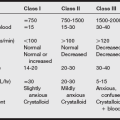
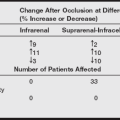
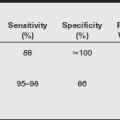
Drugs
Acetaminophen (ofirmev)
Dose: The recommended dose of Ofirmev for patients 13 years old or older weighing 50 kg or more is 1000 mg every 6 hours or 650 mg every 4 hours intravenously; the maximum daily dose of acetaminophen by any route is 4000 mg. For patients older than 2 years old weighing less than 50 kg, the recommended dose is 15 mg/kg every 6 hours or 12.5 mg/kg every 4 hours intravenously.
Adverse effects: The antipyretic effect of acetaminophen may mask fever. In clinical trials of intravenous acetaminophen, adverse effects were minor and similar to those with placebo.
Adenosine (adenocard)
Dose: 6-mg bolus administered over 1 to 2 seconds followed by normal saline line flush; may increase to 12-mg bolus if arrhythmia persists past 2 minutes. May repeat 12-mg bolus once.
Precautions and contraindications: Adenosine should not be used in patients receiving methylxanthine therapy (i.e., aminophylline, theophylline). Dipyridamole (Persantine) inhibits cellular uptake of adenosine. Use it with caution in patients with asthma. It is contraindicated in patients with second- or third-degree heart block.
Albuterol sulfate (proventil, ventolin)
Dose: Inhaler (metered dose): two deep inhalations 1 to 5 minutes apart; may be repeated every 4 to 6 hours (daily dose should not exceed 16 to 20 inhalations; each metered aerosol actuation delivers approximately 90 mcg/puff). Oral: 2 to 4 mg three to four times daily (total dose not to exceed 16 mg). Syrup: 2 mg/5 mL is available.
Onset and duration: Onset: inhalation: 5 to 15 minutes; oral: 15 to 30 minutes. Peak effect: inhalation: 0.5 to 2 hours; oral: 2 to 3 hours. Duration: inhalation: 3 to 6 hours; oral: 4 to 8 hours.
Adverse effects: Tachycardia, arrhythmias, hypertension, tremors, anxiety, headache, nausea, vomiting, hypokalemia
Alfentanil HCL (alfenta)
Onset and duration: Onset: intravenous: 1 to 2 minutes; intramuscular: less than 5 minutes; epidural: 5 to 15 minutes. Duration: intravenous: 1 to 15 minutes; intramuscular: 10 to 60 minutes; epidural: 30 minutes.
Adverse effects: Bradycardia, hypotension, arrhythmias, respiratory depression; euphoria, dysphoria, convulsions, nausea and vomiting, biliary tract spasm, delayed gastric emptying, muscle rigidity, pruritus
Alprostadil, PGE1 (prostin VR)
Indications: Neonates: to maintain temporary patency of the ductus arteriosus until corrective or palliative surgery can be performed
Dose: Children: continuous infusion into large vein: 0.05 to 0.1 mcg/kg/min initially; when a therapeutic response occurs, decrease to lowest possible dose to maintain response (maximum dose: 0.4 mcg/kg/min).
Onset and duration: Onset: 30 minutes; elimination half-life: 5 to 10 minutes; duration: 30 minutes to 2 hours
Adverse effects: Apnea (10%-12%), fever (14%), flushing (10%), bradycardia and seizures (4%), thrombocytopenia (less than 1%), disseminated intravascular coagulation (1%), anemia, tachycardia, hypotension (4%), diarrhea (2%), gastric outlet obstruction secondary to antral hyperplasia (related to cumulative dose)
Precautions and contraindications: Apnea is most frequent in infants weighing less than 2 kg within the first hour of alprostadil administration; ventilatory assistance may be required. It is contraindicated in neonates with respiratory distress syndrome. Use it with caution in patients with bleeding tendencies because of alprostadil’s ability to inhibit platelet aggregation. In all neonates, monitor arterial pressure; if arterial pressure falls significantly, decrease the rate of infusion.
Aminocaproic acid (amicar)
Indications: Control of clinical bleeding in which hyperfibrinolysis is a contributing factor (hyperfibrinolysis should be confirmed by laboratory values such as prolonged thrombin time, prolonged prothrombin time, hypofibrinogenemia, or decreased plasminogen levels); also: open heart surgery; postoperative hematuria after transurethral prostatic resection, suprapubic prostatectomy, and nephrectomy; hematologic disorders such as aplastic anemia, abruptio placentae, cirrhosis, neoplastic diseases, and prophylaxis in patients with hemophilia before and after tooth extraction and other bleeding in the mouth and nasopharynx; reduction of blood loss in trauma and shock; possible prevention of ocular hemorrhaging and bleeding in subarachnoid hemorrhage
Dose: Acute bleeding: 5 g infused during the first hour followed by a continuous infusion of 1 g/hr for 8 hours or until bleeding is controlled
Onset and duration: Onset: 1 to 72 hours; half-life 1 to 2 hours in patients with normal renal function. No single concentration fits all. It must be diluted. Consult the package insert, an intravenous reference, or the pharmacy. Duration: 8 to 12 hours.
Adverse effects: Convulsions; myopathy; rarely muscle necrosis, nausea, vomiting; rapid infusion associated with hypotension, bradycardia, arrhythmias
Precautions and contraindications: A definitive diagnosis of hyperfibrinolysis must be made before aminocaproic acid administration. Use caution in patients with cardiac, renal, or hepatic disease. Administration in the presence of renal or ureteral bleeding is not recommended because of ureteral clot formation and the possible risk of obstruction. Owing to the substantial risk of serious or fatal thrombus formation, aminocaproic acid is contraindicated in patients with disseminated intravascular coagulation unless heparin is administered concurrently.
Aminophylline (theodur, others)
Indications: Long-term therapy for bronchial asthma; reversal of bronchospasm associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Dose: Loading dose: for patients not already receiving a theophylline preparation, intravenous: 5 to 6 mg/kg (administered over 20-30 minutes). Oral or rectal: 6 mg/kg. Maintenance: intravenous: 0.5 mg/kg/hr; oral: 2 to 4 mg/kg every 6 to 12 hours. Therapeutic range: 10 to 20 mcg/mL.
Dilution for infusion loading dose: dilute 500 mg in 500 mL D5W or normal saline (1 mg/mL)
Onset and duration: Onset: intravenous: 2 to 5 minutes; oral: within 30 minutes. Duration: oral: 4 to 8 hours
Adverse effects: Palpitations, sinus tachycardia, supraventricular and ventricular tachycardia, flushing, tachypnea, seizures, headache, irritability, nausea, vomiting, hyperglycemia
Precautions and considerations: Caution when used in patients with seizure disorders, hypertension, or ischemic heart disease.
Anesthetic considerations: Aminophylline potentiates the pressor effects of sympathomimetics and may produce seizures, cardiac arrhythmias, cardiorespiratory arrest, and ventricular arrhythmias with excessive plasma levels or in patients receiving volatile anesthetics. Use isoflurane or sevoflurane in patients who must be administered aminophylline or other exogenous sympathomimetic drugs before or during surgery. Use of halothane may potentiate cardiac dysrhythmia.
Amiodarone (cordarone)
Indications: Treatment of life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias that do not respond to other antiarrhythmics (i.e., recurrent ventricular fibrillation and hemodynamically unstable ventricular tachycardia); selective treatment of supraventricular arrhythmias
Dose: Loading: oral: 800 to 1600 mg/day for 1 to 3 weeks; maintenance: oral: 200 to 600 mg/day; therapeutic level: 1 to 2.5 mcg/mL
Dosage forms: tablets: 200 mg; intravenous: 100 to 300 mg
• Loading infusions: first rapid: 150 mg over the first 10 minutes (15 mg/min). Add 3 mL of amiodarone HCl intravenously (150 mg) to 100 mL D5W (concentration = 1.5 mg/mL). Infuse 100 mL over 10 minutes.
• Followed by slow infusion: 360 mg over the next 6 hours (1 mg/min). Add 18 mL of amiodarone HCl intravenously (900 mg) to 500 mL D5W (concentration = 1.8 mg/mL).
• Maintenance infusion: 540 mg over the remaining 18 hours (0.5 mg/min). Decrease the rate of the slow loading infusion to 0.5 mg/min.
Onset and duration: Onset: 2 to 4 days. Half-life: between 2 weeks and 2 months (including active metabolites). Duration: 45 days
Adverse effects: Arrhythmias, pulmonary fibrosis or inflammation, hepatitis or cirrhosis, corneal deposits, hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, peripheral neuropathy, cutaneous photosensitivity
Precautions and contraindications: Amiodarone increases serum levels of digoxin, warfarin, quinidine, procainamide, phenytoin, and diltiazem. The likelihood of bradycardia, sinus arrest, and atrioventricular block increases with concurrent β-adrenergic antagonist and calcium channel blocker therapy.
Anesthetic considerations: Antiadrenergic effects are enhanced in the presence of general anesthetics and manifest as sinus arrest, atrioventricular block, low cardiac output, or hypotension. Drugs that inhibit the automaticity of the sinus node such as halothane and lidocaine could accentuate the effects of amiodarone and increase the likelihood of sinus arrest. The potential need for a temporary artificial cardiac (ventricular) pacemaker and administration of sympathomimetics such as isoproterenol should be considered in patients receiving this drug.
Amrinone lactate (inocor)
Dose: Loading dose: 0.75 mg/kg over 2 to 3 minutes. A second bolus may follow after 30 minutes. Maintenance is by continuous infusion of 5 to 10 mcg/kg/min (maximum dose: 10 mg/kg/day).
Dosage forms: injection: 5 mg/mL; dilution for infusion: 500 mg in 500 mL normal saline solution
Precautions and contraindications: Use amrinone with caution in hypotensive patients. Avoid exposure of the ampule to light. Do not mix in solutions containing dextrose or furosemide. Use it with caution in patients with allergies to bisulfites. Fluid balance, electrolyte concentrations, and renal function should be monitored carefully during treatment. Monitor platelet counts on a long-term basis. Amrinone contains sodium metabisulfite, a sulfite that may cause allergic-type reactions, including anaphylactic symptoms and life-threatening or less severe asthmatic episodes in susceptible patients. Sulfite sensitivity is seen more frequently in patients with asthma than in patients without asthma.
