Ear and Mastoid Process
Anatomy and Physiology
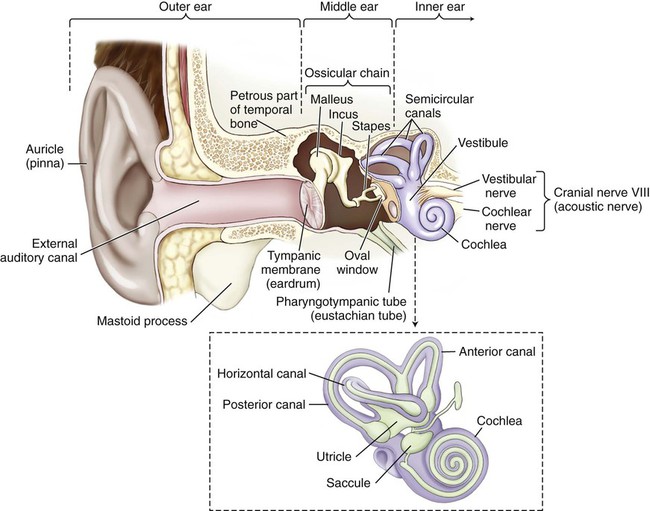
The ear is regionally divided into the outer, middle, and inner ear (Fig. 14-1). Sound travels through air, bone, and fluid across these divisions.
Outer (External) Ear
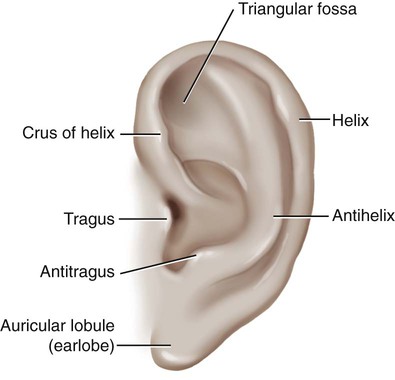
Sound waves are initially gathered by the flesh-covered elastic cartilage of the outer ear called the pinna, or auricle (Fig. 14-2). The auricular cartilage is folded into several distinct structures with separate names. The helix is the upper outer rim of the auricle, whereas the antihelix is the inner curve that is parallel to the helix. The antihelix has two “legs,” or crura (sing. crus), that divide to form a shallow depression between them, referred to as the triangular fossa. The tragus is the fleshy tag of tissue with a tuft of hair on its underside that covers the opening of the external auditory canal. The antitragus is the small raised prominence that is opposite to the tragus. It is important to remember that elastic cartilage is covered by a layer of connective tissue called perichondrium. When this is separated from the cartilage by trauma, deformities of the pinna may occur. The lobule, usually referred to as the earlobe, is the only noncartilaginous part of the external ear. This fleshy protuberance is composed of adipose tissue.
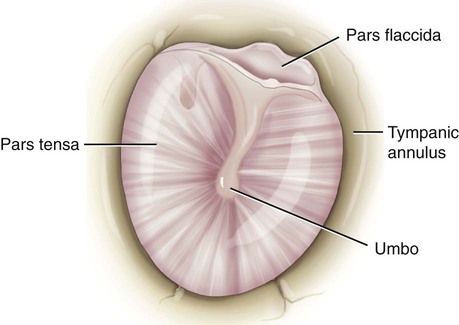
The tympanic membrane (TM), or eardrum, marks the end of the external ear and the beginning of the middle ear (Fig. 14-3). This concave membrane of the eardrum is attached to an almost complete ring of bone called the tympanic annulus. The membrane is composed of a thick, taut part (the pars tensa) and a thin, flexible part (the pars flaccida). The center of the membrane is pulled inward, forming a shallow depression termed the umbo. Because the membrane is extremely delicate and vulnerable to perforation and infection, the additional terms naming structures of the eardrum are necessary to specify where the injury occurs.
Inner Ear
Once sound is conducted to the oval window, it is transmitted to a structure called the labyrinth, or the inner ear. A membranous labyrinth is enclosed within a bony labyrinth. Between the two, and surrounding the inner labyrinth, is a fluid called perilymph. Within the membranous labyrinth is a fluid called endolymph. Hair cells within the inner ear fluids act as nerve endings that function as sensory receptors for hearing and equilibrium. Tiny calcium carbonate crystals called otoliths are attached to these hair cells and act as receptors to aid in balance. The outer, bony labyrinth is composed of three parts: the vestibule, the semicircular canals, and the cochlea. The vestibule and semicircular canals provide information about the body’s sense of equilibrium, whereas the cochlea is an organ of hearing. Within the vestibule, two structures called the utricle and the saccule function to determine the body’s static (nonmoving) equilibrium (Fig. 14-1, inset). A specialized patch of epithelium, called the macula, found in both the utricle and the saccule, provides information about the position of the head and a sense of acceleration and deceleration. The semicircular canals detect dynamic equilibrium or a sense of sudden rotation through the function of a structure called the crista ampullaris.

