CHAPTER 11 DERMATOPATHOLOGY
APPROACH TO PEDIATRIC SKIN BIOPSY INTERPRETATION
SPECIFIC ENTITIES IN PEDIATRIC DERMATOPATHOLOGY
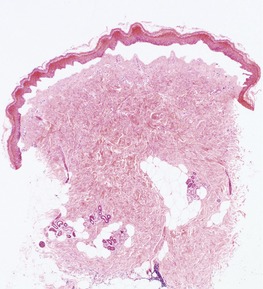
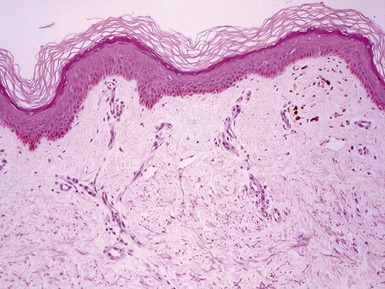
CUTIS LAXA
Genetics
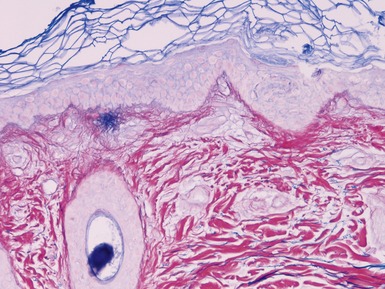
FOCAL DERMAL HYPOPLASIA (GOLTZ SYNDROME)
Clinical features
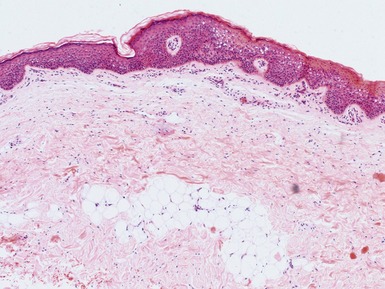
RESTRICTIVE DERMOPATHY
ICHTHYOSES
Introduction
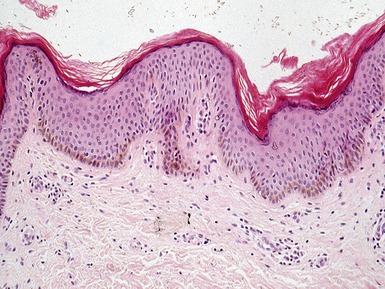
ICHTHYOSIS VULGARIS
X-LINKED RECESSIVE ICHTHYOSIS
LAMELLAR ICHTHYOSIS / CONGENITAL ICHTHYOSIFORM ERYTHRODERMA (NON-BULLOUS ICHTHYOSIFORM ERYTHRODERMA)
Clinical features
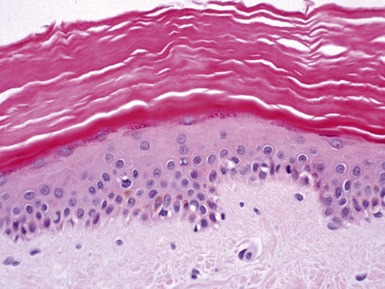
BULLOUS ICHTHYOSIFORM ERYTHRODERMA / EPIDERMOLYTIC HYPERKERATOSIS
Genetics