Aprepitant (emend)
Adverse effects: The most frequent adverse events reported in clinical trials of aprepitant for postoperative nausea and vomiting were constipation, nausea, pruritus, pyrexia, hypotension, headache, and bradycardia.
Precautions and contraindications: Aprepitant produces a dose-dependent inhibition of CYP3A4 and should be used with caution in patients receiving drugs that are primarily metabolized through CYP3A4. Weak inhibition of CYP3A4 by a single 40-mg dose is not expected to alter the plasma concentrations of these products to a clinically significant degree.
Atracurium (tracrium)
Indications: Relaxation of skeletal muscles during surgery; adjunct to general anesthesia or mechanical ventilation; facilitation of endotracheal intubation
Dose: Initially for paralyzing: intravenous: 0.3 to 0.5 mg/kg; maintenance: intravenous: 0.08 to 0.1 mg/kg
Onset and duration: Onset: less than 3 minutes. Duration: 30 to 45 minutes. Elimination: plasma (Hofmann elimination, ester hydrolysis). The primary metabolite is laudanosine (a cerebral stimulant) produced in low doses, excreted primarily in the urine.
Adverse effects: Primarily resulting from histamine release: vasodilation, hypotension, sinus tachycardia, sinus bradycardia, hypoventilation, apnea, bronchospasm, laryngospasm, dyspnea, inadequate block, prolonged block, rash, and urticaria
Atropine sulfate
Indications: Symptomatic bradycardia, asystole, cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR); antisialagogue; for vagolytic effects to block bradycardia during surgery from stimulation of the carotid sinus, traction on abdominal viscera, or extraocular muscles; blockade of muscarinic effects of anticholinesterases; adjunctive therapy in the treatment of bronchospasm, peptic ulcer disease
Dose: Adults: sinus bradycardia. CPR: intravenous, intramuscular, subcutaneous, via endotracheal tube (diluted in 10 mL of sterile water or normal saline): 0.5 to 1 mg every 3 to 5 minutes as indicated (maximum dose: 40 mcg/kg/event). Preoperative: 0.4 mg intramuscular, subcutaneous, or oral: 30 to 60 minutes preinduction.
Onset and duration: Inhibition of salivation occurs within 30 minutes to 1 hour and peaks in 1 to 2 hours after oral or intramuscular atropine administration. Increase in heart rate occurs within 3 to 10 minutes after intravenous or intramuscular administration. Duration: 15 to 45 minutes after intravenous administration and 2 to 4 hours after intramuscular administration.
Adverse effects: Transient bradycardia resulting from a weak peripheral muscarinic cholinergic agonist effect in small doses (less than 0.5 mg in adults), tachycardia (high doses), urinary hesitancy, retention, mydriasis, blurred vision, increased intraocular pressure, decreased sweating, excitement, agitation, drowsiness, confusion, hallucinations, dry nose and mouth, allergic reactions, constipation.
Children and elderly patients are more susceptible to these adverse effects.
Precautions and contraindications: Avoid atropine in situations in which tachycardia would be harmful (i.e., thyrotoxicosis, pheochromocytoma, coronary artery disease). Avoid in hyperpyrexial states because it inhibits sweating. It is contraindicated in acute-angle glaucoma, obstructive disease of the gastrointestinal tract, obstructive uropathy, paralytic ileus or intestinal atony, and acute hemorrhage in patients with unstable cardiovascular status. Use it with caution in patients with tachyarrhythmias, hepatic or renal disease, congestive heart failure, chronic pulmonary disease (because a reduction in bronchial secretions may lead to formation of bronchial plugs), autonomic neuropathy, hiatal hernia, gastroesophageal reflux, gastric ulcers, gastrointestinal infections, and ulcerative colitis.
Anesthetic considerations: Additive anticholinergic effects may occur when atropine is administered concomitantly with meperidine, some antihistamines, phenothiazines, tricyclic antidepressants, and antiarrhythmic drugs that possess anticholinergic activity (e.g., quinidine, disopyramide, procainamide).
Bumetanide
Indications: Treatment of edema of cardiac, hepatic, or renal origin; hypertension, pulmonary edema; usually reserved for patients who do not respond to thiazide diuretics or in whom a rapid onset of diuresis is desired.
Dose: Initial dose: 0.5 to 1 mg intravenously over 1 to 2 minutes. If response is not adequate after the initial dose, a second or third dose may be administered at intervals of up to 2 to 3 hours, up to a maximum of 10 mg/day.
Children: intravenous, intramuscular, oral: 0.015 to 0.1 mg/kg. maximum, 2 mg/day
Onset and duration: Onset: intravenous: few minutes. Peak effect: 15 to 30 minutes. Duration: 4 hours with normal doses of 1 to 2 mg and up to 6 hours with higher doses. Elimination half-life: 1 to 1.5 hours
Adverse effects: Transient leukopenia, granulocytopenia, thrombocytopenia, hypotension, chest pain, dizziness; electrolyte abnormalities such as hyperuricemia, hypomagnesemia, hypokalemia, hypochloremia, azotemia, hyponatremia, or metabolic alkalosis; hyperglycemia; diarrhea; pancreatitis; nephrotoxicity; muscle cramps; arthritic pain; ototoxicity (less frequent than with furosemide)
Bupivacaine HCL (marcaine, sensorcaine)
Dose: Infiltration or peripheral nerve block: less than 150 mg (0.25%-0.5% solution). Epidural: 50 to 100 mg (0.25%-0.75% solution); children: 1.5 to 2.5 mg/kg (0.25%-0.5% solution). Caudal: 37.5 to 150 mg (15-30 mL of 0.25% or 0.5% solution); children: 0.4 to 0.7 mL/kg. Spinal bolus/infusion: 7 to 17 mg (0.75% solution); children: 0.5 mg/kg with minimum of 1 mg. Do not exceed 400 mg in 24 hours (maximum single dose, 175 mg).
Onset and duration: Onset: infiltration: 2 to 10 minutes. Epidural: 4 to 7 minutes. Spinal: less than 1 minute. Peak effect: infiltration and epidural: 30 to 45 minutes. Spinal: 15 minutes. Duration: infiltration, spinal, epidural: 200 to 400 minutes (prolonged with epinephrine).
Adverse effects: Hypotension, arrhythmias, cardiac arrest, respiratory impairment or arrest, seizures, tinnitus, blurred vision, urticaria, anaphylactoid symptoms; high spinal: urinary retention, lower extremity weakness and paralysis, loss of sphincter control, backache, palsies, slowing of labor
Precautions and contraindications: Use bupivacaine with caution in patients with hypovolemia, severe congestive heart failure, shock, and all forms of heart block. It is not recommended for obstetric paracervical block or in concentrations higher than 0.5% because of the incidence of intractable cardiac arrest. It is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to amide-type local anesthetics.
Chloroprocaine HCL (nesacaine)
Indications: Regional anesthesia; local anesthesia, including infiltration, epidural (including caudal), peripheral nerve block, sympathetic nerve block
Dose: Infiltration and peripheral nerve block: less than 40 mL (1%-2% solution). Epidural: bolus 10 to 25 mL (2%-3% solution), approximately 1.5 to 2 mL for each segment to be anesthetized. Repeat doses at 40- to 60-minute intervals. Infusion: 30 mL/hr (0.5% solution). Caudal: 10 to 25 mL (2%-3% solution); children: 0.4 to 0.7 mL/kg (L2-T10 level of anesthesia). Repeat doses at 40- to 60-minute intervals.
Onset and duration: Rate of onset and potency of local anesthetic action may be enhanced by carbonation. Onset: infiltration or epidural: 6 to 12 minutes. Peak effect: infiltration or epidural: 10 to 20 minutes. Duration: infiltration or epidural: 30 to 60 minutes (prolonged with epinephrine).
Adverse effects: Hypotension, arrhythmias, bradycardia, respiratory depression or arrest, seizures, tinnitus, tremors, urticaria, pruritus, angioneurotic edema; high spinal: backache; loss of perianal sensation and sexual function; permanent motor, sensory, autonomic (sphincter control) deficit in lower segments; slowing of labor
Precautions and contraindications: Use with caution in patients with severe disturbances of cardiac rhythm, shock, heart block, or impaired hepatic function. Inflammation or infection may occur at the injection site. Elderly and pregnant patients are most at risk. It is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to ester-type local anesthetics and to para-aminobenzoic acid or parabens. Do not use for spinal anesthesia.
Cimetidine (tagamet)
Indications: Treatment of duodenal or gastric ulcers, gastroesophageal reflux disease; prophylaxis of aspiration pneumonitis in patients at high risk during surgery
Dose: Prophylaxis of aspiration pneumonitis: adults: 300 to 400 mg orally 1.5 to 2 hours before induction of anesthesia with or without a similar dose the preceding evening. When a more rapid onset of effect is needed, intravenous: dilute 300 to 400 mg in D5W or normal saline to a volume of at least 20 mL and inject over a period not less than 5 minutes. A slower infusion, over 15 to 30 minutes, may be preferable owing to association of occasional severe bradycardia and hypotension with rapid infusion. Children younger than 12 years: use not indicated.
Dosage forms: tablets: 300, 400 mg; parenteral injection: 150 mg/mL
Onset and duration: Onset: 15 to 45 minutes. Peak effect: 1 to 2 hours orally. Duration: 2 to 4 hours. Elimination half-life: 2 hours. Plasma cimetidine levels that suppress gastric acid secretion by 50% were maintained 4 to 5 hours after intravenous injection.
Adverse effects: Mental status changes such as delirium, confusion, depression, primarily in elderly patients or those with hepatic or renal impairment; leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, and gynecomastia rarely (1%)
Precautions and contraindications: Caution is suggested in renal or hepatic insufficiency. Microsomal metabolism of many drugs may be inhibited. It is contraindicated in patients allergic to cimetidine or other H2 antagonists.
