore be used for the patient with EB. Transferring the patient from the OR bed to the stretcher or hospital bed must be accomplished with utmost care and gentleness. Whenever the patient can accomplish transfers, that is preferred in order to minimize, if not avoid, shearing forces.
General and regional anesthesia have been utilized with patients with EB. Regional anesthesia is an appropriate choice for obstetric patients if the skin at the injection site is normal.
Airway management is a cause for concern. Providing general anesthesia via the external mask for a prolonged time period can produce significant facial injury that can be disfiguring. Placement of a laryngeal mask airway (LMA) can produce significant injury to the oral and oropharyngeal tissues and is probably best avoided. Direct laryngoscopy for endotracheal intubation may also produce significant injury to the airway structures: the epiglottis, base of the tongue, glottic folds, and posterior oropharynx. The smallest size endotracheal tube possible should be used for the patient with EB and copious amounts of water-soluble lubricant should be applied to the tube to reduce the possibility of injury to the vocal cords.
Fluid resuscitation and medication injection must be done with care. Overly aggressive fluid delivery or medication injection pressure can be the cause of infiltration of the IV line, which in turn may cause skin lesions. The patency of the intravenous line must be verified on a continual basis. Extravasation of fluids and/or medications in the patient with EB can cause serious injury.