13. The mucous membrane–lined structure that connects the ear to the throat is the ___________________.
14. The __________________ is a hard, small projection of the temporal bone full of air cells.
15. The ear is regionally divided into the ________________, ________________, and _________________ ears.
16. Another word for outer ear is _________________ or _______________________________________________.
17. The outer, bony labyrinth is composed of three parts: the _________________, the _____________________, and the ______________________________________________________________.
18. The _________________ and the _________________ function within the vestibule to determine the body’s static (nonmoving) equilibrium.
Combining Forms for Anatomy and Physiology of the Ear
| Meaning | Combining Form |
| antrum | antr/o |
| auricle, pinna | auricul/o |
| cartilage | chondr/o, cartilag/o |
| cerumen, earwax | cerumin/o |
| cochlea | cochle/o |
| ear | ot/o |
| eardrum | tympan/o, myring/o |
| eustachian tube | salping/o |
| hearing | acous/o, audi/o, aur/o |
| helix, coil | helic/o |
| labyrinth, inner ear | labyrinth/o |
| mastoid process | mastoid/o |
| ossicle, small bone | ossicul/o |
| petrous bone | petros/o |
| spot, macula | macul/o |
| stapes | staped/o |
| stone | petr/o, lith/o |
| vestibule | vestibul/o |
Suffixes for Anatomy and Physiology of the Ear
| Suffix | Meaning |
| -cusis, -acusis | hearing |
Pathology
Terms Related to Congenital Disorders of the Ear (QØØ-Q99)
| Term | Word Origin | Definition |
| macrotia | macro- large ot/o ear -ia condition |
A condition of abnormally large auricles. |
| microtia | micro- small, tiny ot/o ear -ia condition |
A condition of abnormally small auricles. |
Terms Related to Diseases of the External Ear (H6Ø-H62)
| Term | Word Origin | Definition |
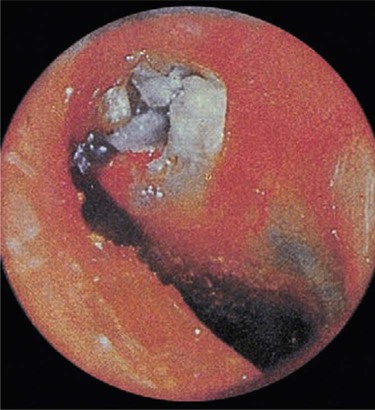
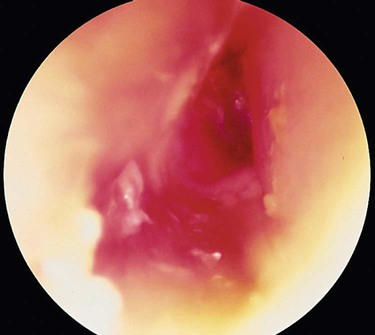
| cholesteatoma, external ear | chol/e bile steat/o fat -oma mass, tumor |
Cystic mass composed of epithelial cells and cholesterol. Can occur also in middle ear (Fig. 14-4). |
| exostosis of external ear | ex- out oste/o bone -osis abnormal condition |
Bony growth usually due to chronic irritation. |
| otitis externa | ot/o ear -itis inflammation extern/o outer -a noun ending |
Inflammation of the pinna/auricle (Fig. 14-5). |
| perichondritis, auricular | peri- around, surrounding chondr/o cartilage -itis inflammation |
Inflammation of the perichondrium of the external ear. May result in a deformity referred to as “cauliflower ear.” |
| stenosis of external ear canal, acquired | stenosis abnormal condition of narrowing | A narrowing of the auditory canal that develops after birth. |
Terms Related to Diseases of Middle Ear and Mastoid (H65-H75)
| Term | Word Origin | Definition |
| ankylosis of ear ossicles | ankyl/o stiff -osis abnormal condition |
Abnormal condition of stiffening of the tiny bones of the ear. |
| cholesteatoma of attic | chol/e bile steat/o fat -oma mass, tumor |
Cystic mass of epithelial cells and cholesterol in the epitympanic recess. |
| eustachian salpingitis | salping/o eustachian tube -itis inflammation |
Inflammation of the eustachian tube. |
| mastoiditis | mastoid/o mastoid process –itis inflammation |
Inflammation of the mastoid process. |
| myringitis | myring/o eardrum -itis inflammation |
Inflammation of the eardrum. |
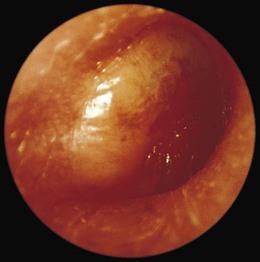
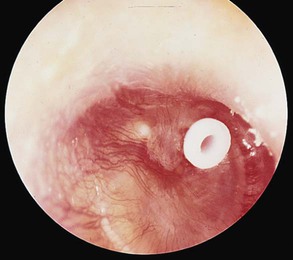
| otitis media (OM) | ot/o ear -itis inflammation medi/o middle –a noun ending |
Inflammation of the middle ear (Fig. 14-6). May be suppurative (as a result of an infection) or nonsuppurative, without infection. Nonsuppurative can be serous (with fluid) or sanguineous (with bloody discharge). |
| patulous eustachian tube | patul/o open -ous pertaining to |
A continually open eustachian tube. |
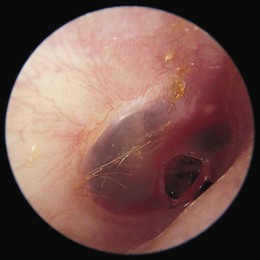
| perforation of tympanic membrane | tympan/o eardrum -ic pertaining to |
A puncture of the eardrum (Fig. 14-7). |
