Chapter 11 Diseases of the Uterus
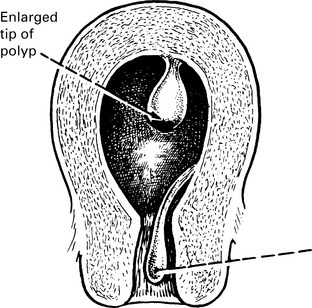
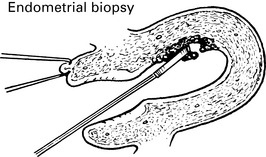
Uterine polyps
Fibroids
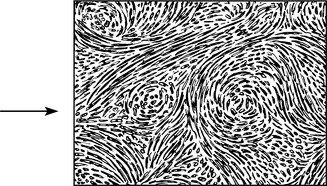
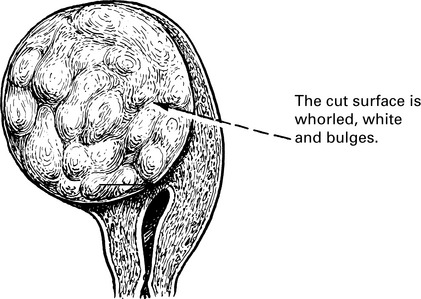
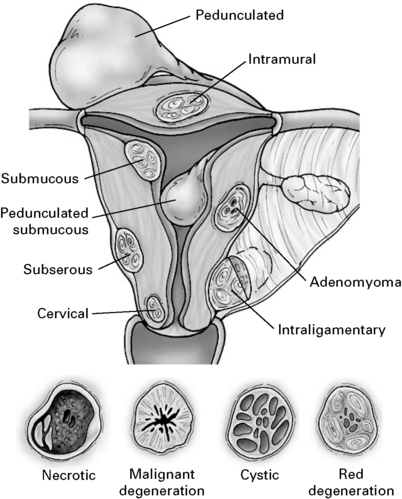
Fibroids (leiomyoma)
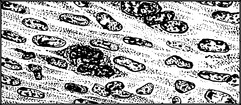
Fibroid is the gynaecological term for a leiomyoma of the uterus or, occasionally, of the cervix.
It is a circumscribed tumour of non-striped muscle with supporting fibrous tissue.
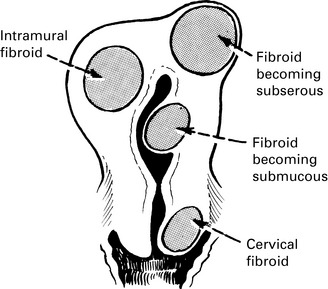
The location of the fibroid describes the type.
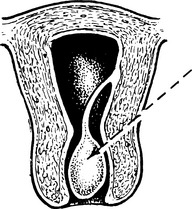
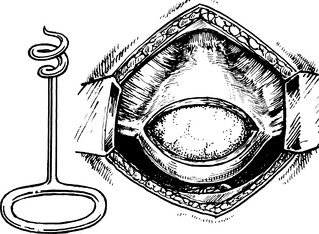
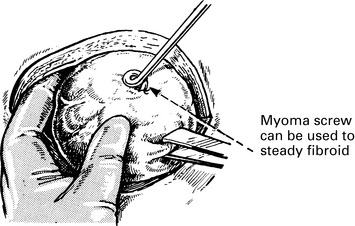
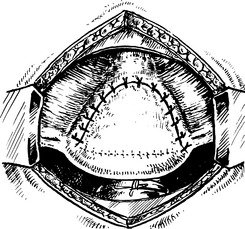
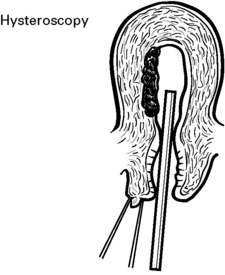
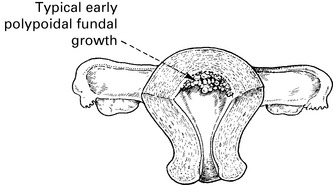
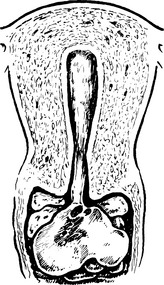
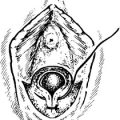
Some fibroids develop a long pedicle and present as polyps.