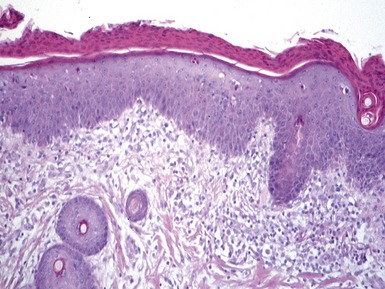
SJÖGREN–LARSSON SYNDROME
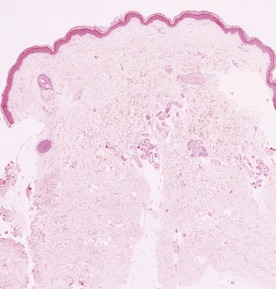
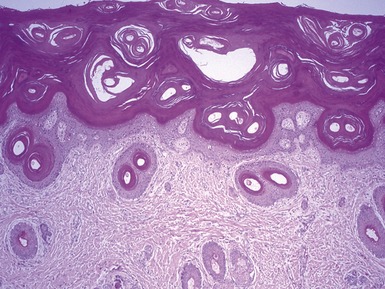
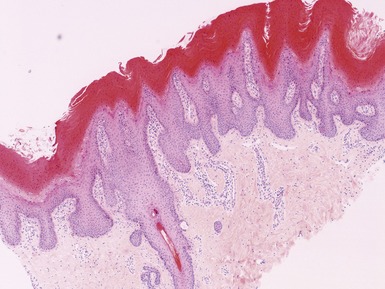
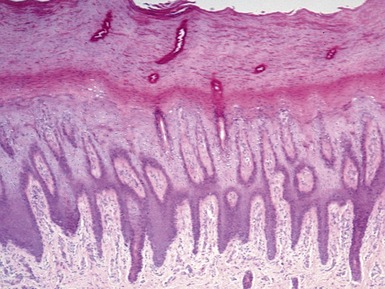
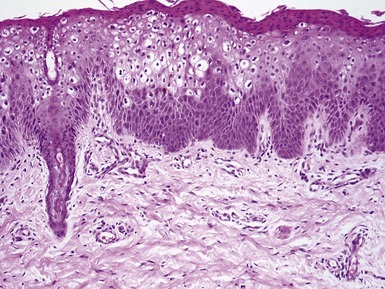
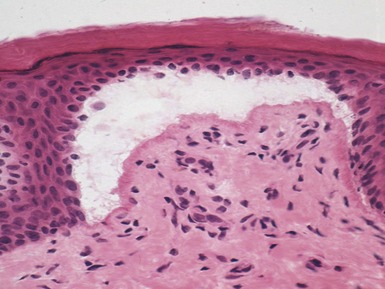
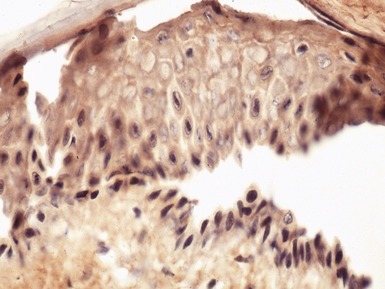
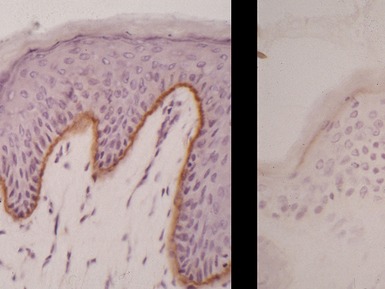
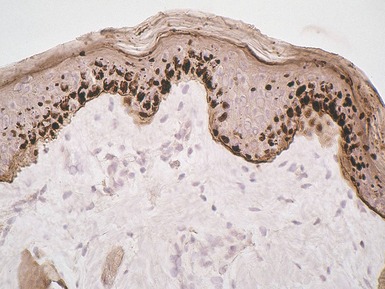
Histopathological features (Figs 11.14, 11.15)
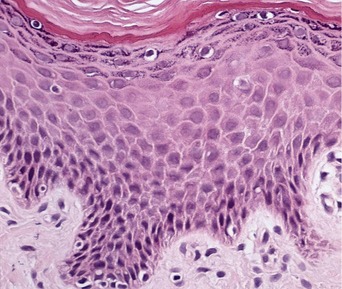
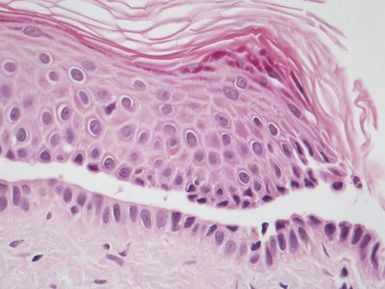
Fig 11.14 Photomicrograph of skin biopsy from a patient with Sjogren–Larsson syndrome demonstrating papillomatosis, acanthosis, hyperkeratosis and thickening of the granular layer.
