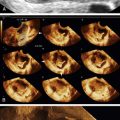
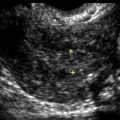
Müllerian Duct Anomalies
Synonyms/Description
Etiology
Class I: Agenesis of the Uterus, Cervix, and/or Upper Vagina
Class II: Unicornuate Uterus (20% of Uterine Anomalies)
Class III: Didelphic Uterus (5% of Uterine Anomalies)
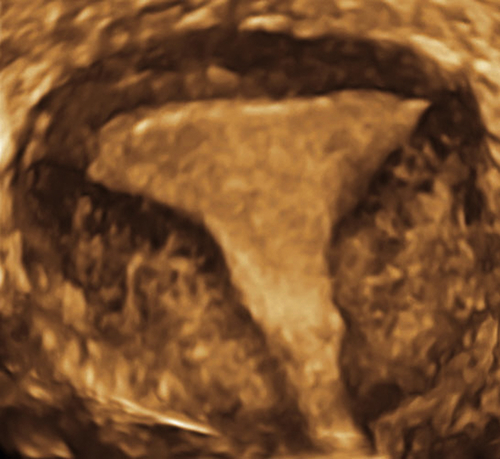
Class IV: Bicornuate Uterus (10% of Uterine Anomalies)
Class V: Septate Uterus (55% of Uterine Anomalies)
Ultrasound Findings
Differential Diagnosis
Clinical Aspects and Recommendations
Figures
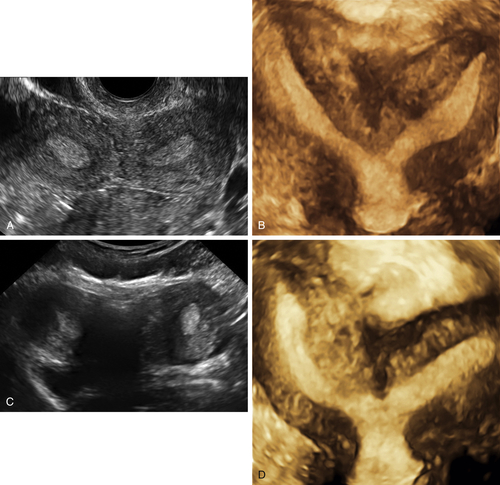
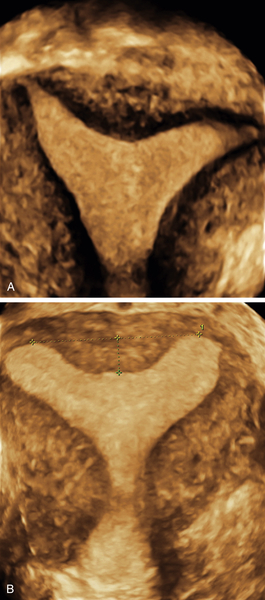
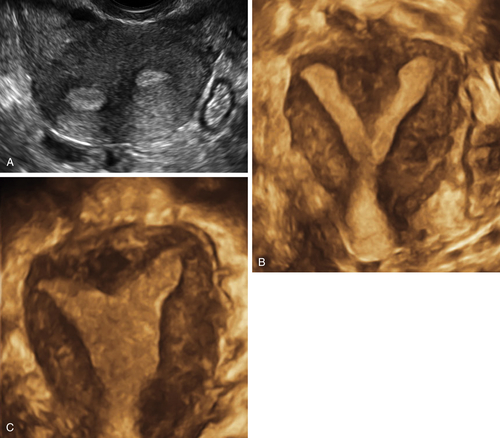
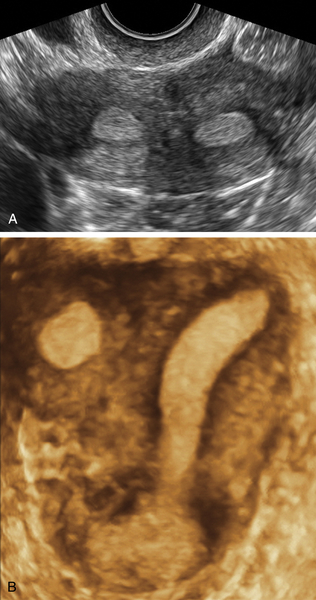
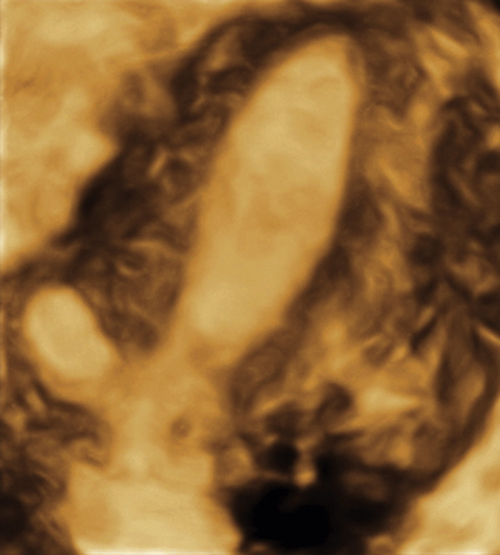
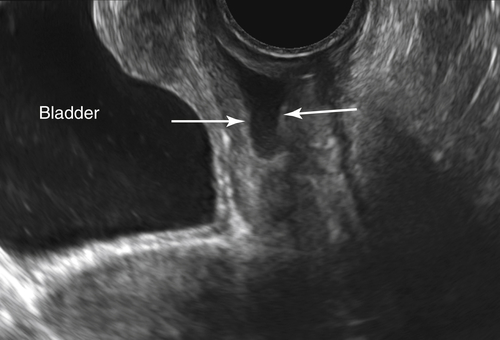
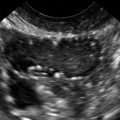
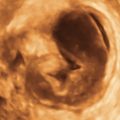
Figure M3-4 Bicornuate uterus seen in 2-D and 3-D in two different patients. The 2-D image is a transverse view through the fundus of the uterus, showing two islands of endometrium and indicating a Müllerian anomaly. The 3-D image shows the typical bicornuate uterus with a deep indentation at the fundus, dividing the uterus into two distinct horns. These horns merge in the lower uterine segment. Figures A and B are one patient and C and D are another.
