Chapter 43 Emergency department haematology
COMMON HAEMATOLOGICAL EMERGENCIES
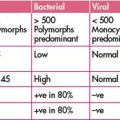
Neutropenic sepsis
(Also see Chapter 42, ‘The immunocompromised patient’.)
Patients presenting with a fever above 38°C require urgent investigation and therapy.
Severe thrombocytopenia and bleeding
Severe bleeding with thrombocytopenia is not usually a problem until the platelet count is less than 10 × 109/L. When patients present with bleeding secondary to thrombocytopenia, an urgent assessment of the cause of the thrombocytopenia is necessary.
Differential diagnosis
THE ANAEMIC PATIENT
Normocytic (normal MCV)
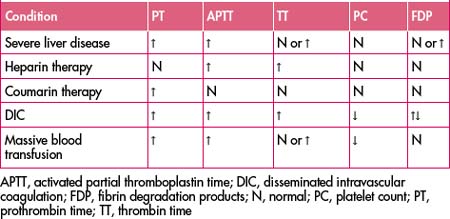
THE PATIENT WITH ABNORMAL BLEEDING
The usual screening tests are:
The following is a guide to the interpretation of these tests.
Platelet and vascular defects
Coagulation defects
ANTICOAGULANT THERAPY
Unfractionated heparin
Vitamin K antagonists/oral anticoagulants (e.g. coumadin)
Changing from heparin to vitamin K antagonists
When commencing vitamin K antagonists, the INR will begin to fall within 36 hours, but this only reflects factor VII levels. It is necessary to continue heparin at lower doses for at least a 3-day overlap when commencing oral anticoagulants.
Reversal
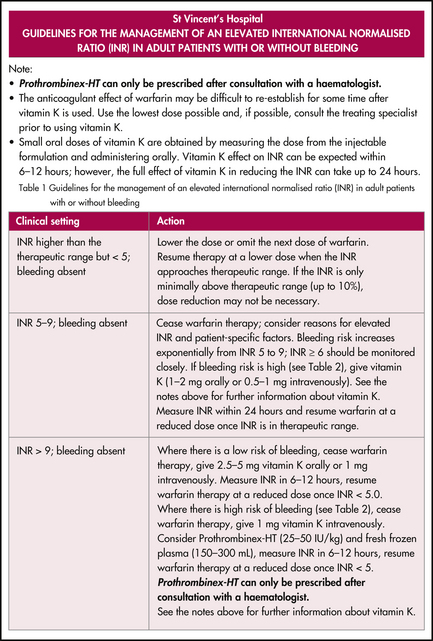
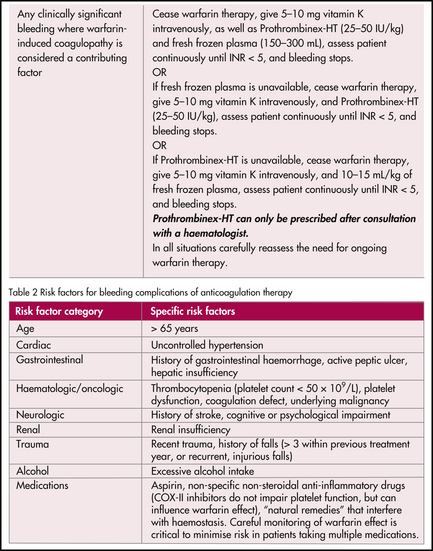
A protocol for the management of an elevated INR is shown in Figure 43.1.
BLOOD TRANSFUSION
Transfusion reactions
Urticarial and anaphylactic reactions
Table 43.2 Commonly used blood products in emergency medicine
| Product | Emergency indications |
|---|---|
| Fresh whole blood | Massive blood loss |
| Red cell concentrate | Severe or refractory anaemia Moderate blood loss |
| Platelet concentrate | Thrombocytopenia with bleeding Platelet dysfunctional bleeding |
| Fresh frozen plasma | Massive transfusion Severe liver disease with bleeding Reversal of coumarin therapy |
| Prothrombinex-HT | Reversal of coumarin therapy |
Reactions to bacterial pyrogens and bacteria
Massive transfusion. Hypothermia (use blood warmer).
Infectious complications—possible risk with nucleic acid testing (NAT)
Inappropriate use of blood components
RCPA pathology test manual. Available: http://www.rcpamanual.edu.au/default.asp.
Australian Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis. Available: http://www.asth.org.au/resources/publications.
Consensus guidelines for warfarin therapy. Available: http://www.mja.com.au/public/issues/172_12_190600/gallus/gallus.html
Australian Red Cross Blood Service. Available: http://www.transfusion.com.au/
National Blood Authority of Australia. Available: http://www.nba.gov.au/.
Australian clinical practise guidelines for the use of blood components. Available: http://www.asth.org.au/resources/publications/synopses/cp77syn.htm.