7 Diseases of the Aorta
Anatomy of the Aorta
The Aortic Wall
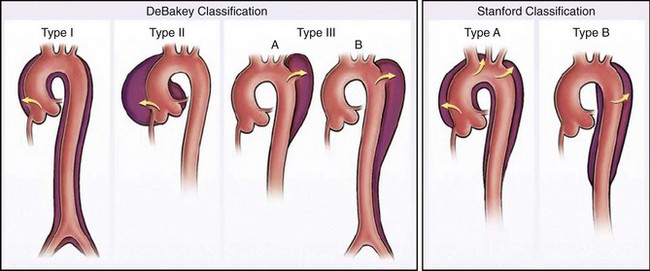
Segmental Anatomy of the Aorta
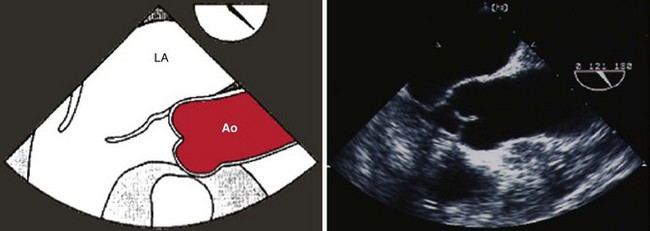
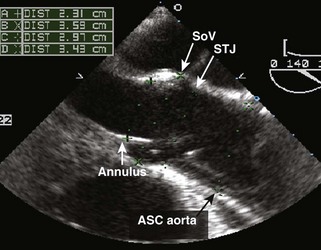
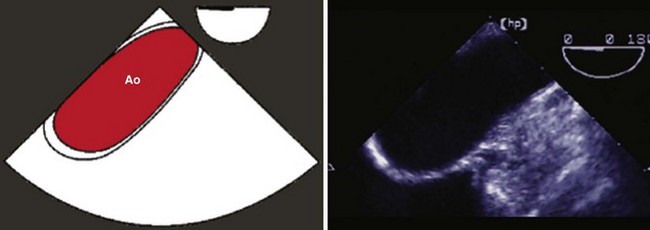
The aortic root consists of the aortic valve annulus, the three aortic valve cusps, the sinuses of Valsalva, and the sinotubular junction where the aortic root joins with the ascending aorta (Figures 7-1 and 7-2).
The aortic arch is the segment containing the origin of the aortic arch branch vessels, the innominate artery, the left carotid artery, and the left subclavian artery (Figures 7-5 and 7-6).
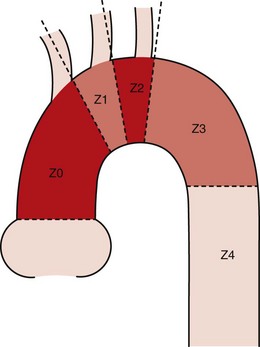
Segmental Anatomy of the Aorta for Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair (Figure 7-9)
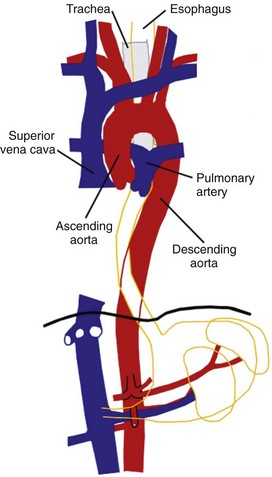
Position of the Aorta in Relation to the Esophagus and Other Structures
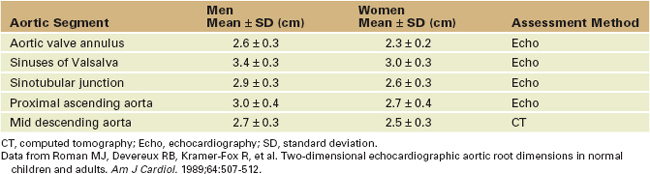
The Normal Size of the Aorta
Step-By-Step Approach to Transesophageal Echocardiographic Imaging of the Thoracic Aorta (Box 7-1)
Step 1: Image the Aortic Valve in Short Axis
BOX 7-1 Comprehensive Reporting of the Transesophageal Echocardiographic Examination of the Thoracic Aorta
Step 2: Image the Aortic Valve in Long Axis (see Figure 7-1)
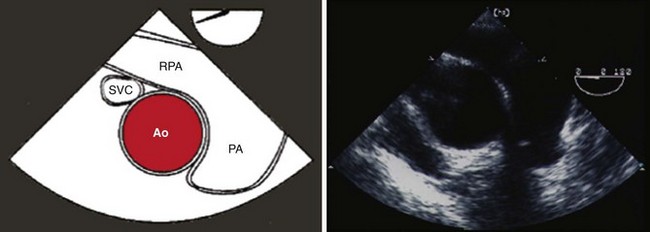
