Endocrine System and Nutritional and Metabolic Diseases
Anatomy and Physiology
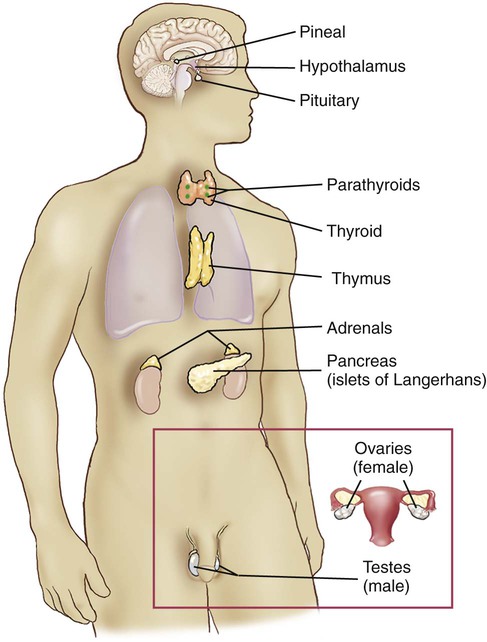
The endocrine system is composed of several single and paired ductless glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream. The hormones regulate specific body functions by acting on target cells with receptor sites for those particular hormones only. See Figure 15-1 for an illustration of the body with the locations of the endocrine glands.
Pituitary Gland
The anterior lobe, or adenohypophysis, is composed of glandular tissue and secretes hormones in response to stimulation by the hypothalamus. The hypothalamus sends hormones through blood vessels, which cause the adenohypophysis either to release or to inhibit the release of specific hormones. The adenohypophysis has a wide range of effects on the body, as Figure 15-2 and the table below illustrate.
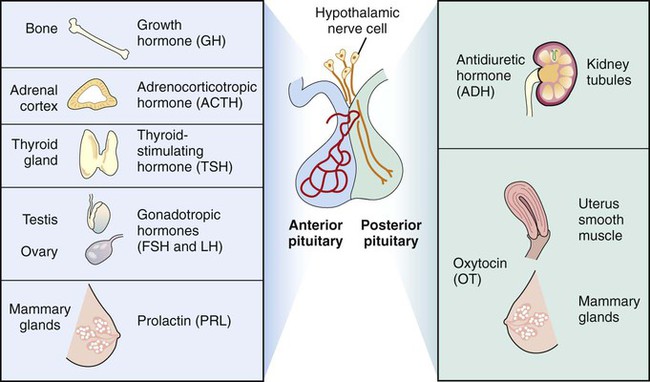
The posterior lobe (neurohypophysis) of the pituitary gland is composed of nervous tissue. The hormones that it secretes are produced in the hypothalamus, transported to the neurohypophysis directly through the tissue connecting the organs, and released from storage in the posterior lobe by neural stimulation from the hypothalamus. The two hormones released by this lobe are antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and oxytocin (OT). See the following table and Figure 15-2 for the hormones secreted by the neurohypophysis and their effects.
