Chapter 689 Disorders Involving Transcription Factors
Campomelic Dysplasia
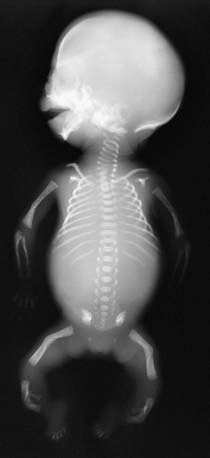
Apparent in newborn infants, campomelic dysplasia (OMIM 114290) is characterized by bowing of long bones (especially in the lower legs), short bones, respiratory distress, and other anomalies that include defects of the cervical spine, central nervous system, heart, and kidneys. Several cases of sex reversal of XY males have been reported. Radiographs confirm the bowing and often show hypoplasia of the scapulae and pelvic bones (Fig. 689-1). Affected infants usually die of respiratory distress in the neonatal period. Complications in children and adolescents who survive include short stature with progressive kyphoscoliosis, recurrent apnea and respiratory infections, and learning difficulties.
Cleidocranial Dysplasia
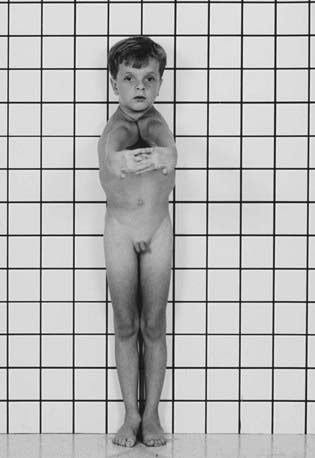
Cleidocranial dysplasia (OMIM 114290) is recognized in infants because of drooping shoulders, open fontanelles, prominent forehead, mild short stature, and dental abnormalities (Fig. 689-2). Radiographs reveal hypoplastic or absent clavicles, delayed ossification of the cranial bones with multiple ossification centers (wormian bones), and delayed ossification of pelvic bones. The course is usually uncomplicated except for dislocations, especially of the shoulders, and dental anomalies (numerous teeth) that require therapy.
Dreyer SD, Zhou G, Baldini A, et al. Mutations in LMX1B cause abnormal skeletal patterning and renal dysplasia in nail patella syndrome. Nat Genet. 1998;19:47-50.
Gimovsky M, Rosa E, Tolbert T, et al. Campomelic dysplasia: case report and review. J Perinatol. 2008;28:71-73.
Granata A, Nori G, Ravazzolo R, et al. Nail-patella syndrome and renal involvement. Description of three cases and literature review. Clin Nephrol. 2008;69:377-382.
Mansour S, Offiah AC, McDowall S, et al. The phenotype of survivors of campomelic dysplasia. J Med Genet. 2002;39:597-602.
Meyer J, Sudbeck P, Held M, et al. Mutational analysis of the sox9 gene in campomelic dysplasia and autosomal sex reversal: lack of genotype/phenotype correlations. Hum Mol Genet. 1997;6:91-98.
Mundlos S, Otto F, Mundlos C, et al. Mutations involving the transcription factor CBFA1 cause cleidocranial dysplasia. Cell. 1997;89:773-779.