Chapter 43 Diathermy
OVERVIEW.
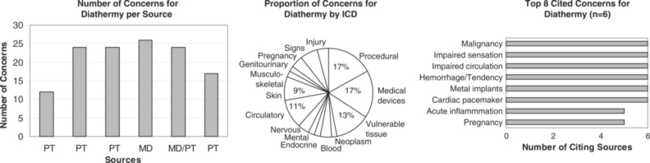
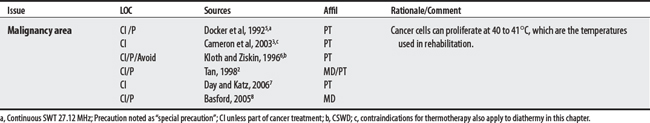
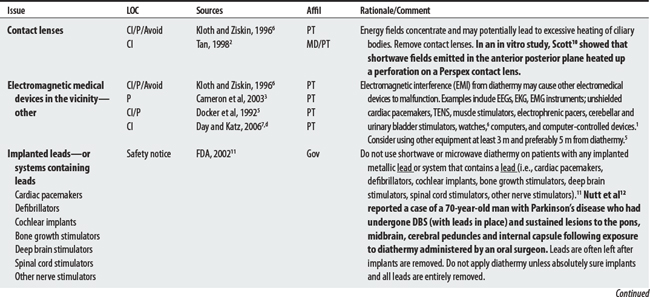
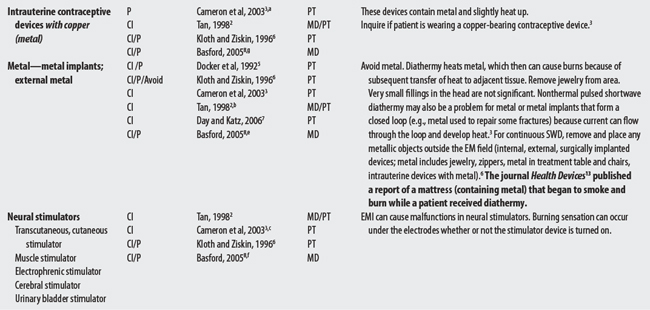
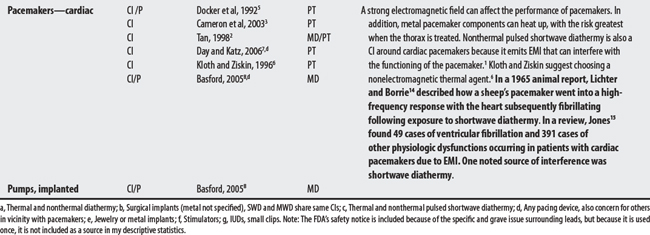
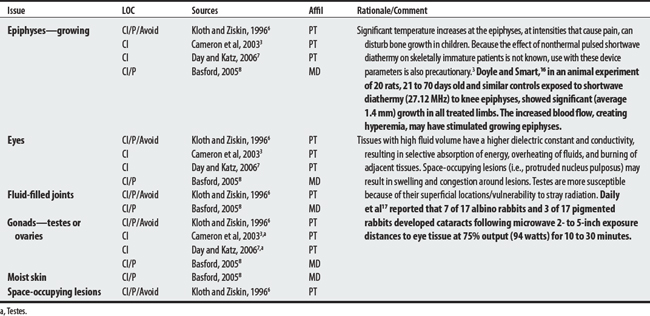
Diathermy (or “through heating”) employs physical agents that convert high-frequency electric current or electromagnetic waves to deep heat to promote healing.1–3 Heat is generated in tissue by its resistance to the passage of the high-frequency EM energy.4 Shortwave diathermy converts non-ionizing radiation (radio waves) between 10 and 100 MHz, with a commonly used frequency at 2712 MHz, to deep-heat tissue. Microwave diathermy uses non-ionizing electromagnetic radiation between 300 and 300,000 MHz with a commonly used frequency of 2450 MHz.1–3 Note: Sound waves may also be considered a form of diathermy but are discussed elsewhere (see Therapeutic ultrasound).