Adenohypophysis Hormones and Their Effects
| Adenohypophysis Hormones | Effect |
| Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) | Stimulates the adrenal cortex to release steroids. |
| Gonadotropic hormones (include follicle-stimulating hormone [FSH], luteinizing hormone [LH], and interstitial cell-stimulating hormone [ICSH]) | FSH stimulates the development of gametes in the respective sexes. LH stimulates ovulation in the female and the secretion of sex hormones in both the male and the female. ICSH stimulates production of reproductive cells in the male. |
| Growth hormone (GH) (also called human growth hormone [hGH] or somatotropin hormone [STH]) | Stimulates growth of long bones and skeletal muscle; converts proteins to glucose. |
| Prolactin (PRL) (also called lactogenic hormone) | Stimulates milk production in the breast. |
| Thyrotropin (also called thyroid-stimulating hormone [TSH]) | Stimulates thyroid to release two other thyroid hormones. |
Neurohypophysis Hormones and Their Effects
| Neurohypophysis Hormones | Effect |
| Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) (also called vasopressin) | Stimulates the kidneys to reabsorb water and return it to circulation; is also a vasoconstrictor, resulting in higher blood pressure. |
| Oxytocin (OT) | Stimulates the muscles of the uterus during the delivery of an infant and the muscles surrounding the mammary ducts to contract, releasing milk. |
Thyroid Gland
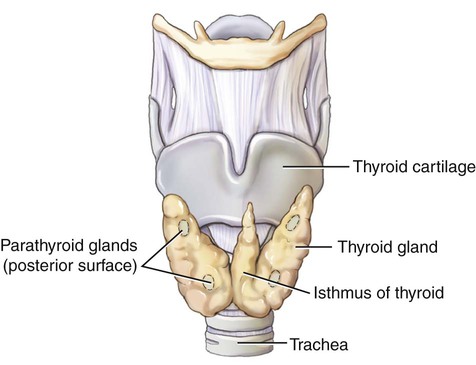
The thyroid gland is a single organ, but is divided into right and left lobes that are joined by a thin structure termed the isthmus (Fig. 15-3). It is located in the anterior part of the neck and is bounded by the trachea behind it and the thyroid cartilage above it. It regulates the metabolism of the body and normal growth and development, and controls the amount of calcium (Ca) deposited into bone. The thyroid gland is composed of small sacs, called follicles, that absorb iodine. The sacs are surrounded by follicular cells that produce triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). Parafollicular cells in the thyroid produce and secrete calcitonin, which controls the amount of calcium in the blood. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), released by the anterior pituitary gland, causes the thyroid to release T3 and T4.
Thyroid Gland Hormones and Their Effects
| Thyroid Gland Hormone | Effect |
| Calcitonin | Regulates the amount of calcium in the bloodstream. |
| Tetraiodothyronine (also called thyroxine [T4]) | Increases cell metabolism. |
| Triiodothyronine (T3) | Increases cell metabolism. |
Adrenal Glands (Suprarenals)
The adrenal cortex secretes three hormones that are called steroids.
Adrenal Cortex Hormones and Their Effects
| Adrenal Cortex Hormones | Effect |
| Glucocorticoids (e.g., cortisol [hydrocortisone]) | Respond to stress; have antiinflammatory properties. |
