Disorders of Cornification (Ichthyosis)
Catherine C. Foley, Amy S. Paller, Alan D. Irvine
Introduction
The term ‘inherited disorders of cornification’ covers a wide range of genetic conditions with molecular defects that preclude the formation of a normal epidermis. The term is usually considered to include entities divided on morphological grounds into ichthyoses, follicular keratoses, and palmoplantar keratodermas. In addition, many inherited disorders usually considered as ectodermal dysplasias have significant defects in epidermal development or differentiation. Several ichthyotic conditions first manifest in the neonatal period, usually as either collodion baby or scaling erythroderma, or more rarely as a harlequin fetus. In some situations, such as harlequin ichthyosis or Netherton syndrome, associated complications are life-threatening. For most of these conditions, therapy during the neonatal and early infantile periods is supportive (Box 19.1), involving frequent application of bland emollients and monitoring for evidence of infection or fluid and electrolyte imbalance. The use of topical medications with keratolytic agents neonatally and during the first 6 months of life is usually unnecessary and risks significant absorption of potentially toxic substances (e.g., lactic acid, salicylic acid).
General principles of care for affected infants over 6 months of age include prevention of water loss, emolliating and softening of the stratum corneum. This can be achieved with short, 5 minute baths twice daily, and regular application of emollients. Keratolytic agents, such as urea, lactic acid or salicylic acid compounded with emollients, may be used to remove hyperkeratotic scales. These are not always well tolerated in younger children. Topical corticosteroids may be used for concomitant inflammation, however systemic absorption may be increased in patients with poorly formed cornified layers. Antibacterial washes or bleach baths are beneficial in patients with thick scale, who are at increased risk of cutaneous infection, especially from Staphylococcus and dermatophytes. In patients with suspected dermatophyte infection, skin scrapings should be taken for confirmation prior to local or systemic treatment with antifungal agents. Affected individuals may have impaired sweating due to occlusion of eccrine ducts and care should be taken to avoid overheating. Consider vitamin D3 supplementation in affected children as they may be at increased risk of developing rickets, due to a reluctance to expose their skin to sunlight.
In the past 15 years, the molecular bases of the great majority of these disorders have been elucidated, thereby laying the groundwork for confirmatory molecular diagnosis and opening up the possibility of genotype–phenotype correlation and DNA-based prenatal diagnosis for several of the devastating forms of ichthyosis. An international consensus for the classification of inherited ichthyosis was published in 2010.1 Tables 19.1 and 19.2 summarize relevant conditions based on this consensus classification. At present, molecular diagnosis is not available for all forms of ichthyosis and therapy is not yet gene-based. In addition, access to genetic diagnostics is costly and varies from country to country and among different health insurance providers. A wonderful support group is available for all families with a disorder of cornification, the Foundation for Ichthyosis and Related Skin Types (FIRST; www.firstskinfoundation.org).
TABLE 19.1
Inherited ichthyoses – syndromic
| Disorder | Previous name | MIM # | Inh | Cutaneous findings | Extracutaneous findings | Gene defect(s) | Protein(s) | Class of protein/ function |
| X-linked ichthyosis syndromes | ||||||||
| RXLI (recessive X-linked ichthyosis) syndromic presentation | 308100 | XR | Large, dark scales Sparing of body folds |
Prolongation of labor Cryptorchidism Corneal opacities, asymptomatic |
STS Larger deletions with contiguous gene defects |
Steroid sulfatase | Enzyme | |
| IFAP syndrome (ichthyosis-follicularis-atrichia-photophobia) | 398205 | XR | Spiny follicular ichthyosis Nail dystrophy Alopecia |
Photophobia Psychomotor delay Short stature |
MBTPS2 | Membrane-bound transcription factor peptidase, site 2 | Enzyme | |
| Conradi–Hünermann–Happle syndrome (CDPX2) | X-linked chondro-dysplasia punctata (Conradi–Hünermann syndrome) | 302960 | XD | Striated ichthyosiform hyperkeratosis Follicular atrophoderma Alopecia |
Cataracts Frontal bossing Short proximal limbs |
EBP | Emopamil-binding protein | Enzyme involved in cholesterol biosynthesis |
| CHILD syndrome | 308050 | XD | Unilateral ichthyosiform erythroderma | Chondrodysplasia punctata Cataracts Limb reduction defects Asymmetric organ hypoplasia |
NSDHL | 3-β-hydroxysteroid-Δ8,Δ7-isomerase | Enzyme involved in cholesterol biosynthesis | |
| Autosomal ichthyosis syndromes with prominent hair abnormalities | ||||||||
| NS (Netherton syndrome) | 256500 | AR | Erythroderma in infancy Ichthyosis linearis circumflexa Alopecia |
Atopic diathesis Food allergies Structural hair defects (trichorrhexis invaginata) Growth delay |
SPINK5 | LETKI | Serine protease inhibitor | |
| IHS (ichthyosis hypotrichosis syndrome) | 610765 | AR | Adherent plate-like scale Hypohidrosis Hypotrichosis |
Photophobia Pingueculum |
ST14 | Serine protease 14 | Enzyme | |
| IHSC syndrome (ichthyosis-hypotrichosis-sclerosing cholangitis) | 607626 | AR | Fine thin scale Hypotrichosis with coarse thick hair |
Sclerosing cholangitis Congenital paucity of bile ducts |
CLDN1 | Claudin 1 | Membrane protein involved in tight junctions | |
| TTD (trichothiodystrophy) | 601675 | AR | May have collodion membrane Can vary from mild scaling to marked adherent plaques |
Photosensitivity Brittle hair with ‘tiger tail’ pattern Decreased fertility Short stature Susceptibility to infection |
ERCC2, XPD ERCC3, XPB GTF2H5, TTDA | Xeropigmentosum group D protein Xeropigmentosum group B protein |
DNA repair enzymes also involved in regulation of transcription | |
| TTD (not associated with congenital ichthyosis) | 234050 | AR | Delayed onset Fine scale |
Non-photosensitive Brittle hair Short stature Decreased fertility |
C7Orf11, (TTDN1) | M-phase-specific PLK1-interacting protein, (TTD non-photosensitive 1 protein) |
Protein function not fully characterized | |
| Autosomal ichthyosis syndromes with fatal disease course | ||||||||
| Gaucher syndrome, type 2 | 230900 | AR | Collodion baby, mild scaling later | Hepatosplenomegaly retroflexion of the head, strabismus, dysphagia, choking spells, hypertonicity Death usually occurs in the first year |
GBA | Acid β-glucosidase | Enzyme | |
| Multiple sulfatase deficiency | 272200 | AR | Mild scale | Mental retardation Mucopolysaccharidosis Metachromatic leukodystrophy Death within first year of life |
SUMF1 | Sulfatase-modifying factor-1 | Modifier of sulfatase enzyme activity | |
| CEDNIK syndrome (cerebral dysgenesis-neuropathy-ichthyosis-palmoplantar keratoderma) | 609528 | AR | Coarse plate-like white scale Fine, sparse hair |
Sensorineural deafness Cerebral dysgenesis Neuropathy Microcephaly Neurogenic muscle atrophy Optic nerve atrophy Cachexia Lethal within first decade |
SNAP29 | Synaptosomal-associated protein, 29kDA | Membrane trafficking | |
| ARC syndrome (arthrogryposis-renal dysfunction-cholestasis) | 208085 | AR | Fine scale | Arthrogryposis Intrahepatic bile duct hypoplasia with cholestasis Renal tubular degeneration Metabolic acidosis Abnormal platelet function Death within first year of life |
VPS33B | Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 33B | Sorting intracellular molecules | |
| Autosomal ichthyosis syndromes with other associated signs | ||||||||
| SLS (Sjögren–Larsson syndrome) | 270200 | AR | Fine lamellar scale | Di- or tetraplegia Retinal glistening white dots |