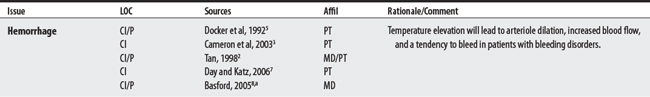
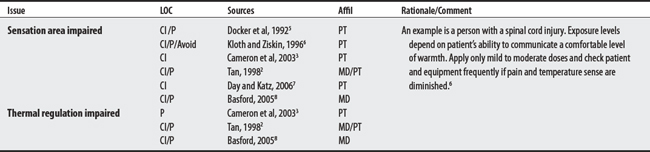
CONTRAINDICATIONS AND PRECAUTIONS
D50-D89 DISEASES OF BLOOD AND BLOOD-FORMING ORGANS, AND CERTAIN DISORDERS
E00-E90 ENDOCRINE, NUTRITIONAL, AND METABOLIC DISEASES
F00-F99 MENTAL AND BEHAVIORAL DISORDERS
G00-99 DISEASES OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
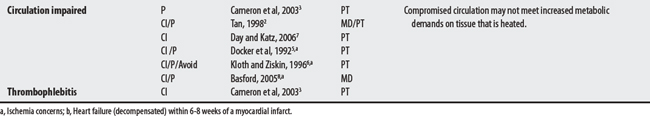
I00-I99 DISEASES OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
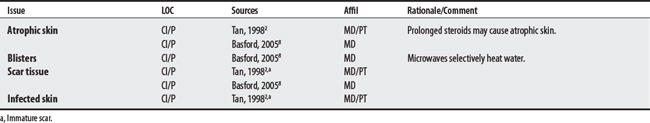
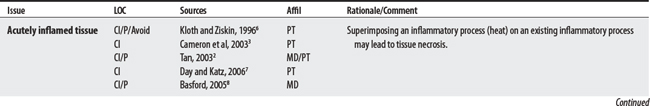
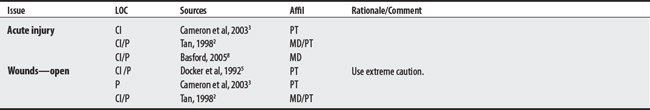
L00-L99 DISEASES OF THE SKIN AND SUBCUTANEOUS TISSUE
M00-M99 DISEASES OF THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE
N00-N99 DISEASES OF THE GENITOURINARY SYSTEM
1 Eisenberg MG. Dictionary of rehabilitation. New York: Springer, 1995.
2 Tan JC. Practical manual of physical medicine and rehabilitation: diagnostics, therapeutics, and basic problems. St. Louis: Mosby, 1998.
3 Cameron MH, Perez D, Otáno-Lata S. Electromagnetic radiation. In: Cameron MH, editor. Physical agents in rehabilitation: from research to practice. St. Louis: Saunders; 2003:369-413.
4 Prentice WE, Draper DO. Shortwave and microwave diathermy. In Prentice WE, editor: Therapeutic modalities for physical therapists, ed 2, New York: McGraw-Hill, 2002.
5 Docker M, Bazin S, Dyson M, et al. Guidelines for the safe use of continuous shortwave therapy equipment. Physiotherapy. 1992;78:755-757.
6 Kloth LC, Ziskin MC. Diathermy and pulsed radio frequency radiation. In Michlovitz SL, editor: Thermal agents in rehabilitation, ed 3, Philadelphia: F.A. Davis, 1996.
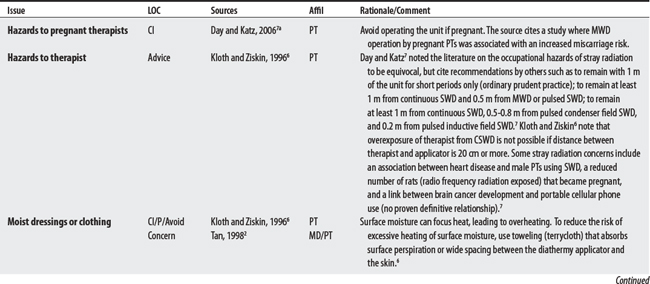
7 Day MJ, Katz JS. Diathermy. In: Hecox B, Mehreteab TA, Weisberg J, editors. Integrating physical agents in rehabilitation. Upper Saddle River (NJ): Pearson Prentice Hall, 2006.
8 Basford JR. Therapeutic physical agents. Delisa JA, editor. Physical medicine and rehabilitation: principles and practices, ed 4, vol 1. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2005.
9 Rubin A, Erdman WJ. Microwave exposure of the human female pelvis during early pregnancy and prior to conception. Am J Phys Med. 1959;38:219-220.
10 Scott BO. Effects of contact lenses on shortwave field distribution. Br J Ophthalmol. 1956;40:696-697.
11 U.S. Food and Drug Administration. FDA Public Health Notification: Diathermy Interactions with Implanted Leads and Implanted Systems with Leads. Available at: http://www.fda.gov/cdrh/psn/show4.html. Accessed November 14, 2005
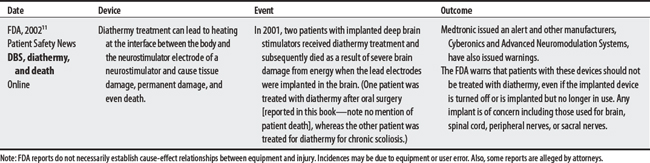
12 Nutt JG, Anderson VC, Peacock JH, et al. DBs and diathermy interaction induces severe CNS damage. Neurology. 2001;56:1384-1386.
13 Shortwave diathermy units. Health Dev. 1988;17(8):247.
14 Lichter I, Borrie J. Radio-frequency hazards with cardiac pacemakers. BMJ. 1965;5449(1):1513-1518.
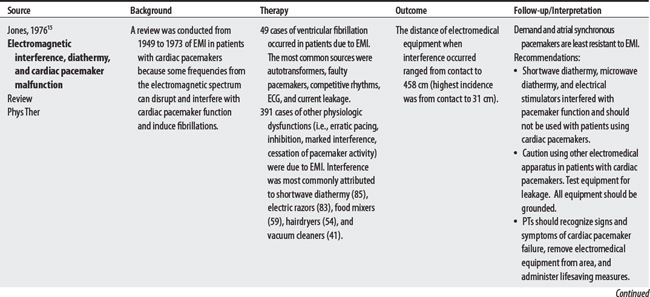
15 Jones SL. Electromagnetic field interference and cardiac pacemakers. Phys Ther. 1976;56(9):1013-1018.
16 Doyle JR, Smart BW. Stimulation of bone growth by shortwave diathermy. J Bone Joint Surg. 1963;45A:15-24.
17 Daily LJr, Wakim KG, Herrick JF, et al. The effect of microwave diathermy on the eye: an experimental study. Am J Ophthalmol. 1952;35:1001-1017.
18 Arledge RL. Prevention of electric shock hazards in physical therapy. Phys Ther. 1978;58(10):1215-1217.