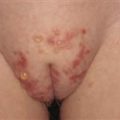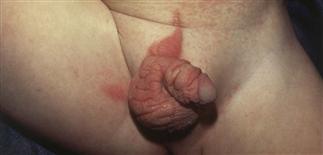
Red, warty, curvilinear, unilateral plaque on toddler’s scrotum, adjacent abdomen and thigh.
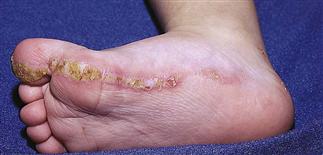
Linear epidermal nevus on the plantar surface of child’s foot.
CLINICAL FEATURES
Children with widespread skin involvement have a higher risk of associated abnormalities and should have referral to a children’s genetic center or multidiscipline clinic. The pattern of skin involvement follows the embryonic skin lines of Blaschko, indicating genetic mosaicism. Affected skin areas may have mutations of the FGFR 3 gene or keratin 1 or 10 genes.
Small epidermal nevi may be confused with warts.
TREATMENT
Small lesions may be excised. For the child with widespread skin involvement, topical keratolytics such as retinoid creams may be useful when combined with topical lubrication. The affected areas will revert to their previous state when topical therapy is discontinued. Oral retinoids have been helpful in severe involvement.