ALDH3A2 | Long-chain-aldehyde dehydrogenase | Enzyme | |
| RS (Refsum syndrome) (HMSN4: hereditary motor sensory neuropathy type 4) | Refsum disease | 266500 | AR | Late onset, fine scale | Retinitis pigmentosa Cardiac failure |
PAHX or PHYH PEX7 |
Phytanoyl-CoA hydroxylase Peroxin-7 |
Enzymes involved in phytanic acid metabolism |
| KID syndrome (keratitis–ichthyosis–deafness syndrome) |
KID; includes HID syndrome | 242150 602540 |
AD | Verrucous plaques Stippled pattern of keratoderma |
Keratitis Sensorineural deafness |
GJB2 (GJB6) | Connexin 26 | Gap junction protein |
| Neutral lipid storage disease with ichthyosis | Chanarin–Dorfman syndrome (also termed NCIE2) | 275630 | AR | Fine scales with occasional background erythema | Myopathy Hepatosplenomegaly |
ABHD5 | CGI-58 | Enzyme, a member of the esterase/lipase/thioesterase subfamily |
| IPS (ichthyosis prematurity syndrome) |
608649 | AR | White caseous scale, attenuated on scalp and eyebrows Follicular keratosis |
Atopic manifestations | SLC27A4 | Long-chain fatty acid transport protein 4 | Transport and activation of fatty acids | |
| CHIME syndrome | 280000 | AR | Ichthyotic erythema Occasionally migratory plaques |
Colobomas Conductive hearing loss Mental retardation |
NK | NK | NK | |
| MEDNIK syndrome (mental retardation-enteropathy-deafness-neuropathy-ichthyosis-keratodermia) | Not on OMIM | AR | Rough, thickened skin | Congenital sensorineural deafness Psychomotor and growth retardation Chronic diarrhea |
AP1S1 | Adapter-related protein complex 1 sigma-1A subunit | Endocytosis and Golgi processing | |
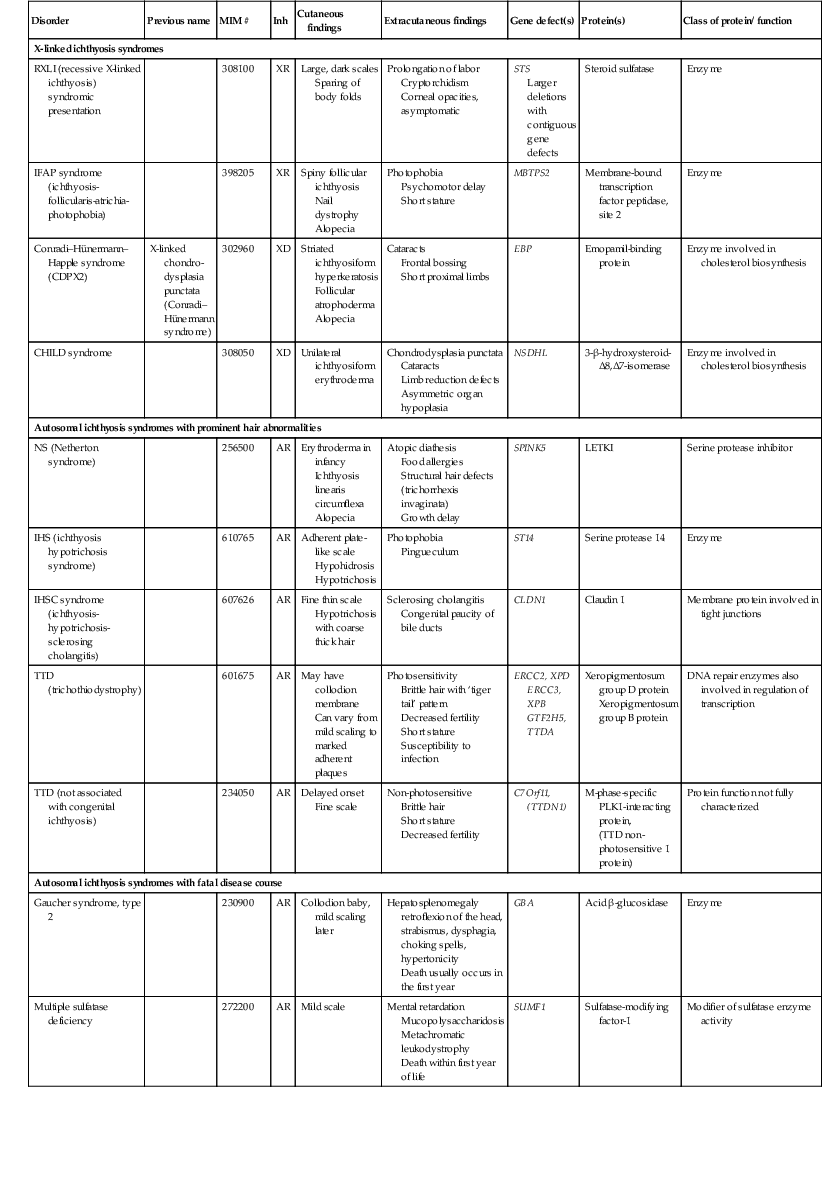
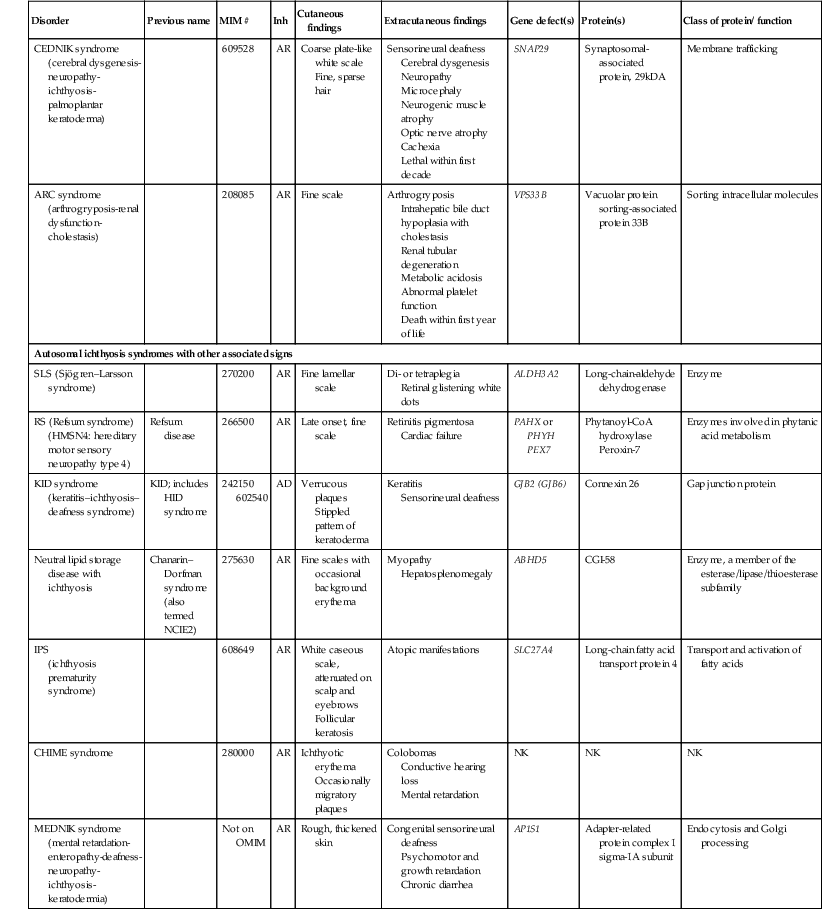
Table 19.2
Inherited ichthyoses – non-syndromic
| Disorder | Previous name | MIM # | Inh | Cutaneous findings | Extracutaneous findings | Gene defect(s) | Protein(s) | Class of protein/ function |
| Common ichthyoses | ||||||||
| IV (ichthyosis vulgaris) | 146700 | AD (autosomal semidominant) | Fine, white scale Accentuated palmoplantar markings |
Strong association with atopic manifestations | FLG | Filaggrin | Structural component of stratum corneum | |
| RXLI (recessive X-linked ichthyosis) (non-syndromic presentation) | 308100 | XR | Large, dark scales Sparing of body folds |
Prolongation of labor Cryptorchidism Corneal opacities, asymptomatic |
STS | Steroid sulfatase | Enzyme | |
| Autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis (ARCI) | ||||||||
| MAJOR TYPES | ||||||||
| HI (harlequin ichthyosis) | 242500 | AR | Rigid plates Severe erythema Hypohidrosis Scarring alopecia |
Ectropion Eclabion Contractures Failure to thrive Short stature |
ABCA12 | ATP-binding cassette, subfamily a, member 12 | ABC transporter | |
| LI (lamellar ichthyosis) | 242300 601277 604777 |
AR | Large adherent plates Hypohidrosis |
Ectropion Eclabium Short stature if severe |
TGM1, ABCA12, PNPLA1, LIPN |
Transglutaminase 1, ABCA12 transporter, PNPLA1, Lipase N | Enzyme involved in crosslinking of stratum corneum ABC lipid transporter Glycerophospholipid synthesis or remodeling |
|
| CIE (congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma) | 242100 | AR | Fine white scales Background erythema Hypohidrosis Mild PPK White nails |
Failure to thrive Short stature if severe Occasional neurologic |
TGM1, ALOX12B, ALOXE3, ABCA12, CYP4F22, NIPAL4 |
Transglutaminase 1, Arachidonate lipoxygenases, cytochrome P450 enzyme, ichthyin, ABCA12 transporter |
Cornified envelope crosslinking Lipoxygenase/hepoxilin pathway Lipid transporter |
|
| MINOR VARIANTS | ||||||||
| SHCB (self-healing collodion baby) | 242300 | AR | Collodion baby at birth, not subsequent ichthyotic phenotype | None | TGM1, ALOX12B, ALOXE3 | Keratinocyte transglutaminase 1 | Enzyme involved in crosslinking of stratum corneum | |
| Acral SHCB (self-healing collodion baby) | 242300 | AR | Acral collodion membranes that heal | None | TGM1 | Transglutaminase 1 | Cornified envelope crosslinking | |
| BSI (bathing suit ichthyosis) | 242300 | AR | Collodion membrane at birth, extremities heal | None | TGM1 | Transglutaminase 1 | Cornified envelope crosslinking | |
| Keratinopathic ichthyosis (KPI) | ||||||||
| MAJOR TYPES | ||||||||
| EI (epidermolytic ichthyosis) | BCIE/EH | 113800 | AD, rarely AR | Widespread skin blistering in neonates Warty hyperkeratosis |
Growth failure if severe | KRT1, KRT10 | Keratins 1 and 10 | Cytoskeleton structural protein |
| SEI (superficial EI) | Ichthyosis bullosa of Siemens | 146800 | AD | Mild flexural hyperkeratosis Adherent fine scale Pruritus |
None | KRT2E | Keratin 2 | Cytoskeleton structural protein in suprabasal layer |
| MINOR VARIANTS | ||||||||
| AEI (annular epidermolytic ichthyosis) | 607602 | AD | Intermittent annular, polycyclic erythematous scaly plaques | KRT1, KRT10 | Keratins 1 and 10 | Cytoskeleton structural protein | ||
| ICM (ichthyosis Curth–Macklin) | Ichthyosis hystrix | 146590 146600 |
AD | Spiky hyperkeratosis | None | KRT1 | Keratin 1 | Cytoskeleton structural protein |
| Epidermolytic epidermal nevi | Not in OMIM | Somatic mutations | KRT1, KRT10 | Keratins 1 and 10 | Cytoskeleton structural protein | |||
| Other forms | ||||||||
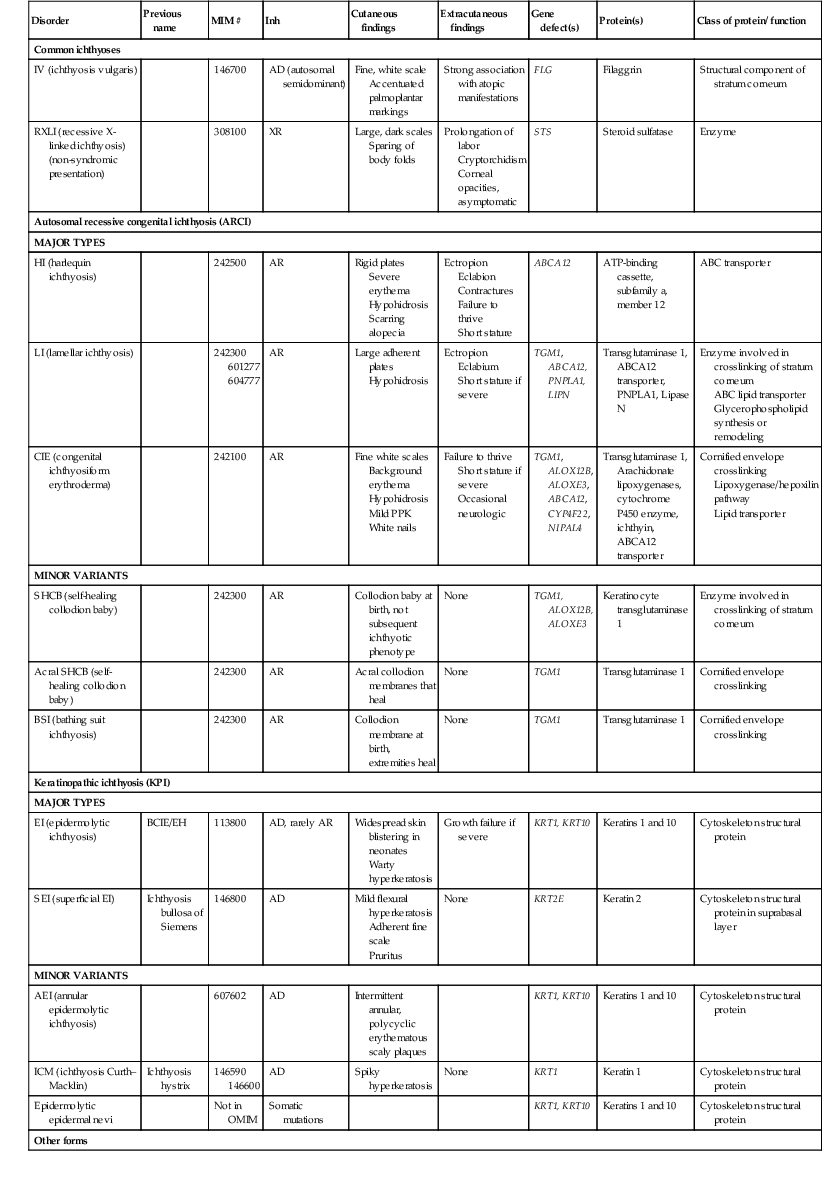
| LK (loricrin keratoderma) | 604117 | AD | Collodion baby Mild, fine, white scale Diffuse PPK |
None | LOR | Loricrin | Abnormal intranuclear granules | |
| EKV (erythrokeratoderma variabilis) | 133200 | AD | Transient, migratory erythematous patches Hyperkeratosis Diffuse PPK |
None | GJB3, GJB4 | Connexins 31, 30.3 | Gap junction proteins | |
| PSD (peeling skin disease) | 270300 | AR | None | CDSN, TGM5 | Corneodesmin, Transglutaminase 5 |
Corneocyte adhesion Epidermal crosslinking |
||
| CRIE (congenital reticular ichthyosiform erythroderma) | 609165 | AD (isolated cases) | None | KRT10 | Keratin | Structural protein | ||
| KLICK (keratosis linearis-ichthyosis congenita-keratoderma) | Not in OMIM | AR | Linear keratoses in skin folds Sclerosing PPK |
None | POMP | Proteasome maturation protein | Molecular chaperone | |
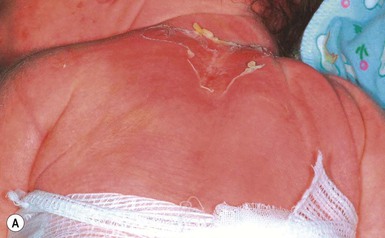
Collodion baby
Cutaneous features
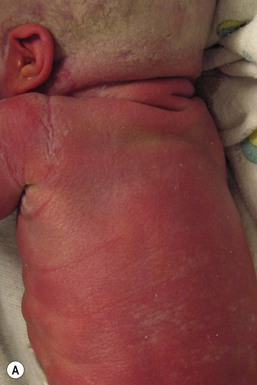
Collodion babies are encased at birth in thickened, shiny, variably erythematous skin that resembles cellophane (Fig. 19.1). The collodion baby (Figs 19.1, 19.2) is the phenotype at birth of several ichthyotic disorders, but variable severities of autosomal recessive congenital ichthyoses (ARCI, non-syndromic) are the eventual phenotype in most patients.2 Others (syndromic forms) include Sjögren–Larsson syndrome, Conradi–Hünermann syndrome, trichothiodystrophy, and neonatal Gaucher disease.3 In 5–6% of collodion babies, normal-appearing skin replaces the collodion membrane, and these babies have the mildest form of ARCI, termed spontaneously healing, self-healing, or self-improving collodion baby.4
Extracutaneous features
Despite the thickening of the stratum corneum, the collodion membrane is actually a poor barrier, which can result in excessive transcutaneous fluid and electrolyte loss with resultant hypernatremic dehydration,5,6 increased metabolic requirements, and temperature instability owing to increased evaporative cooling. Collodion babies are often premature, and the combined skin disorder and prematurity further increase the risk of complications. In addition, numerous cutaneous fissures may be present which, together with the poor skin barrier, increase the risk of the skin being a site of entry for bacteria and subsequent sepsis. Infection may also be difficult to diagnose owing to the intrinsic temperature instability and fluid imbalances associated with the underlying skin condition. Aspiration of squamous material in the amniotic fluid may lead to neonatal pneumonia.7 In addition, the thickening of the skin may restrict movement, making sucking, eye closure, and rarely respiration, difficult.