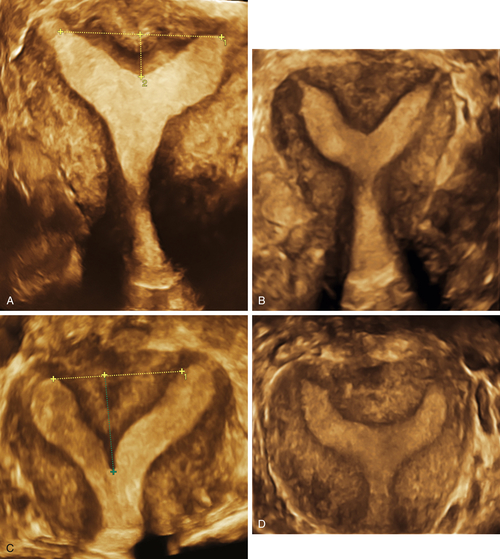
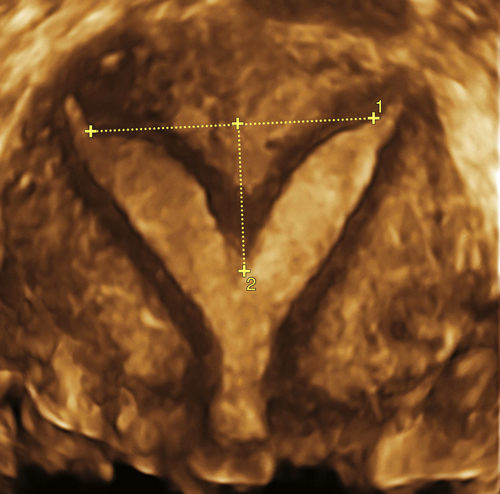
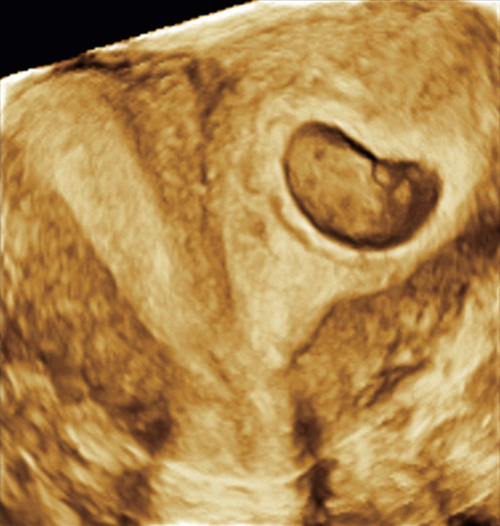
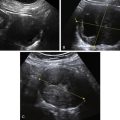
Figure M3-7 A to D, Four different patients with partially septate uteri. Note the very different widths and depths of the septae when comparing the appearance of these uteri. The smallest septum (A) measured 12 mm and has an appearance similar to the arcuate uterus in Figure M3-3.
