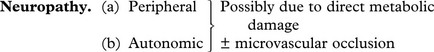Chapter 16 Endocrine System
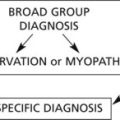
Endocrine Diseases
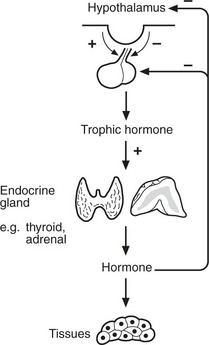
Most endocrine glands are controlled by hormones produced in the anterior pituitary, themselves under control of substances produced in the hypothalamus. A variety of stimuli control pituitary and hypothalamic hormone release, especially feedback control from hormone levels from the target glands. Levels of pituitary hormones show a circadian rhythm.
Pituitary Gland
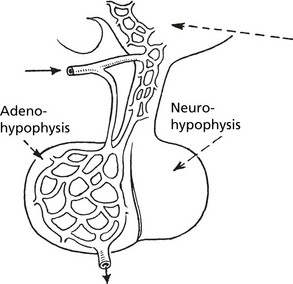
The pituitary has two parts; the anterior (adenohypophysis) and the posterior (neurohypophysis).
Pituitary Hyperfunction
In most cases, this is associated with pituitary adenoma.
Small tumours present only if they produce excess hormones, while larger tumours may cause pressure effects (e.g. on optic chiasma, page 141) or with hypopituitarism due to destruction of normal pituitary. Occasionally haemorrhage into a pituitary adenoma causes raised intracranial pressure (pituitary apoplexy).
Hypopituitarism
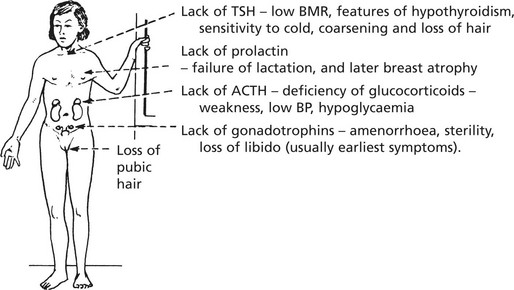
Failure of pituitary secretion may affect one or several hormones. Causes include:
In time, the peripheral endocrine organs – thyroid, adrenals, ovaries – show atrophy.
Note: Some individuals treated with human growth hormone have developed Creutzfeld–Jacob disease (p.555).
In adults, GH deficiency leads to lethargy, diminished muscle mass, obesity and premature atheroma.
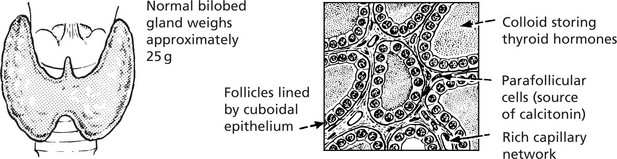
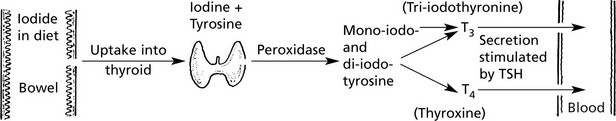
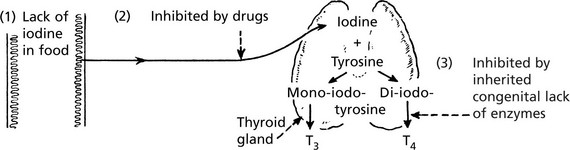
Thyroid Gland – Underactivity
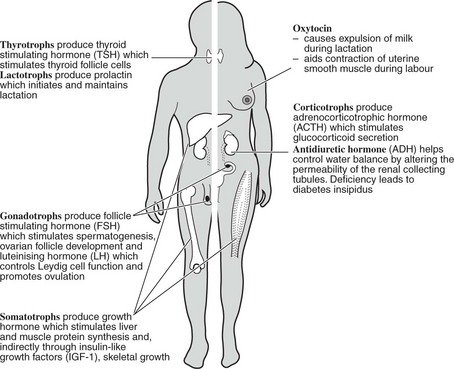
The thyroid gland is under the control of the pituitary thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH p.623).