Etiology and pathogenesis
The underlying basis for collodion babies is varied, reflecting the different forms of ichthyosis that present as collodion babies, and these are discussed below. The most common cause is mutations in transglutaminase 1 (TGM1). The self-healing collodion baby phenotype was first shown to be due to mutations in TGM1.8 In two affected siblings, increased hydrostatic pressure significantly reduced the activity of the mutant enzyme, suggesting that this pressure both traps water molecules and locks the mutated enzyme in an inactive trans conformation in utero. After birth, these water molecules are removed and the enzyme is predicted to isomerize back to a partially active cis form, explaining the dramatic improvement of this skin condition.8
Subsequent publications have shown that the ‘self-healing’ variant can reflect underlying mutations in ALOX12B or ALOXE3, in addition to TGM1.9
Differential diagnosis
Several conditions can result in the collodion baby phenotype (Box 19.2). Occasionally, severe cases can be confused with harlequin ichthyosis.
Treatment and care
Collodion babies should be placed in high-humidity environments to increase hydration, and bland emollients should be applied (see Box 19.1). Electrolytes should be monitored,5 as should fluid intake and output. The membrane usually sloughs during the first month of life (Fig. 19.2). The use of topical keratolytic agents should be avoided in view of the increased potential for toxicity resulting from absorption through the compromised permeability barrier.5
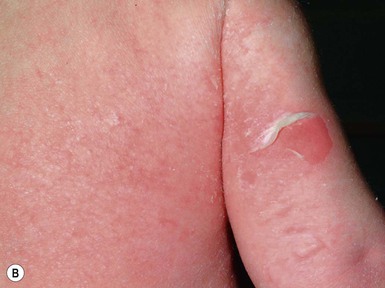
Ichthyosis vulgaris
Cutaneous features
Ichthyosis vulgaris is one of the most common genetic disorders of skin, occurring in approximately 1 in 250 individuals, based on a survey of healthy English schoolchildren.10 In contrast to other forms of ichthyosis, ichthyosis vulgaris does not manifest during the neonatal period. The condition usually appears after 3 months of age as fine, light-colored scales that are larger and coarser on the lower extremities. Palmoplantar markings are accentuated (hyperlinearity).
Extracutaneous features
There is an association in some cases with atopic asthma and rhinitis in later life, and ichthyosis vulgaris is associated with a strong risk for atopic dermatitis.
Etiology and pathogenesis
Mutations in the filaggrin gene (FLG) have now clearly been shown to underlie ichthyosis vulgaris, leading to decreased to absent expression of filaggrin.11 These mutations are semidominant; heterozygotes exhibit a very mild phenotype with incomplete penetrance, whereas homozygotes or compound heterozygotes show much more severe disease. The mutations show a combined allele frequency of ~4% in Caucasian populations, explaining the high incidence of ichthyosis vulgaris. FLG gene mutations are now well established as the highest genetic risk for atopic dermatitis.
Differential diagnosis
In affected boys, ichthyosis vulgaris in the young infant may need to be distinguished from X-linked recessive ichthyosis (see below).
Treatment and care
In the neonatal period no specific care is necessary. Good skin care with regular emollients and the avoidance of irritants such as detergents is advisable, as these infants tend to have lifelong dry skin and a high incidence of atopic dermatitis.10
Recessive X-linked ichthyosis
Cutaneous features
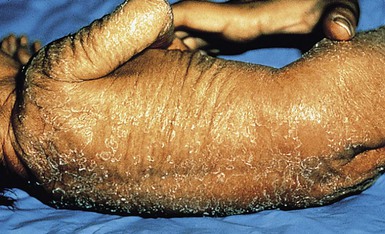
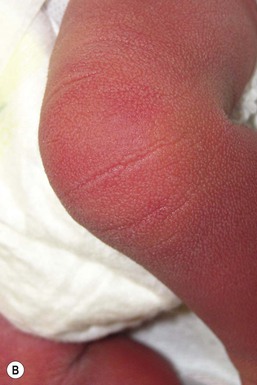
Recessive X-linked ichthyosis (RXLI) is a disorder that affects 1 : 6000–1 : 2000 males. The ichthyosis manifests by 3 months of age in 84% of patients, although only 17% show evidence of exaggerated neonatal desquamation and peeling at birth. Extensor surfaces, the preauricular areas, and the sides of the neck are most severely affected by the large, dark, adherent scales (Fig. 19.3).
Extracutaneous features
RXLI is regarded as syndromic when accompanied by associated manifestations and non-syndromic when ichthyosis is isolated.1 The absence of steroid sulfatase activity during fetal life also leads to increased fetal production of DHEAS (dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate) and decreased placental estrogen production, which may delay the progression of parturition. Rarely, affected boys have hypogonadism with undescended testes, hypoplasia of the penis and scrotum, and/or failure of normal sexual maturation. The development of testicular cancer has been described in one patient without undescended testes. Approximately 10% of affected boys have a contiguous gene deletion syndrome, a larger deletion which encompasses genes that are contiguous with the steroid sulfatase gene on the terminal short arm of the X chromosome. Deletion of surrounding genes results in mental retardation, hypogonadism, and anosmia (Kallmann syndrome), or a bone dysplasia characterized radiographically by stippled epiphyses (X-linked recessive chondrodysplasia punctata).
Etiology and pathogenesis
X-linked ichthyosis results from mutations of the STS gene encoding steroid sulfatase (arylsulfatase C), particularly deletions (90% of patients). In a study assessing the clinical and molecular features in 28 patients with Kallmann syndrome 1, submicroscopic deletions were found at Xp22.3 in four contiguous genes, VCXA, STS, KAL1, and OA1.12
Differential diagnosis
Recessive X-linked ichthyosis (RXLI) in the neonate is not associated with collodion membrane and is therefore distinguishable from other ichthyotic disorders associated with collodion membranes and early skin thickening. Ichthyosis vulgaris is an important differential diagnosis in older male infants and can be distinguished by fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) and other genetic analyses. Patients with RXLI, who additionally have a concomitant FLG mutation, have a more severe manifestation of their RXLI. Babies with the rare autosomal recessive disorder, multiple sulfatase deficiency, show scaling typical of RXLI and decreased steroid sulfatase due to a global deficiency of sulfatases. Affected patients also show neurologic abnormalities characteristic of metachromatic leukodystrophy, and features of storage diseases because of the deficiency of several additional sulfatases.
Treatment and care
In the neonatal period, no specific care is necessary, but patients will generally need lifelong skin care advice and appropriate emollients. RXLI may be detected prenatally. The most common scenario for this is in pregnancies not known to be at risk with an abnormal ‘triple screen’ test that detects decreased maternal estriol levels. RXLI may then be confirmed by FISH, STS (steroid sulfatase), and DHEAS for deletions and/or the demonstration of decreased placental sulfatase activity in amniotic fluid cells and increased DHEAS levels in amniotic fluid.
Inherited syndromic ichthyoses – X-linked
Ichthyosis follicularis, alopecia, and photophobia (IFAP syndrome)
Cutaneous features
Patients are born with thickening of the skin, including the palms and soles, with generalized prominent follicular keratoses and mild erythema.13,14 The clinical findings have been described as a ‘nutmeg grater’.15 The scalp is hairless, and severe photophobia is noted from birth. The nails may be dystrophic, and follicular pustules may be present. Biopsies show a hyperkeratotic stratum corneum with a thinned dermis. The hair follicles are atrophic and shortened, with abnormal localization of the bulbs to the deep portion of the dermis, rather than a subcutaneous location. There are no normal hair shafts, and sebaceous glands are absent. It is possible that at least two other forms exist in addition to this classic form.16,17
Etiology and pathogenesis
IFAP syndrome is an X-linked disorder caused by functional deficiency of membrane-bound transcription factor protease, site 2 (MBTPS2).20 This results in disturbed differentiation of epidermal structures evoking the triad of ichthyosis follicularis, atrichia and photophobia.20 Female carriers may have linear involvement.21 An autosomal recessive form has also been described.
Differential diagnosis
The constellation of clinical signs should make the diagnosis apparent.
Treatment and care
Systemic retinoids have been used in children as young as 3 years, with reported improvement.22
Conradi–hünermann–happle syndrome (X-linked chondrodysplasia punctata)
Cutaneous features
Most cases of chondrodysplasia punctata are the X-linked dominant Conradi–Hünermann–Happle form. Affected neonates are usually female, because the disorder is considered lethal to male fetuses. However, Conradi syndrome has been described in a few male patients with and without Klinefelter syndrome.23 At birth, patients most commonly have patterned erythroderma with overlying thin to thick psoriasiform scale (Fig. 19.4). In severe cases, generalized ichthyosiform erythroderma with thick scale is seen at birth,24 and later shows typical patterning along Blaschko’s lines with scale desquamation. Involvement may be predominantly unilateral. With advancing age the ichthyosiform erythroderma and stippling improve, leaving finer scaling without underlying erythema and follicular atrophoderma. Cicatricial alopecia occurs as scalp scaling resolves. Psychotropism may be seen (see ‘CHILD syndrome’, below).