Pressure symptoms
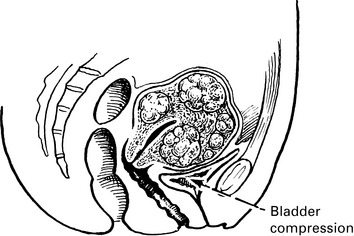
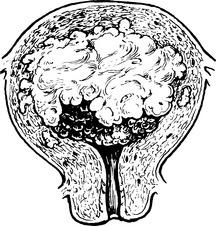
| The bulk of fibroids in the uterus gives |
Urinary frequency
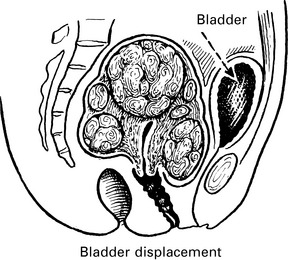
A growth filling the pelvis leading to bladder displacement, retention and overflow and difficulty with defecation.
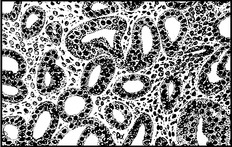
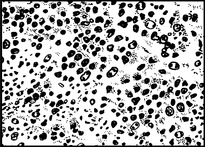
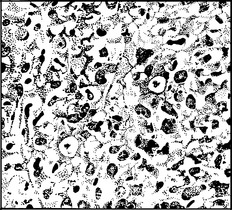
Endometrial hyperplasia
Endometrial hyperplasia may be classified as simple, complex or atypical.
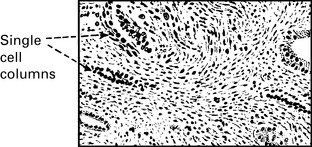
Carcinoma of the endometrium
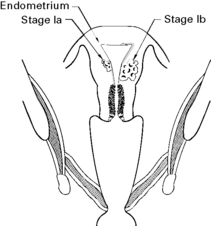
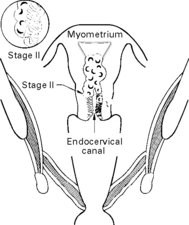
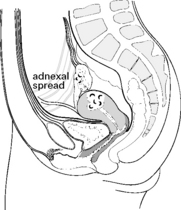
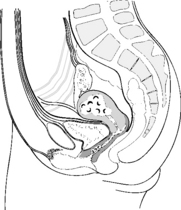
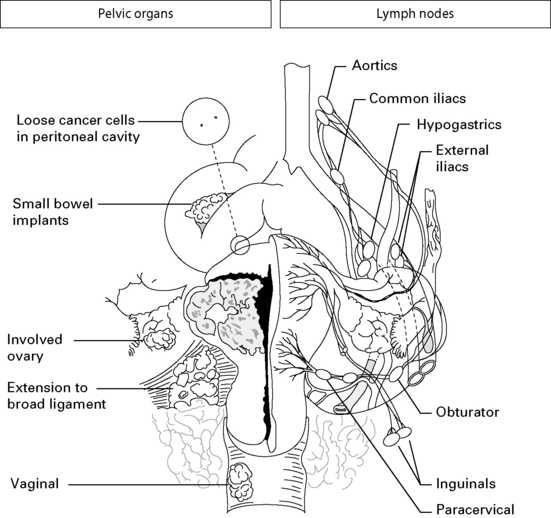
Staging of endometrial carcinoma
B Growth into the outer half of the uterus
The growth has extended to the cervix.
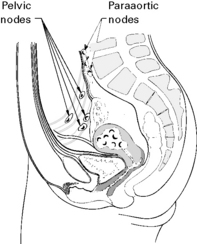
C Pelvic or paraaortic lymph nodes
Histological grading, G1, G2 or G3 is applied to Stages I, II and III only.
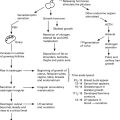
Aetiological factors in endometrial carcinoma
There are two suggested types of endometrial carcinoma, based on aetiology.
Type 1 – arising in patients with a background history of oestrogen excess.
Type 2 – arising without evidence of oestrogenic stimulation.
Prognosis of endometrial carcinoma
Lympho-vascular space involvement (LVSI)
5-year survival rates according to clinical staging are as follows:
| Stage | 5-year survival (%) |
|---|---|
| I | 85 |
| II | 75 |
| III | 45 |
| IV | 25 |
| Grading | 5-year survival (%) |
|---|---|
| G1 | 92 |
| G2 | 90 |
| G3 | 81 |
| Stage and histology | 5-year survival (%) |
|---|---|
| I, G1 and 2 | 80 |
| I, G3 | 60 |
Sarcoma of the uterus
These are rare tumours and include:
Endometrial stromal sarcomas
These are tumours of the endometrial stromal cells and form two groups: