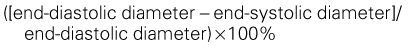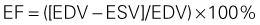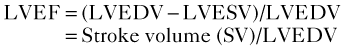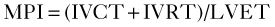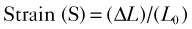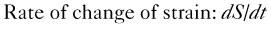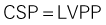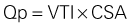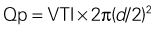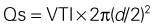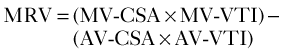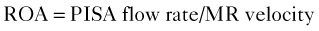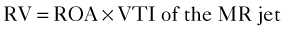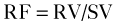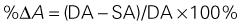6 Echocardiographic Assessment of Heart Failure Resulting from Coronary Artery Disease
Acute and Chronic Ischemic Heart Failure
Basic Principles
Key Points
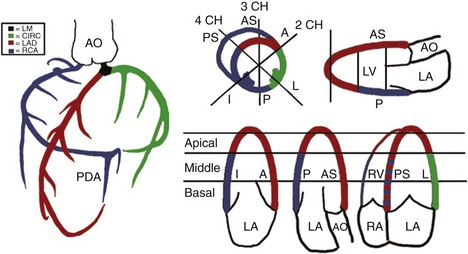
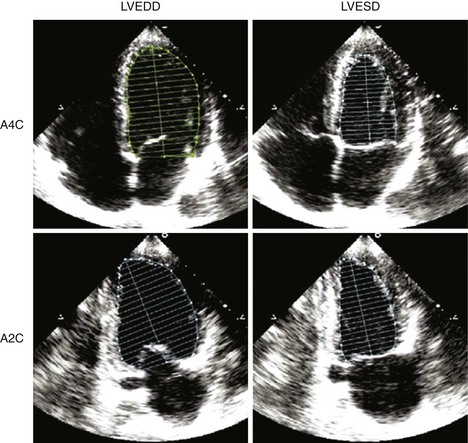
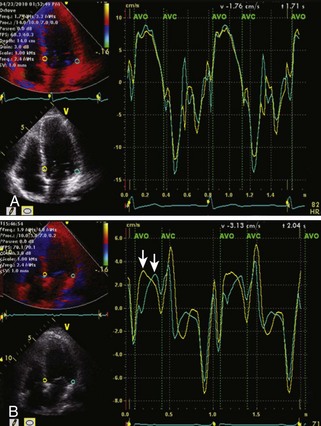
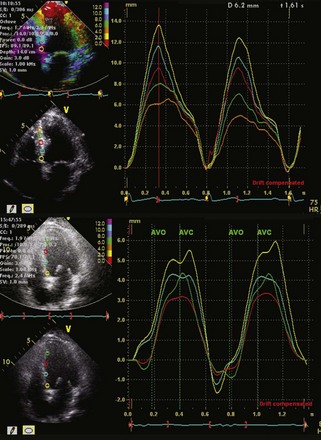
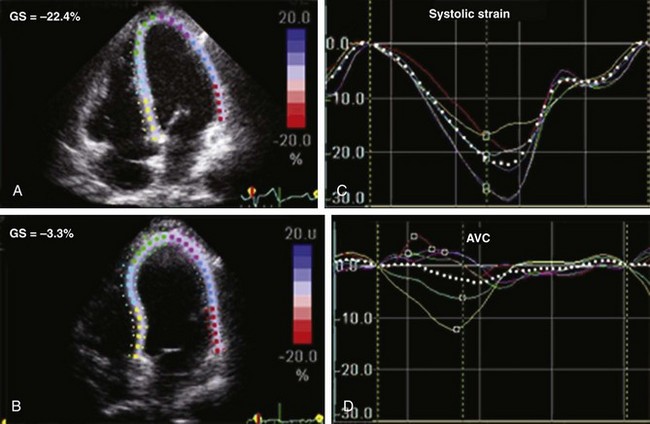
Quantification of LV Size and Function in HF
Basic Principles
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
where IVRT is the isovolumic relaxation time, IVCT is the isovolumic contraction time, and LVET is the LV ejection time.