Extracutaneous features
Extracutaneous features include limb reduction, typically asymmetric, and facies with frontal bossing, saddle nose, and malar hypoplasia. Asymmetric, focal stippled calcifications of the epiphyseal regions are common in childhood but typically disappear in adulthood. Bone defects normally begin soon after birth and during childhood as punctate calcifications, as a result of abnormal calcium deposition during endochondral bone formation. They typically appear in the epiphyses of the long bones, but may also develop in the scapulae, clavicles, sternum, ribs, and spinal column. These lesions usually disappear during adulthood.25
Cataracts usually develop later during childhood, but may be present at birth.23
Etiology and pathogenesis
The underlying molecular basis is mutations in emopamil binding protein (3β-hydroxysteroid-Δ8, Δ7-isomerase), which is involved in cholesterol synthesis (see below).26 Chondrodysplasia punctata can be inherited in both autosomal and X-linked fashion, and may also be the result of an environmental insult, particularly fetal exposure to warfarin.24
Differential diagnosis
The differential diagnosis usually includes two other forms of chondrodysplasia punctata: autosomal recessive rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata,24 and X-linked recessive chondrodysplasia punctata with steroid sulfatase deficiency.27 The rhizomelic form is also associated with multiple peroxisomal defects. The ichthyosis occurs in approximately one-third of patients and is poorly described. Affected patients have developmental retardation and tend to die as infants. The X-linked recessive form of chondrodysplasia punctata occurs as a contiguous gene deletion syndrome of Xp, not at the site of Conradi syndrome. The ichthyosis is consistent with recessive X-linked ichthyosis, but stippled epiphyses are associated. Affected infants are deficient in steroid sulfatase activity, and have no peroxisome defects.
Treatment and care
There is no specific care for the neonate with Conradi syndrome.
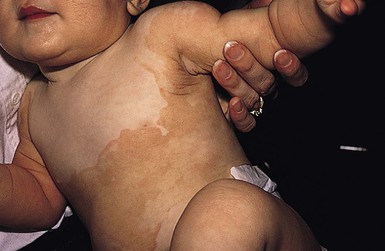
CHILD syndrome
Cutaneous features
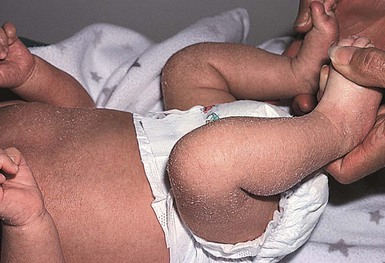
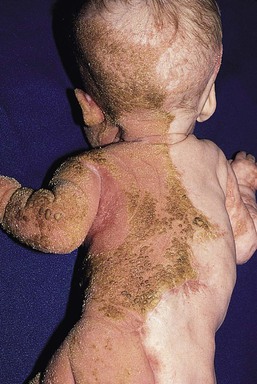
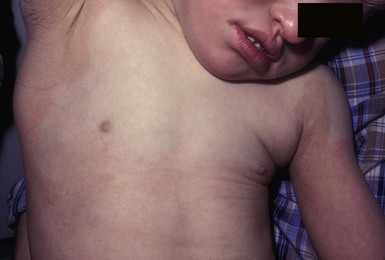
The term ‘CHILD syndrome’ is an acronym for ‘congenital hemidysplasia with ichthyosiform nevus and limb defects’. The condition occurs almost exclusively in girls, and is presumed to be lethal in affected males. The only case in a boy is thought to represent early postzygotic mosaicism.28 The inflammatory ichthyosiform skin lesion of CHILD syndrome may be present at birth or develop during the first few months of life.28,29 It is characterized by yellow, waxy scaling and is strikingly unilateral, generally with a sharp demarcation at the ventral and dorsal midline regions (Fig. 19.5). Streaks of inflammation and scaling can also follow Blaschko’s lines, with involvement of the apparently unaffected side of the body. Similarly, streaks of normal skin may be interspersed within the area of the CHILD nevus. With increasing age, the skin lesions may improve or clear spontaneously, but thickened erythematous plaques in intertriginous areas tend to persist and be the most severely affected sites (psychotropism).30 The skin lesions of CHILD syndrome nevus can occur without any other abnormalities, but the occurrence of all features of CHILD syndrome in a sibling of a patient with only the CHILD nevus suggests variable expressivity within the spectrum of CHILD syndrome.31
Extracutaneous features
A variable degree of ipsilateral skeletal hypoplasia is an important feature of CHILD syndrome. As with the skin changes, unilaterality is not absolute and slight changes may be present on the contralateral side. Punctate epiphyseal calcifications may be demonstrable by X-ray, but tend to disappear after the first few years of life. Cardiovascular and renal abnormalities are the major visceral problems in CHILD syndrome, although anomalies of other viscera have been described.29
Etiology and pathogenesis
Biopsy of skin lesions shows epidermal acanthosis with marked parakeratosis alternating with orthokeratosis. Basophilic ghost cells of the granular layer are common. The papillary dermis is often filled with histiocytes showing foamy cytoplasm, resulting in the characteristic histopathologic pattern of verrucous xanthoma. Patients with CHILD syndrome have mutations in 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, an enzyme in the cholesterol biosynthetic pathway.32
Differential diagnosis
The nevus of CHILD syndrome needs to be distinguished from inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus and linear psoriasis by the histopathologic features and the constellation of other clinical manifestations, if present. CHILD syndrome shares features with Conradi–Hünermann syndrome (see above), a disorder that results from mutation in another gene within the cholesterol biosynthetic pathway; shared characteristics include the prevalence in girls with a presumed X-linked dominant inheritance pattern, ichthyosiform erythroderma, limb reduction defects, stippled epiphyses, and peroxisomal defects. The unilateral nature of the nevus and limb deformities helps to distinguish these conditions.
Treatment and care
Patients with CHILD syndrome tend to tolerate topical medications poorly, other than bland emollients. However, dramatic improvement has been demonstrated in adults with twice daily application of compounded 2% lovastatin and 2% cholesterol.33 Orthopedic involvement may be needed to manage the limb hypoplasia, including with a prosthesis or even partial amputation. Multisystem care may include cardiology and renal evaluation as needed.
Inherited syndromic ichthyoses with prominent hair signs
Netherton syndrome
Cutaneous features
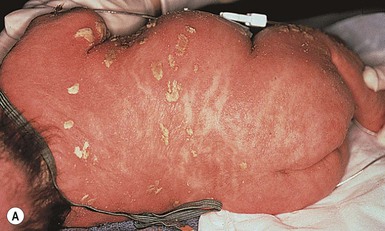
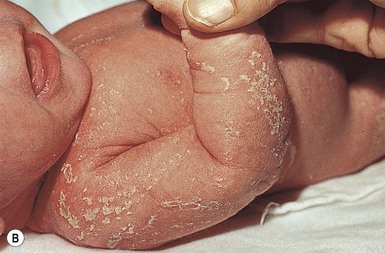
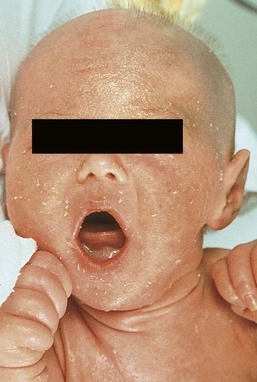
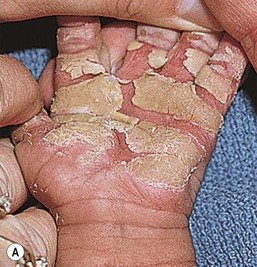
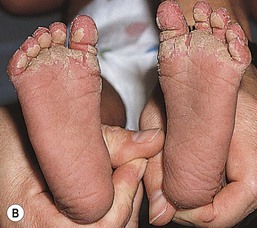
Netherton syndrome should be suspected in the neonate with generalized scaling erythroderma, especially if there is failure to thrive (Fig. 19.6).34 Affected infants are often born prematurely and develop the typical ichthyosiform erythroderma in utero or during the first weeks of life. A collodion baby phenotype is not associated. The classic hair shaft abnormality, trichorrhexis invaginata (‘bamboo hairs’, ‘ball-and-socket deformity’), is thought to result from a defect in keratinization of the internal root sheath. Multiple hairs from different areas should be examined, as only 20–50% of hairs may be affected. Although trichorrhexis invaginata may be present in the neonatal period, delayed and sparse hair growth at this time, as well as the easy breakage of these hairs, makes demonstration of the hair defect in the neonatal period difficult. Ichthyosis linearis circumflexa, the characteristic skin change associated with Netherton syndrome, is usually not seen before 2 years of age, but occurs eventually in 70% of patients. It manifests episodically, often lasting for a few weeks and then clearing for weeks or months. The ichthyosiform erythroderma, however, frequently improves with age. The atopic diathesis becomes problematic in two-thirds of patients, with the development of pruritic atopic dermatitis, multiple food allergies, and often accompanying urticaria, angioedema, asthma, and/or anaphylaxis.
Extracutaneous features
The failure to thrive is often profound, requiring hospitalization for nutritional support and correction of the hypernatremic dehydration that may be associated. Patients may have diarrhea, and occasionally demonstrate villus atrophy if intestinal biopsy is performed. Most patients have increased levels of IgE, but other laboratory and clinical evidence of immune dysfunction may be present as well. The increased risk of sepsis occurs as a result of both the abnormal skin barrier and the associated immune defects that are only in part owing to malnutrition.
Etiology and pathogenesis
The underlying molecular basis for Netherton syndrome is mutations in SPINK5, a serine protease inhibitor.35,36 Lymphoepithelial Kazal-type-related inhibitor (LEKTI), a putative serine protease inhibitor, is strongly expressed in differentiated keratinocytes in normal skin. The lamellar granule system transports and secretes LEKTI earlier than its potential serine protease targets kallikrein 5 and kallikrein 7, thus preventing degradation of desmoglein 1 and premature loss of stratum corneum integrity/cohesion.37,38 Deficiency of LETKI also leads to excessive cleavage of profilaggrin to filaggrin, further affecting differentiation.
Differential diagnosis
Netherton syndrome in the neonatal period must be distinguished from several other disorders with extensive scaling erythroderma, failure to thrive, and increased risk of infection, particularly several immunodeficiency disorders, other ichthyoses, and atopic or psoriasiform erythroderma (see Chapter 18). Skin biopsy sections show subacute or chronic seborrheic or psoriasiform dermatitis with spongiosis.39 The stratum corneum is thin and focally parakeratotic, and the granular layer is reduced. Electron microscopic studies have revealed features in skin biopsy specimens that are specific to Netherton syndrome, particularly the premature secretion of lamellar body contents, foci of electron-dense material separating lipid membranes, and disturbed maturation of lamellar membrane structures. Immunohistochemical staining to LETKI, the protein product of SPINK5, is also possible and with increasing availability will become a highly useful diagnostic investigation,40 but is currently not widely available.
Treatment and care
Treatment of Netherton syndrome is extremely difficult. Despite their pruritic, erythematous skin, patients tend to respond poorly to topical steroids, although some have improved after topical application of calcineurin inhibitors or calcipotriol. The poor cutaneous barrier of patients with Netherton syndrome may result in significant absorption of topically applied agents. For example, high blood levels of tacrolimus have been found following topical application for the associated dermatitis.41 The application of keratolytic agents or administration of systemic retinoids often worsens the severity of the disorder, and their use is inappropriate during the neonatal period. Most patients prefer to use bland, thick emollients as the only therapy throughout life.