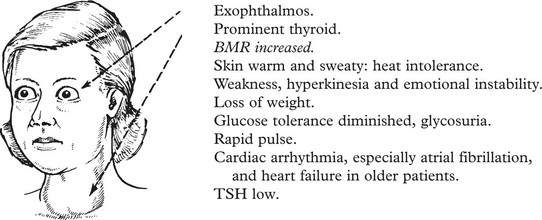
Thyroid Gland – Overactivity
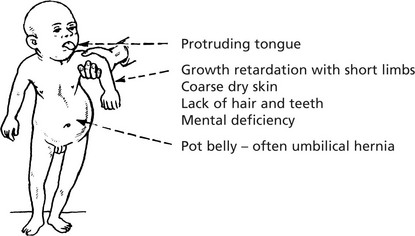
Endemic Cretinism
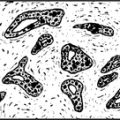
This occurs in districts where goitre is common due to iodine deficiency. The infantile thyroid is usually enlarged and nodular. Histologically, there are hyperplastic foci containing colloid which compress the intervening tissue. The incidence of this disorder has reduced following addition of iodine to salt.
Thyroid Hyperfunction
Graves’ Disease
In some cases there are foci of thyroiditis with lymphocytes and plasma cells.
Thyroid Gland
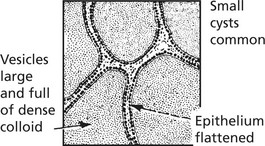
Non-Toxic Goitre
This is a simple enlargement of the thyroid gland, not associated with increased secretion of thyroid hormone.
The gland is enlarged and pale pink. Two phases can be recognised:
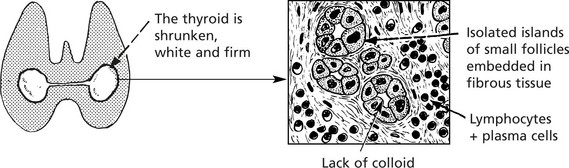
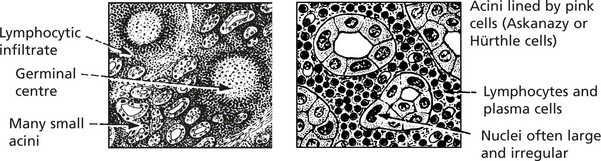
Autoimmune Thyroiditis
This type of disease is associated with the appearance of thyroid antibodies in the blood and inflammation with lymphocytes and plasma cells in the thyroid gland. There is an associated risk of development of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma in each.
This is the most distinctive type of autoimmune thyroid disease, and the changes are widespread.
Clinical effects: The patient may be euthyroid but eventually may develop hypothyroidism.
Any attempt to reduce the size of the goitre by surgery inevitably causes hypothyroidism.
Antibodies to thyroid hormones and epithelium are found in this disease (p.626).
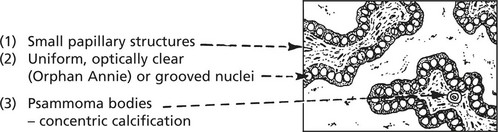
Tumours of Thyroid
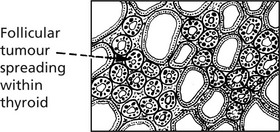
Follicular Adenoma
This fairly common benign tumour is usually single and is encapsulated with compression of the surrounding gland. Very occasionally there is hypersecretion with thyrotoxicosis. Degenerative changes including haemorrhage into the tumour are common.
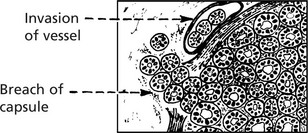
MALIGNANT TUMOURS are common. Five forms are recognised:
Blood spread particularly to bones and lungs is usual in follicular carcinoma.
