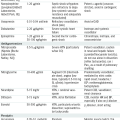
Pain localized to the dermatome that will be affected by the skin lesions → precedes skin manifestation by 3-5 days.
Pain localized to the dermatome that will be affected by the skin lesions → precedes skin manifestation by 3-5 days. Rash: erythematous maculopapules affecting one dermatome → maculopapules evolve into vesicles and pustules of various sizes (a distinguishing characteristic from HSV, in which the vesicles are of uniform size) by the 4th day → vesicles subsequently become umbilicated and then form crusts that generally fall off within 3 wk.
Rash: erythematous maculopapules affecting one dermatome → maculopapules evolve into vesicles and pustules of various sizes (a distinguishing characteristic from HSV, in which the vesicles are of uniform size) by the 4th day → vesicles subsequently become umbilicated and then form crusts that generally fall off within 3 wk. Ramsay Hunt syndrome: involvement the trigeminal nerve → painful ear, w/vesicles on the pinna and external auditory canal, facial palsy.
Ramsay Hunt syndrome: involvement the trigeminal nerve → painful ear, w/vesicles on the pinna and external auditory canal, facial palsy.Treatment
 PO antivirals can ↓ acute pain, inflammation, and vesicle formation when Rx is begun within 72 hr of onset of rash. Rx options are (adjust dose for renal failure):
PO antivirals can ↓ acute pain, inflammation, and vesicle formation when Rx is begun within 72 hr of onset of rash. Rx options are (adjust dose for renal failure):• Valacyclovir 1000 mg × 7 days
• Famciclovir 500 mg tid × 7 days
• Acyclovir 800 mg 5× qd × 7-10 days
 Immunocompromised pts: IV acyclovir 10 mg/kg q8h (infusion over 1 hr ) for 7-14 days
Immunocompromised pts: IV acyclovir 10 mg/kg q8h (infusion over 1 hr ) for 7-14 days Consider adding prednisone in pts >50 yr old within 72 hr of clinical presentation or if new lesions are still appearing. Initial dose is prednisone 40 mg/day ↓ by 5 mg/day until finished. Corticosteroids ↓ in the use of analgesics and time to resumption of usual activities, but there is no effect on the incidence and duration of postherpetic neuralgia.
Consider adding prednisone in pts >50 yr old within 72 hr of clinical presentation or if new lesions are still appearing. Initial dose is prednisone 40 mg/day ↓ by 5 mg/day until finished. Corticosteroids ↓ in the use of analgesics and time to resumption of usual activities, but there is no effect on the incidence and duration of postherpetic neuralgia. Postherpetic neuralgia Rx:
Postherpetic neuralgia Rx:• Gabapentin 100-600 mg tid
• Lidocaine patch 5% applied to intact skin to cover the most painful area for up to 12 hr within a 24-hr period
Vaccination
 Immunocompetent adults ≥50 yr old: single dose of varicella-zoster vaccine (VZV, Zostavax)
Immunocompetent adults ≥50 yr old: single dose of varicella-zoster vaccine (VZV, Zostavax) Adults who are VZV sero(−) (never had varicella): immunize w/2 doses of varicella vaccine (Varivax).
Adults who are VZV sero(−) (never had varicella): immunize w/2 doses of varicella vaccine (Varivax).B. Pressure Ulcers
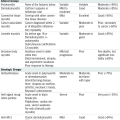
 Stage I: Nonblanchable erythema of intact skin and/or boggy, mushy texture.
Stage I: Nonblanchable erythema of intact skin and/or boggy, mushy texture. Stage II: Partial-thickness skin loss involving the epidermis and/or dermis. May also manifest as an intact or ruptured serum-filled blister.
Stage II: Partial-thickness skin loss involving the epidermis and/or dermis. May also manifest as an intact or ruptured serum-filled blister. Stage III: Full-thickness loss/damage or necrosis of subcutaneous tissue that may extend down to underlying fascia/muscle. Possible undermining/tunneling.
Stage III: Full-thickness loss/damage or necrosis of subcutaneous tissue that may extend down to underlying fascia/muscle. Possible undermining/tunneling. Stage IV: Full-thickness skin loss with exposed muscle, bone, or joint capsule. Sloughing or eschar may be present, often with undermining/tunneling.
