47 Deep Peroneal Nerve Block
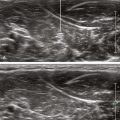
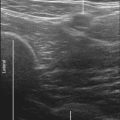
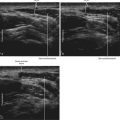
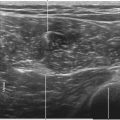
The deep peroneal nerve is a small branch of the common peroneal nerve. The deep peroneal nerve innervates the web space between the first and second toes. The nerve crosses over the anterior tibial artery from medial to lateral just proximal to the ankle joint near the surface of the distal tibia. The deep peroneal nerve can appear as a homogeneous hypoechoic structure surrounded by hyperechoic fat without polyfascicular echotexture. The deep peroneal nerve is more difficult to image in the proximal leg.1 This probably relates to the course of the nerve and its division into a large number of motor branches.2
Ultrasound guidance may provide some advantages over landmark-based approaches to deep peroneal nerve block. One study reported the use of ultrasound improved the onset of deep peroneal nerve block at the ankle although the overall quality of this block was no different.3 Another study has reported high success rates with deep peroneal nerve blocks that combine ultrasound with nerve stimulation.4
Suggested Technique
Key Points
| Deep Peroneal Nerve Block | The Essentials |
|---|---|
| Anatomy | The DPN often crosses over the AT. |
| This crossing point is near where the AT lies on the surface of the tibia. | |
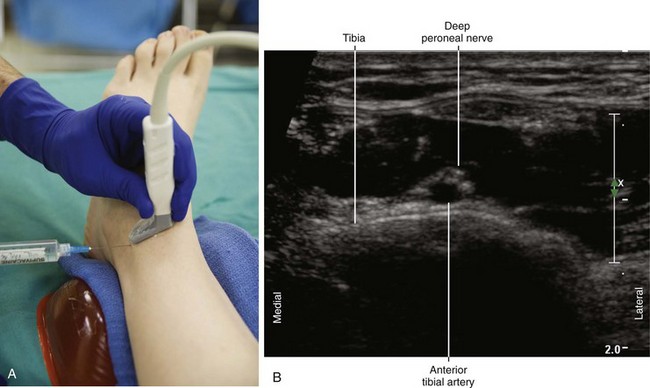
| Positioning | Supine |
| Operator | Standing on the side of the patient |
| Display | Across the table |
| Transducer | High-frequency linear, 23- to 38-mm footprint |
| Initial depth setting | 20 mm |
| Needle | 25 gauge, 38 mm in length |
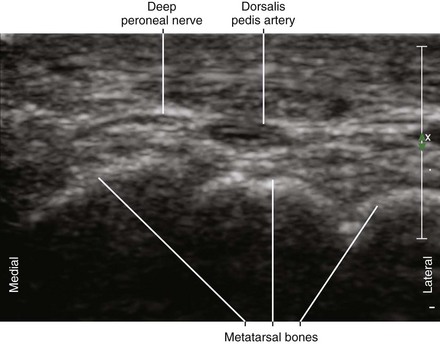
| Anatomic location | Begin by scanning between the malleoli over the dorsum of the foot. |
| Slide the probe proximal and distal to identify the DPN and AT. | |
| Light touch is needed to avoid compressing the AT. | |
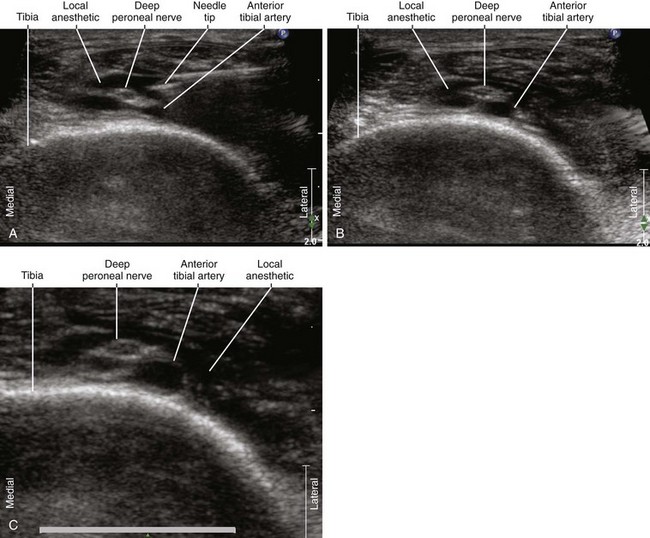
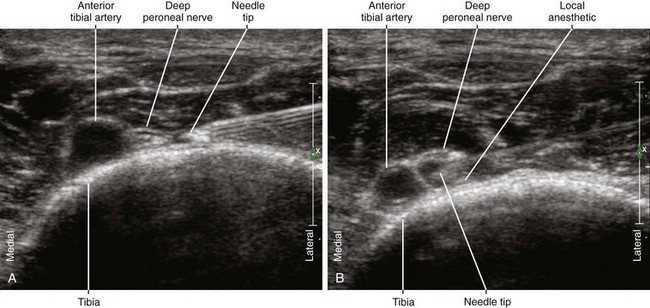
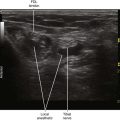