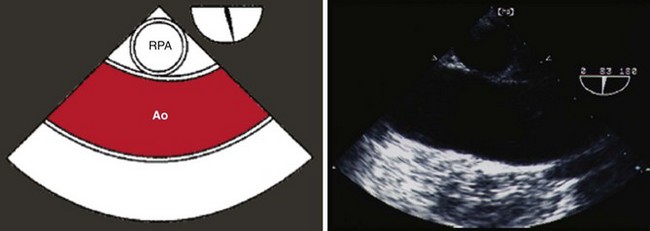
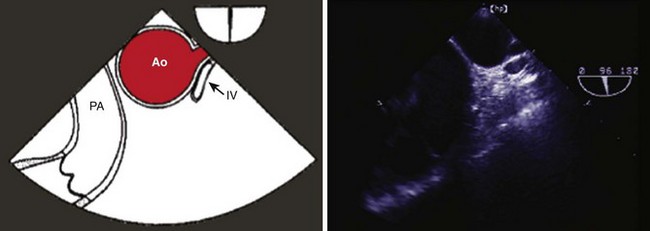
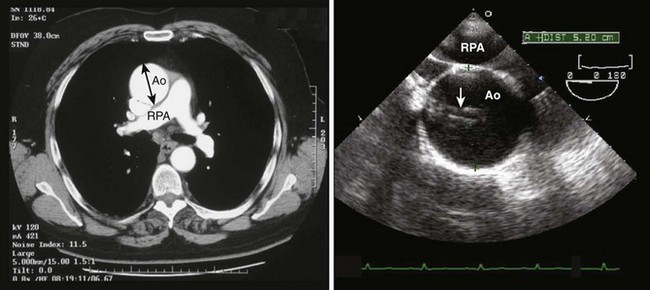
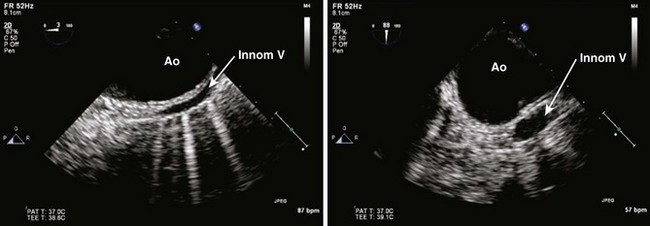
Step 3: Image the Proximal Ascending Aorta in Short Axis at the Level of the Right Pulmonary Artery
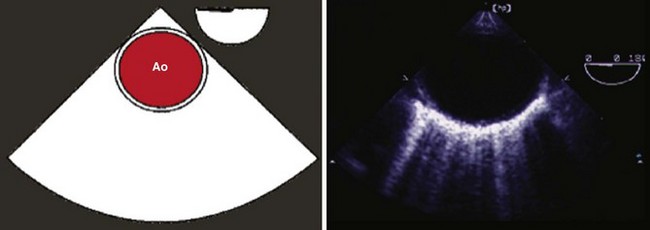
Step 6: Image the Descending Thoracic Aorta in Long Axis
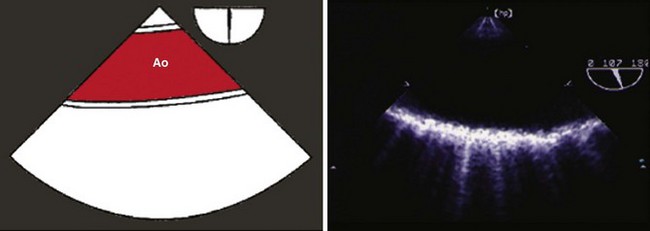
Step 7: Image the Distal Aortic Arch
Echocardiographic Imaging Artifacts
Linear Artifacts
Side Lobe Artifacts
Mirroring Artifacts
Key Points Echocardiographic Imaging Pitfalls
Aortic Diseases
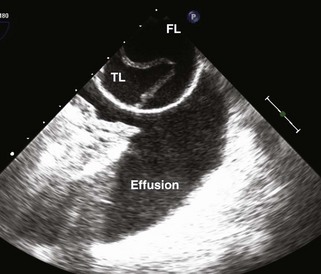
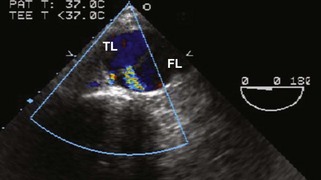
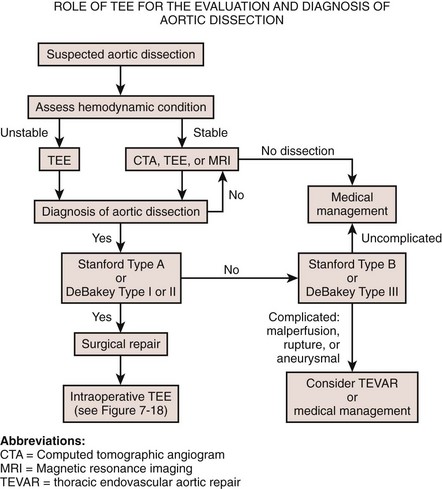
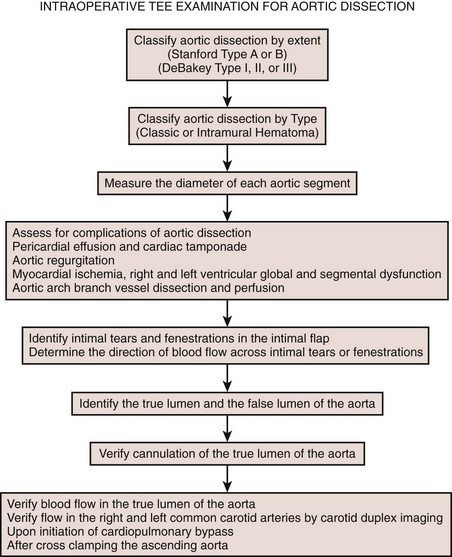
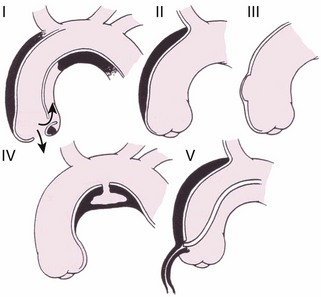
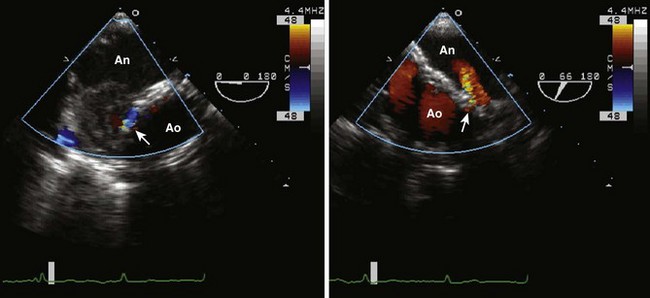
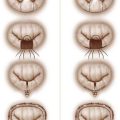
Aortic Dissection
Key Points
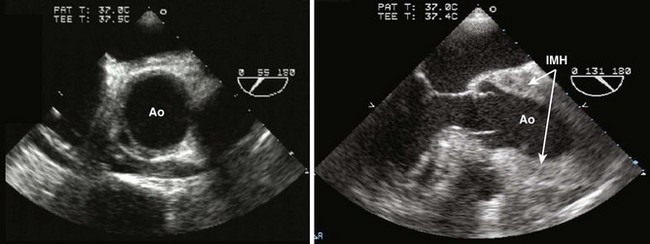
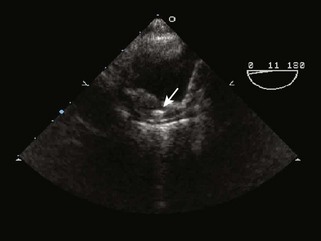
Intramural Hematoma
Echocardiographic Diagnosis of Complications of Aortic Dissection
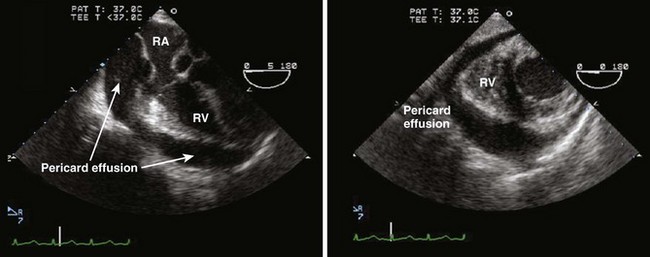
Cardiac Tamponade
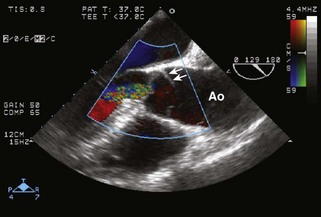
Aortic Regurgitation
Coronary Artery Malperfusion
Carotid Artery Malperfusion
Cardiopulmonary Bypass
Aortic Aneurysm
TABLE 7-2 INDICATIONS FOR SURGICAL REPAIR FOR THORACIC AORTIC ANEURYSM ACCORDING TO DISEASE CHARACTERISTICS AND AORTIC DIAMETER