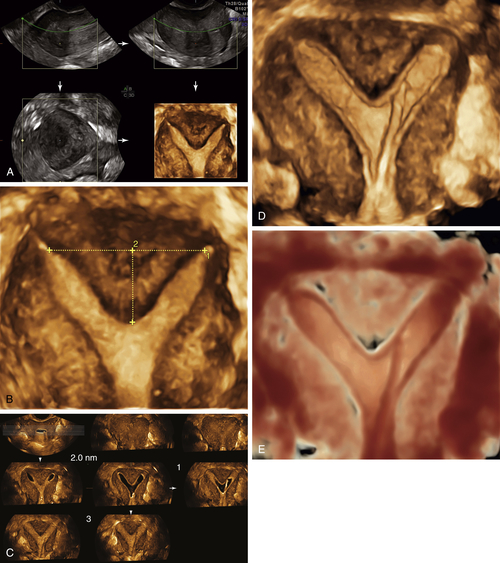
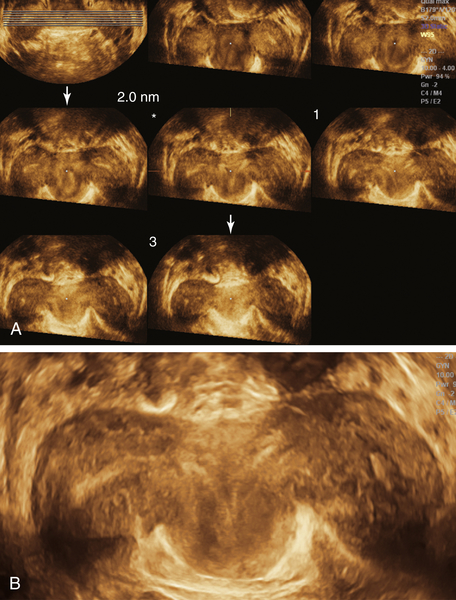
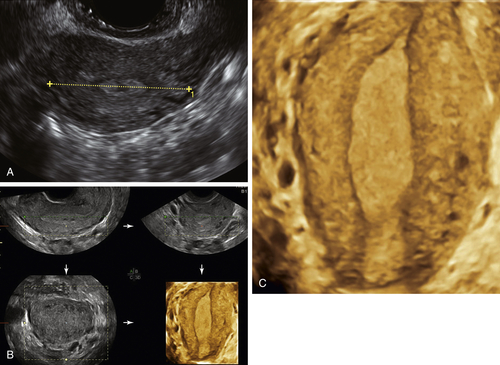
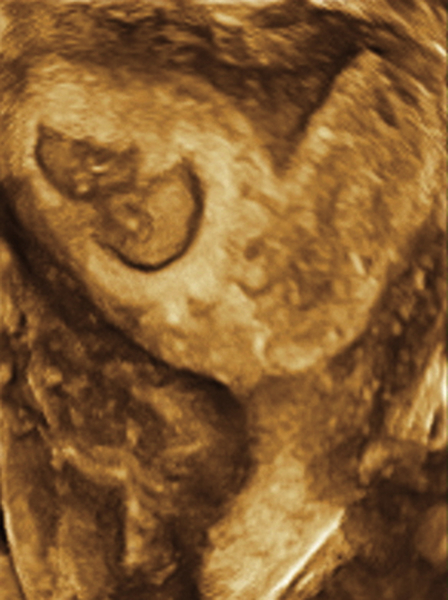
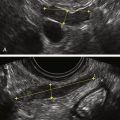
Figure M3-9 Partially septate/subseptate uterus seen using 3-D and sonohysterography. A and B show the 3-D volume displaying the partial septum. C to E show the sonohysterogram images of the same septum (C is a parallel tomographic cut through the uterus). Note that the catheter is visible inside the left endometrial cavity.
Suggested Reading
Deutch T.D., Abuhamad A.Z. The role of 3-dimensional ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of Müllerian duct anomalies: a review of the literature. J Ultrasound Med. 2008;27:413–423.
Faivre E., Fernandez H., Deffieux X., Gervaise A., Frydman R., Levaillant J.M. Accuracy of three-dimensional ultrasonography in differential diagnosis of septate and bicornuate uterus compared with office hysteroscopy and pelvic magnetic resonance imaging. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2012;19:101–106.
Ghi T., Casadio P., Kuleva M., Perrone A.M., Savelli L., Giunchi S., Meriggiola M.C., Gubbini G., Pilu G., Pelusi C., Pelusi G. Accuracy of three-dimensional ultrasound in diagnosis and classification of congenital uterine anomalies. Fertil Steril. 2009;92:808–813.
Homer H.A., Li T.C., Cooke I.D. The septate uterus: a review of management and reproductive outcome. Fertil Steril. 2000;73:1–14.
Khati N.J., Frazier A.A., Brindle K.A. The unicornuate uterus and its variants: clinical presentation, imaging findings, and associated complications. J Ultrasound Med. 2012;31:319–331.
Troiano R.N., McCarthy S.M. Müllerian duct anomalies: imaging and clinical issues. Radiology. 2004;233:19–34.
Woelfer B., Salim R., Banerjee S., Elson J., Regan L., Jurkovic D. Reproductive outcomes in women with congenital uterine anomalies detected by three-dimensional ultrasound screening. Obstet Gynecol. 2001;98:1099–1103.