| Mineralocorticoids (e.g., aldosterone) | Regulate blood volume, blood pressure, and electrolytes. |
| Sex hormones (e.g., estrogen, androgen) | Responsible for secondary sex characteristics. |
Adrenal Medulla Hormones and Their Effects
| Adrenal Medulla Hormones (Catecholamines) | Effect |
| Dopamine | Dilates arteries and increases production of urine, blood pressure, and cardiac rate. Acts as a neurotransmitter in the nervous system. |
| Epinephrine (also called adrenaline) | Dilates bronchi, increases heart rate, raises blood pressure, dilates pupils, and elevates blood sugar levels. |
| Norepinephrine (also called noradrenaline) | Increases heart rate and blood pressure and elevates blood sugar levels for energy use. |
Pancreas
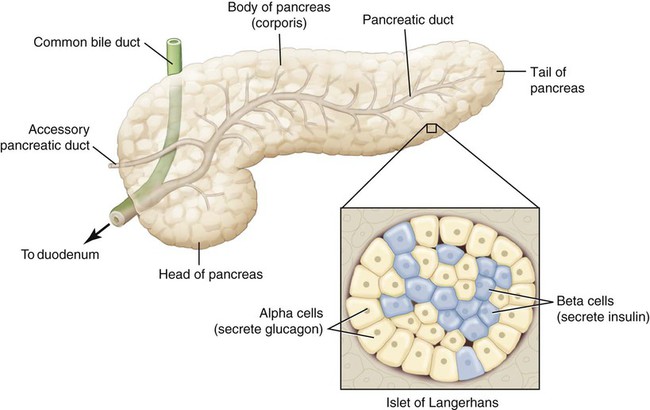
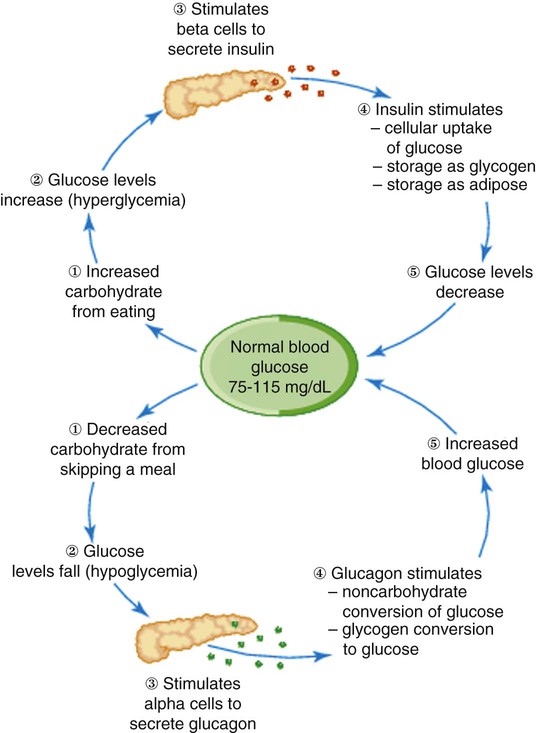
The pancreas, located inferior and posterior to the stomach, is a gland with both exocrine and endocrine functions (Fig. 15-4). The exocrine function is to release digestive enzymes through a duct into the small intestines. The endocrine function, accomplished through a variety of types of cells called islets of Langerhans, is to regulate the level of glucose in the blood by stimulating the liver. The two main types of islets of Langerhans are alpha and beta cells. Alpha cells produce the hormone glucagon, which increases the level of glucose in the blood when levels are low. Beta cells secrete insulin, which decreases the level of glucose in the blood when levels are high. Insulin is needed to transport glucose out of the bloodstream and into the cells. In the absence of glucose in the cells, proteins and fats are broken down, causing excessive fatty acids and ketones in the blood. Normally, these hormones regulate glucose levels through the metabolism of fats, carbohydrates, and proteins. See Figure 15-5 for a diagram explaining the effects of insulin and glucagon.

Combining Forms for the Anatomy and Physiology of the Endocrine System
| Meaning | Combining Form |
| adrenal gland | adren/o, adrenal/o |
| calcium | calc/o, calc/i |
| cortex | cortic/o |
| gland | aden/o |
| glucose, sugar | gluc/o, glyc/o, glycos/o |
| gonads | gonad/o |
| ketone | ket/o, keton/o |
| kidney | ren/o, nephr/o |
| lobe | lob/o |
| medulla | medull/o |
| pancreas | pancreat/o |
| parathyroid gland | parathyroid/o |
| pituitary gland | hypophys/o, pituitar/o, pituit/o |
| thalamus | thalam/o |
| thymus gland | thym/o |
| thyroid gland | thyr/o, thyroid/o |
| to secrete | crin/o |
| turning | trop/o |
Prefixes for the Anatomy of the Endocrine System
| Prefix | Meaning |
| endo- | within |
| exo- | outward |
| hypo- | under, deficient |
| supra- | above |
Suffixes for the Anatomy of the Endocrine System
| Suffix | Meaning |
| -al | pertaining to |
| -crine | to secrete |
| -us, -is | structure |
Pathology
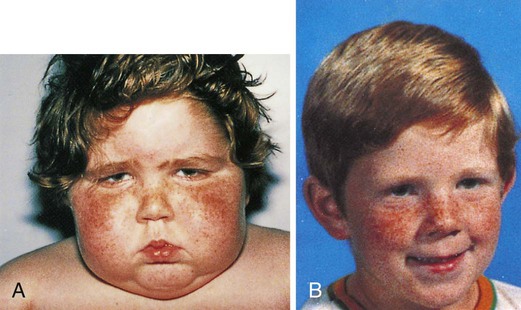
A, First diagnosed with Cushing’s syndrome. B, Four months later after treatment.