Ichthyosis hypotrichosis sclerosing cholangitis syndrome
Cutaneous features
Collodion membrane and absent hair may be presenting features at birth. Patients display varying degrees of ichthyosis, jaundice, scarring alopecia and hypotrichosis, not necessarily all obvious from birth.
Extracutaneous features
Congenital paucity of the bile ducts may be a primary feature leading to hepatomegaly, cholestasis and hepatic fibrosis, without fatty infiltration.42 Hepatic involvement varies from transient cholestasis to liver failure. Mild psychomotor delay and bilateral anterior uveal synechiae have been described along with oligodontia, hypodontia and dysplastic enamel.42,43
Etiology and pathogenesis
This is a rare autosomal recessive disorder caused by homozygous mutations affecting the CLDN1 gene coding for the tight junction component claudin-1, leading to lack of expression of CLDN1 in skin and liver.44
Differential diagnosis
Consider this syndrome in any child born with collodion membrane, alopecia and neonatal cholestasis.
Treatment and care
Treatment should follow recommendations for collodion babies. In addition, the hepatic manifestations should be evaluated and managed by specialists.
Trichothiodystrophy (IBIDS syndrome (Tay syndrome), PIBIDS syndrome, SIBIDS syndrome)
Cutaneous features
Three autosomal recessive subsets of trichothiodystrophy (TTD) are associated with ichthyosis: IBIDS (ichthyosis with brittle hair, intellectual impairment, decreased fertility, and short stature; Tay syndrome), PIBIDS (IBIDS with photosensitivity), and SIBIDS (IBIDS with osteosclerosis). Of these, PIBIDS is the most common, comprising approximately 50% of cases of TTD. Neonates with TTD and ichthyosis are usually born with a collodion membrane. The severity of the ichthyosis after the membrane is shed is variable, ranging from a mild to a severe lamellar ichthyosis phenotype. In trichothiodystrophy the hair has a 10–50% reduction in sulfur content, leading to brittle hair that shows transverse fractures (trichoschisis), a decreased cuticular layer with twisting, and a nodular appearance that mimics trichorrhexis nodosa. Polarizing microscopy shows a ‘tiger-tail’ pattern of alternating light and dark bands consistent with the alternating content of sulfur in the hair. Examination of hairs at birth by polarizing microscopy may not reveal the tiger-tail pattern, and repeated examinations may be necessary later in the first months of life.45
Extracutaneous features
Several other clinical features may be associated, including low birthweight, nail dystrophy, increased susceptibility to infection, neutropenia, hypothyroidism, nystagmus, optic atrophy, cataracts, and hypertonia.46 Not uncommonly, patients die of sepsis during childhood.
Etiology and pathogenesis
Cells from patients with PIBIDS show decreased DNA repair levels similar to those of patients with xeroderma pigmentosum (XP), but the development of skin cancer has not been described. The variable and multiple clinical features of PIBIDS may be due in part to the many genes that can result in this phenotype. TTD syndromes have been shown to be due to phenotype-specific mutations in either XPB or XPD. These genes encode the helicase subunits of TFIIH, a DNA repair factor that is also required for transcription of class II genes,47 so that the brittle hair of PIBIDS syndrome may result from decreased transcription of the genes that encode the sulfur-rich matrix of hair and nails. TFIIH is a complex factor that includes the XPD and XPB gene products.48 Recently, a 75 amino-acid protein, designated p8 or GTF2H5, was identified as the tenth protein in this complex. This peptide appears to be critical in maintaining TFIIH base levels, which are known to be diminished in TTD-A, where there is an isolated congenital hair defect.49 Inactivating mutations in this gene have been shown to cause TTD-A.50
Differential diagnosis
In the neonatal period, other causes of collodion membrane need to be excluded. The development of extracutaneous features facilitates the diagnosis.
Other inherited syndromic ichthyoses
Sjögren–larsson syndrome
Cutaneous features
This autosomal recessive disorder usually manifests in the neonatal period with slight or moderate widespread ichthyosis,52–54 although rarely features may not occur until the infant is older than 6 months. Mild erythema is occasionally present at birth, which clears within months. Only one baby with Sjögren–Larsson syndrome has been reported to have had a collodion membrane at birth. Affected babies usually show thickening of the skin, especially at the umbilicus, neck, and flexural areas, that resembles lichenification. Scaling, if present, is fine and lamellar, so that some neonates have been misdiagnosed as being postmature. Some neonates with Sjögren–Larsson syndrome have had taut, shiny fingers and toes. By 1 year of age the ichthyosis is fully developed, with generalized thickening, lamellar scaling, often a yellowish hue, and relative sparing of the central face, and often the palms and soles. The ichthyosis of Sjögren–Larsson is less scaly and more lichenified in appearance, reminiscent of a mild generalized acanthosis nigricans, and pruritus is typically more prominent than in other forms of ichthyosis (Fig. 19.7). Hair and nails are normal. Histopathologic examination of biopsied skin shows significant hyperkeratosis and papillomatosis, with abnormal lamellar or membranous inclusions.55
Extracutaneous features
Most infants with SLS are born preterm.56 Mental and motor retardation and spastic diplegia or tetraplegia are the most common extracutaneous features. Many patients have speech abnormalities, seizures, short stature, and kyphosis. Pathognomonic retinal ‘glistening dots’ are not present in all patients. The neurologic disease usually becomes apparent in the first year of life, often by 3 months of age, with failure to reach normal developmental milestones and the onset of spasticity. Phenotypic variability may be seen: in one family three of four siblings had skin findings but none were typical of SLS, and one lacked skin lesions entirely.57
Etiology and pathogenesis
Sjögren–Larsson syndrome results from mutations in fatty aldehyde dehydrogenase, a component of fatty alcohol: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide oxidoreductase (FAO), which converts fatty alcohol to fatty acid.54–58 Fatty alcohol is used for the biosynthesis of wax esters, which are largely produced in skin, and of glycerol ether lipids, which are prominent in myelin. There appears to be no genotype–phenotype correlation.56 Prenatal diagnosis of Sjögren–Larsson syndrome is possible by measurement of FAO activity in cultured amniocytes or chorionic cells, histologic analysis, and/or analysis of fetal DNA if the gene defect is known.59
Differential diagnosis
The pruritus and resemblance to lichenification could be confused with atopic dermatitis. The development of neurological manifestations distinguishes SLS. The ethnic background may provide a useful clue to diagnosis, given the high prevalence in northern Sweden (8.3 in 100 000 persons; elsewhere in Sweden and worldwide the incidence is 0.4 per 100 000).56 Diagnosis may be made by demonstrating enzyme deficiency or by mutation analysis of fatty aldehyde dehydrogenase gene (FALDH).
Treatment and care
There are no well-established specific treatments, but rare patients have shown improved behavior and pruritus with 5-lipoxygenase inhibitors.60
Gaucher disease
Cutaneous features
Gaucher disease (β-glucocerebrosidase deficiency) is an autosomal recessive disorder that results from the deficient activity of lysosomal glucocerebrosidase. Several infants with the type II (acute infantile cerebral or acute neuronopathic) form of Gaucher disease have been born with a collodion membrane.3,61,62 The enzyme deficiency with resultant abnormalities in glucocerebrosidase degradation appears directly responsible for the abnormal skin of these infants. Glucosylceramide and ceramide are components of the intercellular bilayers in the stratum corneum that participate in skin permeability barrier function, so that the absence of glucocerebrosidase (which increases glucosylceramide and reduces the generation of ceramide) leads to abnormal skin thickening and increased transepidermal water loss.
Extracutaneous features
Extracutaneous features of type II Gaucher disease include enlargement of the abdomen due to hepatosplenomegaly, and neurologic signs such as retroflexion of the head, strabismus, dysphagia, choking spells, and hypertonicity. Death usually occurs before the age of 1 year. Although patients with type II typically have acute neurologic progression and those with type III have slow progression, some children have been reported with an intermediate phenotype of delayed age of onset, rapid progression of neurologic disease with refractory seizures, and oculomotor abnormalities.63
Etiology and pathogenesis
Gaucher disease type II is caused by mutation in the gene encoding acid β-glucosidase (GBA). Mutations in this gene also cause Gaucher disease type I and type IIII. Type II is the least common form.64
Keratitis, ichthyosis, deafness (KID) syndrome
Cutaneous features
The constellation of vascularizing keratitis, ichthyosiform hyperkeratosis, and sensorineural deafness is the characteristic feature of KID syndrome. Patients are usually born with erythematous or erythrokeratodermatous skin that is mildly scaling, although in some the presence of excessive vernix-like material is the presenting finding. Occasionally skin abnormalities are not noted until a few weeks of age.67 The characteristic thick, leathery skin with tiny stippled papules develops during the first year of life, particularly during the first 3 months (Fig. 19.8). Well-defined verrucous hyperkeratotic plaques develop in 90% of patients, often localized to the face and limbs. Diffuse palmoplantar hyperkeratosis with a stippled or leathery pattern also occurs in almost all patients. Alopecia occurs overall in 80% of patients, ranging from minimal loss of eyebrows or eyelashes to total scalp alopecia; in 25% of patients the alopecia is congenital. An additional 17% of patients have sparse, fine hair without frank alopecia. The scalp may be markedly thickened in the affected neonate. Nails are dystrophic in the majority of patients. Sweating may be decreased or absent. Biopsy of skin shows nonspecific acanthosis with papillomatosis and basket-weave hyperkeratosis. Hair follicles may be atrophic. Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin and tongue has been described in more than 10% of patients, and may occur during childhood.
Extracutaneous features
The hearing loss is sensorineural, congenital, and can be progressive. It can be detected in the neonate by brainstem-evoked auditory potential testing. Unlike the auditory changes, ophthalmologic features are progressive and most commonly develop in childhood or early adolescence, although photophobia from birth has been described. The keratoconjunctivitis sicca with corneal vascularization leads to pannus formation and markedly decreased visual acuity.68 Approximately 45% of patients have recurrent infections, especially bacterial and candidal infections of the skin, auditory canals, and eyes. Some patients have shown evidence of immunodeficiency, with moderate increases in IgE levels, defective chemotaxis, and absent lymphocyte proliferative responses to Candida albicans.69 Death from infection during infancy or early childhood has been reported.70
Etiology and pathogenesis
Mutations in the GJB2 gene encoding the gap junction protein connexin 26 are now known to be the cause of KID syndrome in a majority of cases.71 There does appear to be genetic heterogeneity, however, with mutations also identified in GJB6, which encodes connexin 30.72 Connexins are the major proteins of gap junctions, which facilitate efficient cell–cell communication between all cells in multicellular organisms. This system facilitates a synchronized cellular response to a variety of intercellular signals by regulating the direct passage of low-molecular-weight metabolites (<1 kDa) and ions between the cytoplasm of adjacent cells.73 The skin and inner ear have a high number of gap junctions, and in the skin they appear to have a role in the coordination of keratinocyte growth and differentiation.74 Mutations in these connexins underlie epidermal disease, sensorineural hearing loss, and peripheral neuropathy.75,76
Differential diagnosis
Distinction from Clouston syndrome, another connexin 30 gene disorder (see below), can be difficult.72 In both conditions the associated keratoderma has a characteristic ‘stippled’ quality that is quite distinctive. Detection of deafness is indicative of KID syndrome. Molecular diagnosis is now relatively straightforward, as connexin genes are small and easily screened for mutations.
Treatment and care
Therapy is supportive, but corneal and cochlear implants77 have been successfully performed to treat corneal vascularization and the hearing loss, respectively. Oral fluconazole therapy of recalcitrant fungating candidiasis can result in complete resolution and remission for at least a year.78
Neutral lipid storage disease with ichthyosis (Chanarin–dorfman syndrome)
Cutaneous features
This autosomal recessive disorder is characterized by the multisystemic accumulation of neutral lipids (triglycerides).79 Approximately 65% of affected patients have associated ichthyosis, which is always present at birth as congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma, or occasionally as a collodion membrane.