NEUTRAL LIPID STORAGE DISEASE
NETHERTON’S SYNDROME
Clinical features
OMENN SYNDROME
KID SYNDROME (KERATITIS, ICHTHYOSIS AND DEAFNESS)
CONRADI–HUNERMANN–HAPPLE SYNDROME
CHILD SYNDROME (CONGENITAL HEMIDYSPLASIA WITH ICHTHYOSIFORM ERYTHRODERMA AND LIMB DEFECTS)
HEREDITARY PALMO-PLANTAR KERATODERMAS (PPKs)
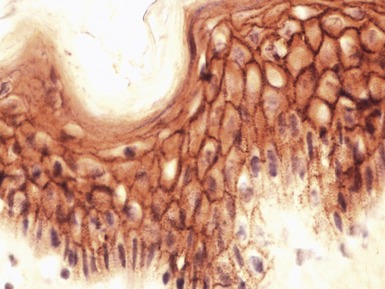
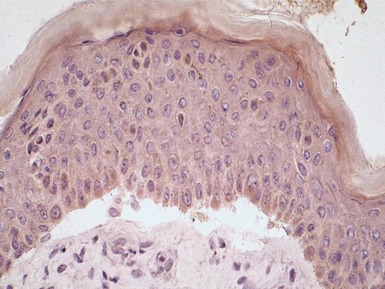
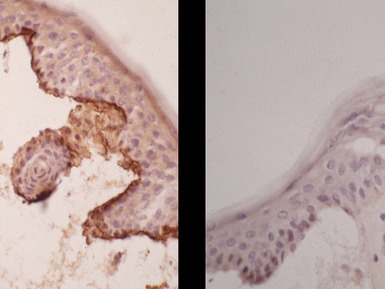
Histopathological features (Figs 11.23, 11.24)
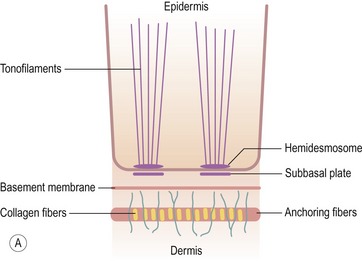
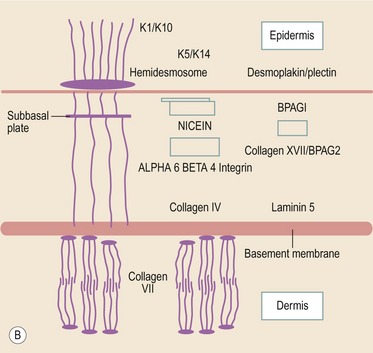
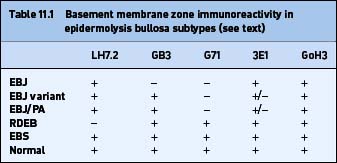
EPIDERMOLYSIS BULLOSA
Introduction
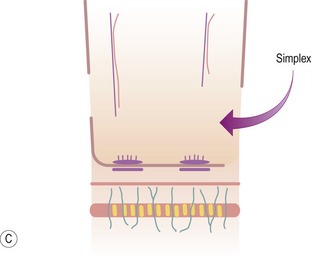
EPIDERMOLYSIS BULLOSA SIMPLEX