| petrositis | petros/o petrous bone -itis inflammation |
Inflammation of the petrous portion of the temporal bone. |
| tympanosclerosis | tympan/o eardrum -sclerosis abnormal condition of hardening |
Abnormal hardening of the eardrum. |

11. tympanosclerosis _______________________________________________________________________________
12. cholesteatoma __________________________________________________________________________________
13. otitis media ____________________________________________________________________________________
Terms Related to Diseases of Inner Ear (H8Ø-H83)
| Term | Word Origin | Definition |
| aural vertigo | aur/o hearing –al pertaining to vert/o turn -igo condition |
Dizziness associated with a disorder of the ear. |
| labyrinthitis | labyrinth/o inner ear, labyrinth -itis inflammation |
Inflammation of the labyrinth, the inner ear. |
| Ménière’s disease | Chronic condition of the inner ear characterized by vertigo, hearing loss, and tinnitus. Of unknown etiology. | |
| otosclerosis | ot/o ear -sclerosis abnormal condition of hardening |
Abnormal condition of hardening of the inner ear characterized by a development of spongy bone that can grow toward or away from the oval window. Usually results in progressive deafness. |
| vestibular neuronitis | vestibul/o vestibule -ar pertaining to neuron/o nerve -itis inflammation |
Inflammation of the vestibular nerve. |
Terms Related to Other Disorders of the Ear (H9Ø-H94)
| Term | Word Origin | Definition |
| conductive hearing loss | con- with duct/o carry -ive pertaining to |
Hearing loss resulting from damage to or malformation of the middle or outer ear. |
| diplacusis | dipl/o double -acusis hearing |
Hearing disorder characterized by the perception of a single sound being two. |
| hyperacusis | hyper- above, excessive -acusis hearing |
Hearing that is above normal. Patient is able to hear more acutely than normal. |
| otalgia | ot/o ear –algia pain |
Pain in the ear. An earache. |
| otorrhagia | ot/o ear -rrhagia bursting forth |
A rapid discharge of blood from one or both ears. |
| otorrhea | ot/o ear –rrhea discharge, flow |
A discharge from the ears. If the discharge is purulent (pus filled), it is termed otopyorrhea. |
| ototoxic hearing loss | ot/o ear tox/o poison -ic pertaining to |
Hearing loss that is drug-induced. |
| presbycusis | presby- old age –cusis hearing |
Loss of hearing due to the aging process. |
| sensorineural hearing loss | sensor/i sense neur/o nerve –al pertaining to |
Hearing loss resulting from damage to the cochlea of the inner ear or auditory nerve. |
| tinnitus | tinnit/o jingling -us noun ending |
Ringing in the ears. |
| transient ischemic deafness | isch/o hold back -emic blood condition |
Intermittent hearing loss due to a lack of blood supply to the ear. |
Terms Related to Benign Neoplasms
| Term | Word Origin | Definition |
| acoustic neuroma | acous/o hearing -tic pertaining to neur/o nerve -oma mass, tumor |
A benign tumor of the eighth cranial nerve (vestibulocochlear) that causes tinnitus, vertigo, and hearing loss. Also called vestibular schwannoma. |
| ceruminoma | cerumin/o cerumen, earwax -oma mass, tumor |
A benign adenoma of the glands that produce earwax. |

9. excessive hearing _______________________________________________________________________________
10. inflammation of the inner ear ___________________________________________________________________
11. discharge from the ear __________________________________________________________________________
12. pain of the ear _________________________________________________________________________________
13. mass of ear wax ________________________________________________________________________________
Procedures
Terms Related to Procedures of the Ear
| Term | Word Origin | Definition |
| audiology, diagnostic | audi/o hearing -logy study of |
A diagnostic study of an individual’s ability to hear. |
| audiometry | audi/o hearing –metry measuring |