Extracutaneous features
Hepatomegaly occurs in 46% of patients, although fatty liver may be universal. Liver levels of transaminases are often elevated.80,81 Almost 70% of patients have either elevated serum creatine kinase activity or muscle weakness, or both, usually mild and first symptomatic in adulthood. Other features may include ataxia, mental retardation, sensorineural hearing loss, and cataracts.
Etiology and pathogenesis
Sections of skin show accumulation of neutral lipids and these non-membrane-bound cytosolic triacylglycerol droplets are also found in liver, muscle, intestinal mucosa, and neutrophils. Vacuolated neutrophils are considered the most consistent marker for neutral lipid storage disease. Mutations in the CGI-58 gene have been found in several families.82 The gene product belongs to a large series of proteins most of which are enzymes in the esterase/lipase/thioesterase subfamily. It is widely expressed in skin, lymphocytes, liver, skeletal muscle, and brain.
Differential diagnosis
In the neonate, the ichthyosis may be impossible to distinguish from other CIE phenotypes and possible causes of collodion baby. Diagnosis is usually made by a peripheral blood smear, which shows lipid droplets in granulocytes.83
Treatment and care
Preliminary observations suggest that a low-fat diet, including medium-chain triglycerides, may improve liver function and the skin, especially if begun in early childhood.84
Ichthyosis prematurity syndrome
Cutaneous features
Ichthyosis prematurity syndrome (IPS) is a distinct form of ichthyosis that is reported primarily in the Norwegian population.85 At birth, the skin, particularly on the head and peripheral extremities, is covered by a thick, caseous, desquamating epidermis. The skin changes observed at birth improve within 2 weeks, and after a few months, IPS is characterized by dryness, mild skin stippling (particularly on the distal extremities), a leather-like thickening on the lower back and atopic manifestations, often with hypereosinophilia.86
Extracutaneous features
Pregnancies are complicated by polyhydramnios, and ultrasound shows opaque amniotic fluid. The birth is premature, and delivery usually takes place at around 30–32 weeks’ gestation. Affected children may suffer from postnatal asphyxia, possibly related to aspiration of amniotic debris.
Etiology and pathogenesis
The pattern on electron microscopy is characterized by membrane aggregations in the upper epidermal cells. Mutations occur in a gene encoding the fatty acid transporter 4 (SLC27A4).87 SLC27A4, expressed in the suprabasal layer of the epidermis, encodes a protein, FATP4, that functions as a fatty acid transporter and an acyl coenzyme A synthetase. Reduced function of this protein most likely leads to disturbance of the intercellular lipid layer of the stratum corneum.
Differential diagnosis
The differential diagnosis in the neonatal period includes collodion membrane and harlequin ichthyosis.
Treatment and care
For general neonatal management principles, see Box 19.1.
CHIME syndrome: colobomas of the eye, heart defects, ichthyosis, mental retardation, ear defects
Cutaneous features
The skin is thick and dry at birth. There may be a diffuse, erythematous, pruritic, migratory rash at or shortly after birth which becomes increasingly ichthyotic, especially at flexural surfaces, and ultimately resembles lichenification (Fig. 19.9).88 Examination of biopsied skin specimens shows nonspecific changes.89 The hair may be fine and sparse, with trichorrhexis nodosa seen on light microscopy.
Extracutaneous features
Affected individuals have a distinctive facies with ocular hypertelorism, brachycephaly, epicanthal folds, macrostomia, and a broadened nasal root. The ear defects can be morphologic, with a cupped appearance and rolled helices, or functional. The colobomas are most commonly retinal, although choroidal colobomas have been described.90 Heart defects are common including tetralogy of Fallot, transposition of the great vessels and ventricular septal defect.88 Other frequent characteristics include seizures and a wide-based gait. Cleft palate and renal anomalies have been described.
Etiology and pathogenesis
This extremely rare neuroectodermal disorder is thought to be autosomal recessive. Mutations in the PIGL gene have recently been described in five previously reported cases.91
Differential diagnosis
Other ichthyoses with neurologic manifestations should be considered including Sjögren–Larsson syndrome, Netherton syndrome, Refsum disease, KID syndrome and Tay syndrome. The characteristic ocular, cardiac, ear and dysmorphic features help confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment and care
Affected neonates should have ophthalmology, otorhinolaryngology and cardiology assessments.
MEDNIK syndrome: mental retardation-enteropathy-deafness-neuropathy-ichthyosis-keratoderma
MEDNIK syndrome is a recently described, rare autosomal recessive condition, in a French Canadian population. The phenotype is a result of a mutation in the AP1S1 gene, which is expressed in the skin and spinal cord. Cutaneous features are similar to erythrokeratoderma variabilis (see below). Extracutaneous features include severe psychomotor retardation, peripheral neuropathy, sensorineural hearing loss and severe congenital diarrhea.92
Inherited ichthyoses – non-syndromic
Autosomal recessive congenital ichthyosis (ARCI)
Within months of shedding their collodion membranes, the majority of babies with ARCI declare their clinical phenotype along a spectrum of manifestations ranging from generalized erythroderma with finer scale (congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma or CIE) to larger, lamellar scaling and variable underlying erythroderma (lamellar ichthyosis or LI). Neonates with harlequin ichthyosis present with and ultimately have a more severe phenotype than the rest of the ARCI group (see below). Because the underlying genetic basis within the ARCI spectrum is varied, without strong genotype-phenotype correlation with respect to scale morphology or erythroderma, other than for harlequin ichthyosis, the etiology/pathogenesis of this group of disorders is discussed together.
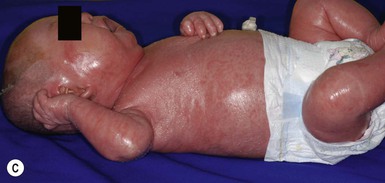
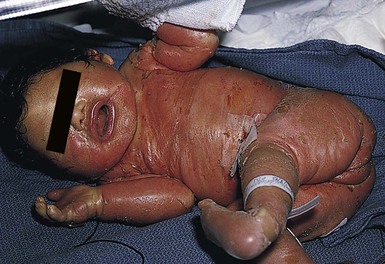
Harlequin ichthyosis
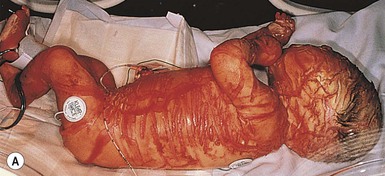
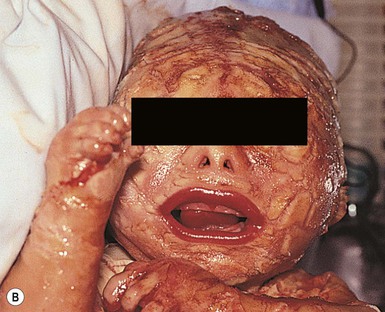
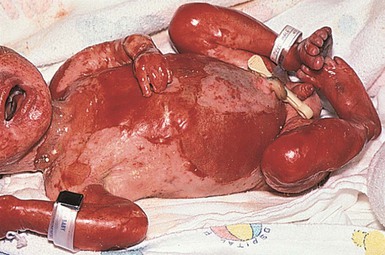
Cutaneous features
Harlequin ichthyosis (HI) is a rare autosomal recessive disorder in which the neonate is born with a thick covering of armor-like scales, severe ectropion and eclabium, and underdeveloped nose and ears (Fig. 19.10). It is likely that the dysmorphic features observed in harlequin ichthyosis are at least in part secondary to restricted fetal movement; this condition has been termed ‘fetal deformation sequence’ (FADS).93 Occasionally infants with HI present with a thick vernix-like coating. Those who survive the perinatal period go on to express a severe and very scaly erythroderma.1
Extracutaneous features
There is high neonatal mortality due to respiratory complications, infections through the defective skin barrier, and dehydration.
Differential diagnosis
Severe forms of collodion baby may cause confusion but the diagnosis of harlequin ichthyosis is usually straightforward.
Treatment and care
In general, harlequin babies require vigorous supportive therapy, including a humid environment, the aggressive use of emollients, and careful monitoring of fluid and electrolyte needs. Survival past the neonatal period is uncommon, but reported. Most affected infants have complications, such as systemic infection through fissured skin, difficulties with feeding and respiration, and distal gangrene. Therapy with retinoids may improve the clinical appearance, but the condition at best evolves into a severe generalized ichthyosiform erythroderma phenotype.94–98 Harlequin ichthyosis is the only ichthyotic condition that may justify the use of systemic retinoid therapy during the newborn period. Treatment with retinoids, first undertaken in 1985, encourages shedding of the grossly thickened skin.99,100 A recent review of 45 cases reported an overall survival rate of 56%, ages 10 months to 25 years.100 Death usually occurred in the first three months from sepsis and/or respiratory failure. The administration of systemic retinoids should generally be considered in infants who have survived the first few weeks with intensive nursing support, although a possible exception is in infants with particularly thick areas of plate-like scale causing digital constriction, in which the early use of retinoids may cause faster desquamation, potentially helping to avoid digital gangrene. The parental decision to use retinoids should be made with the knowledge that the resultant ichthyotic condition is severe and associated with a poor quality of life. The recovery of lipid secretion after gene correction of ABCA12 in cultured cells raises hope for future therapeutic approaches.101
Lamellar ichthyosis phenotype of ARCI
Cutaneous features
Lamellar ichthyosis (LI) is a phenotype of ARCI, although an autosomal dominant form has been described.102 Most affected babies have a collodion membrane at birth (see above). After the first months, infants show large and plate-like scales that are often hyperpigmented, particularly in patients with darker skin.103 Underlying erythroderma is minimal, but ectropion and alopecia may be severe. Biopsies from patients with LI have massive thickening of the stratum corneum, mild acanthosis, and a normal granular layer. The epidermis in LI may show papillomatosis with regular psoriasiform blunting and broadening of the rete ridges. Bathing suit ichthyosis, a rare minor variant, is characterized by scaling in a bathing suit pattern confined to the trunk.104
Extracutaneous features
Neonates and infants with severe forms of ARCI can face similar problems to those with Harlequin ichthyosis (discussed above). Care needs to be taken to carefully monitor and take corrective action for variations in body temperature, fluid balance and caloric intake. In later childhood, exposure keratitis can result from prolonged ectropion.
Differential diagnosis
Lamellar ichthyosis can be difficult to distinguish from nonbullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma in the neonatal period.
Treatment and care
In the neonatal period, general supportive measures are appropriate (see Box 19.1). In older children and adults more potent topical keratolytic preparations and oral retinoids may be appropriate, but these should be avoided in infancy.
Congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma phenotype of ARCI
Cutaneous features
Patients with congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma (CIE) also usually present as collodion babies (Fig. 19.11). Underlying erythroderma is common, and the scales tend to be finer and lighter in color than those of infants with lamellar ichthyosis. Alopecia and ectropion may be associated.103
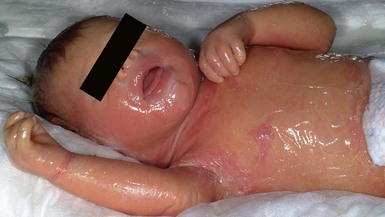
Extracutaneous features
Not uncommonly, patients with CIE have associated neurologic abnormalities, and the CIE phenotype may be part of syndromic ichthyosis, such as neutral lipid storage disease (Chanarin–Dorfman syndrome). These patients have failure to thrive and short stature, if severe.