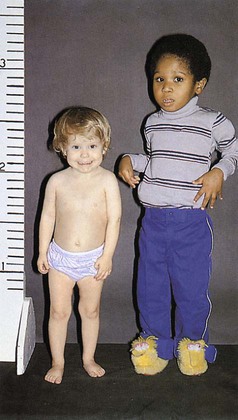
 -year-old boy is in the 50th percentile for height. The short, 3-year-old girl exhibits the characteristic “kewpie doll” appearance, suggesting a diagnosis of growth hormone (GH) deficiency.
-year-old boy is in the 50th percentile for height. The short, 3-year-old girl exhibits the characteristic “kewpie doll” appearance, suggesting a diagnosis of growth hormone (GH) deficiency.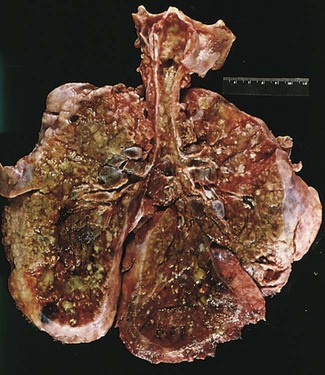
Terms Related to Signs and Symptoms of Endocrine Disorders (RØØ-R99)
| Term | Word Origin | Definition |
| anorexia | an- no, not, without orex/o appetite -ia condition |
Lack of appetite. Anorexia nervosa is an eating disorder. |
| glycosuria | glycos/o sugar, glucose -uria urinary condition |
Presence of glucose in the urine. May indicate diabetes mellitus. Also called glucosuria. |
| hyperalimentation | hyper- excessive, above aliment/o nutrition -ation process of |
An excessive intake of food. May be used to describe overeating. |
| hyperglycemia | hyper- excessive, above glyc/o glucose, sugar -emia blood condition |
Excessive glucose in the blood. |
| ketonuria | keton/o ketone -uria urinary condition |
Presence of ketones in urine. May indicate diabetes mellitus or malnutrition. |
| paresthesia | par- abnormal esthesi/o feeling -ia condition |
Abnormal sensation, such as prickling. |
| polydipsia | poly- many, much, excessive dips/o thirst -ia condition |
Condition of excessive thirst. |
| polyphagia | poly- many, much, excessive phag/o to eat, swallow -ia condition |
Condition of excessive appetite. |
| polyuria | poly- many, much, excessive –uria urinary condition |
Condition of excessive urination. |
| prediabetes | A condition in which an individual’s blood glucose level is higher than normal, but not high enough for a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes. | |
| tetany | Continuous muscle spasms. |

9. hyperglycemia __________________________________________________________________________________
10. glycosuria ______________________________________________________________________________________
Terms Related to Thyroid Disorders (EØØ-EØ7)
| Term | Word Origin | Definition |
| goiter | Enlargement of the thyroid gland, not due to a tumor (Fig. 15-6). | |
| hyperthyroidism | hyper- excessive, above thyroid/o thyroid gland -ism condition |
Excessive thyroid hormone production; also called thyrotoxicosis, the most common form of which is Graves’ disease, which may be accompanied by exophthalmos, in which the eyeballs protrude from their orbits. The extreme form is called thyroid storm or thyroid crisis and is life threatening (Fig. 15-7). |
| hypothyroidism | hypo- deficient, under thyroid/o thyroid gland -ism condition |
Deficient thyroid hormone production. If it occurs during childhood, it causes a condition called cretinism, which results in stunted mental and physical growth. The extreme adult form is called myxedema, which is characterized by facial and orbital edema. |
| thyroiditis | thyroid/o thyroid -itis inflammation |
Inflammation of the thyroid. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is a chronic autoimmune form of thyroiditis. |
Terms Related to Diabetes Mellitus (EØ8-E13)
| Term | Word Origin | Definition |
| diabetes mellitus (DM) | Diabetes mellitus is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by high glucose levels that result from inadequate amounts of insulin, resistance to insulin, or a combination of both. Secondary diabetes is a condition secondary to another condition or the result of a pancreatectomy. Complications include diabetic neuropathy, diabetic nephropathy, diabetic retinopathy (destruction of retina due to blockage of blood vessels), and ulcers of the foot and toes. | |