| Conditions | Indication for Surgical Repair |
|---|---|
| Degenerative aneurysm | Asc Ao ≥ 5.5 cm |
| Asc Ao < 5.5 cm and growth rate > 0.5 cm/yr | |
| Desc Ao > 6.0 cm | |
| Desc Ao > 5.5 cm and candidate for TEVAR | |
| Saccular aneurysm | |
| Pseudoaneurysm | |
| Marfan’s | Asc Ao 4.0-5.0 cm |
| Ehlers-Danlos | Asc Ao 4.0-5.0 cm and family history of aortic dissection |
| Turner’s | Asc Ao 4.0-5.0 cm and rapidly expanding aneurysm |
| Bicuspid aortic valve | Asc Ao 4.0-5.0 cm and planned pregnancy |
| Familial TAA | Asc Ao 4.0-5.0 cm and significant aortic regurgitation |
| Familial dissection | Desc Ao > 5.5 cm |
| Loeys-Dietz syndrome | Asc Ao ≥ 4.2 cm by TEE |
| Asc Ao ≥ 4.4 cm by CT or MRI | |
| Aortic valve repair or replacement | Asc Ao > 4.5 cm |
Asc Ao, ascending aortic diameter; CT, computed tomography; Desc Ao, descending aortic diameter; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; TAA, thoracic aortic aneurysm; TEVAR, thoracic endovascular aortic repair.
Adapted from Hiratzka LF, Bakris GL, Beckman JA, et al. 2010 ACC/AHA/AATS/ACR/ASA/SCA/SCAI/SIR/STS/SVM Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of patients with thoracic aortic disease. Circulation. 2010;121:e266-e369.
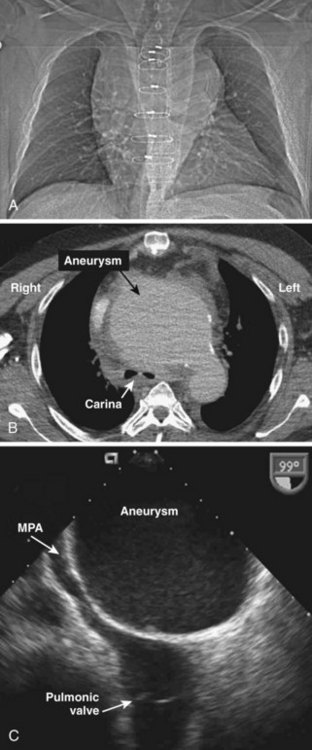
