Chapter 43 Dental/Periodontal Emergencies
2 Which are the first permanent teeth to erupt? Which teeth come next?
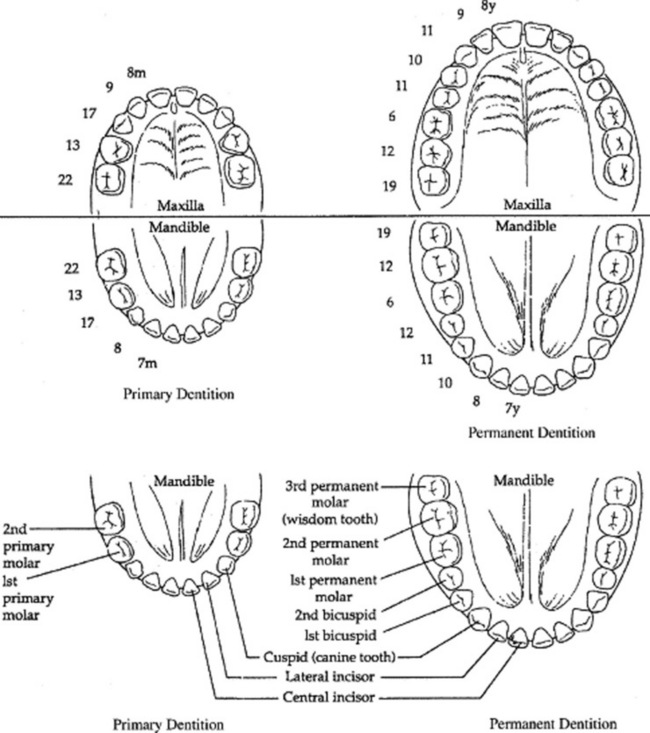
The first permanent teeth to erupt are usually the first permanent molars (“6-year” molars), followed by the mandibular central incisors, maxillary central incisors, lateral incisors, cuspids, and bicuspids. The mixed dentition phase concludes at about age 12 years with the eruption of the second permanent (“12-year”) molars, but the adult complement of 32 teeth is not achieved until the eruption of the third molars (“wisdom” teeth) in late adolescence (Fig. 43-1).
3 What are Epstein’s pearls? How do they differ from Bohn’s nodules and dental laminal cysts?
 Epstein’s pearls are tiny, 1- to 2-mm keratin-filled cystic lesions located along the midpalantine raphe.
Epstein’s pearls are tiny, 1- to 2-mm keratin-filled cystic lesions located along the midpalantine raphe.
 Bohn’s nodules are small mucous gland cysts found on the alveolar ridges or posterior palate.
Bohn’s nodules are small mucous gland cysts found on the alveolar ridges or posterior palate.
 Dental laminal cysts are larger, more lucent, fluctuant cysts consisting of remnants of dental laminal epithelium. They are usually single lesions, and they are found only on the crest of the alveolar mucosa.
Dental laminal cysts are larger, more lucent, fluctuant cysts consisting of remnants of dental laminal epithelium. They are usually single lesions, and they are found only on the crest of the alveolar mucosa.
7 Are dental caries contagious?
Berkowitz RJ: Mutans streptococci: Acquisition and transmission. Pediatr Dent 28:106–109, 2006.
8 Why is a dentoalveolar abscess more likely to “point” toward the buccal aspect of the gingiva than the lingual aspect?
11 What are the complications of oral piercings? Can they be life-threatening?
12 What is meant by the term geographic tongue?
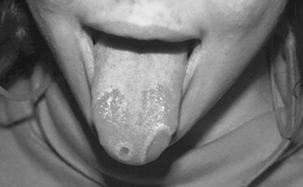
Geographic tongue, or benign migratory glossitis, is a painless condition notable for erythematous “islands” of denuded papillae surrounded by elevated whitish borders (Fig. 43-2). The islands appear to migrate over the surface of the tongue over time, akin to the movement of continents on the globe. The etiology is unknown, with allergy, infection, and stress all implicated as potential contributors. It generally resolves without specific treatment over a period of weeks to months.
13 What is a ranula? How does it differ from a mucocoele?
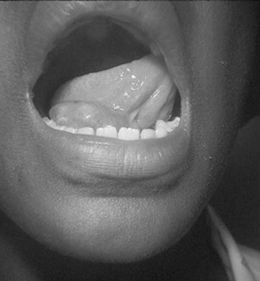
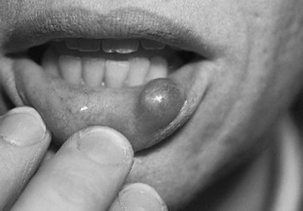
A ranula is a mucous retention cyst on the floor of the mouth, under the tongue (Fig. 43-3). A mucocele is a retention cyst located most commonly in the mucosa of the lower lip (Fig. 43-4). Both can range from several millimeters to a centimeter in diameter, are painless, and are felt to arise following trauma to the ducts of minor salivary glands. Treatment is surgical excision.
15 Name three eponymous anaerobic infections associated with the mouth
 Vincent’s disease, also known as acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivostomatitis, or trench mouth, is a painful ulcerative gingivostomatitis caused by overgrowth of a spirochete, Borrelia vincentii. It is most common in adolescents. Treatment consists of vigorous oral hygiene, with the addition of penicillin in severe cases.
Vincent’s disease, also known as acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivostomatitis, or trench mouth, is a painful ulcerative gingivostomatitis caused by overgrowth of a spirochete, Borrelia vincentii. It is most common in adolescents. Treatment consists of vigorous oral hygiene, with the addition of penicillin in severe cases.
 Ludwig’s angina is a life-threatening cellulitis of the sublingual and submandibular spaces. Rapid spread of infection into the neck may result in airway obstruction.
Ludwig’s angina is a life-threatening cellulitis of the sublingual and submandibular spaces. Rapid spread of infection into the neck may result in airway obstruction.
 Lemierre syndrome, or postanginal sepsis, involves infection of the lateral pharyngeal space with septic thrombophlebitis of the jugular vein, potentially leading to septic embolization to the lungs or brain. The most commonly associated organism is Fusobacterium sp.
Lemierre syndrome, or postanginal sepsis, involves infection of the lateral pharyngeal space with septic thrombophlebitis of the jugular vein, potentially leading to septic embolization to the lungs or brain. The most commonly associated organism is Fusobacterium sp.