Anesthetic considerations: Cimetidine inhibits the hepatic mixed-function oxidase system; therefore, it may prolong the half-life of many drugs, including diazepam, midazolam, metoprolol, propranolol, theophylline, lidocaine, and other amide local anesthetics. Ranitidine may be the drug of choice in patients receiving lidocaine local or regional anesthesia.
Cleviprex (clevidipine)
Dose: Clevidipine is a milky white lipid emulsion. Titrate to achieve desired blood pressure reduction. Initial dose is 1 to 2 mg/hr. Double the dose every few minutes until blood pressure goals are met. Maintenance doses usually range from 4 to 6 mg/hr. Maximum doses are usually less than 16 mg/hr.
Clonidine (catapres, dixarit); epidural clonidine (catapres, duraclon)
Classification: Central-acting α2-adrenergic agonist; reduces sympathetic outflow by directly stimulating α2-receptors in the medulla vasomotor center
Indications: Hypertension; epidural and spinal anesthesia; symptomatic control of alcohol, opiate, nicotine, and benzodiazepine withdrawal; diagnosis of pheochromocytoma; growth hormone stimulation test; cancer-related pain; Tourette syndrome; attention deficit disorder; migraines.
Dose: Maintenance: 0.2 to 0.6 mg/day orally in two divided doses. Hypertensive emergencies: 0.15 mg intravenously over 5 minutes. Transdermal patch: every 7 days (maximum dose: 0.6 mg/day). The same doses are used in renal impairment.
All dosages must be titrated to pain relief and the incidence of side effects.
Onset and duration: Onset: intravenous or oral: 30 to 60 minutes. Peak effect: 2 to 4 hours. May take too long for a true hypertensive crisis. Duration: antihypertensive: 6 to 10 hours, dose dependent.
Adverse effects: Rebound hypertension, atrioventricular block, bradycardia, congestive heart failure, orthostatic hypotension, sedation, nightmares, constipation, dry mouth, pruritus, urinary retention, contact dermatitis
The most common noncardiovascular adverse reactions to epidural clonidine include anxiety, asthenia, chest pain, confusion, diaphoresis, dizziness, drowsiness, dyspnea, fever, nausea or vomiting, and xerostomia.
Precautions and contraindications:
• Avoid in conduction or sinoatrial disorders, hypersensitivity to clonidine, pregnancy, severe renal or hepatic disease. Concomitant administration of tricyclic antidepressants may increase the serum level.
• If the dose is held or when changing to transdermal application, watch for a rapid increase in blood pressure from unopposed α stimulation.
• It crosses the placenta easily and should be discontinued 8 to 12 hours before delivery.
• Epidural clonidine is not recommended for intrathecal administration or as an analgesic during labor and delivery or for postpartum or perioperative analgesia because of the risks of hemodynamic instability.
• Severe rebound hypertension may result from abrupt withdrawal, with neurologic sequelae and myocardial infarction. Labetalol has been successfully used in treatment of hypertensive crisis. Continue on the day of surgery.
• Clonidine reduces perioperative requirements of narcotics and volatile agents.
• Female patients and lower weight patients have an increased risk of the hypotensive effects of epidural clonidine (use cautiously in patients with severe cardiac disease or hemodynamic instability). More profound decreases in blood pressure may be seen if the drug is administered into the upper thoracic spinal segments.
Cocaine HCL (cocaine)
Indications: Topical anesthesia and vasoconstriction of mucous membranes (oral, laryngeal, and nasal)
Dose: Topical: 1.5 mg/kg (1%-4% solution). Nasal: 1 to 2 mL each nostril (1%-10% solution). Concentrations greater than 4% increase potential for systemic toxic reactions. Maximum dose: 1.5 mg/kg.
Onset and duration: Onset: less than 1 minute. Peak effect: 2 to 5 minutes. Duration: 30 to 120 minutes. It is rapidly absorbed from all areas of application.
Precautions and contraindications: Cocaine is for topical use only, not for intraocular or intravenous use. It potentiates other sympathomimetics; therefore, use reduced doses (if any at all) in patients receiving pressors or ketamine. Use it with caution in patients with nasal trauma.
Anesthetic considerations: Hypertension, bradyarrhythmias, tachyarrhythmias, ventricular fibrillation, tachypnea, respiratory failure, euphoria, excitement, seizures, and sloughing of corneal epithelium may occur. Use it with caution in patients with a history of drug sensitivities or drug abuse (high addiction potential) and pregnancy. Prolonged use can cause ischemic damage to nasal mucosa. Cocaine is contraindicated for intraocular or intravenous use. It sensitizes the heart to catecholamines (epinephrine and monoamine oxidase inhibitors may increase cardiac arrhythmias, ventricular fibrillation, hypertensive episodes). It potentiates arrhythmogenic effects of sympathomimetics, and it has a high addiction potential.
Codeine
Onset and duration: Onset: oral: 30 to 60 minutes; intramuscular or subcutaneous: 20 to 60 minutes. Duration: oral: 2 to 4 hours; intramuscular or subcutaneous: 2 to 3 hours.
Adverse effects: Sedation, clouded sensorium, euphoria, dizziness, seizures with large doses, hypotension, bradycardia, nausea, vomiting, constipation, dry mouth, ileus, urinary retention, pruritus, flushing
Precautions and contraindications: Use codeine with caution in patients with head injury, owing to respiratory depression and resulting increased intracranial pressure; in hepatic or renal disease; hypothyroidism; Addison disease; acute alcoholism; seizures; severe central nervous system depression; bronchial asthma; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; respiratory depression; and shock. Use it with caution in patients with known hypersensitivity to the drug and in elderly patients. It may produce histamine release.
Cyclosporine (sandimmune, others)
Indications: Prevention of rejection of organ or tissue (kidney, liver, heart) allograft in combination with steroid therapy
Dose: Initial: oral: 15 mg/kg as a single dose 4 to 24 hours before transplantation; continue for 1 to 2 weeks. Taper to maintenance dose: 5 to 10 mg/kg/day. Intravenous: 5 to 6 mg/kg/day as a single dose 4 to 12 hours before transplantation; continue until the patient is able to take oral medication.
Coadministration of a corticosteroid is recommended, as well as possibly azathioprine.
Onset and duration: Onset: 1 to 6 hours (variable). Duration: 1 to 4 days. After oral administration, onset is variable. Elimination half-life: 10 to 27 hours.
Adverse effects: Hypertension, hirsutism, tremor, acne, gum hyperplasia, headache, blurred vision, diarrhea, nausea, paresthesia, mild nephrotoxicity or hepatotoxicity
Precautions and contraindications: History of hypersensitivity to cyclosporine or polyoxyethylated castor oil. Use it with caution in patients with impaired hepatic, renal, cardiac function, or malabsorption syndrome and in those who are pregnant.
Anesthetic considerations: Altered laboratory values may occur. Cyclosporine may elevate blood urea nitrogen, serum creatinine, serum bilirubin, serum glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase (aspartate aminotransferase), serum glutamic-pyruvic transaminase (alanine aminotransferase), and lactate dehydrogenase. It may prolong the duration of neuromuscular blockade by nondepolarizing muscle relaxants.
Dantrolene sodium (dantrium)
Indications: Treatment of malignant hyperthermia (MHT); prophylaxis of MHT in patients with a family history; control of spasticity secondary to multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injury, cerebral palsy, or stroke
Dose: Adults: MHT: 1 mg/kg rapid intravenous bolus; repeat every 5 to 10 minutes until symptoms are controlled; the dose may be repeated to a cumulative dose of 10 mg/kg; oral doses of 4 to 8 mg/kg/day for 1 to 3 days may be administered in three or four divided doses to prevent recurrence of the manifestations. Prophylaxis of MHT: 2.5 mg/kg intravenous bolus 10 to 30 minutes preinduction; then 1.25 mg/kg intravenous bolus 6 hours later.
Onset and duration: Effective blood concentrations: 100 to 600 ng/mL. Intravenous blood concentrations of the drug remain at approximately steady-state levels for 3 or more hours after infusion is completed. Mean half-life: 5 to 9 hours. Onset: oral: 1 to 2 hours; intravenous: less than 5 minutes. Duration: 8 to 12 hours.
Adverse effects: Hepatotoxicity (hepatitis): 0.5%, with mortality reported as high as 10%; muscle weakness, tachycardia, erratic blood pressure, fatigue, central nervous system (CNS) depression, visual and auditory hallucinations, bowel obstruction, hematuria, crystalluria, urinary frequency, phlebitis, pericarditis, pleural effusion, postpartum uterine atony, myalgias
Precautions and contraindications: Monitor liver function at the beginning of dantrolene therapy. Observe for hepatotoxicity, hepatitis. Owing to the increased risk of hepatotoxicity, use it with caution in patients with severely impaired cardiac or pulmonary function and in women or patients older than 35 years. It is contraindicated in active hepatic disease such as hepatitis or cirrhosis, when spasticity is used to maintain motor function, and in lactation.
Desflurane (suprane)
Dose: Titrate to effect for induction or maintenance of anesthesia. Minimum alveolar concentration: 6%.
Onset and duration: Onset: loss of eyelid reflex: 1 to 2 minutes. Duration: emergence time: 8 to 9 minutes.
Adverse effects: Hypotension, arrhythmia, respiratory depression, apnea, dizziness, euphoria, increased cerebral blood flow and intracranial pressure, nausea, vomiting, ileus, hepatic dysfunction, MHT
Desmopressin (DDAVP)
Indications: Treatment of neurogenic diabetes insipidus; nocturnal enuresis; and, in hemophilia A or von Willebrand disease, to increase factor VIII activity; reduction of perioperative blood loss after cardiac surgery
Dose: Preoperative: 30 minutes before the procedure. Diabetes insipidus: 2 to 4 mcg intravenously or subcutaneously daily in two divided doses; intranasal: 10 to 40 mcg (0.1-0.4 mL) in one to three doses.