| Approach | SAX view of DPN, in-plane from lateral to medial |
| Place the needle tip between the DPN and AT. | |
| Sonographic assessment | The injection should separate the DPN and AT. |
| Anatomic variation | The DPN can divide into medial and lateral branches proximally. |
AT, Anterior tibial artery; DPN, deep peroneal nerve; SAX, short axis.
Clinical Pearls
• Because the deep peroneal nerve is small, it is difficult to visualize where it branches off from the common peroneal nerve in the proximal leg.
• The point at which the deep peroneal nerve crosses over the anterior tibial artery is typically proximal to the ankle joint where the artery lies on the surface of the tibia.
• The deep peroneal nerve divides into medial and lateral branches. These branches lie on their respective sides of the anterior tibial artery.
• The deep peroneal nerve can be blocked by peeling off the nerve from the anterior tibial artery where it lies in the 12-o’clock position with respect to the artery (at the crossing point). The injection should separate the deep peroneal nerve from the surface of the anterior tibial artery.
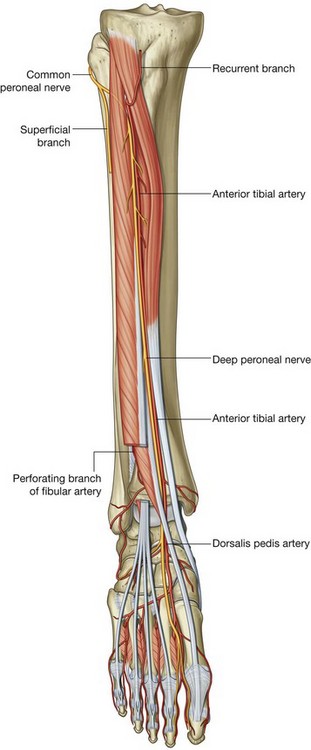
FIGURE 47-1 Course of the deep peroneal nerve.
(Adapted from Drake RL, Vogl W, Mitchell AWM. Gray’s anatomy for students. Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone; 2004.)
1 Beekman R, Visser LH. High-resolution sonography of the peripheral nervous system: a review of the literature. Eur J Neurol. 2004;11:305–314.
2 Aigner F, Longato S, Gardetto A, et al. Anatomic survey of the common fibular nerve and its branching pattern with regard to the intermuscular septa of the leg. Clin Anat. 2004;17:503–512.
3 Antonakakis JG, Scalzo DC, Jorgenson AS, et al. Ultrasound does not improve the success rate of a deep peroneal nerve block at the ankle. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2010;35(2):217–221.
4 Benzon HT, Sekhadia M, Benzon HA, et al. Ultrasound-assisted and evoked motor response stimulation of the deep peroneal nerve. Anesth Analg. 2009;109(6):2022–2024.