8 Doppler Imaging
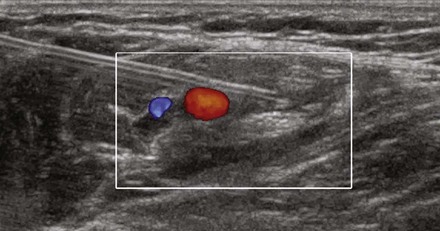
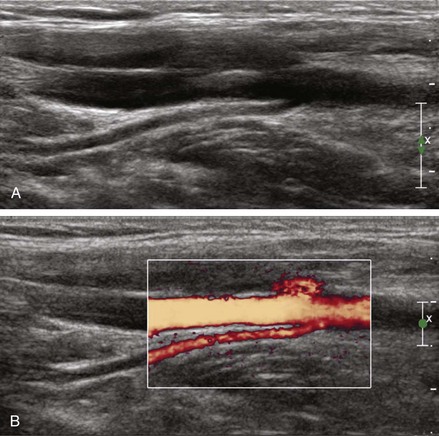
The Doppler shift is the change in frequency of sound when the sound wave strikes a moving object. This means the frequency of the transmitted and reflected sound waves is not the same. Doppler shifts in clinical imaging are in the audible range (±10 KHz). Red blood cells are the primary reflectors that produce Doppler shifts. Ultrasound machines can color-encode the mean velocity (color Doppler), variance within the sample volume (variance Doppler), and power spectrum of the frequency shift (power Doppler).1
Clinical Pearls
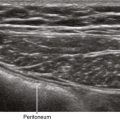
• Blood has a low ultrasound attenuation coefficient. Red blood cells are the primary reflectors within blood.
• In power Doppler, the gain threshold can be adjusted to the level at which there is no observed signal in bone.2
• In low-flow states (e.g., heart failure or atrial arrhythmias), aggregates of red blood cells can cause spontaneous contrast within blood vessels.