Onset and duration: Onset: intranasal: 1 hour; intravenous: 30 minutes. Duration: 8 to 20 hours. Elimination half-life: 3.6 hours.
Adverse effects: Hypotension, hypertension, transient headache (with higher doses), psychosis, seizures, water retention, hyponatremia, abdominal cramps, nasal congestion, rhinitis, facial flushing, hypersensitivity reactions
Precautions and contraindications: This agent is contraindicated in hypersensitivity to desmopressin acetate and in children younger than 3 months. Patients with type IIB von Willebrand disease should not receive desmopressin because platelet aggregation may be reduced. Owing to an increased risk of thrombosis, use it with caution in patients with coronary artery disease. Fluid intake should be decreased in those who do not need the antidiuretic effects of desmopressin. Seizure activity may be related to rapid decreases in serum sodium concentrations secondary to desmopressin. Avoid overhydration; postoperative abdominal cramping may occur.
Dexamethasone (decadron)
Indications: Croup, septic shock, cerebral edema, respiratory distress syndrome including status asthmaticus, acute exacerbations of chronic allergic disorders, corticosteroid-responsive bronchospastic states, allergic or inflammatory nasal conditions, and nasal polyps
Dose: Initial: 0.5 to 9 mg, intramuscularly or intravenously daily, depending on the disease being treated. In less severe diseases, doses lower than 0.5 mg intramuscularly or intravenously may suffice, but in others, doses higher than 9 mg may be required.
Onset and duration: Onset: intravenous or intramuscular: within 10 to 30 minutes; inhalation: within 20 minutes. Elimination half-life: 200 minutes; however, metabolic effects at the tissue level persist for up to 72 hours.
Adverse effects: Cushing syndrome, adrenal suppression, hyperglycemia, hyperthyroidism, hypercalcemia, peptic ulcer, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, increased intraocular pressure, glaucoma, irritability, psychosis, osteoporosis
Precautions and contraindications: Dexamethasone is contraindicated in patients with peptic ulcer, osteoporosis, psychosis or psychoneurosis, acute bacterial infections, herpes zoster, herpes simplex ulceration of the eye, and other viral infections. Use it with caution in patients with diabetes mellitus, chronic renal failure, or infectious disease and in elderly patients. Corticosteroids may increase the risk of developing tuberculosis in patients with a positive purified protein derivative test. They may increase the risk of development of serious or fatal infection in persons exposed to viral illnesses such as chickenpox.
Dexmedetomidine (precedex)
Indications: A selective α2-receptor agonist with sedative properties for short-term sedation in critical care settings. Patients are commonly intubated and mechanically ventilated. Administered by continuous infusion not exceeding 24 hours. Off-label use as an anesthesia adjunct.
Onset and duration: Onset: 10 to 30 minutes, depending on the dose. Duration: 15 minutes to 4 hours, depending on the dose and duration of infusion
Adverse effects: Hypotension, bradycardia, hypertension, nausea, vomiting, and fever are most frequently reported.
Precautions and contraindications: Because of the known pharmacologic effects of dexmedetomidine, patients should be continuously monitored while receiving dexmedetomidine. Clinically significant episodes of bradycardia and sinus arrest have been associated with dexmedetomidine administration in young, healthy volunteers with high vagal tone or with different routes of administration, including rapid intravenous or bolus administration.
Diazepam (valium)
Indications: Anxiety, alcohol withdrawal, status epilepticus, preoperative sedation, sedation for cardioversion; used adjunctively for relief of skeletal muscle spasm associated with cerebral palsy, paraplegia, athetosis, stiff man syndrome, tetanus
Dose: Status epilepticus: adults: intramuscular or intravenous: 5 to 10 mg; repeat if needed at 10- to 15-minute intervals up to 30 mg; repeat if needed in 2 to 4 hours. Children: intramuscular or intravenous: younger than 5 years: 0.2 to 0.5 mg slowly 2 to 5 minutes, up to 5 mg total dose. Children older than 5 years: 1 mg slowly 2 to 5 minutes up to 10 mg; repeat if needed in 2 to 4 hours.
Onset and duration: Onset: oral: 30 to 60 minutes; intramuscular: 15 to 30 minutes; intravenous: 1 to 5 minutes. Peak effect: 1 to 2 hours orally. Duration: intravenous: 15 minutes to 1 hour; oral: up to 3 hours. Elimination half-life: 20 to 50 hours; excreted primarily in urine. It is metabolized in liver to active metabolites.
Adverse effects: Drowsiness, fatigue, ataxia, confusion, paradoxical dizziness, vertigo, amnesia, vivid dreams, headache, slurred speech, tremor, muscle weakness, electroencephalogram changes, tardive dyskinesia, hypotension, tachycardia, edema, cardiovascular collapse, blurred vision, diplopia, nystagmus, xerostomia, nausea, constipation, incontinence, urinary retention, changes in libido
Precautions and contraindications: Diazepam is contraindicated in acute narrow-angle glaucoma, untreated open-angle glaucoma, and during or within 14 days of monoamine oxidase inhibitor therapy. Safe use during pregnancy (category D) and lactation has not been established.
Anesthetic considerations: Diazepam reduces requirements for volatile anesthetics. A potential for thrombophlebitis exists with intravenous administration. Elderly patients have decreased clearance and dosage requirements. Its effects are antagonized by flumazenil. It may cause neonatal hypothermia.
Digoxin (lanoxin)
Dose: Adults: loading: intravenous or oral: 0.5 to 1 mg in divided doses (administer 50% of loading dose as first dose; then 25% fractions at 4- to 8-hour intervals until adequate therapeutic response is noted, toxic effects occur, or the total digitalizing dose has been administered). Monitor clinical response before each additional dose. Maintenance: intravenous or oral: 0.0625 to 0.25 mg; dosages should be individualized. Elderly patients (older than 65 years): oral: 0.125 mg or less daily as maintenance dose. Small patients may require less.
Onset and duration: Onset: intravenous: 5 to 30 minutes; oral: 30 minutes to 2 hours. Duration: intravenous or oral: 3 to 4 days.
Adverse effects: Enhanced toxicity in hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, hypercalcemia; wide range of arrhythmias, atrioventricular block, headache, psychosis, confusion, nausea, vomiting, ocular changes, diarrhea, gynecomastia
Anesthetic considerations: Decrease the dosage in patients with impaired renal function and in elderly patients. Monitor serum potassium, calcium, and digoxin levels. The use of synchronized cardioversion in patients with digitalis toxicity should be avoided because it may initiate ventricular fibrillation.
Diltiazem (cardizem)
Dose: Bolus intravenous: 0.25 mg/kg over 2 minutes. If needed, follow after 15 minutes with 0.35 mg/kg over 2 minutes. Maintenance infusion: 5 to 15 mg/hr. Adults: oral: 30 mg three or four times daily before meals and at bedtime. Dosage may be gradually increased to a maximum of 360 mg/day in divided doses. Sustained-release capsules: 90 mg; oral: twice daily, titrate dosage to effect (maximum dose: 360 mg/day).
Onset and duration: Onset: oral: 30 minutes; intravenous: 1 to 3 minutes. Elimination half-life: 3 to 5 hours. Duration: 4 to 6 hours.
Adverse effects: Hypotension, flushing, atrioventricular block, constipation, pruritus, bradycardia, edema, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, depression, headache, fatigue, dizziness
Diphenhydramine (benadryl)
Indications: Adjuvant with epinephrine in the treatment of anaphylactic shock and severe allergic reactions; treatment of drug-induced extrapyramidal effects, motion sickness; antiemetic
Dose: Antihistamine or antiemetic: 10 to 50 mg intramuscularly or intravenously every 2 to 3 hours (maximum dose: 400 mg/day).
Onset and duration: Onset: oral: 1 hour. Duration: 4 to 6 hours. Elimination half-life: 4 to 8 hours
Adverse effects: Sedation (most frequent); dizziness, tinnitus, tremors, euphoria, blurred vision, nervousness, palpitations, hypotension, psychotic reactions, hypersensitivity
Precautions and contraindications: Diphenhydramine is contraindicated in patients with a hypersensitivity to it and other antihistamines of a similar chemical structure. Antihistamines are contraindicated in patients taking monoamine oxidase inhibitor therapy. Avoid in patients with narrow-angle glaucoma.
Dobutamine HCL (dobutrex)
Dose: Infusion: 0.5 to 30 mcg/kg/min. Note: Must be diluted, and an intravenous pump (syringe pump in pediatric patients) must be used.
Adverse effects: Hypertension, tachycardia, arrhythmias, angina, shortness of breath, headache, phlebitis at injection site
Precautions and contraindications: Arrhythmias and hypertension occur at high dobutamine doses. Use it with caution in patients with idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis. Do not mix dobutamine with sodium bicarbonate, furosemide, or other alkaline solutions; correct hypovolemia before or during treatment.
Dolasetron (anzemet)
Dose: 12.5 mg (intravenous) 15 minutes before the cessation of anesthesia or 100 mg (oral) within 2 hours before surgery
Dopamine HCL (intropin)
Dose: Infusion: 1 to 5 mcg/kg low dose; pressor dose range: 5 to 20 mcg/kg, greater than 20 mcg/kg for extreme cases. Note: Must be diluted, and an intravenous pump must be used.
Onset and duration: Onset: 2 to 4 minutes. Duration: less than 10 minutes after termination of infusion
Precautions and contraindications: Caution administering through a peripheral line; may see excessive tachycardia at higher doses.
Anesthetic considerations: Avoid dopamine or use it at greatly reduced dose if the patient has received a monamine oxidase inhibitor. Infuse it into a large vein; extravasation may cause sloughing. Treat extravasation by local infiltration of phentolamine (≈1 mg in 10 mL normal saline). Correct hypovolemia as quickly as possible before or during dopamine treatment.
Edrophonium chloride (tensilon)
Indications: Reversal of neuromuscular blockade; diagnostic assessment of myasthenia gravis, and supraventricular tachycardia
Dose: Reversal: slow intravenous: 0.5 to 1 mg/kg (maximum dose: 40 mg), with atropine (0.007-0.015 mg/kg), administered before the edrophonium
Onset and duration: Onset: intravenous: 30 to 60 seconds; intramuscular: 2 to 10 minutes. Duration: intravenous: 20 to 40 minutes; intramuscular: 20 to 60 minutes.
