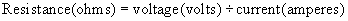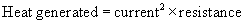Chapter 31 Electrical injuries
In a two-year period from 2002, 1493 people in Australia were hospitalised as a result of an electrical injury, including 77 from lightning strikes. Of the 1493, 209 were aged 0–14 years, with 18 of those sustaining injury from high voltage lines.
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Electricity may cause injury via three broad mechanisms:
The site of either direct tissue or thermal energy damage depends on the pathway of current flow.
PHYSICS
In order to avoid lightning there are some simple measures which should be followed:
Wide-band magnetic direction finders are increasingly used to warn of incoming lightning storms.
LOW AND HIGH VOLTAGE ELECTRICAL INJURY
Infants and young children are prone to sustaining oral electrical injuries from electrical appliances. Mucous membranes have less resistance than skin and the current is therefore higher. These injuries may lead to eventual scarring and deformity of the face in later years. If the current travels close to the eyes, cataracts may form.
Management
Hospital
A good urine flow (1 mL/kg/h) in the face of myoglobinuria (urine dipstick positive for blood) or shock is essential as with standard treatment of rhabdomyolysis. Urinary alkalinisation and use of mannitol and/or frusemide may be indicated, and late renal failure with acidosis must be anticipated.
A check of tetanus immunisation status is mandatory.
Electrical burns should be referred to a specialist burns centre.
LIGHTNING INJURIES
Physics
Mechanisms of strike
Pathophysiology
As the injuries sustained are both multisystemic and multifactorial in aetiology (from diverse sources such as electricity, heat, blunt trauma and anoxia), the clinical possibilities are vast. Certain injuries and their sequelae are typical or may even be diagnostic (see Table 31.1):
| Skin | Burns—feathering or flowers (transient, not burns but electrocution showers)Superficial (often in patterns of sweat lines, or wet exploded clothing)Deep entry and exit wounds; imprints of metal buttons, belt clips, ignited clothing |
| Ear | Tympanic membrane rupture, barotrauma |
| Eye | Onset of cataracts, eye trauma and disruption of anatomy |
| Heart | Asystole, ventricular fibrillation, arrythmias, infarct (rare), transient hypotension or hypertension |
| Limbs | Trauma; keraunoparalysis, a temporary neurovascular dysfunction in the majority of serious strikes, usually resolves in hours but permanent sequelae are possible |
| Central nervous system | Seizures, mental state similar to that after electroconvulsive therapyAmnesia (very common), psychological sequelae |
Severe burns, with their sequelae of renal failure, anaemia and tissue damage, are very uncommon.
Management
Hospital
Usually the surviving victim needs mainly supportive treatment.
Special attention should be paid to the ear and eye examinations for tympanic rupture and corneal defects, respectively. Other ocular pathology will also need to be excluded, most easily when the patient is alert and able to cooperate with full eye examination. Basal visual acuity should be recorded if possible.
PEARLS AND PITFALLS
Daley BJ. Electrical Injuries. June 2008. Online. Available: http://www.emedicine.medscape.com/article/433682-overview.
Pointer S, Harrison J. Electrical injury and death. AIHW National Injury Surveillance Unit. April 2007. Online. Available: http://www.nisu.flinders.edu.au/pubs/reports/2007/injcat99.php.
Rosen P., Barkin R.M., Braen G.R., et al, editors. Emergency medicine—concepts and clinical practice, 5th edn, St Louis: CV Mosby, 2001.
Wright RK. Electrical Injuries. eMedicine; July 2007. Online. Available: http://www.emedicine.com/EMERG/topic162.htm.