Clinical features
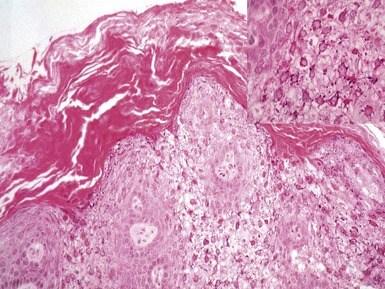
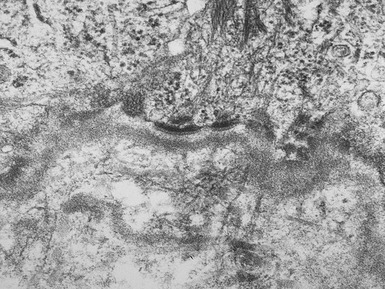
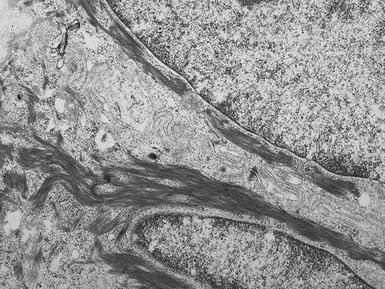
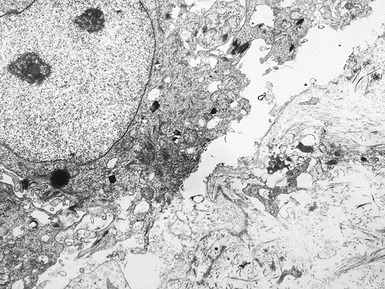
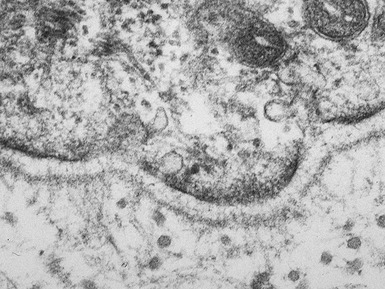
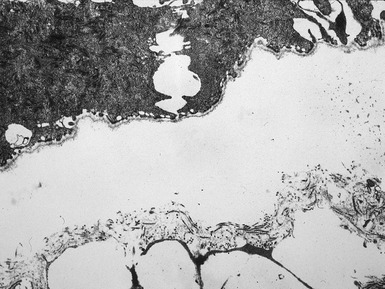
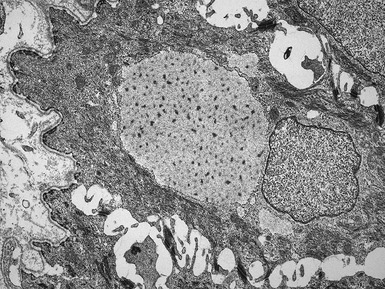
Histopathological features (Figs 11.27–11.35)
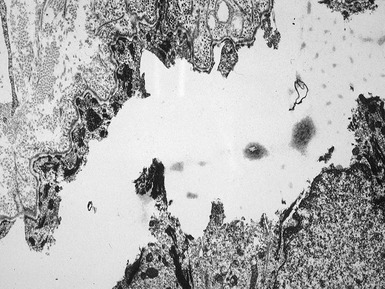
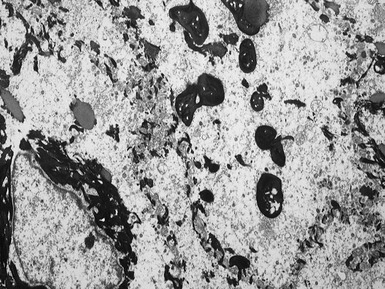
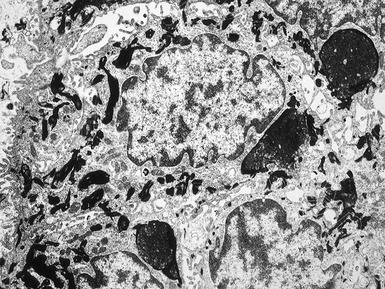
Fig 11.30 Electron micrograph of a skin biopsy from a patient with epidermolysis bullosa simplex demonstrating that the split is within the basal keratinocyte. A fragment of the keratinocyte can be seen in the lower part of the split.
