Dysgerminoma
Synonyms/Description
Etiology
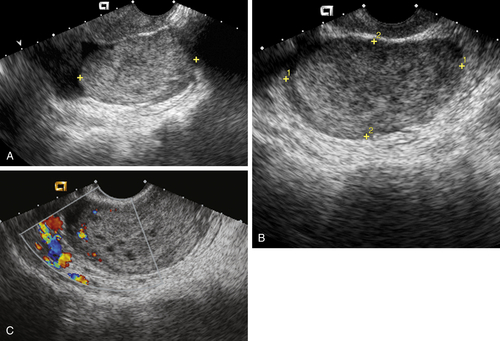
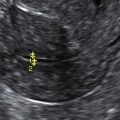
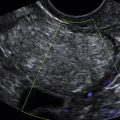
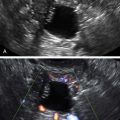
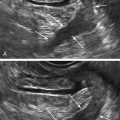
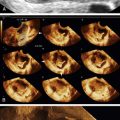
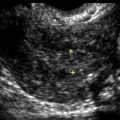
Ultrasound Findings
Differential Diagnosis
Clinical Aspects and Recommendations
Suggested Reading
Gordon A., Lipton D., Woodruff J.D. Dysgerminoma: a review of 158 cases from the Emil Novak Ovarian Tumor Registry. Obstet Gynecol. 1981;58:497–504.
Guerriero S., Testa A.C., Timmerman D., Van Holsbeke C., Ajossa S., Fischerova D., Franchi D., Leone F.P., Domali E., Alcazar J.L., Parodo G., Mascilini F., Virgilio B., Demidov V.N., Lipatenkova J., Valentin L. Imaging of gynecological disease (6): clinical and ultrasound characteristics of ovarian dysgerminoma. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2011;37:596–602.
Kim S.H., Kang S.B. Ovarian dysgerminoma: color Doppler ultrasonographic findings and comparison with CT and MR imaging findings. J Ultrasound Med. 1995;14:843–848.
Vicus D., Beiner M.E., Klachook S., Le L.W., Laframboise S., Mackay H. Pure dysgerminoma of the ovary 35 years on: a single institutional experience. Gynecol Oncol. 2010;117:23–26.