99
Dermatitis herpetiformis
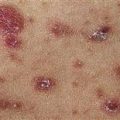
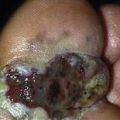
Vesicles appear singly or in clusters and resemble herpes simplex. Patients scratch lesions, making it difficult to find an intact lesion to biopsy.
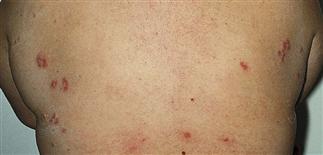
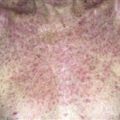
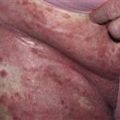
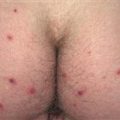
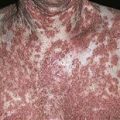
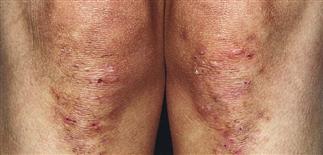
Vesicles are symmetrically distributed and appear on elbows, knees, occipital scalp, shoulders, and buttocks.
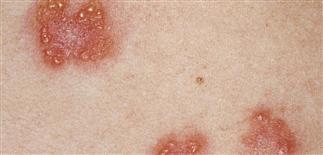
‘Herpetiform’ refers to the typical grouping of vesicles.
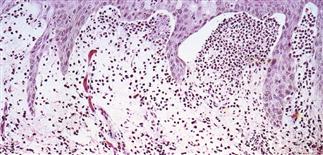
Skin biopsy shows subepidermal clefting and papillary dermal tips stuffed with neutrophils and occasional eosinophils in the upper dermis.
DESCRIPTION
A rare, chronic, intense and unremitting itching and burning, vesicular and bullous dermatosis associated with a gluten-sensitive enteropathy.
HISTORY
• Age of onset usually between the second and fifth decades. • Rare in children. • Prevalence 11–39 per 100 000. • Affects males twice as often as females. • Rare in black and Asian people. • Increased incidence in association with human leukocyte antigens DRw3, B8, and DQw2.
PHYSICAL FINDINGS
• Clustered vesicles and/or excoriations, erythematous or urticarial papules, symmetrically localized to the elbows, knees, sacrum, and occipital scalp. Less often generalized. Oral lesions rare. • Gastrointestinal involvement usually asymptomatic. Severity of skin disease does not correlate with degree of intestinal involvement. Small bowel biopsy shows villous atrophy. Increased risk of small bowel lymphoma and non-intestinal lymphoma. Risk is reduced with gluten-free diet though 100% dietary compliance is difficult to maintain. • Skin biopsy with immunofluorescence recommended for all blistering diseases; shows inflammatory infiltrate of neutrophils and occasional eosinophils in upper dermis. • Direct immunofluorescence of skin biopsy from adjacent normal perilesional skin shows granular or fibrillar IgA deposits in dermal papillae in 90% of cases.
TREATMENT
• Dermatologists are trained well in bullous disorders and the biopsy techniques and tests required for accurate diagnosis. • The goal of therapy is to arrest blister formation and relieve itching. • Oral dapsone 100–150 mg q.d. relieves itching and burning within 48–72 h; maintenance dose varies in the range of 25–200 mg q.d. Check glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase before starting dapsone. • A gluten-free diet can control the disease alone or allow decreased requirement for oral medication.