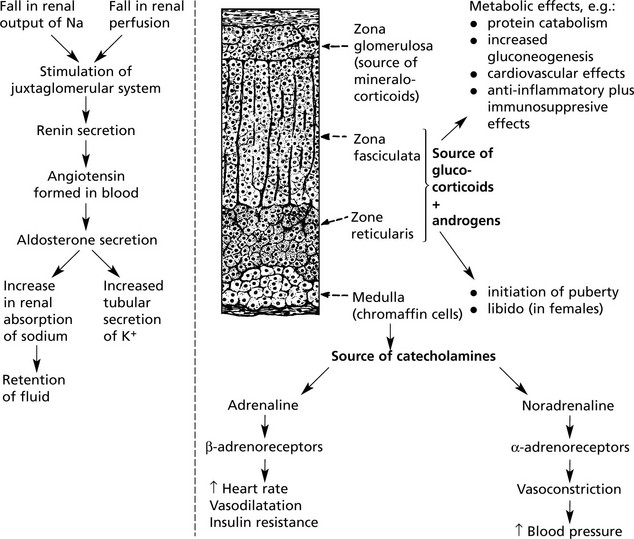
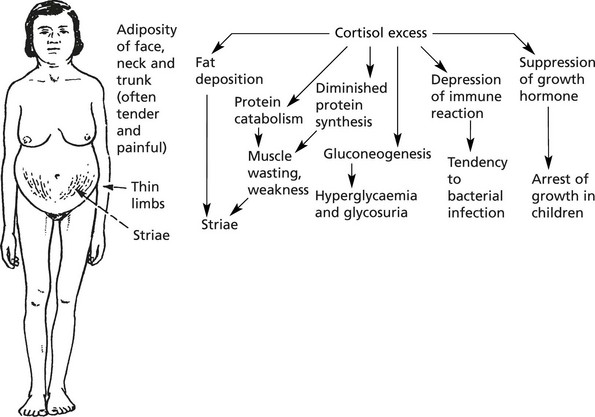
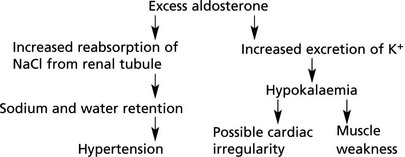
Adrenal Cortex – Overactivity
Overactivity manifests itself in three ways:
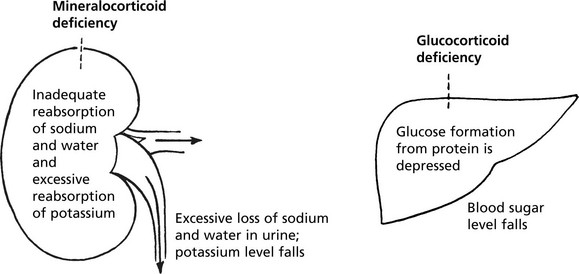
Adrenal Cortex – Hypofunction
Adrenal cortical insufficiency may be due to panhypopituitarism or destruction of about 90% of the adrenal cortex. Acute adrenal failure is usually due to septicaemia, especially meningococcal (Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome).
Chronic Hypofunction
Adrenal Cortex And Medulla
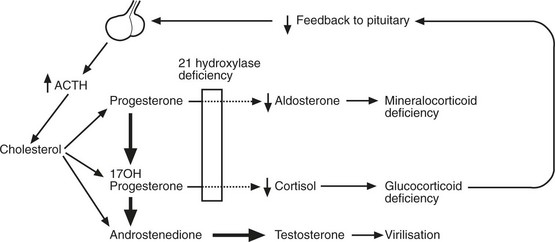
Congenital Adrenocortical Enzyme Defects
These are rare, inherited conditions due to autosomal recessive traits.
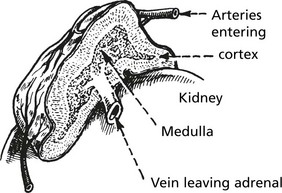
Adrenal Medulla
Excess production of catecholamines may occur with some tumours of the medulla. Three are described:
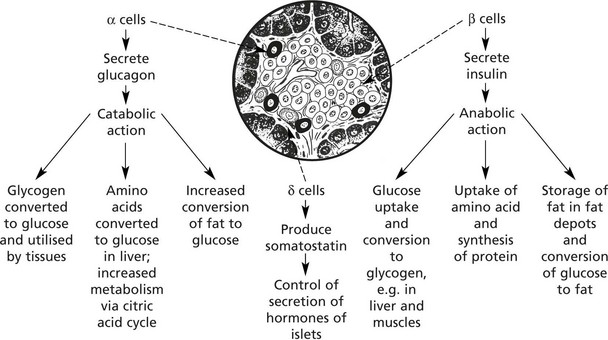
Endocrine Pancreas
The islets of Langerhans form 1–2% of the pancreatic tissue. Four types of cell make up the islets. The majority are β cells.
Insulin also stimulates reabsorption of glucose from the renal glomerular filtrate
Types of Diabetes
Primary Forms
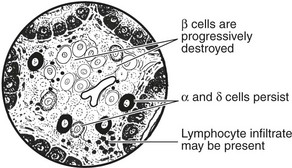
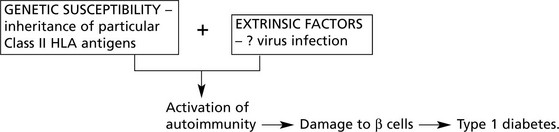
Type 1 Diabetes
This form is due to destruction of β cells in the islets of Langerhans.
This has given rise to a theory of pathogenesis:
Other forms of auto-antibody, e.g. gastric, thyroid, adrenal, have been demonstrated.