Stage IV: Full-thickness skin loss with exposed muscle, bone, or joint capsule. Sloughing or eschar may be present, often with undermining/tunneling. Deep tissue injury: Purple/maroon localized area of discolored, intact skin or blood-filled blister resulting from damage of underlying tissue from pressure and/or shear.
Deep tissue injury: Purple/maroon localized area of discolored, intact skin or blood-filled blister resulting from damage of underlying tissue from pressure and/or shear. Unstageable: Full-thickness tissue loss with the base of the ulcer covered by slough or eschar in wound bed.
Unstageable: Full-thickness tissue loss with the base of the ulcer covered by slough or eschar in wound bed.Treatment
 ↓ Prolonged skin exposure to moisture, urine, or stool. Rx dry, cracking skin.
↓ Prolonged skin exposure to moisture, urine, or stool. Rx dry, cracking skin. Use repositioning and pressure-reducing devices for support while in bed or chair.
Use repositioning and pressure-reducing devices for support while in bed or chair. Clean at each dressing change; necrotic tissue should be débrided quickly because it delays wound healing (except for heel ulcers).
Clean at each dressing change; necrotic tissue should be débrided quickly because it delays wound healing (except for heel ulcers). ↓ Pressure by using foam mattress, dynamic support surface (e.g., low-air loss bed), and frequent repositioning (e.g., q2h or, in cases of poor perfusion, more frequently).
↓ Pressure by using foam mattress, dynamic support surface (e.g., low-air loss bed), and frequent repositioning (e.g., q2h or, in cases of poor perfusion, more frequently). (−) Pressure devices (Vac devices) help in wounds that have significant drainage.
(−) Pressure devices (Vac devices) help in wounds that have significant drainage. Correct poor nutrition through improved diet.
Correct poor nutrition through improved diet.C. Psoriasis
 Primary psoriatic lesion: erythematous papule topped by a loosely adherent scale. Scraping the scale results in several bleeding points (Auspitz’s sign).
Primary psoriatic lesion: erythematous papule topped by a loosely adherent scale. Scraping the scale results in several bleeding points (Auspitz’s sign). Chronic plaque psoriasis (80% cases): symmetric, sharply demarcated, erythematous, silver-scaled patches affect primarily the intergluteal folds, elbows, scalp, fingernails, toenails, and knees.
Chronic plaque psoriasis (80% cases): symmetric, sharply demarcated, erythematous, silver-scaled patches affect primarily the intergluteal folds, elbows, scalp, fingernails, toenails, and knees. Guttate psoriasis: multiple droplike lesions on the extremities and the trunk are usually preceded by strep pharyngitis.
Guttate psoriasis: multiple droplike lesions on the extremities and the trunk are usually preceded by strep pharyngitis. Psoriasis at the site of any physical trauma (sunburn, scratching) is known as Koebner’s phenomenon.
Psoriasis at the site of any physical trauma (sunburn, scratching) is known as Koebner’s phenomenon. Joint involvement → sacroiliitis, spondylitis.
Joint involvement → sacroiliitis, spondylitis.Treatment
 Limited disease (<20% of the body):
Limited disease (<20% of the body):• Topical steroids
• Calcipotriene (vitamin D analogue)
• Tar products (Estar, LCD, PsoriGel) + UVB light (Goeckerman’s regimen)
• Anthralin + UVB
• Retinoids (tazarotene 0.05%, 0.1% cream or gel)
• Others: tape or occlusive dressing, UVB and lubricating agents, and interlesional steroids
 Generalized disease (affecting >20% of the body)
Generalized disease (affecting >20% of the body)• UVB light exposure 3×/wk
• Oral PUVA administered 2-3×/wk
 Systemic Rxs: methotrexate 25 mg/wk, etretinate, cyclosporine, alefacept, etanercept, efalizumab, adalimumab, ustekinumab, briakinumab
Systemic Rxs: methotrexate 25 mg/wk, etretinate, cyclosporine, alefacept, etanercept, efalizumab, adalimumab, ustekinumab, briakinumab