| type 1 diabetes | Total lack of insulin production resulting in glycosuria, polydipsia, polyphagia, polyuria, blurred vision, fatigue, and frequent infections. Thought to be an autoimmune disorder. Previously called insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) and juvenile diabetes. | |
| type 2 diabetes | Deficient insulin production, with symptoms similar to type 1 diabetes. Cause unknown but associated with obesity and family history; previously called non–insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM). |
Terms Related to Other Disorders of Glucose Regulation and Pancreatic Internal Secretion (E15-E16)
| Term | Word Origin | Definition |
| hypoglycemia | hypo- deficient, under glyc/o sugar, glucose -emia blood condition |
Condition of deficient sugar in the blood. The opposite would be hyperglycemia—excessive sugar in the blood. |
| hyperinsulinism | hyper- excessive, above insulin/o insulin -ism condition |
Oversecretion of insulin; seen in some newborns of diabetic mothers. Causes severe hypoglycemia. |
Terms Related to Disorders of Other Endocrine Glands (E2Ø-E35)
| Term | Word Origin | Definition |
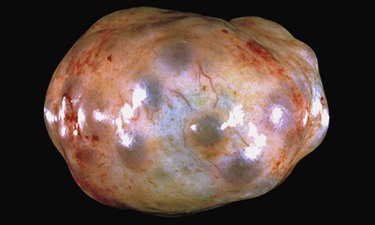
| acromegaly and pituitary gigantism | acro- extremities -megaly enlargement |
Acromegaly is the hypersecretion of somatotropin from adenohypophysis during adulthood; leads to an enlargement of the extremities (hands and feet), jaw, nose, and forehead (Fig. 15-8). Usually caused by an adenoma of the pituitary gland. Pituitary gigantism is hypersecretion that occurs during childhood. |
| Cushing’s syndrome | Excessive secretion of cortisol by the adrenal cortex causes symptoms of obesity, leukocytosis, hirsutism (excessive hairiness), hypokalemia, hyperglycemia, and muscle wasting (Fig. 15-9). | |
| diabetes insipidus (DI) | Deficiency of antidiuretic hormone (ADH), which causes the patient to excrete large quantities of urine (polyuria) and exhibit excessive thirst (polydipsia). | |
| growth hormone deficiency (GHD) | Somatotropin deficiency due to dysfunction of the adenohypophysis during childhood results in dwarfism (Fig. 15-10). If during adulthood, patients may develop obesity and may experience weakness and cardiac difficulties. | |
| hyperparathyroidism | hyper- excessive, above parathyroid/o parathyroid gland -ism condition |
Overproduction of parathyroid hormone; symptoms include polyuria, hypercalcemia, hypertension, and kidney stones. |
| hypoparathyroidism | hypo- deficient parathyroid/o parathyroid gland -ism condition |
Deficient parathyroid hormone production results in tetany, hypocalcemia, irritability, and muscle cramps. |
| hypopituitarism | hypo- deficient pituitar/o pituitary -ism condition |
Deficiency or lack of all pituitary hormones causing hypotension, weight loss, weakness; also includes Simmonds’ disease and panhypopituitarism. |
| polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) | poly- many, much, excessive cyst/o sac -ic pertaining to |
Bilateral presence of numerous cysts in the ovaries, caused by a hormonal abnormality leading to the secretion of androgens. Can cause acne, facial hair, and infertility (Fig. 15-11). |
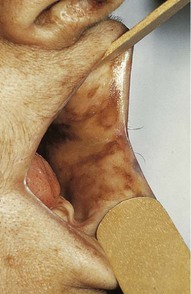
| primary adrenocortical insufficiency | Insufficient secretion of adrenal cortisol from the adrenal cortex is manifested by gastric complaints, hypotension, dehydration, fatigue, and hyperpigmentation of skin and mucous membranes (Fig. 15-12). Also called Addison’s disease. | |
| progeria | pro- forward, in front of ger/o old age -ia condition |