Adverse effects: Bradycardia, tachycardia, atrioventricular block, nodal rhythm, hypotension; increased oral, pharyngeal, bronchial secretions; bronchospasm; respiratory depression; seizures; dysarthria; headaches; lacrimation; miosis; visual changes; nausea; emesis; flatulence; increased peristalsis; rash; urticaria; allergic reactions; anaphylaxis
EMLA (mixture of lidocaine and prilocaine)
Dose: Adults: A thick layer of lidocaine–prilocaine cream is applied to intact skin and covered with an occlusive dressing, or alternatively, a lidocaine–prilocaine anesthetic disc is applied to intact skin:
• Minor dermal procedures: For minor procedures such as intravenous cannulation and venipuncture, apply 2.5 g of lidocaine–prilocaine cream, half the 5-g tube) over 20 to 25 cm2 of skin surface or 1 lidocaine–prilocaine anesthetic disc (1 g over 10 cm2) for at least 1 hour. In controlled clinical trials using lidocaine–prilocaine cream, two sites were usually prepared in case there was a technical problem with cannulation or venipuncture at the first site.
• Major dermal procedures: For more painful dermatologic procedures involving a larger skin area, such as split-thickness skin graft harvesting, apply 2 g of lidocaine–prilocaine cream per 10 cm2 of skin and allow it to remain in contact with the skin for at least 2 hours.
Onset and duration: The onset, depth, and duration of dermal analgesia on intact skin provided by EMLA depend primarily on the duration of application. To provide sufficient analgesia for clinical procedures such as venipuncture, EMLA should be applied under an occlusive dressing for at least 1 hour. To provide dermal analgesia for clinical procedures such as split-thickness skin graft harvesting, EMLA should be applied under occlusive dressing for at least 2 hours. Satisfactory dermal analgesia is achieved 1 hour after application, peaks at 2 to 3 hours, and persists for 1 to 2 hours after removal. Absorption from the genital mucosa is more rapid and onset time is shorter (5-10 minutes) than after application to intact skin. After a 5- to 10-minute application of EMLA to female genital mucosa, the average duration of effective analgesia to an argon laser stimulus (which produces a sharp, pricking pain) is 15 to 20 minutes (with individual variations in the range of 5-45 minutes).
Adverse effects: During or immediately after treatment with lidocaine or prilocaine on intact skin, possible erythema, edema, or abnormal sensation of skin at treatment site
Precautions and contraindications: Application of EMLA to larger areas or for longer times than those recommended could result in sufficient absorption of lidocaine and prilocaine to result in serious adverse effects. EMLA is contraindicated in patients who exhibit allergies to amide local anesthetics. EMLA should be used with care in patients with conditions or therapy associated with methemoglobinemia.
Anesthetic considerations: EMLA is generally safe. When EMLA is used, the patient should be aware that the production of dermal analgesia may be accompanied by the block of all sensations in the treated skin. For this reason, the patient should avoid inadvertent trauma to the treated area caused by scratching, rubbing, or exposure to extreme hot or cold temperatures until complete sensation has returned.
Enalaprilat (vasotec IV)
Enoxaparin (lovenox, low-molecular-weight heparin)
Classification: Anticoagulant (antithrombotic), inhibiting factors Xa and IIa and only slightly affecting clotting times
Indications: Prevention of postoperative pulmonary embolism (PE) or deep venous thrombosis (DVT); reduction of ischemic complications in patients with cardiovascular disease who have unstable angina and non–Q-wave myocardial infarctions
Dose: Immediately after surgery: 30 mg or 40 mg subcutaneously every 12 hours to prevent DVT or PE; 1 mg/kg subcutaneously every 12 hours with 100 to 325 mg oral aspirin daily to treat patients with unstable angina or non–Q-wave myocardial infarction.
Onset and duration: Onset: subcutaneous: 20 to 60 minutes. Peak effect: 3 to 5 hours. Duration: 12 hours. Elimination half-life: 3 to 4.5 hours.
Adverse effects: Hemorrhage; epidural or subarachnoid or injection site hematomas; thrombocytopenia; increased aspartate aminotransferase; alanine aminotransferase; liver enzymes; chills, fever, urticaria
Precautions and contraindications: Avoid intramuscular injections of enoxaparin. Use it with caution in pregnant patients and those with a history of coagulopathies or gastrointestinal bleeding. Enoxaparin is absolutely contraindicated in patients with active bleeding, thrombocytopenia, a history of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, and pork or heparin sensitivities.
Anesthetic considerations: Central axis blocks or removal of indwelling catheters should not occur at least 12 hours before or after the last administration of enoxaparin or, conservatively, not within the previous 24 hours. Coagulation tests do not need to be routinely ordered while the patient is taking enoxaparin. However, if coagulation test results are abnormal or bleeding occurs, anti–factor Xa is the most sensitive test to indicate therapeutic anticoagulation levels. Treat an overdose with protamine sulfate. Each milligram of protamine will neutralize 1 mg of enoxaparin.
Ephedrine sulfate
Classification: Noncatecholamine sympathomimetic with mixed direct and indirect actions as well as central nervous system effects
Dose: Intravenous: 5 to 25 mg (or 100-300 mcg/kg); intramuscular: 25 to 50 mg; oral: 25 to 50 mg every 3 hours
Onset and duration: Onset: intravenous: almost immediate; intramuscular: a few minutes. Duration: intravenous: 10 to 60 minutes.
Adverse effects: Hypertension, tachycardia, arrhythmias, pulmonary edema, anxiety, tremors, hyperglycemia, transient hyperkalemia and then hypokalemia, necrosis at the site of injection, possible tolerance
Epinephrine HCL (adrenaline chloride)
Indications: Inotropic support; treatment of anaphylaxis; to increase duration of action of local anesthetic; hemostasis; cardiac arrest; bronchodilation
Dose: Cardiac arrest: 0.5 to 1 mg intravenous bolus every 5 minutes as necessary. Inotropic support: 2 to 20 mcg/min (0.1-1 mcg/kg/min). Anaphylaxis: 100 to 300 mcg intravenous push, depending on severity.
Adverse effects: Restlessness, fear, throbbing headache, tachycardia, tachydysrhythmias, premature ventricular contractions, ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, severe hypertension, angina, extension of myocardial infarction, pulmonary edema
Esmolol (brevibloc)
Dose: SVT: loading: 50 to 200 mcg/kg/min for 1 minute; follow by infusion of 50 mcg/kg/min for 4 minutes. If the desired effect is not achieved, repeat loading dose and increase infusion to 100 mcg/kg/min. May repeat the process up to a maximum of 300 mcg/kg/min.
Onset and duration: Onset: 1 to 2 minutes. Duration: 10 to 20 minutes. Peak effect: 5 to 6 minutes. Do not infuse for more than 48 hours.
Adverse effects: Hypotension, bradycardia, congestive heart failure, bronchospasm, confusion, depression, urinary retention, nausea and vomiting, rash
Ethacrynic acid (edecrin)
Indications: Edema of cardiac, hepatic, or renal origin; hypertension, pulmonary edema; usually reserved for patients who do not respond to thiazide diuretics or in whom a rapid onset of diuresis is desired
Dose: 0.5 to 1 mg/kg slowly over several minutes up to a maximum of 100 mg in a single dose. The usual average dose is 50 mg. Children: 1 mg/kg over 20 to 30 minutes.
Onset and duration: Onset: intravenous: 5 to 15 minutes. Duration: intravenous: 2 hours but may last 6 to 7 hours. Elimination half-life: 1 to 4 hours.
Adverse effects: Fluid and electrolyte imbalance, including hypomagnesemia, hypocalcemia, hypokalemia, hypochloremia, metabolic alkalosis, hyperuricemia; hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia; thrombocytopenia; agranulocytopenia; vertigo; ototoxicity (associated with rapid intravenous injection); pancreatitis; gastrointestinal hemorrhage; hepatotoxicity; hypotension; diarrhea
Precautions and contraindications: Avoid rapid intravenous injection of ethacrynic acid. Use it with extreme caution in patients with impaired renal or hepatic function. It is contraindicated for use in patients after anuric renal failure is established, as well as in patients with hypotension; dehydration with low serum sodium or metabolic alkalosis with hypokalemia; nursing mothers; infants; and patients with severe watery diarrhea.
Etomidate (amidate)
Dose: Adult: intravenous: 0.2 to 0.3 mg/kg over 30 to 60 seconds.
Dosage forms: injection: 2 mg/mL, ampules and prefilled syringe.
Onset and duration: Onset: 1 minute. Duration: 3 to 10 minutes. Metabolized in the liver. Half-life: 75 minutes; excreted primarily in the urine.
Adverse effects: Myoclonus, tonic movements, eye movements, hypertension, hypotension, tachycardia, bradycardia, other arrhythmias, postoperative nausea and vomiting, hypoventilation, hyperventilation, transient apnea, laryngospasm, hiccups, snoring, adrenocortical suppression
Famotidine (pepcid)
Indications: Treatment of duodenal or gastric ulcers and gastroesophageal reflux; prophylaxis of aspiration pneumonitis in patients at high risk during surgery
Dose: Prophylaxis of aspiration pneumonitis: adults: 20 to 40 mg orally the evening before surgery or the morning of surgery before induction of anesthesia (or both the evening before and the morning of surgery). If a more rapid onset is desired, 2 mL of intravenous famotidine (10 mg/mL) may be diluted to a concentration of 5 to 10 mL with D5W, normal saline, or lactated Ringer’s solution and administered over at least 2 minutes before induction.
Dosage forms: tablets: 20, 40 mg; parenteral injection: 10 mg/mL in 2- or 4-mL vials
Onset and duration: Onset: 20 to 45 minutes. Peak effect: 1 to 3 hours orally. Duration: Plasma famotidine concentrations that suppress gastric acid secretion by 50% are maintained for 12 hours after an oral dose of 40 mg and 7 to 9 hours after a 20-mg dose.