The process of measuring hearing, usually with an instrument called an audiometer. The graphic representation of the results is called an audiogram (Fig. 14-8). |
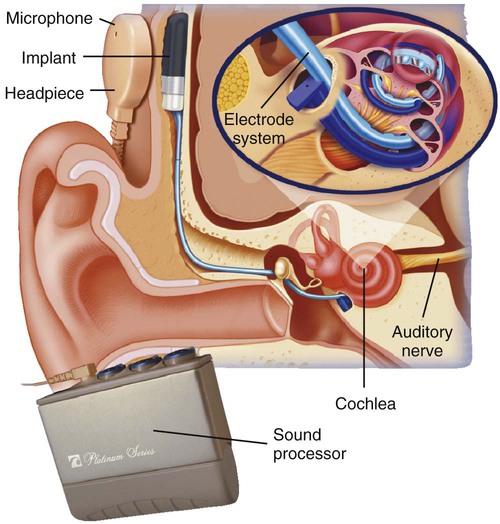
| cochlear implant | cochle/o cochlea -ar pertaining to |
Implanted device that assists those with hearing loss by electrically stimulating the cochlea (Fig. 14-9). |
| electrocochleography (ECOG) | electr/o electricity cochle/o cochlea –graphy recording |
Recording the electrical activity of the cochlea to test hearing. |
| mastoidectomy | mastoid/o mastoid –ectomy cutting out |
Cutting out part or all of the mastoid process to treat necrotic mastoiditis. |
| myringostomy | myring/o eardrum -stomy creating a new opening |
Making a new opening in the eardrum. Done to promote drainage and/or allow the introduction of artificial tubes to maintain the opening (Fig. 14-10). Also called a tympanostomy. |
| myringotomy | myring/o eardrum -tomy cutting |
Cutting the eardrum to drain pus. Also called a tympanotomy. |
| ossiculectomy | ossicul/o small bone -ectomy cutting out |
Cutting out part or all of the ossicles of the ear to treat ankylosis of ear ossicles. |
| otoplasty | ot/o ear –plasty surgically forming |
Forming part or all of the ear. Done to correct conditions such as macrotia. |
| otoscopy | ot/o ear –scopy viewing |
Process of viewing the ear using an otoscope. |
| paracentesis of tympanum | para- near, beside -centesis surgical puncture |
Surgical puncture of the eardrum to drain fluids resulting from otitis media. |
| stapediolysis | staped/o stapes -lysis breaking down |
Releasing the stapes to restore hearing in cases of otosclerosis. |
| stapedoplasty | staped/o stapes -plasty surgically forming |
Forming part or all of the stapes. Reconstruction performed to restore hearing. |
| tympanometry | tympan/o eardrum, tympanum –metry measuring |
Process of measuring the eardrum. A tympanogram is the resulting record. A tympanometer is the instrument that measures the function of the eardrum. |
| tympanoplasty | tympan/o eardrum, tympanum -plasty surgically forming |
Forming part or all of the eardrum to reconstruct a perforated eardrum. |
| Universal Newborn Hearing Screening (UNHS) test | Test that uses otoacoustic emissions (OAEs), which are measured by the insertion of a probe into the baby’s ear canal, and auditory brainstem response (ABR), which involves the placement of four electrodes on the baby’s head to measure the change in electrical activity of the brain in response to sound while the baby is sleeping. |

11. tympanometry__________________________________________________________________________________
12. otoplasty________________________________________________________________________________________
13. audiometry ____________________________________________________________________________________
Pharmacology
antibiotics: Treat bacterial infections. A commonly used oral agent to treat ear infections is amoxicillin (Amoxil). A topical example is ciprofloxacin with hydrocortisone (Cipro HC Otic).
ceruminolytics: Soften and break down earwax. An example is triethanolamine polypeptide oleate (Cerumenex).
decongestants: Relieve congestion associated with a cold, allergy, or sinus pressure. These drugs may be available as a nasal spray or an oral product. Examples include pseudoephedrine (Sudafed) and oxymetazoline (Afrin).
otics: Drugs applied directly to the external ear canal. These may be administered in the form of solutions, suspensions, or ointments.

Recognizing Suffixes for PCS
Suffixes and Root Operations for the Ear
| Suffix | Root Operation |
| -centesis | Drainage |
| -ectomy | Excision, resection |
| -lysis | Release |
| -plasty | Repair, replacement, supplement |
| -scopy | Inspection |
| -stomy | Drainage |
| -tomy | Drainage |
| Abbreviation | Meaning |
| ABR | auditory brainstem response |
| ECOG | electrocochleography |
| OAEs | otoacoustic emissions |
| OM | otitis media |
| TM | tympanic membrane |
| UNHS | universal newborn hearing screening |
| AS | left ear |
| AD | right ear |
| AU | each ear |