Genetic condition of rapid aging. Also called Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome (HGPS). |
| syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH) | Oversecretion of ADH from the neurohypophysis leading to severe hyponatremia and the inability to excrete diluted urine. |

18. condition of excessive thyroid gland _____________________________________________________________
19. blood condition of deficient glucose ______________________________________________________________
20. enlargement of the extremities ___________________________________________________________________
21. condition of before old age ______________________________________________________________________
Terms Related to Overweight, Obesity, and Other Hyperalimentation (E65-E68)
| Term | Word Origin | Definition |
| adiposity | adipos/o full of fat -ity noun ending |
Accumulation of adipose (fat) tissue in specific body areas. |
| morbid obesity | morb/o disease -id pertaining to |
A condition of patients who are 50% to 100% over their ideal body weight. The body mass index (BMI) is used to measure the relationship between a person’s height and weight to determine obesity. |
Terms Related to Metabolic Disorders (E7Ø-E88)
| Term | Word Origin | Definition |
| cystic fibrosis (CF) | cyst/o sac -ic pertaining to fibr/o fiber -osis abnormal condition |
Inherited disorder of the exocrine glands resulting in abnormal, thick secretions of mucus that causes COPD. Caused by a defect in the gene that allows for the normal mucous secretions of the lungs to be diluted and excreted (Fig. 15-13). |
| dehydration | de- lack of hydr/o water -ation process of |
Condition of deficient water in the body. |
| hypercholesterolemia | hyper- excessive, above cholesterol/o cholesterol -emia blood condition |
Excessive cholesterol, a waxy substance, in the blood. |
| hyperlipidemia | hyper- excessive, above lipid/o fat -emia blood condition |
Excessive fat in the blood. May be due to genetic causes. |
| hypocalcemia | hypo- deficient, under calc/o calcium -emia blood condition |
Condition of deficient calcium (Ca) in the blood. The opposite would be hypercalcemia—excessive calcium in the blood. |
| hypokalemia | hypo- deficient, under kal/i potassium -emia blood condition |
Condition of deficient potassium (K) in the blood. The opposite would be hyperkalemia—excessive potassium in the blood. |
| hyponatremia | hypo- deficient, under natr/o sodium -emia blood condition |
Condition of deficient sodium (Na) in the blood. The opposite would be hypernatremia—excessive sodium in the blood. |
| hypovolemia | hypo- deficient, under vol/o volume -emia blood condition |
Deficient volume of circulating blood. |
| ketoacidosis | ket/o ketone acid/o acid -osis abnormal condition |
Excessive amount of ketone acids in the bloodstream. |
| phenylketonuria (PKU) | A deficiency of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase, which is responsible for converting phenylalanine, found in certain foods, into tyrosine. Failure to treat this condition will lead to brain damage and mental retardation. | |
| Tay-Sachs disease | A fatal genetic disorder in which lipids accumulate in the tissues and brain due to an enzyme deficiency. |

11. hyperlipidemia __________________________________________________________________________________
12. hypocalcemia ___________________________________________________________________________________
13. hypercholesterolemia ____________________________________________________________________________
Terms Related to Benign Neoplasms
| Term | Word Origin | Definition |
| pheochromocytoma | phe/o dark chrom/o color cyt/o cell -oma tumor, mass |