Adverse effects: Headache (2%-4.5%), constipation (1.4%), and drowsiness (most frequently reported); mental confusion in elderly patients (occasionally)
Potential bradydysrhythmias and hypotension may be associated with rapid infusion.
Fenoldopam (corlopam)
Indications: A potent vasodilator that stimulates the postsynaptic dopamine DA receptors, thereby lowering blood pressure, peripheral vascular resistance, and renal vascular resistance and increasing cardiac hemodynamics; short-term use (up to 48 hours) for patients with severe hypertension or malignant hypertension
Dose: Administer fenoldopam as a continuous infusion; no loading dose is needed. The infusion range is 0.04 to 0.8 mcg/kg/min; titrate slowly for blood pressure reduction. Initial doses less than 0.1 mcg/kg/min are marginally antihypertensive but have less reflex tachycardia. Initial doses higher than 0.3 mcg/kg/min have been associated with reflex tachycardia.
Onset and duration: Onset: 5 minutes. Peak effect: 15 minutes. Rapidly metabolized. Half-life: 5 minutes.
Adverse effects: Reflex tachycardia with a higher initial dosing regimen possibly causing increased intraocular pressure, hypotension, hypokalemia (infusion time greater than 6 hours can cause potassium to fall to less than 3 mEq), headache, flushing, nausea
Precautions and contraindications: Fenoldopam has no absolute contraindications. Use it with caution in patients with severe hepatic disease. It contains a metabisulfite compound, so do not use this drug in patients sensitive to sulfites (especially patients with asthma) because allergic reaction may result. The concomitant use of other antihypertensive agents (calcium channel blockers, nitrates, β1-blockers, and α2-blockers) may result in unexpected hypotension.
Anesthetic considerations: Titrate the drug slowly to prevent reflex tachycardia. Check the patient’s potassium level if titrating a long-term infusion (greater than 6 hours). Review for sulfite allergies, especially in patients with asthma. Use with caution in patients with open globe injuries or glaucoma because fenoldopam may increase intraocular pressure. It is generally used as an alternative to nitroprusside.
Fentanyl (sublimaze, duragesic, oralet)
Onset and duration: Onset: intravenous: within 30 seconds; intramuscular: less than 8 minutes; epidural or spinal: 4 to 10 minutes. Duration: intravenous: 30 to 60 minutes; intramuscular: 1 to 2 hours; epidural or spinal; 4 to 8 hours.
Adverse effects: Hypotension, bradycardia, respiratory depression, apnea, dizziness, blurred vision, seizures, nausea, emesis, delayed gastric emptying, biliary tract spasm, muscle rigidity
Precautions and contraindications: Reduce fentanyl doses in elderly, hypovolemic, or high-risk surgical patients and with concomitant use of sedatives and other narcotics. It crosses the placental barrier and may produce depression of respiration in neonates. Prolonged depression may occur after cessation of transdermal patch use.
Anesthetic considerations: Narcotic effects reversed by naloxone (0.2-0.4 mg intravenously). Circulatory and ventilatory depressant effects are potentiated by narcotics, sedatives, volatile anesthetics, nitrous oxide, and possibly monoamine oxidase inhibitors, phenothiazines, and tricyclic antidepressants; analgesia is enhanced by α2-agonists. Muscle rigidity in higher dose range sufficient to interfere with ventilation.
Flumazenil (romazicon)
Dose: Intravenous: 0.2 to 1 mg (4-20 mcg/kg); titrate to patient response; may repeat at 20-minute intervals (maximum single dose: 1 mg; maximum total dose: 3 mg in any 1 hour)
Onset and duration: Onset: 1 to 2 minutes. Duration: 30 to 90 minutes, depending on the dose of flumazenil and plasma concentration of benzodiazepine to be reversed.
Adverse effects: Arrhythmia, tachycardia, bradycardia, hypertension, angina, flushing, reversal of sedation, seizures, agitation, emotional lability, nausea and vomiting, pain at injection site, thrombophlebitis
Fospropofol (lusedra)
Dose: Loading dose: 6.5 mg/kg; initial dose not to exceed 16.5 mL
Furosemide (lasix)
Indications: Edema of cardiac, hepatic, or renal origin; hypertension; pulmonary and cerebral edema; usually reserved for patients who do not respond to thiazide diuretics or in whom a rapid onset of diuresis is desired
Dose: Diuresis: adult: 20 to 40 mg intramuscularly or intravenously as a single dose. Intravenous doses should be injected slowly over 1 to 2 minutes. Additional doses of 20 mg greater than the previous dose may be administered every 2 hours until desired response is obtained. For intravenous bolus injections, do not exceed 1 g/day administered over 30 minutes. Acute pulmonary edema: 40 mg intravenously initially; may repeat in 1 hour with 80 mg if necessary. Children: intramuscular or intravenous: 1 mg/kg single dose initially, increasing by 1 mg/kg every 2 hours or more until desired response is obtained or to a maximum of 6 mg/kg/day.
Dosage forms: tablets: 20, 40, 80 mg; injection: 10 mg/mL; oral solutions: 10 mg/mL and 40 mg/5 mL.
Onset and duration: Onset: intravenous: onset of diuresis usually occurs in 5 minutes. Duration: 2 hours. Elimination half-life: widely variable; normal is 0.5 to 1 hour, but a period of 11 to 20 hours has been reported in patients with hepatic or renal insufficiency.
Adverse effects: Dehydration, hypotension, hypochloremic alkalosis, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, hyperglycemia, hyperuricemia
Precautions and contraindications: Furosemide is contraindicated in anuria (except for a single dose in acute anuria) and pregnancy. Use it with caution in patients with severe or progressive renal disease and hepatic disease. Discontinue it if renal function worsens. Use caution in patients who are allergic to sulfonamides and patients with severe electrolyte imbalance.
Glucagon
Indications: Treatment of hypoglycemia or β-blocker overdose; inotropic agent used to relax smooth muscle of gastrointestinal tract for radiologic studies; anaphylaxis resistant to epinephrine
Dose: Diagnostic aid for radiologic examination: intravenous or intramuscular: 0.25 to 2 mg before initiation of radiologic procedure. Hypoglycemia: intravenous, intramuscular, or subcutaneous: 0.5 to 1 mg.
Onset and duration: Onset: less than 5 minutes. Peak effect: 5 to 20 minutes. Duration: 10 to 30 minutes
Adverse effects: Hypertension, hypotension, respiratory distress, dizziness, lightheadedness, nausea and vomiting, urticaria, hypoglycemia, hyperglycemia
Glycopyrrolate (robinul)
Indications: Vagolytic premedication to block bradycardia from stimulation of the carotid sinus or traction on abdominal viscera or extraocular muscles during surgery; blockade of muscarinic effects of anticholinesterases; adjunctive therapy in the treatment of bronchospasm and peptic ulcer disease
Dose: Adults: Premedication or vagolysis: intravenous, intramuscular, subcutaneous: 0.1 to 2 mg (4-6 mcg/kg) administered 30 to 60 minutes preinduction; may repeat in 2- to 3-minute intervals for vagolysis up to 1 mg total. Blockade of muscarinic effects of anticholinesterase: 0.2 mg for each 1 mg of neostigmine or 5 mg of pyridostigmine. Bronchospasm: inhalation 0.4 to 0.8 mg every 8 hours; dilute injectate solution in 2 to 3 mL normal saline and deliver by compressed air nebulizer.
Onset and duration: Onset: oral: 1 hour; intramuscular or subcutaneous: 15 to 30 minutes; inhalation: 3 to 5 minutes; intravenous administration: less than 1 minute. Duration: antisialagogue effect: 7 to 12 hours, depending on the route of administration and dose; vagal blockade: 2 to 3 hours intravenously, 8 to 12 hours orally.
Adverse effects: Tachycardia (high doses), headache, urinary hesitancy, retention, decreased sweating, dry nose and mouth, constipation
Precautions and contraindications: Avoid glycopyrrolate when tachycardia would be harmful (i.e., thyrotoxicosis, pheochromocytoma, coronary artery disease). Avoid it in hyperpyrexial states because it inhibits sweating. Use it with caution in patients with hepatic or renal disease, congestive heart failure, chronic pulmonary disease (because a reduction in bronchial secretions may lead to formation of bronchial plugs), hiatal hernia, gastroesophageal reflux, gastrointestinal infections, and ulcerative colitis. It is contraindicated in acute-angle glaucoma, obstructive disease of the gastrointestinal tract, obstructive uropathy, paralytic ileus, intestinal atony, and acute hemorrhage in patients whose cardiovascular status is unstable.
Anesthetic considerations: Additive anticholinergic effects may occur with meperidine, some antihistamines, phenothiazines, tricyclic antidepressants, and antiarrhythmic drugs that possess anticholinergic activity (e.g., quinidine, disopyramide, procainamide). It is the preferred agent in pregnant patients over atropine and scopolamine because it does not cross the placental barrier.
Granisetron (kytril)
Indications: Effective single agent used to control nausea and vomiting induced by cisplatin and other cytotoxic agents and for postoperative nausea and vomiting
Onset and duration: Onset: peak plasma concentrations demonstrate wide interindividual variation. After a 40-mcg/kg dose, nausea and vomiting subside within several minutes. Duration: serum levels decline to less than 10 ng/mL at 24 hours after a single 40-mcg/kg infusion. Antiemetic effects last up to 24 hours after intravenous infusion of 40 mcg/kg.