Step 4
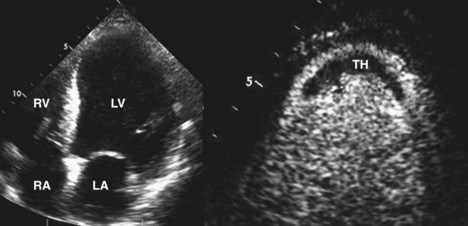
Echocardiographic Detection of Thrombus in HF
Basic Principles
Key Points
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
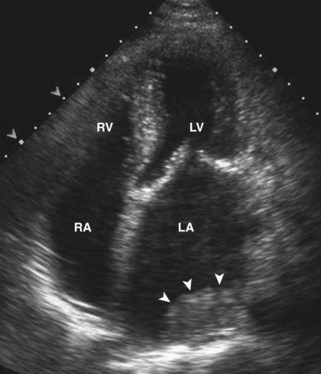
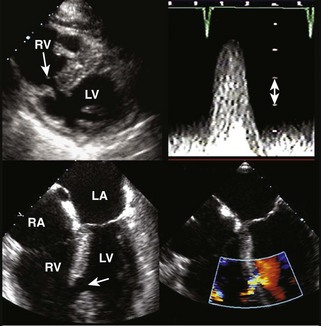
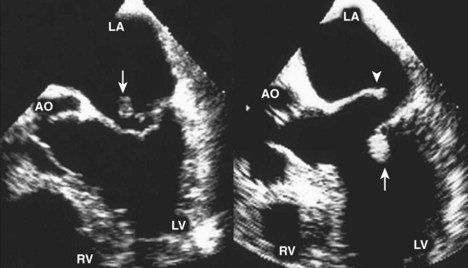
Postinfarction Ventricular Septal Defect
Basic Principles
Key Points
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
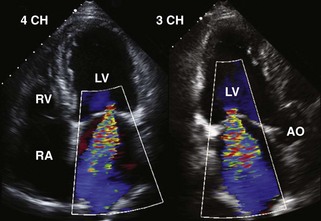
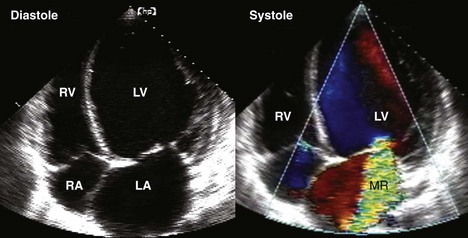
Postinfarction MR
Basic Principles
Mitral Regurgitant Volume
Basic Principles
Key Points
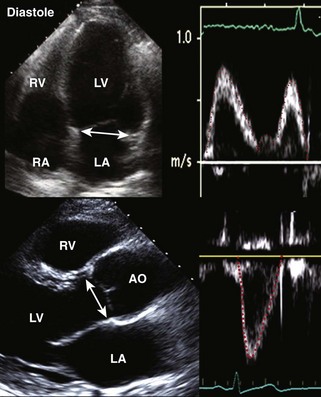
Measurement of the Width of the Vena Contracta
Basic Principles
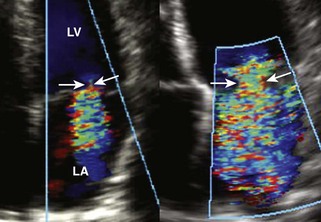
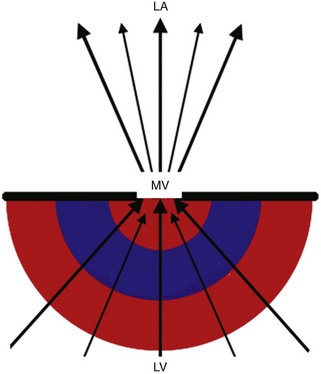
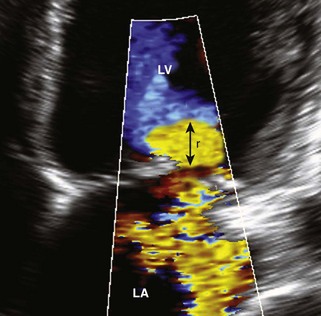
Proximal Isovelocity Surface Area (PISA)
Basic Principles
Key Points
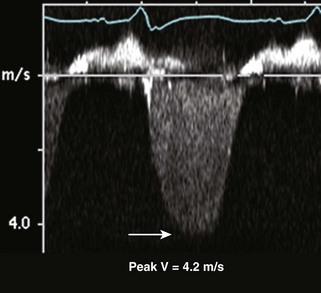
Flow Reversal
Basic Principles
Key Points
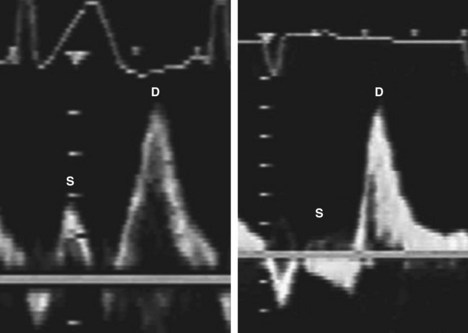
Pericardial Effusion
Basic Principles
Key Points
Step 1
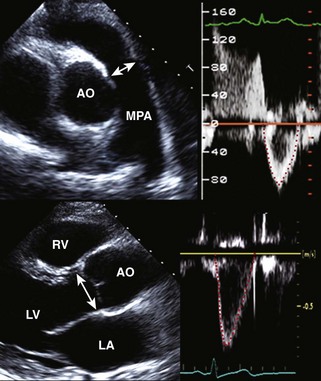
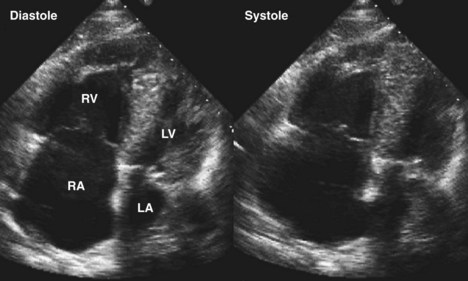
RV Infarction
Basic Principles
Key Points
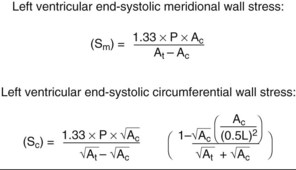
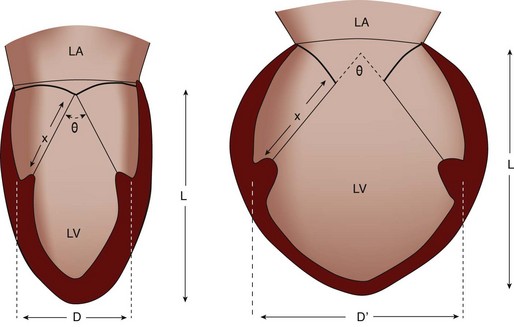