Usually benign tumor of the adrenal medulla. |
| prolactinoma | prolactin/o prolactin -oma tumor, mass |
Most common type of pituitary tumor (Fig. 15-14). Causes the pituitary to oversecrete prolactin. |
| thymoma | thym/o thymus -oma tumor, mass |
Noncancerous tumor of epithelial origin that is often associated with myasthenia gravis. |
Terms Related to Malignant Neoplasms
| Term | Word Origin | Definition |
| islet cell carcinoma | carcin/o epithelial cancer -oma tumor, mass |
Pancreatic cancer; fourth leading cause of cancer death in the United States. Treated surgically with a Whipple procedure (pancreatoduodenectomy). |
| malignant thymoma | thym/o thymus gland -oma tumor, mass |
Rare cancer of the thymus gland. |
| thyroid carcinoma | carcin/o epithelial cancer -oma tumor, mass |
The most common types of thyroid carcinoma are follicular and papillary. Both have high 5-year survival rates. |

Procedures
Terms Related to Diagnostic Tests
| Term | Word Origin | Definition |
| A1c | Measure of average blood glucose during a 3-month time span. Used to monitor response to diabetes treatment. Also called glycosylated hemoglobin or HbA1c. | |
| fasting plasma glucose (FPG) | After a period of fasting, blood is drawn. The amount of glucose present is used to measure the body’s ability to break down and use glucose. 100-125 mg/dL = prediabetes; ≥126 = diabetes. Previously called fasting blood sugar (FBS). | |
| hormone tests | Measure the amount of antidiuretic hormone (ADH), cortisol, growth hormone, or parathyroid hormone in the blood. | |
| oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) | Blood test to measure the body’s response to a concentrated glucose solution. May be used to diagnose diabetes mellitus. | |
| radioimmunoassay studies (RIA) | Nuclear medicine tests used to tag and detect hormones in the blood through the use of radionuclides. | |
| sweat test | Method of evaluating sodium and chloride concentration in sweat as a means of diagnosing cystic fibrosis. | |
| thyroid function tests (TFTs) | Blood tests done to assess T3, T4, and calcitonin. May be used to evaluate abnormalities of thyroid function. | |
| total calcium | Measures the amount of calcium in the blood. Results may be used to assess parathyroid function, calcium metabolism, or cancerous conditions. | |
| urine glucose | Used as a screen for or to monitor diabetes mellitus; a urine specimen is tested for the presence of glucose. | |
| urine ketones | Test to detect presence of ketones in a urine specimen; may indicate diabetes mellitus or hyperthyroidism. |
Terms Related to Endocrine Procedures
| Term | Word Origin | Definition |
| adrenalectomy | adrenal/o adrenal gland -ectomy cutting out |
Bilateral removal of the adrenal glands to reduce excess hormone secretion. |
| adrenalorrhaphy | adrenal/o adrenal gland -rrhaphy suturing |
Suturing the adrenal gland. |
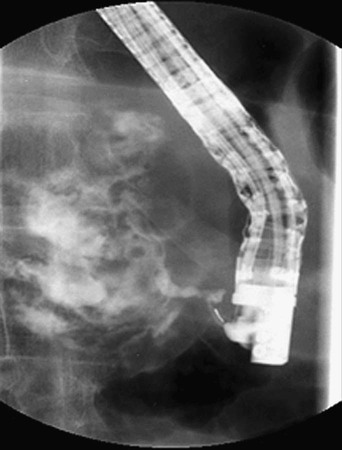
| endoscopic retrograde pancreatography (ERP) | endo- within -scopic pertaining to viewing pancreat/o pancreas -graphy recording |
The recording of the pancreas through the use of an endoscope (duodenoscope) and a contrast medium (Fig. 15-15). |
| pancreatectomy | pancreat/o pancreas –ectomy cutting out |
Excision of all or part of the pancreas to remove a tumor or to treat an intractable inflammation of the pancreas. |
| pancreatoduodenectomy | pancreat/o pancreas duoden/o duodenum -ectomy cutting out |
Excision of the head of the pancreas together with the duodenum. Used to treat pancreatic cancer. Also called Whipple procedure. |
| pancreatolithotomy | pancreat/o pancreas -lithotomy cutting out a stone |