Primary Forms
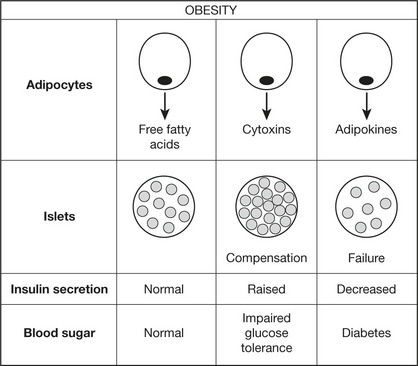
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
This is the commonest form of diabetes affecting 10% of adults over 65 in Western society. It is commoner in Asians and Afro-Caribbeans within Western societies. It is more frequent in females and the incidence increases with age. In contrast to Type 1, the onset is slow and the changes in glucose metabolism mild. (Diet restriction to reduce obesity and oral hypoglycaemic drugs usually control the blood sugar.) Clinical presentation is often due to complications, particularly vascular. Often the disorder is detected by biochemical screening.
Aetiology
The following theory accommodates the known facts:
Note 1: The concordance rate for identical twins is up to 60% in some studies.
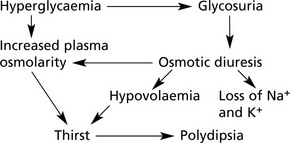
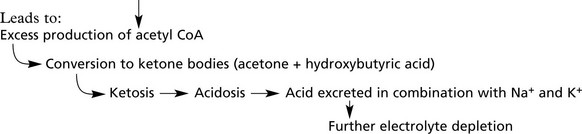
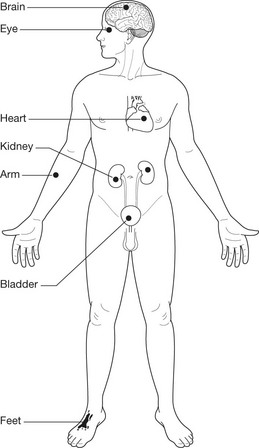
Complications of Diabetes
Pancreatic Endocrine Tumours (Islet Cell Tumours)
These are uncommon. Most are benign and are asymptomatic unless they secrete excess hormones. 10% are malignant. The clinical effects vary with the hormone produced.
These tumours may form part of multiple endocrine neoplasia syndromes (p.643).
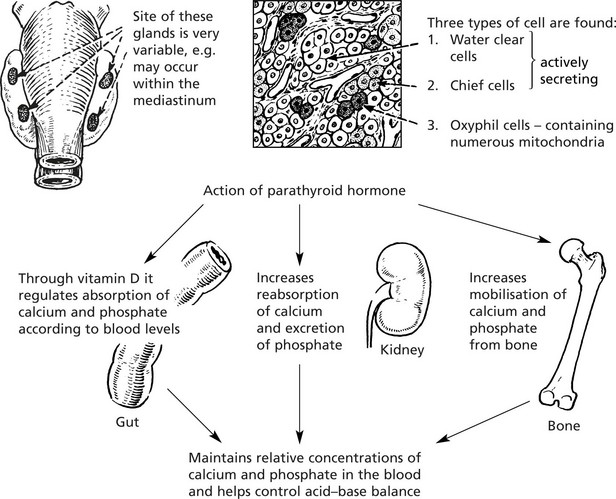
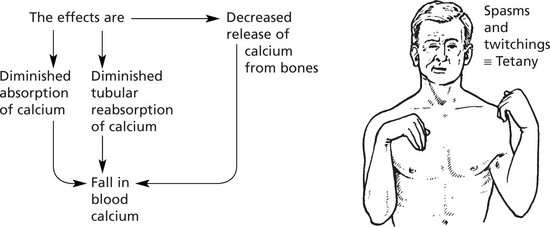
Parathyroid Glands
The parathyroids are four small glands lying posterior to the thyroid gland.
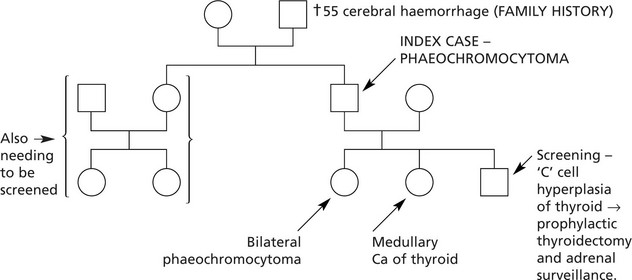
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Syndromes (MENS)
This is a group of familial conditions (autosomal dominant inheritance) characterised by multiple endocrine tumours.
This is due to mutation of the MEN 1 gene on chromosome 11, which encodes menin, a nuclear protein.