Giant Ascending Aortic or Aortic Arch Aneurysms
Endovascular Aortic Repair
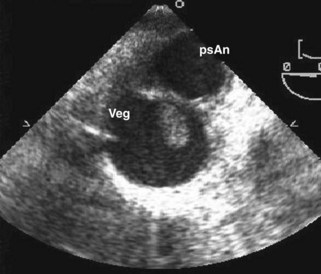
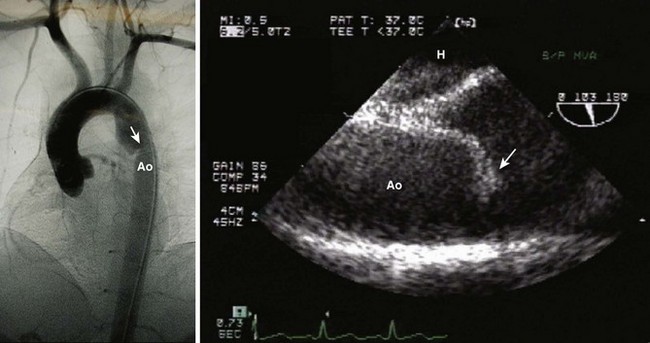
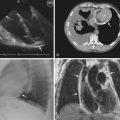
Traumatic Aortic Injury
Key Points
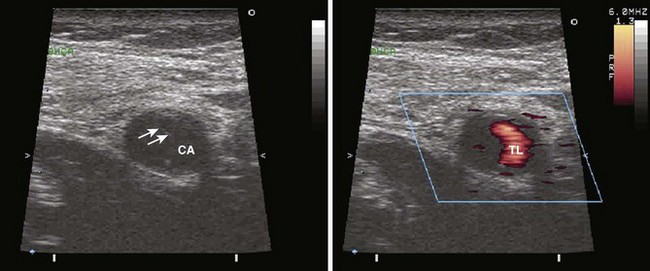
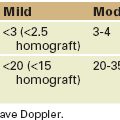
Aortic Atherosclerosis
TABLE 7-3 GRADING OF AORTIC ATHEROSCLEROSIS BY TRANSESOPHAGEAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY
| Grade | Severity | Description |
|---|---|---|
| I | Normal | Normal to mild intimal thickening |
| II | Mild | Intimal thickening ≤ 3 mm without irregularities |
| III | Moderate | Sessile atheroma protruding < 5 mm into the lumen |
| IV | Severe | Sessile atheroma protruding ≥ 5 mm into the lumen |
| V | Severe | Any size atheroma with mobile components |
Adapted from Katz ES, Tunick PA, Rusinek H, et al. Protruding aortic atheromas predict stroke risk in elderly patients undergoing cardiopulmonary bypass: experience with intraoperative transesophageal echocardiography. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1992;20:70-77.
Key Points
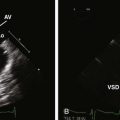
Aortic Coarctation
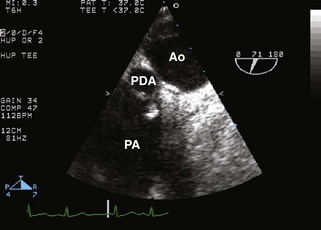
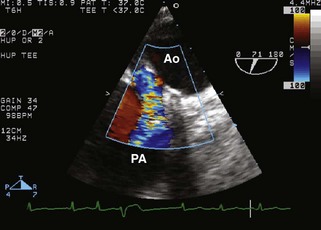
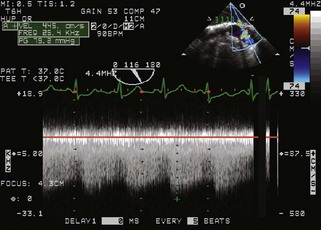
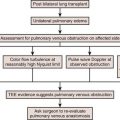
Patent Ductus Arteriosus
Aortic Tumors and Masses
Thrombus
1 Shanewise JS, Cheung AT, Aronson S, et al. ASE/SCA guidelines for performing a comprehensive intraoperative multiplane transesophageal echocardiography examination: Recommendations of the American Society of Echocardiography Council for Intraoperative Echocardiography and the Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists Task Force for Certification in Perioperative Transesophageal Echocardiography. Anesth Analg. 1999;89:870-884.
2 Pantin EJ, Cheung AT. Transesophageal echocardiographic evaluation of the aorta and pulmonary artery. In: Konstadt S, Shernan S, Oka Y, editors. Clinical Transesophageal Echocardiography: A Problem-Oriented Approach. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2003:215-244.
3 Hiratzka LF, Bakris GL, Beckman JA, et al. 2010 ACCF/AHA/AATS/ACR/ASA/SCA/SCAI/SIR/STS/SVM guidelines for the diagnosis and management of patients with thoracic aortic disease: A report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines, American Association for Thoracic Surgery, American College of Radiology, American Stroke Association, Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists, Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, Society of Interventional Radiology, Society of Thoracic Surgeons, and Society for Vascular Medicine. Circulation. 2010;121:e266-e369.
