Chapter 16 Endocrine disorders in pregnancy
DIABETES MELLITUS
Detection of gestational diabetes
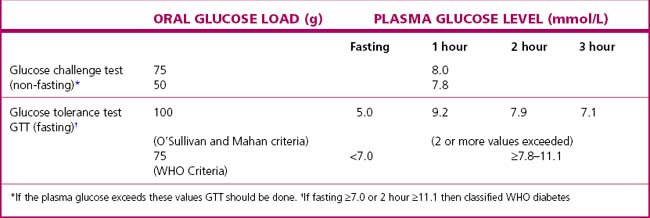
Routine screening of all pregnant women for hyperglycaemia should no longer be considered controversial as two large RCTs have both shown benefit from treating gestational diabetes and the results from the Hyperglycaemia and Adverse Pregnancy Outcome study (HAPO) are being used to define the diagnostic criteria that predict an adverse perinatal outcome. The two currently most widely used criteria are detailed in Table 16.1.
Management of diabetes
Pregnancy
In pregnancy the key principles of management include:
Maternal complications
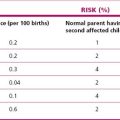
Women with diabetes are more prone to pre-eclampsia (especially if there are any microvascular complications), urinary tract infections, polyhydramnios and candida vaginitis. Diabetic ketoacidosis must be avoided as it may cause fetal death. The incidence of the complications (Table 16.2) depends largely on the quality of the care and blood glucose control of the diabetic woman before and during pregnancy.
| Condition | Risk (Percentage of Women Affected) |
|---|---|
| Pre-eclampsia | 10–20 |
| Polyhydramnios | 20–25 |
| Bacteriuria | 7–10 |
| Congenital malformations | 6 |
| Perinatal mortality | 20–100 per 1000 |
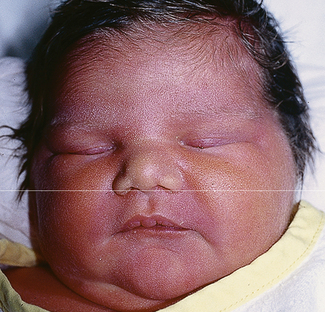
The newborn baby
Following delivery the baby (Fig. 16.1) should be carefully assessed by a neonatologist. Early feeding with oral glucose if necessary is important to minimize the risk of neonatal hypoglycaemia. The blood glucose levels should be monitored before each feed for the following 2 days. If hypoglycaemia persists the baby may require enteral feeding or intravenous glucose or glucagon.