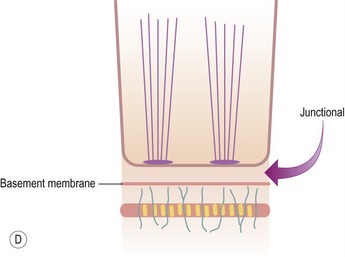
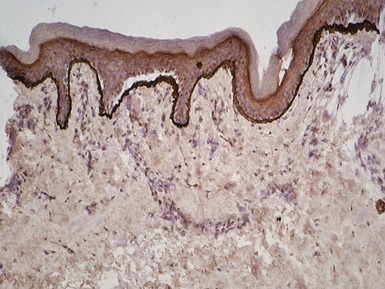
JUNCTIONAL EPIDERMOLYSIS BULLOSA
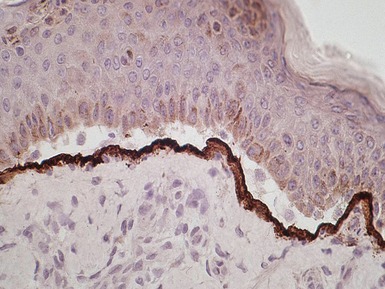
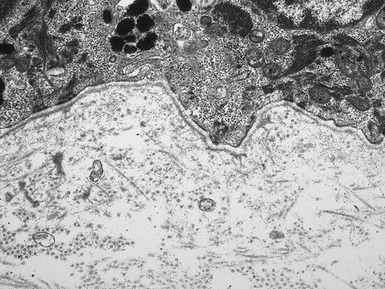
Histopathological features (Figs 11.36–11.43)
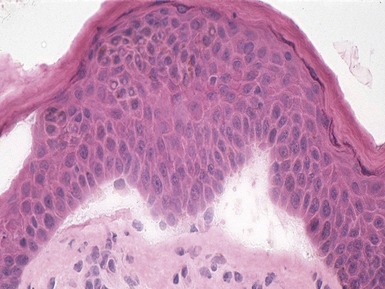
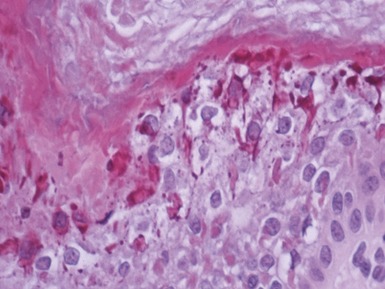
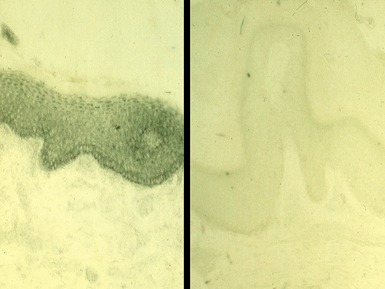
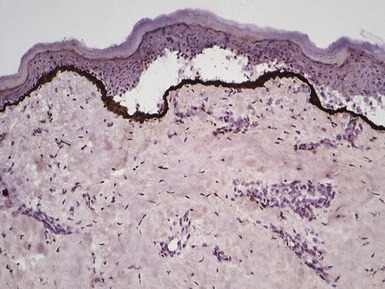
Fig 11.36 Photomicrograph of a frozen section of a skin biopsy from a patient with junctional epidermolysis bullosa demonstrating a split between the epidermis and the dermis.
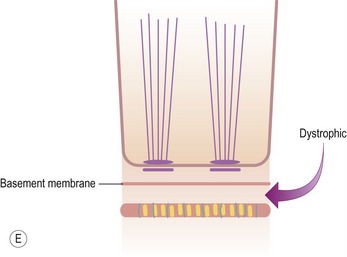
DYSTROPHIC EPIDERMOLYSIS BULLOSA
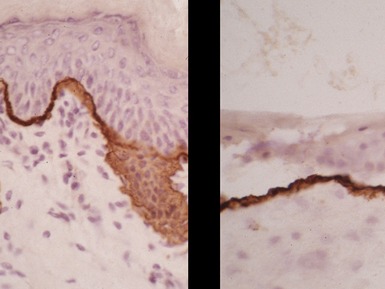
Histopathological features (Figs 11.44–11.49)
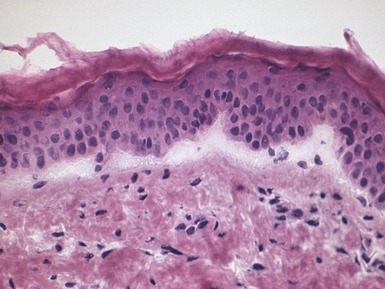
Fig 11.44 Photomicrograph of a frozen section of a skin biopsy from a patient with dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa demonstrating a split between the epidermis and the dermis.