Differential diagnosis
Because of the associated neurological abnormalities and the potential to respond to dietary tailoring, it is important to exclude Chanarin–Dorfman syndrome (see below). However, this is a very uncommon cause of the CIE phenotype.
Treatment and care
See Box 19.1 for general principles of care in the neonatal period.
Etiology and pathogenesis of the ARCI group
The genetic basis for ARCI is heterogeneous, and seven genes have been found to have mutations that lead to ARCI (see Table 19.1).105,106 The gene most commonly altered in ARCI (32% of patients in one series105) is transglutaminase 1 (TGM1),107 encoding an enzyme that is involved in cornified envelope formation by crosslinking precursor proteins such as involucrin. Other genes mutated in ARCI encode proteins of the tepoxalin pathway, including NIPAL4 (ichthyin, 16% of ARCI); ALOX12B (12(R)-lipoxygenase, 12%); CYP4F22 (a cytochrome P450 enzyme of the 12(R)-lipoxygenase pathway, 8%); ALOXE3 (lipoxygenase-3, 5%), as well as the lipid transporter ABCA12.105 Besides their disruption of stratum corneum lipid synthesis, these enzymes (or receptors) within the lipoxygenase pathway may also disrupt the processing of profilaggrin to filaggrin.108 To date, all babies with harlequin ichthyosis have had mutations in the lipid transporter ABCA12.11,101,109 Missense mutations in ABCA12 may result in a milder phenotype that shows a collodion membrane at birth and which progresses into LI or CIE, often with palmoplantar keratoderma (PPK).11 The integrity of the stratum corneum barrier is largely due to corneocytes embedded in intracellular lipid lamellae. These extracellular lipid lamellae are in turn formed from intracellular granules. Absence of ABCA12 prevents the transfer of lipids into lamellar granules, leading to histologic demonstration of lipid accumulation within corneocytes and absence of normal lamellar granules,12 poor barrier and secondary clinical changes.110 A seventh and most recently identified cause of ARCI is mutations in PNPLA1, which contribute to the epidermal lipid barrier.106 Within the ARCI spectrum is also a late onset form with lamellar scaling due to mutations in LIPN, encoding lipase N.111 Prenatal diagnosis by molecular analysis of fetal DNA, obtained by chorionic villus sampling, is a preferred method of prenatal diagnosis of ARCI, once the molecular defect is known.112
Keratinopathic ichthyosis
In this group of disorders, mutations in keratin genes lead to fragile skin and blistering with compensatory thickening of overlying skin.
Epidermolytic ichthyosis (EI)
Previously called ‘epidermolytic hyperkeratosis’.
Cutaneous features
This autosomal dominant disorder manifests in the neonate as widespread areas of denuded skin with only subtle skin thickening and/or scaling (Fig. 19.12). Confusion with other blistering disorders in the neonate is common, particularly epidermolysis bullosa, and secondary cutaneous bacterial infection caused by Staphylococcus aureus often occurs. As patients age, the scaling becomes more verrucous, with large dark scales, particularly at intertriginous sites, and the propensity towards blistering tends to decrease. Annular EI is a subtype characterized by annular polycyclic erythematous plaques over the proximal extremities and trunk.113
Extracutaneous features
In the neonatal period, infants with EI risk dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, and infection; however, most babies do well and death rarely occurs in neonates.
Etiology and pathogenesis
The gene defects of EI involve abnormalities of keratins 1 or 10,114,115 the major differentiation-specific keratins of the upper epidermis. These mutations cause the formation of defective keratin filaments, which are functionally responsible for the tonofilament clumping and blistering of this disorder. Prenatal diagnosis has been performed at 20–24 weeks’ gestation by fetal skin biopsy, based on the abnormal clumping of keratin filaments,116 but also by molecular analysis of keratin 10 in an affected family.117
Differential diagnosis
Distinction from epidermolysis bullosa is important in the neonatal period. The principles of care at this stage remain the same, but accurate diagnosis is important in order to properly inform and counsel parents. The histologic appearance of lesional skin confirms the diagnosis, showing vacuolization of the granular and upper spinous layers. Hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, and papillomatosis are variable, but the granular layer is thickened. On electron microscopy the tonofilaments are seen to be clumped in the lower epidermal layers and form perinuclear shells in the granular cell and upper spinous layers.
Treatment and care
The neonate should be managed according to the same broad principles as outlined in Box 19.1, but with additional specific precautions on skin handling of neonates with fragile skin directed by a detailed nursing protocol.
Ichthyosis curth–macklin
Cutaneous features
Ichthyosis Curth–Macklin (ICM) (previously ichthyosis hystrix), is a rare autosomal dominant ichthyotic disorder characterized by plaques of spiny hyperkeratosis. The extent of involvement varies from patchy to generalized and severe. In patients with patchy involvement, the distribution is not along the lines of Blaschko. Usually, the face, palms, and soles are not affected, but involvement of the penis and scrotum has been described. Affected infants tend to show cutaneous changes within the first weeks of life, with subsequent progression of involvement, although onset during childhood has been described in some patients. Erythroderma may be present at birth, but disappears with time.
Extracutaneous features
None.
Etiology and pathogenesis
Microscopic examination of skin biopsy specimens shows orthokeratosis, papillomatosis, and acanthosis of the granular and upper spinous layers, with perinuclear vacuolization. Keratinocytes may have two nuclei. Ultrastructural examination shows concentric shells of tonofibrils that encase the nuclei with perinuclear vacuoles, lamellar body abnormalities, and binuclear keratinocytes.118 In two families, the ICM phenotype has been attributed to mutations in keratin 1.119,120 The condition is genetically heterogeneous; in other families linkage to the keratin gene clusters has been excluded.121
Differential diagnosis
ICM can be confused with epidermolytic ichthyosis. The lack of erythroderma, blistering, and typical ultrastructural characteristics distinguish these conditions. Epidermal nevi, although they may resemble ICM both clinically and histologically, are distinguishable by their distribution along the lines of Blaschko.
Treatment and care
Neonatal care is outlined in Box 19.1. In older children, keratolytics and oral retinoids may be of value.
Miscellaneous forms of ichthyosis
Peeling skin disease
Cutaneous features
This rare autosomal recessive condition is characterized by spontaneous superficial peeling of skin, sometimes accompanied by pruritus and occasionally by erythema or vesiculation. Skin involvement is usually generalized, but the palms, soles, face, and scalp may be unaffected. The Nikolsky sign tends to be positive, and a skin biopsy often shows psoriasiform epidermal changes and shedding of the stratum corneum just above the granular layer. Pruritus and atopy may be associated.
Extracutaneous features
Transient eosinophilia and elevation of IgE levels, with food allergies is commonly associated.
Etiology and pathogenesis
Peeling skin disease is caused by homozygous nonsense mutations in CDSN leading to complete loss of corneodesmosin, an epidermal adhesion molecule.122 Acral peeling skin syndrome was previously thought to be a variant of PSD but is now known to be a distinct disease caused by a mutation in transglutaminase 5 (TGM5).122
Differential diagnosis
The clinical appearance may initially be confused with staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome but the duration and distribution should make the distinction clear.
Treatment and care
General principles of care apply (see Box 19.1).
Erythrokeratoderma variabilis (EKV)
Cutaneous features
This autosomal dominant disorder manifests as two types of skin change. Some patients have migratory patches of erythema, which are often targetoid or circinate and last for days to months. With time, the lesions become more fixed, erythematous, and hyperkeratotic (Fig. 19.13). In other patients, the disorder manifests as sharply demarcated, fixed hyperkeratotic plaques. Both types of lesion may be seen in the same patient. The typical areas of involvement are the extensor surfaces of the extremities, trunk, buttocks, and face. The palms and soles are not usually involved. Lesions are present at birth in up to one-third of patients.123 Most begin to show evidence of involvement during the first year of life, with progression during childhood and stabilization at puberty. Later improvement has been described, including clearing with fevers.
Extracutaneous features
There are usually no extracutaneous features, although ataxia has been described.124
Etiology and pathogenesis
Mutations in the GJB3 gene which encodes for connexin 31,125 and the GJB4 gene which encodes for connexin 30.3,75,126 have been shown to cause erythrokeratoderma variabilis. There is likely to be further genetic heterogeneity as mutations in these two genes do not account for all cases of EKV.75
Differential diagnosis
KID syndrome and Clouston syndrome can cause diagnostic confusion, but palmoplantar keratoderma is not usually a feature of EKV.
Treatment and care
Treatment with systemic retinoids has resulted in improvement or clearing.
Clouston syndrome: hidrotic ectodermal dysplasia
Cutaneous features
This autosomal dominant genodermatosis was first described in a very extensive family of French Canadian extraction, who subsequently migrated to Scotland and the USA.76,127,128 The characteristic features are total alopecia, severe nail dystrophy, hyperpigmentation over the joints, strabismus, bulbous fingertips, and a distinctive palmoplantar keratoderma. In contrast to hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia, sweating is unimpaired and facial, dental, and breast development are normal.129 The original kindred has been followed extensively for years, and multiple cutaneous carcinomas of the nail bed and palmar tissue have been observed in several affected individuals.130–132
Extracutaneous features
None.
Etiology and pathogenesis
In 1996, Clouston syndrome was linked to chromosome 13q11–q12.1,133 and subsequent studies have shown genetic homogeneity to this locus.134–138 Recently, mutations in the GJB6 gene encoding the β connexin 30 were identified in all available kindreds. Interestingly, only two mutations in GJB6 (G11R and A88V) accounted for all the families tested.139 Mutations in GJB6 had previously been identified in a small family with dominant nonsyndromic hearing loss,140 emphasizing the complexity and diversity of phenotypes caused by dominant-acting connexin mutations.
Differential diagnosis
Distinction from other connexin disorders such as KID syndrome and EKV is important and not always obvious. Alopecia is most commonly associated with Clouston syndrome. The stippled palmoplantar keratoderma is seen in both KID and Clouston syndromes.
Treatment and care
No specific treatment is needed in the neonatal period. In the older child the nail dystrophy can be severe and require podiatric attention. In some individuals the alopecia is a major issue: psychological support and wigs may be required.
Erythrokeratoderma progressiva symmetrica (EPS)
Cutaneous features
This autosomal dominant disorder is characterized by symmetric erythematous scaling plaques that may spare the trunk but which are commonly found on the knees, buttocks, and groin. The palms and soles are affected in approximately 50% of patients, and the face is occasionally involved. Features are usually present during the first few years of life.
Extracutaneous features
There are usually no extracutaneous features.
Etiology and pathogenesis
Skin biopsies show acanthosis with perinuclear vacuolization of granular cells. Ultrastructural studies show lipid vacuoles in the stratum corneum, and increased numbers of swollen mitochondria in granular cells.141 Mutations in loricrin have been shown in some patients with this condition.142,143 Patients with these mutations may show features of Vohwinkel syndrome (VS), EPS, or CIE with a collodion baby phenotype at birth.144 Common clinical features include hyperkeratosis of the palms and soles, with digital constriction. Histologic characteristics common to all of these conditions include parakeratotic hyperkeratosis with hypergranulosis, and nuclear accumulation of mutant loricrin. The term ‘loricrin keratoderma’ has been proposed to encompass all these phenotypes.145 The molecular basis in individuals with no palmoplantar involvement is not clear.
Differential diagnosis
EKV can be distinguished from EPS by absence of palmoplantar involvement and transient migratory plaques (see Table 19.1).
