Hamid, S, et al. Frequency of NSAID induced peptic ulcer disease. J Pak Med Assoc. 2006; 56(5):218–222.
Pun, E, et al. Computed tomography and complicated peptic ulcer disease. Australas Radiol. 2004; 48(4):516–519.
Luzi, G, et al. Duodenal pathology and clinical-immunological implications in common variable immunodeficiency patients. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003; 98(1):118–121.
O’Connor, AS, et al. Pancreatitis and duodenitis from sarcoidosis: successful therapy with mycophenolate mofetil. Dig Dis Sci. 2003; 48(11):2191–2195.
Shankar, RR, et al. Erosive gastroduodenitis and Helicobacter pylori infection. Med Sci Monit. 2003; 9(6):CR222–CR224.
Long, FR, et al. Duodenitis in children: correlation of radiologic findings with endoscopic and pathologic findings. Radiology. 1998; 206(1):103–108.
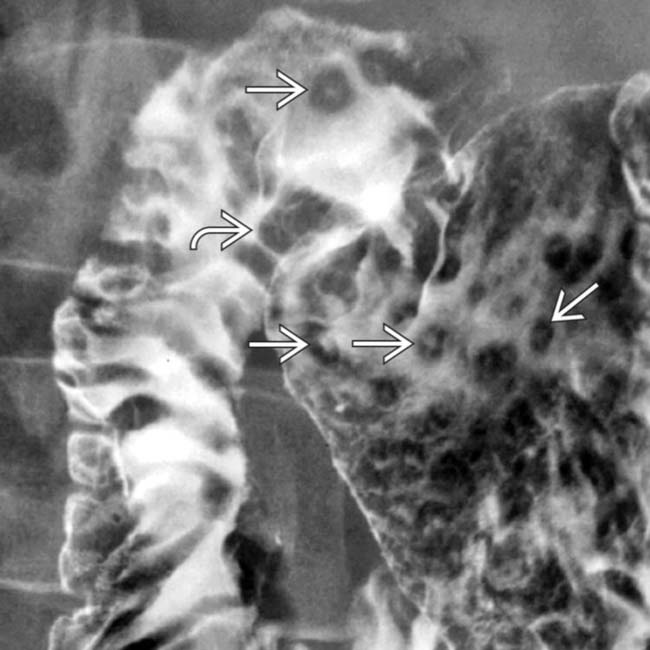
 in the gastric antrum and duodenal bulb, along with thickened duodenal folds
in the gastric antrum and duodenal bulb, along with thickened duodenal folds  , classic features of duodenitis and gastritis.
, classic features of duodenitis and gastritis.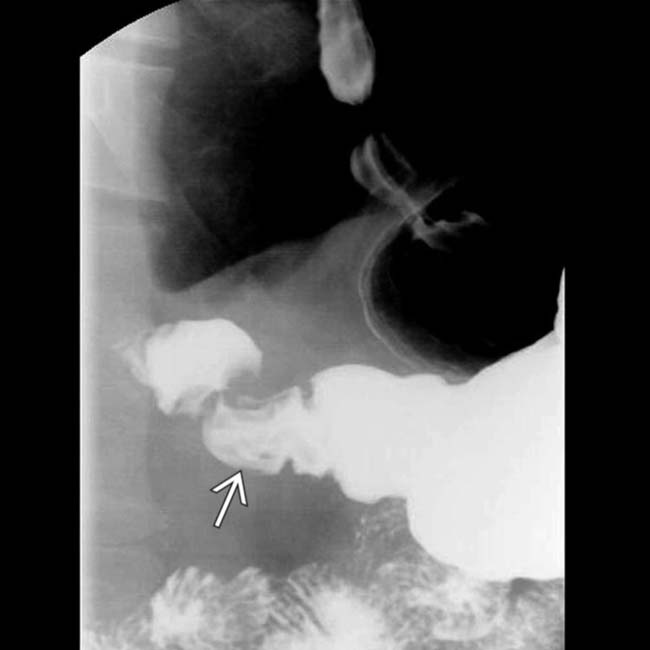
 and lack of distensibility in the gastric antrum due to gastritis.
and lack of distensibility in the gastric antrum due to gastritis.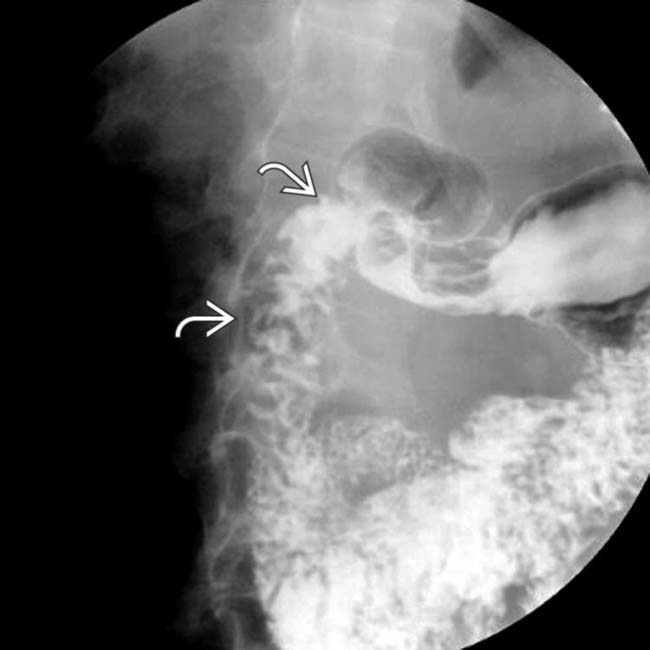
 , due to duodenitis.
, due to duodenitis.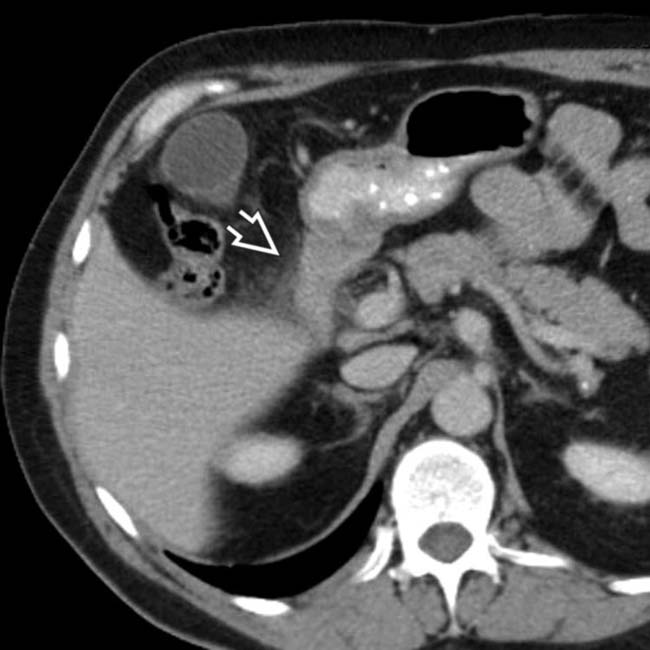
 due to duodenitis.
due to duodenitis.
 in the gastric antrum and duodenal bulb, along with thickened duodenal folds
in the gastric antrum and duodenal bulb, along with thickened duodenal folds  , classic features of duodenitis and gastritis.
, classic features of duodenitis and gastritis.
 and lack of distensibility in the gastric antrum due to gastritis.
and lack of distensibility in the gastric antrum due to gastritis.
 , due to duodenitis.
, due to duodenitis.
 due to duodenitis.
due to duodenitis.