Adverse effects: Headache and constipation (most common); also somnolence, dizziness, diarrhea, flushing, transient elevation of liver enzymes
Heparin
Classification: Anticoagulant; accelerates the rate at which antithrombin III neutralizes thrombin and factors VII, IX, X, and XI
Indications: Prophylaxis and treatment of deep venous thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary thromboembolism (PE); acute arterial occlusion, intracardiac mural thrombosis, after myocardial infarction after intravenous thrombolytic treatment, disseminated intravascular coagulation with gross thrombosis, anticoagulation during cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB), prophylaxis of thromboembolism in patients with mitral valve disease or atrial fibrillation; maintenance of patency of indwelling venipuncture devices (lock flush)
Dose: Dosage is highly individualized and based on daily activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) compared with aPTT 6 hours after each dosage change. Obtain baseline aPTT and adjust the dose according to clinical state. For prophylaxis (i.e., hip surgery, atrial fibrillation, valve disease): the ratio of aPTT to baseline aPTT should be 1.2 to 1.5; for prosthetic heart valves, DVT, PE, recurrent embolism: 1.5 to 2. For CPB, monitor the activated clotting time (ACT) and maintain an ACT of 400 to 480 seconds. Baseline ACT values are 80 to 150 seconds. ACT should be determined 5 minutes after heparin administration. Adequate heparinization must be ensured before initiation of CPB.
Onset and duration: Onset: intravenous: immediate; subcutaneous: 20 to 30 minutes. Elimination half-life: 1 to 2 hours in healthy adults. Duration: half-life and duration increase with increasing doses; prolonged in liver and renal disease.
Adverse effects: Hemorrhage, thrombocytopenia, white-clot syndrome (rare paradoxical thrombosis), necrotizing skin lesions, elevated liver enzymes, osteoporosis, priapism, hypersensitivity
Precautions and contraindications: Avoid intramuscular injections of heparin. It is contraindicated in patients with hemophilia; thrombocytopenia; acute bleeding; peptic ulcer; esophagitis; diverticulitis; esophageal varices; arterial aneurysm; gastrointestinal or urinary tract malignancy; vascular retinopathy; recent liver or renal biopsy; acute pericarditis; threatened abortion; infective endocarditis; recent regional anesthesia; severe hypertension; recent cerebrovascular accident; recent surgery; or trauma to the brain, eye, or spinal cord.
Hetastarch (hespan)
Indications: Adjunct for plasma volume expansion in shock resulting from hemorrhage, burns, sepsis, surgery, or other trauma; mild anticoagulant effects after vascular procedures
Dose: Plasma volume expansion from 500 to 1000 mL. Total dosage does not usually exceed 1500 mL/day (20 mL/kg/day). In acute hemorrhagic shock, rates approaching 20 mL/kg/hr have been used.
Dosage forms: 6% solution in 0.9% sodium chloride, 500-mL intravenous infusion bottle
Adverse effects: Anaphylactic reactions (periorbital edema, urticaria, wheezing); peripheral edema of the lower extremities; chills; mild temperature elevation; muscle pain
Large volumes may alter coagulation times and may result in transient prolongation of prothrombin time, partial thromboplastin time, and bleeding; decreased hematocrit; and excessive dilution of plasma proteins.
Precautions and contraindications: Hetastarch is contraindicated in patients with severe bleeding disorders, severe cardiac failure, and renal failure with oliguria or anuria. Hetastarch does not have oxygen-carrying capacity, nor does it contain plasma proteins such as coagulation factors. Therefore, it is not a substitute for blood or plasma.
Hyaluronidase (vitrase and others)
Indications: Adjunct to increase absorption and dispersion of other injected drugs such as local anesthetics; hypodermoclysis; subcutaneous urography
Dose: Adjunct: 150 units to injection medium containing other medication. Hypodermoclysis (adults and children older than 3 years): 150 units injected subcutaneously before clysis or injected into clysis tubing near needle for each 1000-mL clysis solution. Subcutaneous urography (patient prone): 75 units subcutaneously over each scapula followed by injection of contrast medium at the same sites.
Hydralazine (apresoline)
Dose: Intravenous and intramuscular: 2.5 to 40 mg (0.1-0.2 mg/kg); oral: 10 to 100 mg four times daily
Dosage forms: injection: 20 mg/mL; tablets: 10, 25, 50, and 100 mg
Onset and duration: Onset: intravenous: 5 to 20 minutes; intramuscular: 10 to 30 minutes; oral: 30 to 120 minutes. Duration: intravenous: 2 to 4 hours; intramuscular or oral: 2 to 8 hours.
Adverse effects: Hypotension, paradoxical pressor response, tachycardia, palpitations, angina, dyspnea, nasal congestion, peripheral neuritis, depression, anxiety, headache, dizziness, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, lupuslike syndrome, rash, urticaria, eosinophilia, hypersensitivity, leukopenia, splenomegaly, agranulocytosis
Hydrocortisone sodium succinate (a-hydrocort, solu-cortef)
Indications: Treatment of choice for steroid-replacement therapy; also anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive agent, although glucocorticoids (prednisone) are preferred for this use; adjunctive therapy in anaphylaxis to prevent prolonged antigen-antibody reactions; adjunctive treatment of ulcerative colitis (enema)
Dose: Adults: shock: 500 mg to 2 g (succinate) intravenously every 2 to 6 hours until the condition is stabilized. Not recommended beyond 48 to 72 hours. Adjunctive therapy in anaphylaxis: hydrocortisone phosphate or succinate intravenously 5 mg/kg initially; then 2.5 mg/kg every 6 hours. Adrenal insufficiency: acute, precipitated by trauma or surgical stress: If adrenocorticotropic hormone testing is not being performed, 200 to 300 mg intravenous hydrocortisone succinate over several minutes; then 100 mg intravenously every 6 hours for 24 hours. If the patient is stable, dosage tapering may begin on the second day. Consider steroid replacement in any patient who has received corticosteroid therapy for at least 1 month in the past 6 to 12 months, with 50 to 100 mg intravenously (succinate) before, during, and after surgery. For intraarticular, soft tissue, and intrasynovial injections, use acetate only (acetate is not for intravenous use): 10 to 50 mg combined with local anesthetic such as procaine. Injections may be repeated every 3 to 5 days (for bursae) to once every 1 to 4 weeks (for joints).
Children: 0.16 to 1 mg/kg or 6 to 30 mg/m2 (phosphate or succinate) intramuscularly or intravenously one or two times daily. The dose depends on the disease being treated.
Onset and duration: Onset: intravenous or intramuscular: 5 minutes. Duration: approximates the duration of hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis suppression (i.e., 30-36 hours); after a single oral dose of hydrocortisone, this is 1.25 to 1.5 days.
Adverse effects: Glaucoma and cataracts (long-term therapy); muscle weakness, sodium retention, edema, hypokalemic alkalosis, hyperglycemia, Cushing syndrome, peptic ulcer, increased appetite, delayed wound healing, psychotic behavior, congestive heart failure, hypertension, growth suppression, pancreatitis
Precautions and contraindications: Hydrocortisone is contraindicated in patients with systemic fungal infections. It may mask or exacerbate infections. Use it with caution in patients with ocular herpes simplex or a history of peptic ulcer disease. In patients with myasthenia gravis, hydrocortisone interacts with anticholinesterase agents to produce severe weakness.
Anesthetic considerations: Hypotension from the stress of anesthesia and surgery may occur if regular doses of steroids were taken within 2 months preceding surgery. Supplemental steroids are indicated commencing with preoperative dose and continuing for 3 days for major surgery, for 24 hours for minor surgery, and one dose for a very brief procedure and then tapered to normal therapy.
Because of adrenal suppression, etomidate should be avoided in patients with adrenal insufficiency.
Ibuprofen (caldolor)
Dose: 400 to 800 mg intravenous every 6 hours; 3200 mg maximum per day
Infuse over 30 minutes. Dilute the 400-mg vial in 100 mL; Dilute the 800-mg vial in 200 mL.
Adverse effects: Dizziness with higher doses. Ibuprofen inhibits platelet function and increases bleeding time, but no increase in bleeding was reported in clinical trials. NSAIDs are contraindicated in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass surgery. Extended use may produce gastrointestinal and renal toxicity. Some orthopedic surgeons have been reluctant to use ibuprofen postoperatively because of reports that it may interfere with bone healing.
Ibutilide fumarate (corvert)
Indications: Rapid conversion of atrial fibrillation or flutter of acute onset (less than 90 days) to sinus rhythm
Dose: Adults weighing more than 60 kg: 1 vial (1 mg) infused over 10 minutes (may be repeated once in 10 minutes after completion of first dose). Adults weighing less than 60 kg: 0.01 mL/kg infused over 10 minutes (may be repeated once in 10 minutes after completion of first dose). Not recommended for pediatric patients.
Onset and duration: Onset: intravenous: immediate for antiarrhythmic properties. Peak effect: 10 minutes. Half-life: 6 hours. Atrial arrhythmias usually convert within 30 minutes after ibutilide therapy begins. Duration: 10 to 30 minutes.
Adverse effects: Ventricular arrhythmias (often sustained torsades de pointes), heart block, congestive heart failure, bradycardia, tachycardia, hypotension, nausea, headache
Precautions and contraindications: The drug is contraindicated in patients sensitive to ibutilide, those with second- or third-degree atrioventricular heart blocks or prolonged Q-T interval, and during pregnancy.
Anesthetic considerations: The risk of proarrhythmias or polymorphic ventricular tachycardia is increased when ibutilide is used with other drugs that prolong the Q-T interval (phenothiazines, procainamide, quinidine, antihistamines). Electrocardiographic monitoring for 4 hours after drug therapy is mandatory because arrhythmias (premature ventricular contractions, ventricular tachycardia, tachycardia, bradycardia, varying degrees of heart blocks) can take place. Have emergency equipment available to perform overdrive pacing, defibrillate, or cardiovert the patient. Monitor serum potassium and magnesium because deficiencies in these electrolytes can precipitate polymorphic ventricular tachycardia.
Insulin regular (rapid-acting) (humulin R, novolin R, regular iletin II)
Classification: Antidiabetic agent
| Blood Glucose (mg/dL) | Insulin Regular |
| Less than | 0 units |
| 200-250 | 5 units subcut |
| 250-300 | 10 units subcut |
| 300-350 | 15 units subcut |
Dose: Diabetes mellitus: in general, therapy is initiated with regular insulin, subcutaneously 5 to 10 units in adults and 2 to 4 units in children 15 to 30 minutes before meals and at bedtime. The dose and frequency are carefully individualized based on blood glucose monitoring every 4 to 6 hours. After satisfactory control is achieved, an intermediate form of insulin may be substituted; this is administered before breakfast in a dose approximately two-thirds to three-fourths that of the previous total daily dose established for regular insulin. Treatment plans are highly variable and patient dependent.
