35 Ebstein’s anomaly
Salient features
Advanced-level questions
How would you investigate such a patient?
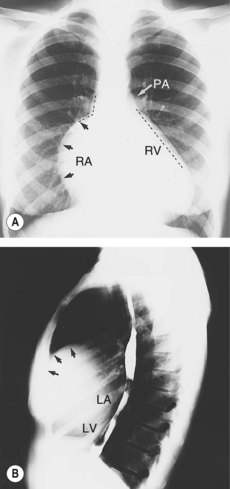
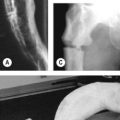
• Chest radiography (Fig. 35.1) shows the large right atrium with oligaemic lung fields.
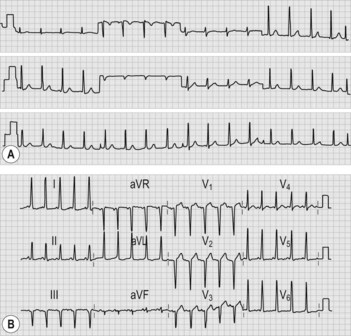
• ECG shows right bundle branch block, prolonged PR interval, P pulmonale (indicating right atrial enlargement), large P waves (Himalayan P waves), type B Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome (where the QRS complex is downward in lead V1) (Fig. 35.2B). (Note: Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome comprises a trial of short PR interval, delta wave and wide QRS complex.) Approximately 10% of patients with Ebstein’s anomaly have the Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome.
• Echocardiography characteristic findings include the abnormal positional relation between the tricuspid valve and mitral valve with septal displacement of the septal tricuspid leaflet.
• Cardiac catheterization has no place in classical cases as in the past it has been associated with serious morbidity and mortality.