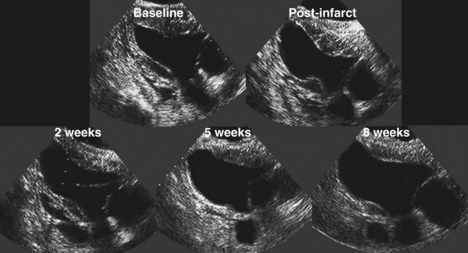
Chronic Heart Failure
Basic Principles
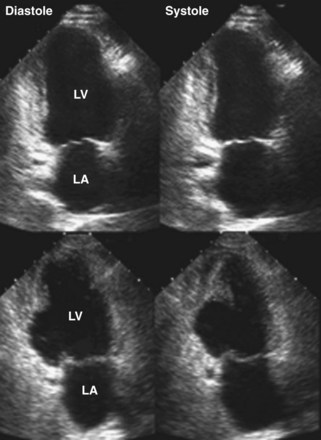
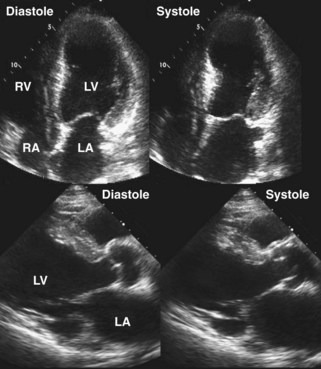
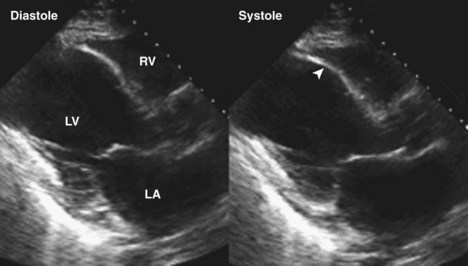
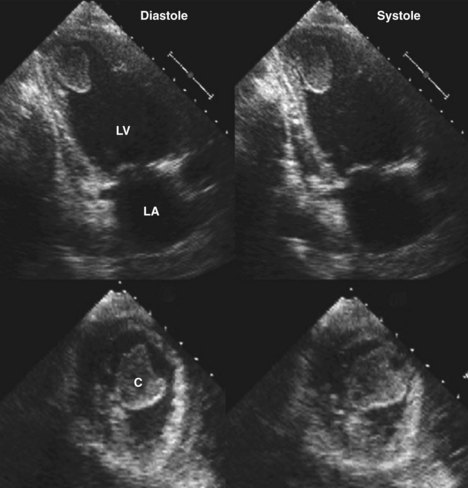
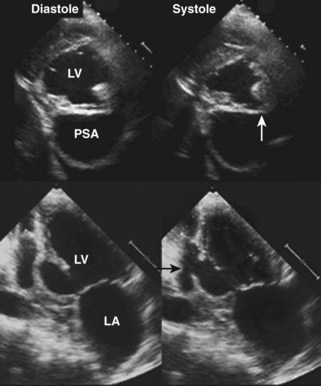
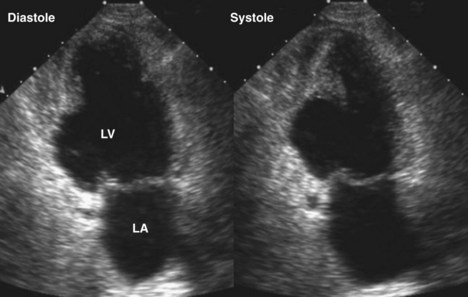
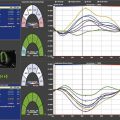
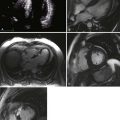
Figure 6-28 Examples of an antero-apical LV aneurysm (upper panels) and an inferior basal LV aneurysm (lower panels).
Key Points
1 Otto CM. The Practice of Clinical Echocardiography, 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier; 2007.
2 Oh JK, Seward JB, Tajik AJ. The Echo Manual. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2005.
This text provides an excellent source of basic clinical and technologic echocardiology.
3 Grigioni F, Enriquez-Sarano M, Zehr KJ, et al. Ischemic mitral regurgitation: Long-term outcome and prognostic implications with quantitative Doppler assessment. Circulation. 2001;103:1759-1764.
4 Lang RM, Bierig M, Devereux RB, et al. Recommendations for chamber quantification: A report from the American Society of Echocardiography’s Guidelines and Standards Committee and the Chamber Quantification Writing Group, developed in conjunction with the European Association of Echocardiography, a branch of the European Society of Cardiology. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2005;18:1440-1463.
5 Bansal M, Cho G-Y, Chan J, et al. Feasibility and accuracy of different techniques of two-dimensional speckle based strain and validation with harmonic phase magnetic resonance imaging. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2008;21:1318-1325.
6 Kahlert P, Plicht B, Schenk IM, et al. Direct assessment of size and shape of non-circular vena contracta area in functional versus organic mitral regurgitation using three-dimensional echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2008;21:912-921.
7 St. John Sutton M. A comprehensive non-invasive assessment of systolic function heart failure with echocardiography. Circ Heart Failure. 2010;3:337-339.
8 Caereji S, La Carrubba S, Canterin FA, et al. The incremental prognostic value of asymptomatic Stage A heart failure. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2010;23:1025-1034.
9 St, John Sutton M, Pfeffer MA, Plappert T, et al. Quantitative two dimensional echocardiographic measurements are major predictors of adverse cardiovascular events following acute myocardial infarction: The protective effects of captopril. Circulation. 1994;89:68-75.