Cutting a stone from the pancreas. |
| parathyroidectomy | parathyroid/o parathyroid gland -ectomy cutting out |
Removal of the parathyroid gland, usually to treat hyperparathyroidism. |
| pinealectomy | pineal/o pineal body -ectomy cutting out |
Cutting out the pineal body. |
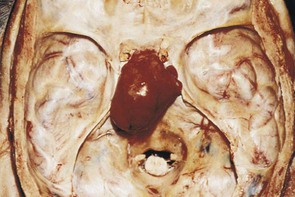
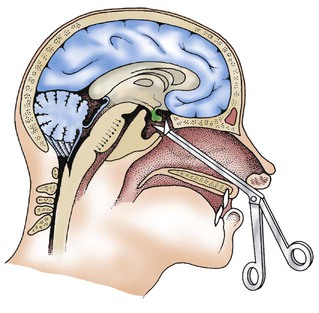
| pituitectomy | pituit/o pituitary gland -ectomy cutting out |
Excision of the pituitary gland; usually done to remove a pituitary tumor (Fig. 15-16). Also called pituitarectomy. |
| thyroidectomy | thyroid/o thyroid gland -ectomy cutting out |
Removal of part or all of the thyroid gland to treat goiter, tumors, or hyperthyroidism that does not respond to medication. Removal of most, but not all, of this gland will result in a regrowth of the gland with normal function. If cancer is detected, a total thyroidectomy is performed. |
Pharmacology
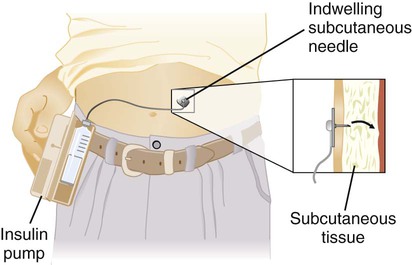
antidiabetics: Manage glucose levels in the body when the pancreas or insulin receptors are no longer functioning properly. These drugs are also known as hypoglycemic agents and encompass various oral agents and replacement insulin. Type 1 diabetes mellitus typically requires insulin therapy, and management of type 2 diabetes mellitus begins with antidiabetic drugs such as metformin (Glucophage), glipizide (Glucotrol), or albiglutide (Tanzeum); Insulin is typically used as a last resort. Figure 15-17 shows an insulin pump in use by patient.
antithyroid agents: Treat hyperthyroidism. Examples include methimazole (Tapazole) and propylthiouracil (PTU).
corticosteroids: Mimic or replace the body’s steroids normally produced by the adrenal glands. Underfunctioning adrenal cortices (Addison’s disease) may be treated with prednisone (Deltasone). Corticosteroids are classified as glucosteroids and mineralocorticoids, depending on structure and function.
growth hormones: Treat various disease-causing growth inhibitions. Human growth hormone (hGH) is available as the prescription somatropin (Genotropin, Nutropin).
posterior pituitary hormones: Vasopressin and desmopressin acetate are used to treat diabetes insipidus.
thyroid hormones: Treat hypothyroidism. Examples include natural thyroid hormones (Armour Thyroid) and levothyroxine (Levoxyl, Synthroid).

Recognizing Suffixes for PCS
Suffixes and Root Operations for the Endocrine System
| Suffix | Root Operation |
| -ectomy | Excision, resection |
| Abbreviation | Meaning |
| ACTH | adrenocorticotropic hormone |
| ADH | antidiuretic hormone |
| BMI | body mass index |
| Ca | calcium |
| CF | cystic fibrosis |
| DI | diabetes insipidus |
| DM | diabetes mellitus |
| ERP | endoscopic retrograde pancreatography |
| FBS | fasting blood sugar |
| FPG | fasting plasma glucose |
| FSH | follicle-stimulating hormone |
| GH | growth hormone |
| GHD | growth hormone deficiency |
| hGH | human growth hormone |
| HGPS | Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome |
| ICSH | interstitial cell-stimulating hormone |
| IDDM | insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus |
| K | potassium |
| LH | luteinizing hormone |
| Na | sodium |
| NIDDM | non–insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus |
| OGTT | oral glucose tolerance test |
| OT | oxytocin |
| PCOS | polycystic ovary syndrome |
| PKU | phenylketonuria |
| PRL | prolactin |
| PTH | parathyroid hormone |
| RIA | radioimmunoassay studies |
| SIADH | syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone |
| STH | somatotropic hormone |
| T3 | triiodothyronine |
| T4 | thyroxine |
| TFTs | thyroid function tests |
| TSH | thyroid-stimulating hormone |