4 Coady MA, Ikonomidis JS, Cheung AT, et al. on behalf of the American Heart Association. Surgical management of descending thoracic aortic disease: Open and endovascular approaches. A scientific statement from the American Heart Council on Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia and Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease. Circulation. 2010;121:2780-2804.
5 Erbel R, Alfonso F, Boileau C, et al. Diagnosis and management of aortic dissection: Recommendations of the Task Force on Aortic Dissection, European Society of Cardiology. Eur Heart J. 2001;22:1642-1681.
6 Glas KE, Swaminathan M, Reeves ST, et al. Council for Intraoperative Echocardiography of the American Society of Echocardiography. Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists. Guidelines for the performance of a comprehensive intraoperative epiaortic ultrasonographic examination: Recommendations of the American Society of Echocardiography and the Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists; endorsed by the Society of Thoracic Surgeons. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2007;20:1227-1235.
7 Nienaber CA, Eagle KA. Aortic dissection: New frontiers in diagnosis and management: Part I: From etiology to diagnostic strategies. Circulation. 2003;108:628-635.
8 Moore AG, Eagle KA, Bruckman D, et al. Choice of computed tomography, transesophageal echocardiography, magnetic resonance imaging, and aortography in acute aortic dissection: International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissection (IRAD). Am J Cardiol. 2002;89:1235-1238.
9 Movsowitz HD, Levine RA, Hilgenberg AD, et al. Transesophageal echocardiographic description of the mechanisms of aortic regurgitation in acute type A aortic dissection: Implications for aortic valve repair. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000;36:884-890.
10 Nienaber CA, Kodolitsch Y, Petresen B, et al. Intramural hemorrhage of the thoracic aorta: Diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Circulation. 1995;92:1465-1472.
11 Mohr-Kahaly S, Erbel R, Kearney P, et al. Aortic intramural hemorrhage visualized by transesophageal echocardiography: Findings and prognostic implications. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1994;23:658-664.
12 von Kodolitsch Y, Csösz SK, Koschyk DH, et al. Intramural hematoma of the aorta: Predictors of progression to dissection and rupture. Circulation. 2003;107:1158-1163.
13 Shiga T, Wajima Z, Apfel CC, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of transesophageal echocardiography, helical computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging for suspected thoracic aortic dissection: systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166:1350-1356.
14 Vignon P, Boncoeur MP, Francois B, et al. Comparison of multiplane transesophageal echocardiography and contrast-enhanced helical CT in the diagnosis of blunt traumatic cardiovascular injuries. Anesthesiology. 2001;94:615-622.
15 Vignon P, Gueret P, Vedrinne JM, et al. Role of transesophageal echocardiography in the diagnosis and management of traumatic aortic disruption. Circulation. 1995;92:2959-2968.
16 Appelbe AF, Walker PG, Yeoh JK, et al. Clinical significance and origin of artifacts in transesophageal echocardiography of the thoracic aorta. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1993;21:754-760.
17 Vignon P, Spencer KT, Rambaud G, et al. Differential transesophageal echocardiographic diagnosis between linear artifacts and intraluminal flap of aortic dissection and disruption. Chest. 2001;119:1778-1790.
18 Katz ES, Tunick PA, Rusinek H, et al. Protruding aortic atheromas predict stroke in elderly patients undergoing cardiopulmonary bypass: Experience with intraoperative transesophageal echocardiography. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1992;20:70-77.
19 Hartman GS, Yao FF, Bruefach MIII, et al. Severity of aortic atheromatous disease diagnosed by transesophageal echocardiography predicts stroke and other outcomes associated with coronary artery surgery: A prospective study. Anesth Analg. 1996;83:701-708.
20 Desai ND, Szeto WY. Complex aortic arch aneurysm and dissections: Hybrid techniques for surgical and endovascular therapy. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2009;24:521-527.
21 Gutsche JT, Cheung AT, McGarvey ML, et al. Risk factors for perioperative stroke after thoracic endovascular aortic repair. Ann Thorac Surg. 2007;84:1195-1200.
22 Swaminathan M, Mackensen GB, Podgoreanu MV, et al. Spontaneous echocardiographic contrast indicating successful endoleak management. Anesth Analg. 2007;104:1037-1039.
Three nice papers describing the diagnostic approach and imaging in endovascular aortic repair.