Treatment and care
The use of oral retinoids has been reported to be effective. Topical keratolytics, retinoids, and glucocorticoids have also been used with more variable effects.146
Palmoplantar keratodermas
Diffuse thickening of the skin on the palms and soles, known as palmoplantar keratoderma, is seen in a number of genetic disorders in infancy. In later life it is most commonly seen in pityriasis rubra pilaris and psoriasis.
The keratoderma of many forms of hereditary palmoplantar keratoderma (PPK) is first apparent during the first months of life, whereas in others (e.g., punctate keratoderma, keratoderma striata, Howell–Evans) it is not seen until early to late childhood.147 In the neonatal period, the affected areas may appear hyperhydrated (Fig. 19.14). The majority of types of palmoplantar keratoderma are autosomal dominant. Some of the more common conditions are discussed briefly below.
In the Unna form of palmoplantar keratoderma (nonepidermolytic, i.e., not associated with fragile skin), the palms and soles are usually red at birth or soon thereafter. The skin progressively thickens on the palms and soles, starting at the margins and extending centrally, with red borders that usually disappear after several years. Keratotic lesions may occasionally be found on the dorsum of the hands and feet, the volar wrists, and the knees and elbows. The overall extent of involvement is variable. Palmoplantar hyperhidrosis is commonly associated with the nonepidermolytic form. A mild defect of keratin 1 and defects in keratins 6a and 16 have been described in families with nonepidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma.148 In Greither syndrome (transgrediens form, i.e., not confined to the volar aspect), the onset of thickening tends to be later, but the diffuse palmoplantar keratoderma extends onto the dorsum of the hands and feet. The knees, elbows, shins, and forearms are often involved. This syndrome is now known to be caused by mutations in keratin 1.149–151
Vorner palmoplantar keratoderma (epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma) can also begin at an early age, and is clinically indistinguishable from the nonepidermolytic form during the first years of life, when the keratoderma is confined to the palms and soles. Epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma results from mutations in keratin 9, a gene that is only expressed in the skin of the palms and soles, limiting its distribution of expression. It should be noted that descendants of the family described by Thost152 as having nonepidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma actually have keratin 9 mutations, demonstrating that the epidermolytic hyperkeratosis found in biopsy sections is an inconstant feature that may require several biopsies for detection.
The keratoses of Vohwinkel syndrome also are first noted shortly after birth, and gradually develop into the typical honeycombed diffuse palmoplantar hyperkeratoses with starfish-like keratoses on the backs of the hands, fingers, and toes. The constricting bands of the digits (pseudoainhum) first develop at 5 years of age or later, and can lead to autoamputation, as well as decreased motility of the hands. Some patients with Vohwinkel syndrome have alopecia, and an erythrokeratoderma has been described as well. The gene defect involves mutations in the gene that codes for loricrin.153 Patients with deafness and the palmoplantar changes of Vohwinkel have connexin 26 mutations, not loricrin gene mutations.
Mal de Meleda, an autosomal recessive form of palmoplantar keratoderma, is not congenital but presents during the first 6 months of life as a diffuse palmoplantar keratoderma. The dorsal surfaces of the hands and feet are involved, and keratotic plaques tend to be present on the knees and elbows as well.154 Koilonychia, nail thickening, and subungual hyperkeratosis are usually associated. Mild perioral erythema and hyperkeratosis may be present. Mal de Meleda is known to be caused by mutations in the secreted protein SLURP1 gene.155,156
Olmsted syndrome
Cutaneous features
This extremely rare disorder usually presents with progressive thickening of the palms and soles during the first few years of life.157 Typically, lesions are absent during the neonatal period, but begin as discrete lesions that become more confluent with time. The borders of keratoderma are erythematous. Contractures of the palms and soles, and autoamputation from progressive digital constriction are common. Lesions, particularly on the feet, tend to be exquisitely painful. After the onset of palmoplantar keratoderma the periorificial areas become hyperkeratotic, with fissured plaques. This involvement of periorificial areas, particularly perioral, perianal, perinasal, pericrural, and periumbilical, distinguishes this condition from other forms of palmoplantar keratoderma. Oral leukokeratosis, alopecia, and nail dystrophy have been described in association.
Extracutaneous features
There are no extracutaneous features.
Etiology and pathogenesis
Olmsted syndrome is caused by a missense mutation in TRPV3, expressed in skin, hair follicles, brain and spinal cord.158
Differential diagnosis
Olmsted syndrome is usually easily distinguished from other mutilating keratodermas.
Treatment and care
In the neonatal period no specific care is necessary, and indeed keratolytics are best avoided as they do not tend to be helpful. In the older child, regular paring and sometimes grafting is needed to preserve good hand function and the ability to walk.
Tyrosinemia II
Cutaneous features
Tyrosinemia II (Richner–Hanhart syndrome) is an autosomal recessive disorder comprising a triad of ocular manifestations, cutaneous hyperkeratoses, and mental retardation. The early cutaneous lesions may be seen during the first year of life as sharply demarcated, yellowish keratotic papules of the palmar and plantar surfaces, but more commonly appear later, sometimes as late as the second decade. The lesions become more erythematous, erosive, and painful with time. In one case the clinical phenotype was of a diffuse PPK.159 Nail dystrophy may also be associated.
Extracutaneous features
The ocular manifestations of the disorder appear soon after birth.160 Photophobia and bilateral tearing commonly occur within the first 3 months of life, and progress to corneal erosions. Ocular lesions are typically transitory, and are subject to intermittent relapses. The corneal lesions are frequently misdiagnosed as herpetic keratitis, and remissions may be misinterpreted as a response to antiviral therapy. The eye changes occasionally develop after the skin manifestations. Varying degrees of intellectual impairment have been described in less than half of affected patients.
Etiology and pathogenesis
Tyrosinemia type II is caused by a deficiency of hepatic tyrosine aminotransferase (TAT)161 that results in elevated tyrosine levels in the plasma and urine.
Differential diagnosis
Diagnosis is occasionally delayed until adulthood. Early diagnosis is important, as appropriate dietary advice can help diminish the severity of neurological and ocular manifestations. In the neonate the corneal erosions can be mistaken for herpetic infections. The focal PPK that occurs later in life can resemble that associated with keratin 6A, 6B, 16, and 17 mutations, but may be more erosive.
Treatment and care
The treatment of choice is dietary restriction of tyrosine with a low-phenylalanine, low-tyrosine diet.
Keratosis linearis with ichthyosis congenita and sclerosing keratoderma: KLICK syndrome
Cutaneous features
KLICK syndrome is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by palmoplantar transgressive keratoderma, congenital ichthyosis and linear hyperkeratotic plaques in the flexor regions.162
Extracutaneous features
None.
Etiology and pathogenesis
KLICK syndrome is caused by a single-nucleotide deletion in the proteasome maturation protein (POMP) gene leading to aberrant processing of profilaggrin to filaggrin.163 Histopathology reveals an epidermis with acanthosis, hypergranulosis and hyperkeratosis and at electron microscopy numerous keratohyalin granules are found in the keratinocytes of the granular layer.162
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnoses include KID syndrome, Vohwinkel syndrome, Olmsted syndrome and the generalized forms of congenital ichthyosis.162
Treatment and care
Treatment with topical keratolytics and oral retinoids results in significant improvement but recurrence is common once treatment is stopped.162
Restrictive dermopathy
Cutaneous features
Neonates with this lethal autosomal recessive condition are born with rigid skin, attributed to fetal akinesia or hypokinesia deformation sequence.164–166 Polyhydramnios with reduced fetal movements usually results in premature delivery at approximately 31 weeks’ gestational age. Premature rupture of the membranes and an enlarged placenta with a short umbilical cord are often associated. The skin typically is thin, shiny, and red, with prominent vessels. Scaling and erosions are frequently seen (Fig. 19.15).
Extracutaneous features
The facies are characterized by micrognathia, a small open mouth (O-shaped), pinched nares with choanal atresia or stenosis, and flattened or low-set pinnae. The constraint of movement in utero also leads to flexion contractures of the joints, and bony changes such as poor ossification of the clavicle; over-tubulation of the radius, ulna, and distal phalanges; and widened sutures and large fontanelles. Natal teeth have been described in 25–50% of patients with restrictive dermopathy. Most patients die of pulmonary hypoplasia with respiratory insufficiency or sepsis.
Etiology and pathogenesis
Restrictive dermopathy may be caused by dominant de novo LMNA (encoding lamin A) mutations167 or, more frequently, by recessive null ZMPSTE24 mutations, most of which lie in a mutational hotspot within exon 9.168 This gene encodes a metalloproteinase specifically involved in the post-translational processing of lamin A. It is likely that many of the dysmorphic features observed in restrictive dermopathy are secondary to restricted fetal movement; this condition has been termed fetal akinesia deformation sequence (FADS).93
Differential diagnosis
Skin biopsy at 20 weeks’ gestational age may be normal,169 and DNA-based prenatal diagnosis is best if the familial gene defect is known. The onset of intrauterine growth retardation, restricted fetal movement, and polyhydramnios that raise suspicion of the diagnosis may occur late in gestation, precluding prenatal testing. Histopathologic examination of skin biopsy sections shows a thick epidermis, and a thin dermis with a paucity and hypoplasia of cutaneous appendages. Collagen bundles are abnormally arranged, and elastic fibers are almost absent.
Treatment and care
Most patients die during the neonatal period; the longest survivor with restrictive dermopathy died at 4 months of age.
Neu–laxova syndrome
Cutaneous features
Neu–Laxova syndrome is a rare, lethal, autosomal recessive trait characterized by severe intrauterine growth retardation, microcephaly with abnormal brain development, edema, and ichthyosis.170,171 The ichthyosis is present at birth, but varies from mildly scaling skin to a harlequin fetus appearance. Histologic findings are nonspecific and show the acanthosis and orthokeratosis of lamellar ichthyosis. Excessive subcutaneous adipose tissue and myxomatous connective tissue may contribute to the characteristic edema.
Extracutaneous features
The lack of brain development is characterized by lissencephaly and agenesis of the corpus callosum. Characteristic facial features include a slanted forehead, protuberant eyes, a flattened nose, deformed ears, micrognathia, and a short neck. Microphthalmia and cleft palate are occasionally associated. The limbs, fingers, and toes are abnormal, with syndactyly, hypoplasia, and contractures. Skeletal X-rays often show poor mineralization. The craniofacial and limb abnormalities are related to the reduced intrauterine movement, and are therefore defined as fetal akinesia/hypokinesis sequence, as has been described in other syndromes.
Etiology and pathogenesis
The etiology of this rare and devastating disorder is unknown, but the term is likely to cover a number of heterogeneous disorders.172
Differential diagnosis
The constellation of features usually makes the diagnosis clear.
Treatment and care
Treatment is palliative.
Neonatal scaling of hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia
The ectodermal dysplasias encompass a complex and highly diverse group of heritable disorders that share in common developmental abnormalities of ectodermal appendages (see Chapter 25). The most common form is hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia, which is most commonly X-linked, but can be autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive. Scaling of the skin during the newborn period has been described in 70% of patients with X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia.173 The skin has been described as ‘like plastic,’ peeling off in sheets, and ‘like a snake peeling.’ Some infants have been described as being very dry at birth, and others as having a collodion membrane-like scale. Later in infancy the typical facial features, sparsity of hair, decreased ability to sweat, and eventually dental abnormalities allow the diagnosis to be confirmed. Patients tend to have an increased risk of upper respiratory tract infections and atopy, particularly manifesting as asthma and atopic dermatitis. The genetic defects underlying both X-linked and autosomal forms of hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia encode proteins of the ectodysplasin/NFκB signaling pathways.174
Access the full reference list at ExpertConsult.com ![]()