Postoperative: sliding scale every 4 to 6 hours. Individualize to the patient.
Adverse effects: Dose-related hypoglycemia; local allergic reactions, lipoatrophy, and resistance (overcome by switching to more highly purified sources); anaphylaxis
Precautions and contraindications:
• Diabetic ketoacidosis is a life-threatening condition requiring prompt diagnosis and treatment.
• Changes in purity, strength, brand, type, or species source may result in the need for a change in insulin dosage.
• Treat hypoglycemia with 0.6 mL/kg 50% dextrose intravenously.
• Insulin requirements may increase dramatically with stress, sepsis, trauma, or pregnancy.
• Only regular insulins (clear insulins) may be administered intravenously. Intermediate insulins may only be administered subcutaneously.
• Hypoglycemic action is increased by the concomitant administration of alcohol, β-blockers, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, salicylates, and sulfonylureas.
• Hypoglycemic action is decreased by thyroid hormones, corticosteroids, dobutamine, epinephrine, furosemide, and phenytoin.
Anesthetic considerations: Blood glucose levels of 120 to 180 mg/dL should be sought, and blood glucose should be monitored frequently intraoperatively. If it is necessary to administer insulin intraoperatively, continuous intravenous infusion may be the best method. If it is administered subcutaneously, variability of skin blood flow during anesthesia may cause unpredictable results.
Ipratropium bromide (atrovent)
Indications: Treatment and prevention of bronchospasm resulting from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), including emphysema and chronic bronchitis
Dose: Metered-dose inhaler in adults: two to four sprays (initially, 18 mcg/spray); then two sprays every 4 hours (maximum dose: 216 mcg or 12 sprays/day).
Onset and duration: Onset: within 15 to 30 minutes. Peak effect: 1 to 2 hours. Duration: 4 to 5 hours
Adverse effects: Local or systemic anticholinergic effects, angina, blurred vision, headache, dizziness
Precautions and contraindications: Use ipratropium cautiously for patients with narrow-angle glaucoma, bladder obstruction, and benign prostatic hypertrophy. It is contraindicated in patients hypersensitive to soya lecithin or related food products such as soybean and peanut, as well as in patients hypersensitive to ipratropium bromide, atropine, and its derivatives.
Isoflurane (forane)
Dose: Titrate to effect for induction or maintenance of anesthesia. Minimum alveolar concentration: 1.14%.
Onset and duration: Onset: a few minutes, dose dependent. Duration: emergence time: 15 to 20 minutes.
Adverse effects: Hypotension, tachycardia, arrhythmia, respiratory depression, respiratory irritation, apnea, dizziness, euphoria, increased cerebral blood flow and intracranial pressure, nausea and vomiting, malignant hyperthermia, glucose elevation
Precautions and contraindications: Isoflurane is contraindicated in patients with known or suspected genetic susceptibility to malignant hyperthermia. Changes in mental function may persist beyond the period of anesthetic administration and the immediate postoperative period.
Anesthetic considerations: Anesthetic requirements decrease with age. It crosses the placental barrier. Abrupt onset of malignant hyperthermia may be triggered by isoflurane; early signs include muscle rigidity, especially of the jaw muscles, tachycardia, and tachypnea unresponsive to increased depth of anesthesia.
Isoproterenol HCL (isuprel)
• For mild or transient episodes of heart block that do not require electric shock or pacemaker therapy
• For serious episodes of heart block and Adams-Stokes attacks (except when caused by ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation)
• For use in cardiac arrest until electric shock or pacemaker therapy, the treatments of choice, is available
• For bronchospasm occurring during anesthesia
• As an adjunct to fluid and electrolyte replacement therapy and the use of other drugs and procedures in the treatment of hypovolemic and septic shock, low cardiac output (hypoperfusion) states, congestive heart failure, and cardiogenic shock
Dose: Intramuscular or subcutaneous: 0.2 mg; intravenous: 0.02 to 0.06 mg; infusion: 2 to 20 mcg/min.
Adverse effects: Tachyarrhythmias, hypertension, angina, paradoxical precipitation of Adams-Stokes attacks, pulmonary edema, headache, dizziness, tremors, nausea and vomiting, anorexia; possible exacerbation of ischemia or hypertension (when used for chronotropic support)
Ketamine HCL (ketalar)
Indications: Sole anesthetic agent for diagnostic and surgical procedures of short duration; induction of anesthesia in critically ill patients; small doses for outpatient analgesia
Dose: Induction: adult: intravenous: 1 to 4.5 mg/kg slowly over 60 seconds; intramuscular: 4 to 6 mg/kg; oral: 6 to 8 mg/kg. Half of the initial dose may be repeated as needed.
Onset and duration: Onset: intravenous: 2 to 5 minutes; intramuscular: 3 to 8 minutes; oral: 15 to 20 minutes. Duration: intravenous: 5 to 10 minutes; intramuscular: 12 to 25 minutes; oral: 30 to 60 minutes.
Adverse effects: Hypertension, tachycardia, arrhythmias, apnea with rapid administration, laryngospasm, tonic or clonic movements, emergence delirium, hypersalivation, nausea and vomiting, diplopia, nystagmus, slight elevation in intraocular tension, serious emergence reactions
Precautions and contraindications: Ketamine is contraindicated in hypertension, coronary heart disease or increased intracranial pressure, history of cerebrovascular accident, increased intraocular pressure, and psychiatric disorders. It is contraindicated for surgery or diagnostic procedures of the pharynx, larynx, and bronchial tree. Use it cautiously in patients with convulsive disorders.
Anesthetic considerations: Do not mix ketamine with barbiturates in the same syringe. Emergence reactions are common in adults with high doses and are reduced by medication with a benzodiazepine. Catecholamine-depleted patients may respond to ketamine with unexpected reductions in blood pressure and cardiac output.
Ketorolac tromethamine (toradol)
Indications: Short-term (less than 5 days) management of moderately severe, acute pain that requires analgesia; generally used in a postoperative setting
Dose: Intramuscular (administer slowly and deeply into the muscle): patients younger than 65 years: one dose of 60 mg; patients older than 65 years, renally impaired, or weighing less than 50 kg: one dose of 30 mg
Onset and duration: Onset: intravenous or intramuscular: 15 to 30 minutes. Peak effect: 1 to 2 hours. Duration: 4 to 6 hours.
Adverse effects: Gastrointestinal: peptic ulcers, gastrointestinal bleeding, or perforation; renal toxicity; risk of bleeding: inhibition of platelet function; hypersensitivity
Precautions and contraindications: Fluid retention, edema, retention of sodium, oliguria, and elevations of serum urea nitrogen and creatinine have been reported. Therefore, ketorolac should be used only with caution in patients with cardiac decompensation, hypertension, or similar conditions. Ketorolac is contraindicated in patients with active peptic ulcer disease or recent gastrointestinal bleeding or perforation and in patients with a history of peptic ulcer disease or gastrointestinal bleeding. Ketorolac is also contraindicated in patients with advanced renal impairment and in patients at risk for renal failure owing to volume depletion. It is contraindicated in patients with suspected or confirmed cerebrovascular bleeding, hemorrhagic diathesis, and incomplete hemostasis and those with a high risk of bleeding. It is contraindicated as a prophylactic analgesic before any major surgery and is contraindicated intraoperatively when hemostasis is critical. Ketorolac is also contraindicated in patients with previously demonstrated hypersensitivity to ketorolac tromethamine or allergic manifestations to aspirin (ASA) or other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). It is contraindicated for patients currently receiving ASA or NSAIDs because of the cumulative risk of inducing serious NSAID-related side effects. Ketorolac is contraindicated for intrathecal or epidural administration owing to its alcohol content. It is contraindicated in labor and delivery because it may adversely affect fetal circulation and inhibit uterine contractions. Because of the potential adverse effects of prostaglandin-inhibiting drugs on neonates, ketorolac is contraindicated in nursing mothers.
Anesthetic considerations: Do not use ketorolac as prophylactic analgesia before any major surgery or intraoperatively when hemostasis is critical; in patients with suspected or confirmed cerebrovascular bleeding, hemorrhagic diathesis, incomplete hemostasis, and at high risk of bleeding; in patients currently receiving ASA or NSAIDs; for epidural or intrathecal administration; or concomitantly with probenecid.
The use of ketorolac is not recommended in children.
Ketorolac reduced the diuretic response to furosemide in normovolemic healthy subjects by approximately 20%. Hypovolemia should be corrected before treatment with ketorolac is initiated. Ketorolac possesses no sedative or anxiolytic properties. The concomitant use with opiate-agonist analgesics can result in reduced opiate analgesic requirements. Ketorolac is highly bound to human plasma protein (99.2%).
Labetalol (normodyne, trandate)
Dose: Intravenous bolus: 0.15 to 0.25 mg/kg administered over 2 minutes; may repeat every 5 minutes up to 300 mg. Continuous infusion: 2 mg/min; titrate to effect. Oral: 100 mg twice daily alone or with diuretic; may increase to 200 mg twice daily after 2 days; further dose increase may be made every 1 to 3 days to maximal response. Maintenance dose: 200 to 400 mg twice daily.
Onset and duration: Onset: intravenous: 1 to 3 minutes; oral: 20 to 40 minutes. Duration: intravenous: 0.25 to 2 hours; oral: 4 to 12 hours.
Adverse effects: Hypotension, bradycardia, ventricular arrhythmias, congestive heart failure, chest pain, bronchospasm, headache, diarrhea
Precautions and contraindications: Use labetalol cautiously in patients with chronic bronchitis, emphysema, preexisting peripheral vascular disease, pheochromocytoma, and diabetes. It is contraindicated in bronchial asthma, overt heart failure, greater than first-degree heart block, and hepatic failure.